
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1851633
해군 함정 MRO 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Naval Vessel MRO - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
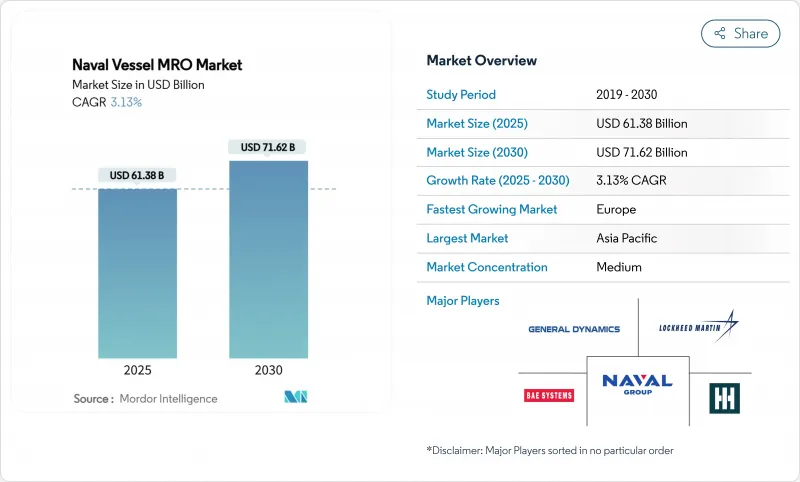
해군 함정 MRO 시장 규모는 2025년 613억 8,000만 달러로 추정됩니다.
2030년에는 CAGR 3.13%로 성장할 전망이고, 716억 2,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예측되고 있으며, 상업적 원동력보다 정부의 방위 우선순위가 꾸준한 성장을 가져왔습니다.
지속적인 현대화 계획, 분쟁 수역에서의 높은 운영 템포, 성과 기반 물류(PBL) 계약으로의 전환이 수요를 지속적으로 지원하고 있습니다. 원자력 함선의 유지관리 및 드라이 독의 오버홀은 전문적인 인프라와 깊은 기술적 전문지식을 필요로 하기 때문에 가장 유리한 틈새 분야인 것에 변함이 없고, 가격이 비쌉니다. 아시아태평양은 중국의 급속한 선대 확대와 동맹국의 대항 조치에 힘입어 최대 투자액을 차지하고 있지만, 유럽은 NATO의 새로운 헌신을 배경으로 가장 급속히 가속하고 있습니다. 공급망의 취약성 및 숙련 노동자의 부족이 큰 역풍이 되고 있지만, 디지털 트윈 애널리틱스와 적층 조형은 다운타임을 경감하고, 추가 비용 절감을 가능하게 합니다.
세계의 해군 함정 MRO 시장 동향 및 인사이트
차량 현대화 프로그램
각국 정부는 단지 차량 수를 확대하는 것이 아니라 능력을 확장하는 것을 목표로 하고 있기 때문에, 거국적인 업그레이드 계획이 해군 함정 MRO 시장 수요를 재구축하고 있습니다. 필리핀의 350억 달러를 투자한 현대화 계획과 튀르키예의 3년 계획을 통한 함대 강화 계획은 정비 인프라 및 플랫폼 업그레이드에 많은 예산을 부과하고 있습니다. 덴마크와 호주에서 유사한 전략은 중견 해군이 리노베이션, 오버홀 및 모듈식 업그레이드에 자금을 제공함으로써 불균형한 능력 향상을 보장할 수 있음을 보여줍니다. 잠수함의 선체 수명 연장은 신조 비용의 거의 1/4로 10-15년의 수명을 추가하여 내구성 있는 MRO 수입을 창출합니다. 단계적 작업 패키지를 통해 계약자는 노동력과 재고를 사전에 충분히 계획할 수 있으므로 예측 가능성이 향상되고 일정 지연을 줄일 수 있습니다.
레거시 선대의 연명
차세대 선체의 도착이 늦어짐에 따라, 구식선을 전투 가능한 상태로 유지하는 것은 절약으로부터 필요성으로 이행하고 있습니다. 미국 해군의 순양함 오버홀 프로그램과 영국 해군의 23형 프리깃함의 수명 연장 대처는 해군이 어떻게 최신 능력의 70-80%를 대체 비용의 불과 15-25%로 획득하고 있는지를 보여줍니다. 향상된 코팅, 구조 건전성 모니터링 및 수명 중반의 전투 시스템 교체는 피로와 진부화를 다루는 반면 예측 분석을 통해 점검 간격을 엄격하게 합니다. 레거시 선박에 대한 의존도 증가는 독립 야드에서 쉽게 재현할 수 없는 저장소 수준의 리노베이션 수요를 안정시키고 기존 계약자의 프리미엄 가격 설정을 강화합니다.
드라이 독 슬롯 오버런 및 비용
시설의 노후화 및 프로젝트의 급진화에 의해 오버홀의 예산은 계획을 크게 상회합니다. 진주만의 드라이독 현대화는 61억 달러에서 160억 달러로 부풀어 오르고, 포츠머스 해군 조선소의 비용은 4배로 부풀어 오르며, 다른 긴급 공사를 위한 용량을 방해하고 있습니다. 조선소 인프라 최적화 프로그램은 210억 달러를 투입하지만, 잠수함의 개조를 12-18개월 지연시키는 단기적인 갭을 해소할 수 없습니다. 민간 조선소는 오버런이 수익성을 위태롭게 하기 때문에 해군과의 계약을 거절하는 경우가 많아 병목 현상을 더욱 심각하게 하고 있습니다.
부문 분석
잠수함은 2024년 해군 함정 MRO 시장의 33.88%를 차지했으며, 그 핵 추진의 복잡성 및 억제력의 가치를 반영하여 다년간의 서비스 계약을 지원하고 있습니다. 높은 규제 장벽은 경쟁을 제한하고 비싼 비율을 지원합니다. 플리게이트함은 분산 수상 작전에서의 역할과 곧 유지 단계에 들어가는 비교적 빠른 건조 주기로 CAGR 5.26%에서 가장 급성장하고 있습니다. 구축함 및 코르벳은 중위에 위치하고, 전자는 이지스 시스템의 보수로부터 혜택을 받고, 후자는 예산에 맞는 초계함을 요구하는 신흥의 해안 해군을 매료하고 있습니다.
다이빙 플랫폼은 대규모 원자로 연료 공급, 음향 시그니처 점검, 선체 압력 테스트 및 저장소 레벨 작업 부하를 잠구야 합니다. 플리게이트 함의 프로그램은 모듈형 전투 시스템 블록을 활용하여 수명 중반의 업그레이드를 간소화하고 새로운 선체 대신 단계적인 능력 향상에 투자하도록 해군을 유혹하고 있습니다. 스페인 ISOPRENE 프로젝트에 의한 디지털 트윈 파일럿은 양함 클래스에서 예정 밖의 다운타임을 15-20% 삭감하는 것을 실증하고 있으며, 예측 기간 중에 광범위한 채용이 진행됨을 시사하고 있습니다.
드라이 독 작업은 2024년 해군 함정 MRO 시장의 39.22%를 차지했습니다. 이것은 도킹을 의무화하는 법정 선체 검사, 샤프트 라인 교환, 추진 시스템의 오버홀 때문입니다. 이 분야는 의무적인 정기 점검이 여러 해의 마스터 스케줄을 지원하기 때문에 안정적인 인지도를 누리고 있습니다. 개조 및 업그레이드 서비스는 해군이 신조선을 기다리는 것보다 오히려 센서, 무기, 전자전 스위트를 개수하기 때문에 매년 3.71% 성장하고 있습니다.
Additive Manufacturing은 부품 수리의 경제성을 재구성합니다. USS Bataan의 금속 3D 프린터는 이미 해상에서 인증된 예비 부품을 생산하고 물류 지연을 줄이고 무거운 작업을 위해 도크 공간을 확보합니다. PBL 프레임워크는 부품 턴어라운드의 가속화가 계약 성과 지표를 높이기 때문에 공급업체가 이 능력에 더 많은 투자를 할 인센티브를 제공합니다.
지역 분석
아시아태평양은 2024년 해군 함정 MRO 시장 지출의 37.59%를 차지하였고, 2030년까지 435척으로 증가하는 중국 선대 및 수상 부대를 두배로 늘리는 호주 계획과 같은 동맹국의 대책에 뒷받침됩니다. 조선대국인 한국과 일본은 오버플로 도크의 능력을 제공합니다. 한화오션은 미국 해군 보수 공사를 획득한 최초의 한국야드가 되어 동맹국의 협력관계 심화를 강조했습니다.
유럽은 NATO 회원국이 국방 지출을 GDP의 2% 이상으로 끌어올리는 중 CAGR 4.00%로 가장 급성장하고 있는 지역입니다. 덴마크의 대규모 함대 확장, 프랑스의 투르빌 잠수함 취역, 그리스의 270억 달러의 재군비에 의해 새로운 선체가 유지 파이프라인에 주입됩니다. 튀르키예의 3억 5,000만 유로를 투입한 액서스 해군기지의 개조는 지중해 안보에 대한 광범위한 우려를 반영하여 이 지역의 유지보수 옵션을 더욱 넓히는 것입니다.
북미는 미국 해군이 근대화 및 노후화 시설에 대해 제약과의 균형을 맞추면서 견조하면서도 안정된 수요를 유지하고 있습니다. 잠수함 노동을 위한 57억 달러의 긴급 보전 및 연간 조선 예산 401억 달러는 재정적 헌신을 강조하지만, 예측 병력 수준은 2027년까지 283척으로 떨어지고, 그 후 2054년까지 381척으로 재건될 예정입니다. 남미와 중동 및 아프리카는 14억 ZAR(7,890만 달러)의 잠수함 리노베이션과 같은 프로그램이 점진적인 상승을 가리키고 있지만, 기여는 여전히 작습니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건 및 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 플릿 근대화 프로그램
- 레거시 플릿의 연명
- 해양 안보에 있어서 긴장의 고조
- PBL계약 채용
- 디지털 트윈 기반 예측형 MRO
- 적층 조형에 의한 예비 부품
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 드라이 독 프레임의 오버런 및 비용
- 숙련 노동자의 부족
- 커넥티드 조선소의 사이버 리스크
- 그린 대응 폐기물 처리 비용
- 밸류체인 분석
- 규제 상황
- 기술의 전망
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업 간 경쟁 관계
제5장 시장 규모 및 성장 예측
- 선박 유형별
- 항공모함
- 구축
- 프리게이트
- 코르벳
- 잠수함
- 기타 선박 유형(지원 및 보조 선박, 무인 수상 선박, 수중 선박)
- MRO 유형별
- 엔진 MRO
- 드라이 독 MRO
- 컴포넌트 MRO
- 개조 및 업그레이드
- 유지관리 레벨별
- 조직 및 운영
- 중급 및 필드
- 디포
- 추진 유형별
- 원자력선
- 기존(디젤 및 가스 터빈)
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 유럽
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 독일
- 이탈리아
- 스페인
- 러시아
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 인도
- 일본
- 한국
- 호주
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 중동
- 사우디아라비아
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 튀르키예
- 기타 중동
- 아프리카
- 이집트
- 남아프리카
- 기타 아프리카
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- General Dynamics Corporation
- Huntington Ingalls Industries, Inc.
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- NAVANTIA, SA, SME
- thyssenkrupp AG
- BAE Systems plc
- Naval Group
- Rolls-Royce plc
- Rhoads Industries, Inc.
- Abu Dhabi Ship Building Company PJSC
- Larsen & Toubro Limited
- Damen Shipyards Group
- Singapore Technologies Engineering Ltd.
- FINCANTIERI SpA
- HD Hyundai Heavy Industries Co., Ltd.
- Saab AB
- Austal Limited
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Kongsberg Gruppen ASA
제7장 시장 기회 및 향후 전망
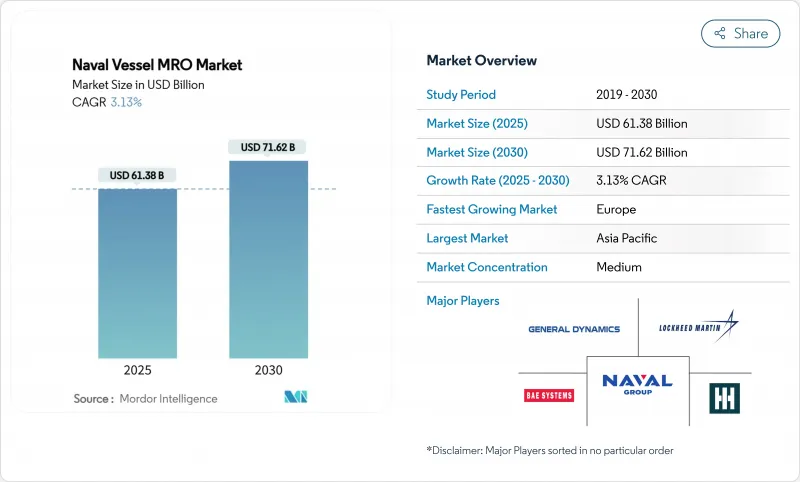
AJY 25.11.24The naval vessel MRO market size stands at USD 61.38 billion in 2025. It is forecasted to reach USD 71.62 billion by 2030 at a 3.13% CAGR, underscoring steady growth driven by government defense priorities more than commercial dynamics.
Sustained modernization programs, higher operational tempos in contested waters, and shifting toward performance-based logistics (PBL) contracts continue to anchor demand. Nuclear-powered vessel upkeep and dry-dock overhauls remain the most lucrative niches as they require specialized infrastructure and deep technical expertise, locking in premium pricing. Asia-Pacific accounts for the largest regional spend, propelled by China's rapid fleet expansion and allied counter-responses, while Europe is accelerating fastest on the back of renewed NATO commitments. Supply-chain fragility and skilled-labor shortages pose measurable headwinds, yet digital twin analytics and additive manufacturing mitigate downtime and unlock incremental savings.
Global Naval Vessel MRO Market Trends and Insights
Fleet-Modernization Programs
Nationwide upgrade plans are reshaping the naval vessel MRO market demand as governments aim to stretch capability rather than merely expand fleet count. The Philippines' USD 35 billion modernization drive and Turkey's three-year fleet enhancement initiative earmark sizable shares for maintenance infrastructure and platform upgrades rather than for acquisition only. Similar strategies in Denmark and Australia show that mid-tier navies can secure disproportionate capability gains by funding refits, overhauls, and modular upgrades. Submarine hull-life extensions add 10-15 years of service at near one-quarter of new-build cost, generating durable MRO revenue. Predictability improves because phased work packages allow contractors to plan labor and inventory well in advance, narrowing schedule slippage.
Life-Extension of Legacy Fleets
Keeping older ships battle-ready has moved from thrift to necessity as next-generation hulls arrive late. The US Navy cruiser overhaul program and the Royal Navy Type 23 frigate life-extension effort illustrate how navies capture 70-80% of modern capability for only 15-25% of replacement cost. Enhanced coatings, structural health monitoring, and mid-life combat-system swaps tackle fatigue and obsolescence while predictive analytics tighten inspection intervals. Growing reliance on legacy vessels stabilizes demand for depot-level refits that independent yards cannot easily replicate, bolstering premium pricing for incumbent contractors.
Dry-Dock Slot Overruns and Costs
Aging facilities and project creep push overhaul budgets well above plan. Pearl Harbor's dry-dock modernization ballooned from USD 6.1 billion to USD 16 billion, while Portsmouth Naval Shipyard costs quadrupled, blocking capacity for other urgent work. The Shipyard Infrastructure Optimization Program injects USD 21 billion, yet it cannot eliminate near-term gaps that delay submarine refits by 12-18 months. Commercial yards often refuse naval contracts because overruns jeopardize profitability, further tightening the bottleneck.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rising Maritime-Security Tensions
- Adoption of PBL Contracts
- Skilled-Labor Shortages
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Submarines accounted for 33.88% of the 2024 naval vessel MRO market, reflecting their nuclear-propulsion complexity and deterrence value that anchor multi-year service contracts. High regulatory barriers restrict competition and support premium rates. Frigates represent the fastest-growing slice at 5.26% CAGR thanks to their role in distributed surface operations and relatively quicker build cycles that soon enter sustainment phases. Destroyers and corvettes sit mid-pack; the former benefit from Aegis-system maintenance, while the latter attract emerging littoral navies seeking budget-friendly patrol craft.
Subsurface platforms require extensive reactor refueling, acoustic signature checks, hull pressure tests, and lock-in depot-level workloads. Frigate programs leverage modular combat-system blocks, simplifying mid-life upgrades and enticing navies to invest in incremental capability paths instead of fresh hulls. Digital twin pilots under Spain's ISOPRENE project have demonstrated 15-20% cuts in unscheduled downtime for both vessel classes, pointing toward broader adoption over the forecast period.
Dry-dock work held 39.22% of the naval vessel MRO market in 2024 due to statutory hull inspections, shaft-line replacements, and propulsion-system overhauls that mandate docking. The segment enjoys steady visibility because mandatory periodicity supports multi-year master schedules. Modification and upgrade services are growing 3.71% annually as navies retrofit sensors, weapons, and electronic-warfare suites rather than wait for new builds.
Additive manufacturing is reshaping component repair economics. Metal 3D printers on the USS Bataan already produce certified spares at sea, cutting logistics lag and freeing dock space for heavier tasks. PBL frameworks incentivize suppliers to invest further in this capability, as faster part turnarounds boost contract performance metrics.
The Naval Vessel MRO Market Report is Segmented by Vessel Type (Aircraft Carriers, Destroyers, Frigates, Corvettes, and More), MRO Type (Engine MRO, Dry-Dock MRO, Component MRO, and More), Maintenance Level (Organizational/Operational, Depot, and More), Propulsion Type (Nuclear-Powered Vessels, Conventional), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific held 37.59% of the 2024 naval vessel MRO market spending, anchored by China's fleet growth toward 435 ships by 2030 and allied counter-moves such as Australia's plan to double its surface force. Shipbuilding powerhouses South Korea and Japan offer overflow dock capacity; Hanwha Ocean became the first Korean yard to win US Navy repair work, underscoring deeper allied collaboration.
Europe is the fastest-growing region at 4.00% CAGR as NATO members lift defense outlays to at least 2% of GDP. Denmark's large-scale fleet expansion, France's Tourville submarine commissioning, and Greece's USD 27 billion rearmament funnel fresh hulls into sustainment pipelines. Turkey's EUR 350 million Aksaz Naval Base upgrade further broadens regional maintenance options and reflects wider Mediterranean security concerns.
North America sustains robust but stable demand as the US Navy balances modernization with aging-yard constraints. Emergency supplements of USD 5.7 billion for submarine labor and a USD 40.1 billion annual shipbuilding budget highlight fiscal commitment, yet projected force levels drop to 283 ships by 2027 before rebuilding toward 381 by 2054. South America and the Middle East/Africa remain smaller contributors, though programs like ZAR 1.4 billion (USD 78.90 million) submarine refit point to gradual upticks.
- General Dynamics Corporation
- Huntington Ingalls Industries, Inc.
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- NAVANTIA, S.A., SME
- thyssenkrupp AG
- BAE Systems plc
- Naval Group
- Rolls-Royce plc
- Rhoads Industries, Inc.
- Abu Dhabi Ship Building Company PJSC
- Larsen & Toubro Limited
- Damen Shipyards Group
- Singapore Technologies Engineering Ltd.
- FINCANTIERI S.p.A.
- HD Hyundai Heavy Industries Co., Ltd.
- Saab AB
- Austal Limited
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Kongsberg Gruppen ASA
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Fleet-modernization programs
- 4.2.2 Life-extension of legacy fleets
- 4.2.3 Rising maritime-security tensions
- 4.2.4 Adoption of PBL contracts
- 4.2.5 Digital-twin based predictive MRO
- 4.2.6 Additive-manufactured spares
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Dry-dock slot overruns and costs
- 4.3.2 Skilled-labor shortages
- 4.3.3 Cyber-risk to connected shipyards
- 4.3.4 Green-compliance waste-disposal cost
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Vessel Type
- 5.1.1 Aircraft Carriers
- 5.1.2 Destroyers
- 5.1.3 Frigates
- 5.1.4 Corvettes
- 5.1.5 Submarines
- 5.1.6 Other Vessel Types (Support and Auxiliary Vessels, Unmanned Surface, and Underwater Vessels)
- 5.2 By MRO Type
- 5.2.1 Engine MRO
- 5.2.2 Dry-Dock MRO
- 5.2.3 Component MRO
- 5.2.4 Modification and Upgrade
- 5.3 By Maintenance Level
- 5.3.1 Organizational/Operational
- 5.3.2 Intermediate/Field
- 5.3.3 Depot
- 5.4 By Propulsion Type
- 5.4.1 Nuclear-Powered Vessels
- 5.4.2 Conventional (Diesel/Gas Turbine)
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.2 France
- 5.5.2.3 Germany
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Russia
- 5.5.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 India
- 5.5.3.3 Japan
- 5.5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.5.3.5 Australia
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Argentina
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.5.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 Egypt
- 5.5.5.2.2 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 General Dynamics Corporation
- 6.4.2 Huntington Ingalls Industries, Inc.
- 6.4.3 Lockheed Martin Corporation
- 6.4.4 NAVANTIA, S.A., SME
- 6.4.5 thyssenkrupp AG
- 6.4.6 BAE Systems plc
- 6.4.7 Naval Group
- 6.4.8 Rolls-Royce plc
- 6.4.9 Rhoads Industries, Inc.
- 6.4.10 Abu Dhabi Ship Building Company PJSC
- 6.4.11 Larsen & Toubro Limited
- 6.4.12 Damen Shipyards Group
- 6.4.13 Singapore Technologies Engineering Ltd.
- 6.4.14 FINCANTIERI S.p.A.
- 6.4.15 HD Hyundai Heavy Industries Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.16 Saab AB
- 6.4.17 Austal Limited
- 6.4.18 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- 6.4.19 Kongsberg Gruppen ASA
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment

















