
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1720934
인도의 양자 통신 여정 : International Quantum Communication Conclave 2025에서 얻은 인사이트 - 정부/학계/산업계가 결집하여 QKD, PQC 및 포토닉 칩 국산 기술로 인도의 양자 미래를 주도Indias Quantum Communication Journey - Insights from the International Quantum Communication Conclave 2025: Government, Academia, and Industry Unite to Drive Indias Quantum Future with Indigenous Innovations in QKD, PQC, and Photonic Chips |
||||||
이 보고서는 International Quantum Communication Conclave 2025에서 발표된 전략적 이니셔티브, 기술 혁신 및 이정표를 개괄하고, 이들이 인도의 미래를 위한 양자 네트워크 구축을 어떻게 촉진하고 있는지를 보여줍니다.
VISUALS
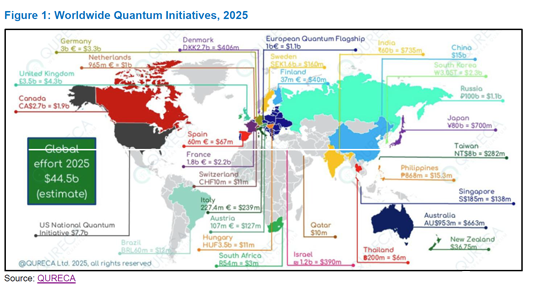
인도는 양자 기반 보안 통신을 위한 세계 경쟁에서 빠르게 중요한 기업로 부상하고 있으며, 2025년 IQCC(International Quantum Communication Conclave)에서는 이 분야에서 인도의 성장하고 있는 기술력이 주목을 받았습니다. 양자통신(QC)은 미래의 안전한 네트워크의 핵심 기술이 될 것으로 기대되고 있습니다. 기존 암호화 방식과 달리 양자통신은 양자 역학의 법칙을 이용하기 때문에 기존 및 양자형 사이버 위협에 대한 높은 내성을 가지고 있습니다. 양자 기술에 대한 전 세계 투자 총액이 445억 달러가 넘는 가운데, 인도는 국산 기술과 국가적 규모의 도입을 무기로 리더십을 확보하기 위해 전략적으로 움직이고 있습니다.
인도 정부는 양자통신을 NQM(National Quantum Mission, 국가 양자 미션)의 핵심 축으로 삼고, 연구, 상용화, 도입을 지원하는 탄탄한 생태계 구축을 목표로 하고 있습니다. 인도공과대학 마드라스(IIT Madras), 통신개발센터(C-DOT), 라만연구소(RRI) 등의 기관이 기초적인 프로젝트를 주도하고 있습니다. 예를 들어, IIT 마드라스는 첸나이에 도시권 양자 액세스 네트워크(MAQAN)의 광섬유 테스트베드를 구축했습니다. 또한, C-DOT는 뉴델리 산차르 바완에서 양자 키 전송(QKD) 라이브 실험을 실시하여 중요한 이정표를 세웠습니다. 또한, IIT Delhi와 국방연구개발기구(DRDO)는 실험실 환경에서 50km의 광섬유 링크를 사용하여 얽힘형 QKD를 성공적으로 시연했으며, 실제 테스트에서도 8km의 광섬유 전송에 성공했습니다. 또한, 우타르 프라데시 주 프라야그라지와 빈디야차르 간(100km)에서 도시 간 QKD 통신 시험도 진행하고 있습니다. 이러한 노력을 바탕으로 QUILA(Quantum Internet with Local Access) 프로그램에서는 지상 및 위성 QKD에 포스트 양자암호(PQC)와 양자 메모리를 통합하여 2,000km의 양자 백본으로 주요 도시를 연결하는 국가 양자 인터넷의 구축을 목표로 하고 있습니다. 구축을 목표로 하고 있습니다.
인도에서 양자 기술 상용화의 엔진으로 부상하고 있는 CDOT는 COW(Coherent One Way) 및 DPS(Differential Phase Shift) 프로토콜을 기반으로 인증된 QKD 시스템을 개발하고 있습니다. 를 방지하기 위해 측정기 독립형 QKD(MDI-QKD) 시제품을 개발하고 있습니다. 또한, CDOT의 다중화 및 멀티코어 파이버 QKD의 기술 혁신을 통해 고가의 다크 파이버(미사용 전용선)를 사용하지 않고도 120km 이상의 안전한 통신 거리를 실현하고 있습니다. 여기서 중요한 것은 CDOT가 단일광자 검출기 등 주요 부품을 국산화하여 비용을 90% 절감하고, 해외 의존도를 크게 낮췄다는 점입니다.
조사 대상
언급된 조직
|
|
목차
요약
서론
- 양자 통신이 중요한 이유
IQCC 2025 주요 하이라이트
- 국가 책무 : NQM, CDOT, IIT Madras 역할
- 파운데이션 프로젝트 : MAQAN·QUILA
- CDOT에 의한 독자적인 혁신
- 소형화와 대규모화 : 칩 스케일 QKD를 향해서
- 위성 기반 양자 통신 : RRI와 ISRO가 선두에 선다
- QNu Labs : 연구개발에서부터 전개까지
- 포스트 양자암호 : 통합 준비 완료
- 글로벌 연계 및 학습 : Toshiba·IBM·Ericsson
인도의 양자 생태계가 중요한 이유는?
결론 : 인도 양자 통신의 결정적인 비약
LSH 25.05.26This brief outlines the strategic initiatives, innovations, and milestones showcased at the International Quantum Communication Conclave 2025 that are steering India's progress toward future-ready quantum networks.
VISUALS
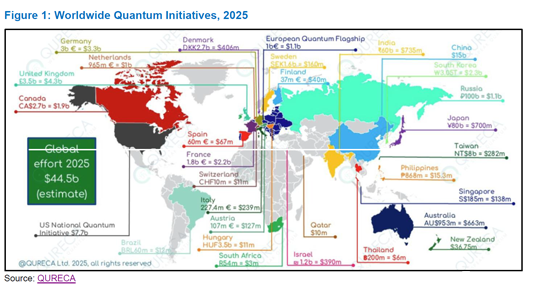
India is fast emerging as a significant player in the global race toward secure, quantum-based communications. The International Quantum Communication Conclave (IQCC) 2025 spotlighted India's growing capabilities in this field, with quantum communications (QC) poised to become the backbone of future secure networks. Unlike traditional encryption, quantum communication leverages the laws of quantum mechanics, offering resilience against classical and quantum cyber threats. As global investments in quantum technologies exceed $44.5 billion, India is strategically positioning itself to lead with indigenous innovations and national-scale deployments.
The Indian government has made quantum communications a core pillar of its National Quantum Mission (NQM), aiming to create a robust ecosystem of research, commercialization, and deployment. Several institutions such as Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras, the Centre for Development of Telematics (CDOT), and the Raman Research Institute (RRI) are spearheading foundational projects. For example, IIT Madras has pioneered the Metro Area Quantum Access Network (MAQAN) metro fiber testbed in Chennai, while C-DOT's live Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) setup at Sanchar Bhawan, New Delhi marks an important milestone. Separately, IIT Delhi and the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) have jointly demonstrated entanglement-based QKD over 50 km of fiber link in lab conditions and 8 km of optical fiber in field trials, in addition to executing a 100 km inter-city QKD trial between Prayagraj and Vindhyachal in Uttar Pradesh. Building on these, the ambitious Quantum Internet with Local Access (QUILA) program aims to link major Indian cities through a 2,000 km quantum backbone, integrating terrestrial and satellite QKD with Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) and quantum memory, laying the foundation for a national quantum internet.
CDOT, emerging as the country's quantum commercialization engine, has developed certified QKD systems based on Coherent One Way (COW) and Differential Phase Shift (DPS) protocols. CDOT also is prototyping Measurement Device Independent (MDI) QKD for mitigating side-channel attacks. Its innovations in multiplexed and multi-core fiber QKD remove the need for costly dark fiber while extending secure communication ranges to 120+ km. Critically, CDOT has indigenized key components like single-photon detectors, cutting costs by 90% and reducing foreign dependency.
Another major leap forward is the shift toward chip-scale QKD. Miniaturizing bulky quantum components into photonic integrated circuits will allow for scalable, cost-effective deployment across telecom and cloud networks. India is investing heavily in this direction via the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY) and the Department of Science and Technology (DST), funding photonic chip R&D at institutions like Indian Institute of Science (IISc) and IITs. These chips will also form the building blocks for future 6G and AI infrastructure.
Satellite quantum communication is the next frontier. RRI, in collaboration with the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), is developing ground-to-satellite QKD systems with adaptive optics and precision tracking, offering a viable solution for long-distance, terrain-agnostic secure links. Their research in device-independent randomness and free-space optics enhances India's readiness for global-scale quantum communication networks.
Finally, industry players like QNu Labs are transitioning research into deployable systems by commercializing hybrid models that integrate QKD, PQC, and quantum random number generators. These efforts, aligned with NQM, mark India's emergence as a serious contender in the global quantum race - strategically, scientifically, and commercially.
Research Coverage
Organizations mentioned:
|
|
Table of Contents
Summary
Introduction
- Why does quantum communications matter?
IQCC 2025 key highlights
- National imperatives: the role of NQM, CDOT, and IIT Madras
- Foundational projects: MAQAN and QUILA
- Indigenous innovation by CDOT
- Miniaturization and scale: Toward chip-scale QKD
- Satellite-Based Quantum Communication: RRI and ISRO lead the charge
- QNu Labs: from R&D to deployment
- Post-Quantum Cryptography: Ready for Integration
- Global alignment and learnings: Toshiba, IBM, and Ericsson



















