
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1723670
캐리어 뉴트럴 오퍼레이터 시장 리뷰(2024년 4분기) : 생성형 AI 붐을 타고 사모펀드 진출 가속화Carrier-Neutral Operator Market Review, 4Q24: GenAI Hype Speeds Up Private Equitys Push into Sector |
||||||
2024년 매출은 약 1,070억 달러로 보합세, 설비투자는 7% 증가한 430억 달러로 증가. 생성형 AI 붐이 성장의 한 요인이 되고 있지만, 특히 Airtrunk와 같은 사모펀드 주도의 대형 프로젝트에서 그 영향이 큽니다.
이 보고서는 2011년 1분기부터 2024년 4분기까지 전 세계 47개 CNNO의 광범위한 재무 데이터를 추적하여 CNNO(Carrier Neutral Network Operator) 시장의 성장과 발전을 조사했습니다.
2024년 한 해 동안 조사 대상 기업의 매출은 1,067억 달러(전년 대비 0.2% 증가), 설비투자는 429억 달러(전년 대비 6.8% 증가)입니다. 2024년 말 현재 이들 CNNO가 보유한 순고정자산은 2,611억 달러(전년 대비 -0.5%), 종업원 수는 약 11만 2,000명(전년 대비 -2.0%)으로 집계되었습니다.
비주얼
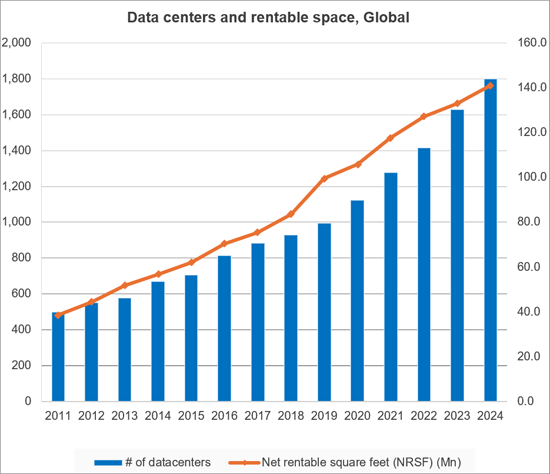
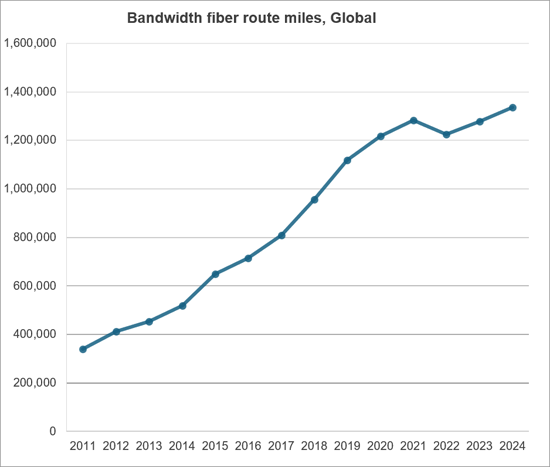
CNNO 시장은 MTN Consulting이 추적하는 세 가지 사업자 부문(통신사업자 및 웹스케일 사업자) 중 가장 작은 시장이지만, 통신 분야에서 매우 중요하고 보완적인 역할을 담당하고 있습니다. 소형 셀, 데이터센터, 도매용 파이버 네트워크의 대부분을 소유 및 운영하고 있습니다. 과거에는 통신사업자가 네트워크 인프라 전체를 소유하고, 스위치와 전송 장비를 자체적으로 제조하고, 고객 가정 내 장비(CPE)까지 제공하는 등 모든 것을 담당했습니다. 그러나 이러한 모델은 이미 구식이며, 2025년 통신사업자들은 물리적 네트워크를 자체 소유의 장비와 임대 또는 임대를 통한 외부 자원을 결합하여 구축할 것입니다. 많은 통신사들은 지금까지 물리적 자산의 일부를 사모펀드 인프라 부문이나 상장된 CNNO에 매각하여 자금을 조달해 왔습니다. 일반적으로 이러한 매각에는 리스백 조항이 포함되어 있어 통신사업자는 설비투자를 실질적으로 운영비용으로 전환할 수 있습니다. 웹스케일 사업자(클라우드 제공업체 등)도 CNNO에 크게 의존하고 있습니다. 이들은 2023년에만 3,040억 달러에 달하는 막대한 설비투자를 하고 있지만, 주로 광케이블과 전송대역을 임대하고, 데이터센터도 자체적으로 소유하고 있지는 않습니다. CNNO는 금융, 미디어, 에너지 등 다양한 업종의 기업 및 정부 기관과 같은 다른 최종 시장에도 서비스를 제공하지만, 가장 큰 고객은 통신 사업자와 웹 스케일 사업자로, CNNO는 이들 사업자의 네트워크 설계 및 비용 구조에서 매우 중요한 역할을 담당하고 있습니다.
보고서 하이라이트:
수익 : 2011년 200억 달러 미만이었던 CNNO의 매출 규모는 2024년 1,067억 달러에 이르렀습니다. 이는 전년 대비 거의 변동이 없는 수준이며, M&A의 움직임이 거의 없었던 해로서는 이례적이라고 할 수 있습니다. 그러나 2018-2024년 기간 동안 CNNO의 매출 성장률은 연평균 7%로 견조한 성장세를 보이고 있으며, 2024년에는 연간 매출이 50억 달러를 초과하는 CNNO가 7곳에 달했습니다.
설비투자 : 2011년 약 60억 달러였던 CNNO의 설비투자비는 2024년 429억 달러에 달했습니다. 이는 2023년 대비 약 7% 증가한 것으로, 건전한 성장률이라고 할 수 있지만, 하이퍼스케일 데이터센터 건설에 특화된 기업들의 설비투자 성장에 비하면 낮은 수치입니다. 예를 들어, 웹 스케일 사업자의 설비 투자는 2024년 50% 이상의 성장을 기록했으며, 생성형 AI 붐은 이미 이 시장을 버블 영역으로 밀어 붙이고 있으며, CNNO 산업에서 생성형 AI의 과열 추세는 주로 사모 펀드 주도의 비상장 기업에 집중되어 있습니다.
수익성 : 2024년 CNNO 부문의 평균 순이익률은 2.1%로 2023년 2.7%와 거의 비슷한 수준입니다. 이는 Crown Castle이 광섬유 네트워크 관련 대규모 손실을 기록했음에도 불구하고 유지된 수치입니다. 2024년 평균 2.8%의 잉여현금흐름마진은 2023년 -0.8%에서 크게 개선되었으며, 2024년 말 CNNO의 대차대조표상 부채는 약 2,400억 달러, 현금 및 투자는 220억 달러 미만, 순부채는 여전히 2,200억 달러에 육박합니다.
조사 대상
본 리뷰에는 다음과 같은 기업이 포함되어 있습니다.
|
|
목차
제1장 보고서 하이라이트
제2장 CNNO 부문 개요
제3장 분석
제4장 운영 지표
제5장 주요 통계
제6장 기업 상세 분석
제7장 기업 벤치마킹
제8장 원시 데이터
제9장 환율
제10장 당사에 대해
ksm 25.05.29Revenues flat at ~$107B in 2024, capex up 7% to $43B; GenAI hype is a driver, but more so in PE-led ventures (e.g. Airtrunk) due to size & scale requirements
This report reviews the growth and development of the carrier-neutral network operator (CNNO) market. The report tracks a wide range of financial stats for 47 CNNOs across the globe, from 1Q11 through 4Q24. For the full-year 2024, the companies covered by this study represented $106.7 billion (B) in revenues (+0.2% YoY), and $42.9 B in capex (+6.8% YoY). At the end of 2024 (EOY24), these CNNOs had $261.1B of net plant, property and equipment (net PP&E) on the books (-0.5% YoY), and employed approximately 112,000 people (-2.0% YoY).
VISUALS
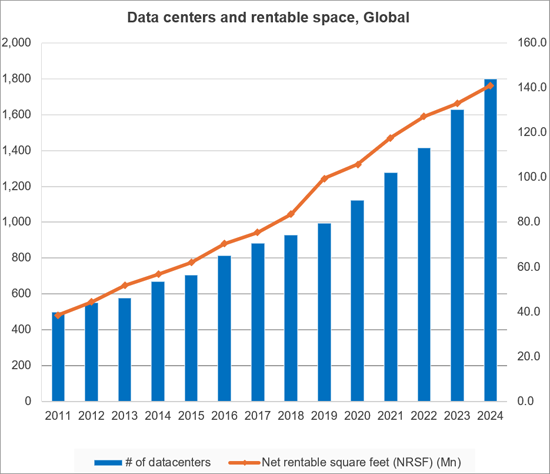
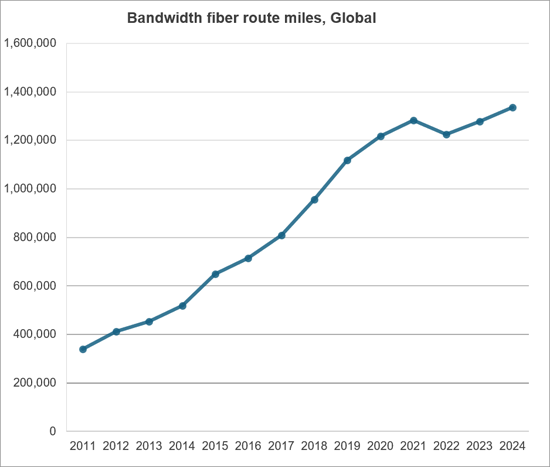
The CNNO market is the smallest of three operator segments tracked by MTN Consulting, alongside telco & webscale, but CNNOs play a crucial, complementary role in the communications sector and own and operate a large portion of the world's cell towers, small cells, data centers, and wholesale fiber networks. In the old days, telcos did it all: they owned all the network infrastructure, they manufactured the switches and transmission gear deployed in the network, and even provided CPE. That model is long since extinct. The telco of 2025 cobbles together its physical network from a mix of owned and leased or rented resources. Over the years, many telcos have raised funds by selling off parts of their physical plant to private equity funds with infrastructure arms, or to public CNNOs. Usually there is a leaseback provision as part of the sale, enabling the telco to effectively turn capex into opex. Cloud providers in the webscale world also rely heavily on CNNOs; while they spend heavily on capex ($304B last year), they generally lease fiber or transmission bandwidth, and only own a portion of their data centers. CNNOs do serve other end markets, including various enterprise verticals (finance, media, and energy), and government. But telcos and webscalers are the biggest targets. CNNOs play a vital role in the network design and cost structure of these operators.
CNNOs are constantly reshuffling their asset base to optimize costs and position for growth. The most effective CNNOs have mastered the art of acquiring companies and/or discrete physical networks or facilities, and integrating them smoothly and quickly into existing operations. Finding cost benefits from the greater scale is key, as is being able to cross-sell across a larger universe of customers. This study attempts to focus on the purely 'neutral' CNNOs, i.e. the ones that do not have key customers also show up as key shareholders. China Tower, for instance, is majority owned by its top 3 customers, the big local telcos. This is an exception to the rule; we do include China Tower, because of its size and China's unusual networks ecosystem.
The figures in this study are based on a thorough bottoms-up assessment of the global CNNO market, focusing on companies that are either publicly traded now, or were public in the recent past. We cannot credibly track a company if it is purely private and reports no audited numbers to regulatory authorities. This is also a challenge in other markets, such as webscale, where we are not able to track ByteDance/TikTok officially because it produces no reliable numbers. In the CNNO world, the biggest challenge is private equity. PE's rising interest in assembling digital infrastructure portfolios is a big reason for the growth of the CNNO market over the last decade. They're attempting to create synergies across their digital investees, sometimes through mergers, and synergies with other parts of their investment portfolio. With the rise of GenAI, for instance, some PE firms are investing directly in energy supply in order to ensure competitive rates and terms (e.g. renewable sources) for the data center players in their portoflio. We include some PE-owned companies in this study, if it's possible to estimate their financials from past reported data. But we also have to exclude some major players; Airtrunk is a good example. It was acquired by PE giant Blackstone late last year, for $16B. This is the CNNO market's biggest M&A deal in 2024, but we have no realistic way to capture Airtrunk in our database.
Below are some highlights from the report:
Revenues: from under $20B in 2011, the CNNO sector recorded revenues of $106.7B in 2024. That is roughly zero growth YoY, which is not unusual in a year when M&A was almost nonexistent; over the 2018-24 timeframe, CNNO revenue growth averaged 7% per year. In 2024, there were 7 CNNOs with over $5B in annual revenues; from largest to smallest, they are: China Tower ($13.6B), American Tower ($10.1B), Equinix ($8.7B), DigitalBridge ($8.6B), Crown Castle ($6.6B), Level 3 ($6.5B), and Digital Realty ($5.6B). A few of these are exclusively focused on one type of infra, while some are hybrid. China Tower is focused on macro cell towers, but it also has extensive DAS coverage (e.g. 13,126km of subway coverage) and is building an energy business focused on battery exchange and power backup. American Tower is a hybrid, beginning its life as a tower specialist but branching into data centers with the 2021 purchase of CoreSite. Equinix and Digital Realty are data center specialists exclusively, just as Level 3 is focused solely on fiber/bandwidth. Crown Castle owns towers, small cells, and fiber, but is selling off the latter two to Zayo & EQT. DigitalBridge is the oddest of the 7, as it is an investment holding company with stakes in a large number of CNNO-type providers, including towers, small cells/DAS, fiber, and data centers. DataBank and Zayo are two of its largest holdings. To grow over five-fold in a decade, the scope of the market has expanded dramatically, largely through M&A. Since 2011, CNNOs' M&A has totaled $229.6B, versus $347B for capex.
Capex: from ~$6B in 2011, CNNO capex was $42.9B in 2024. That is up about 7% up from the 2023 total. That's a healthy level of growth, but nothing like the capex growth of companies focused on hyperscale data center construction. Webscale capex grew by over 50% in 2024. Generative AI hype long ago pushed that market into bubble territory. In CNNO, the GenAI excesses are concentrated in the PE sector, by private companies, being driven by true believer investors who view 'digital infrastructure' as a key driving force for future economic growth. Many believe that GenAI can solve many of the world's problems, including climate change. Among CNNOs without PE backing, some have been using creative financing vehicles to build hyperscale-class facilities for the big cloud providers. In October 2024, for instance, Equinix announced a $15B joint venture with GIC and Canada Pension Plan Investment Board (CPP Investments), to build hyperscale/AI data centers in the US market. Similarly, on a much smaller scale, Digital Realty announced in March 2025 that it would enter the Indonesian market via a JV, with Bersama Digital Infrastructure Asia.
Profitability: average net margin for the CNNO sector was 2.1% in 2024, in line with the 2.7% recorded in 2023, despite Crown Castle booking a big net loss last year related to its fiber network. Free cash flow margin averaged to 2.8% in 2024, up from the -0.8% of 2023. CNNOs had nearly $240B of debt on the balance sheets at EOY24, and just under $22B in cash & investments; net debt, therefore, is still nearly $220B. Both American Tower and Crown Castle have recently announced big asset sales to help lower debt levels, and we can expect more of this to occur in 2025.
Employees: CNNOs ended 2024 with about 112K employees, from 114.3K at EOY2023. CNNOs aim for efficiency in the operation of their infrastructure, and use automation when possible to lower labor costs. However, most CNNOs engage in M&A and hence often need to integrate & rationalize assets before they can reap the scale & synergy benefits. There can be some delay as adjustments to the workforce are made. On a revenue per employee basis, the CNNO sector is impressive, at over $945K per employee in 2024, up slightly from $937K in 2023. These figures are significantly higher than the webscale and telco network operator markets.
Energy: CNNOs consumed an average of 796 MWH per $M of revenues in 2024 (estimated), up from 555 MWh/$M several years ago, in 2019. Data center CNNOs are starting to dominate the market, and they use much higher than average amounts of energy to power their operations. The most energy intensive CNNO in 2023 (the last year with actual data) was ChinData, at 4,403 MWh/$M; Crown Castle was towards the bottom, with just 31MWh/$M.
Research Coverage
The following companies are included in this Market Review:
|
|



















