
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1802915
AI 코파일럿 및 IoT용 코드 생성 : 지능형 어시스턴트에 의한 임베디드 개발의 변혁AI Copilots & Code Generation for the IoT: Transforming Embedded Development with Intelligent Assistants |
||||||
이 보고서 내용
AI는 소프트웨어 개발을 근본적으로 변화시켰습니다. 개발 툴 프로바이더들은 생성형 AI와 자연 언어 처리의 급속한 발전을 활용하여 엔지니어들이 코딩 작업의 대부분을 자동화하고 프로토타이핑을 가속화할 수 있도록 돕고 있습니다. 생산성을 크게 향상시킬 수 있다는 장점이 있지만, 자동화에는 본질적으로 보안 및 품질 위험이 따르기 때문에 임베디드 엔지니어링 조직은 AI 기반 어시스턴트를 신중하게 다뤄야 합니다. 커스텀 가드레일, 툴 통합, 베스트 프랙티스 지침, 모델 개선 등을 통해 보안, 품질, 프로세스 가속화를 효과적으로 조화시킬 수 있는 상용 솔루션은 빠르게 성장하고 있는 AI 코파일럿 및 코드 생성 솔루션 시장에서 빠르게 점유율을 확보할 수 있습니다. 할 수 있을 것입니다.
이 보고서는 IoT 및 임베디드 소프트웨어 개발의 AI 코파일럿 및 코드 생성 생태계에 대한 종합적인 분석을 제공합니다. 현재 에이전트형 AI 및 AI 코딩 툴의 기능과 한계, 주요 IDE, DevOps 파이프라인, 임베디드 툴체인과의 통합, IoT 및 엣지 컴퓨팅 배포에서 이러한 툴이 성능 및 규제 요건을 얼마나 충족시킬 수 있는지를 확인합니다. 검증하고 있습니다.
이 보고서에는 관련 M&A, LLM 생태계, 라이선스 전략, 에이전트형 IDE, AI 생성 코드에 대한 우려, 주요 벤더의 프로파일 분석도 포함되어 있습니다. 또한 2024-2029년까지 시장 규모와 예측, 제품 유형(범용 솔루션 vs. 전용 솔루션), 지역별, 산업별, 주요 벤더별 세분화 및 설명과 함께 2024-2029년까지 시장 규모와 예측을 제공합니다.
어떤 질문에 대응하고 있는가?
- AI 강화 코파일럿 및 코드 생성 솔루션에 대한 수요를 이끄는 요인은 무엇인가?
- AI를 활용한 개발 솔루션에 대한 수요를 수용하기 위해 개발 툴 프로바이더는 어떻게 포트폴리오를 강화할 수 있는가?
- 이 급성장하는 분야 시장 성장을 주도하는 산업 시장은 어떤 산업 시장일까?
- 안전과 보안이 중요한 산업에서 AI 코드 생성을 대규모로 도입하는 시기는 언제쯤일까?
- 엔지니어들이 경량 어시스턴트보다 에이전트형 솔루션을 선호하는 이유는 무엇인가?
- 제품 혁신을 주도하고 시장에 영향을 미치는 기업은?
이 보고서의 기술 프로바이더
|
|
|
보고서 발췌
AI를 활용한 프로젝트 일정 준수율 향상
목차
이 리포트 내용
개요
- 주요 조사 결과
조사 범위와 조사 방법론
- AI의 이해
- AI 코파일럿과 코드 생성 툴
세계 시장 개요
- 에이전트가 AI 코드 생성을 변혁하고, 코파일럿에 도전한다.
- 전략적 고려
- LLM 선정과 지원은 Market Addressability에 직접 영향을 미친다.
- AI 툴 라이선스 전략과 동향
- JetBrains vs Cursor, AI IDE의 부상
- 보안과 코드 품질 우려가 AI 도입을 막는다.
- 최근 동향
- M&A
지역 동향과 예측
- 아메리카
- 유럽, 중동 및 아프리카
- 아시아태평양
수직 시장 동향과 예측
- 항공우주 및 방위
- 자동차
- 통신과 네트워크
- 산업 자동화
경쟁 구도
- 기존 임베디드 소프트웨어 솔루션 프로바이더는 AI에 의한 파괴적 변화에 적응해야 한다.
최종사용자 인사이트
- 임베디드 엔지니어링 조직은 AI 어시스턴트의 도입에 신중하나, 변화는 임박하고 있다.
- AI의 활용은 프로젝트 스케줄 준수를 개선한다.
- AI 생성 코드를 사용하는 임베디드 엔지니어는 소프트웨어 스택에 대해 강력한 선호를 보이고 있다.
- 엔지니어는 조직 유형을 불문하고 유사한 태스크에 AI를 활용하고 있다.
저자 소개
KSA 25.09.11Inside this Report
AI has fundamentally reshaped software development. Development tool providers have successfully leveraged the rapid evolution of generative AI and natural language processing to help engineers automate large portions of the coding process and accelerate prototyping. Despite massive productivity benefits, automation comes with inherent security and quality risks that force embedded engineering organizations to approach AI-powered assistants with caution. Commercial solutions that can effectively blend security, quality, and process acceleration through custom guardrails, tool integrations, best practices guidance, and model refinement will reap early share in this young but rapidly emerging space for AI copilots and code generation solutions.
This report delivers a comprehensive analysis of the AI copilots and code generation ecosystem as it applies to IoT and embedded software development. It examines the capabilities and limitations of current agentic AI and AI coding tools, their integration with popular IDEs, DevOps pipelines, and embedded toolchains, and the extent to which these tools can meet the performance and regulatory requirements of IoT and edge computing deployments. The report also includes an analysis of relevant mergers and acquisitions, LLM ecosystems, licensing strategies, agentic IDEs, concerns with AI generated code, and profiles of leading vendors. The study includes market sizing and forecasts from 2024 to 2029 with commentary and segmentations by product type (general purpose versus application-specialized solutions), region vertical market, and leading vendors.
What Questions are Addressed?
- What factors are driving demand for AI-enhanced copilots and code generation solutions?
- How can development tool providers strengthen their portfolios to capitalize on demand for AI- powered development solutions?
- Which vertical markets will lead market growth in this burgeoning sector?
- When will safety- and security-critical industries adopt AI code generation at scale?
- Why do engineers favor agentic solutions over lightweight assistants?
- Which companies are driving product innovation and influencing the market?
Who Should Read this Report?
This report was written for those making critical decisions regarding product, market, channel, and competitive strategy and tactics. This report is intended for senior decision-makers who are developing, or are a part of the ecosystem of, AI assistants and code generation tools, including:
|
|
Technology Providers in this Report:
|
|
|
Demand-side Research Overview
VDC launches numerous surveys of the IoT and embedded engineering ecosystem every year using an online survey platform. To support this research, VDC leverages its in-house panel of more than 30,000 individuals from various roles and industries across the world. Our global Voice of the Engineer survey recently captured insights from a total of 600 qualified respondents. This survey was used to inform our insight into key trends, preferences, and predictions within the engineering community.
Executive Summary
AI code generation is emerging as one of the most disruptive forces in IoT software development since the advent of open source. Enterprise/IT organizations eagerly adopted AI-powered coding tools with little hesitation, but demand for code generation capabilities from embedded engineering organizations has lagged behind, resulting in a blossoming opportunity for AI copilot and code generation vendors beginning primarily in 2025. AI copilots accelerate software development, helping engineering organizations cope with the increasing complexity of software codebases and their core role in product-level differentiation. For engineering and product development organizations across industries, AI promises to bridge skill gaps, reduce time to market, and improve developer productivity.
This acceleration in automated coding, however, also increases the need for rigorous quality assurance, compliance checks, and additional security. Currently, there is a large gap in the market for a complete solution that offers safety-critical software testing and analysis alongside standards-compliant code generation. AI-generated code can introduce vulnerabilities, licensing risks, or inefficiencies that are difficult to detect without robust testing and software composition analysis (SCA) in the background. Many of the leading AI development tool vendors do not have partnerships or experience in embedded software development, creating an opportunity for organizations with a long tenure in embedded engineering to partner with AI leaders to safely and securely bring AI-generated code to the IoT for all use cases.
Copilots and code generation will take hold in embedded engineering over the next five years. In the near term, adoption will be strongest in non-safety-critical IoT segments such as communications & networking, consumer electronics, and smart home, where AI-assisted coding can quickly prove ROI without extensive regulatory overhead. As certification bodies and standards organizations formalize guidelines for AI-generated code, safety-critical engineering organizations will adopt copilots more eagerly. To capture a portion of the growing safety-critical market share, vendors must add compliance support, code provenance tracking, and integrate with popular software verification and validation tools.
Key Findings:
- Demand for application- and domain-specialized code generation will accelerate rapidly as embedded engineering organizations embrace AI to add greater amounts of software-driven value to their products.
- As secure, purpose-built AI copilots go to market, the automotive vertical will grow the fastest as OEMs transition toward software-defined vehicle architectures and value-added software features that generate recurring revenue.
- Agentic AI will not only transform code generation but also the complete software development lifecycle as it automates design planning, QA, and project management.
- The Americas is a home market for many of the world's leading AI copilot and code generation solution vendors, contributing to its early market leadership.
- VDC's Voice of the Engineer survey data shows that AI tooling is effectively accelerating project timelines, helping engineers meet and exceed deadlines.
Report Excerpt
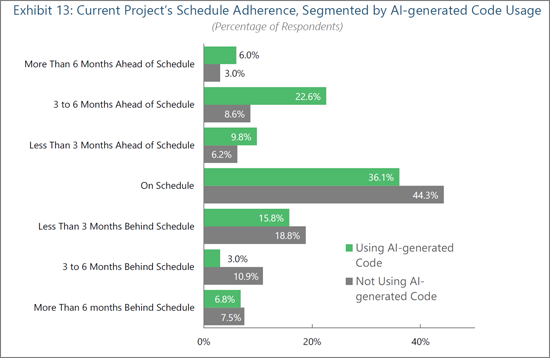
AI Usage Improves Project Schedule Adherence
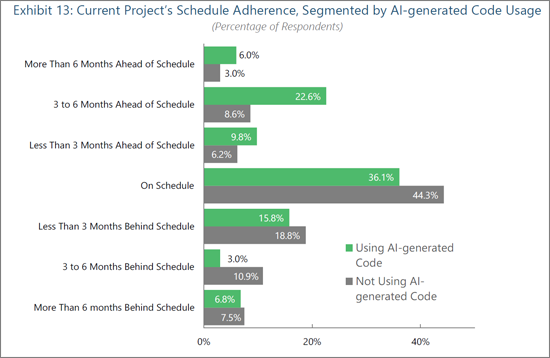
Organizations leveraging AI for code generation are measurably outperforming their peers in project execution timelines. Engineering organizations employing AI-generated code are significantly more likely to beat expectations, with 38% reportedly ahead of their project schedules (2.1x more likely than organizations not using AI code generation). This discrepancy reflects AI's ability to automate foundational coding tasks, accelerate iteration cycles, and reduce delays caused by manual development bottlenecks.
The sharp difference in three to six month delays (3.0% of AI users versus 10.9% of non-AI users) and overall reduction in delays among AI code users suggest that engineering organizations benefit from AI's ability to preempt errors and improve code reliability earlier in the lifecycle. AI code generation tools that generate boilerplate or repetitive code components allow engineers to focus on architecture, integration, and optimization, which are key elements for fueling product innovation and differentiation in traditional workflows. In edge AI contexts, where deployment environments are heterogeneous and performance tuning is critical, complex task automation (e.g., model integration or hardware abstraction) enables teams to compress development cycles and better align with shifting project requirements. AI-integrated software development strategies free up developers to work proactively on value-creating features. As a result, solution providers should position AI code generation not just as a developer aid, but as a catalyst for predictable, repeatable acceleration, which is especially compelling in embedded markets defined by deployment complexity and constrained engineering resources.
Table of Contents
Inside this Report
Executive Summary
- Key Findings
Report Scope & Methodology
- Understanding AI
- AI Copilots & Code Generation Tools
Global Market Overview
- Agents Will Transform AI Code Generation and Challenge Copilots
- Strategic Considerations
- LLM Selection and Support Directly Impacts Market Addressability
- AI Tool Licensing Strategies and Trends
- JetBrains Versus Cursor and the Rise of AI IDEs
- Security and Code Quality Concerns Deter AI Adoption
- Recent Developments
- Mergers and Acquisitions
Regional Trends & Forecast
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East, and Africa
- Asia-Pacific
Vertical Market Trends & Forecast
- Aerospace & Defense
- Automotive
- Communications & Networking
- Industrial Automation
Competitive Landscape
- Incumbent Embedded Software Solution Providers Must Adapt to AI Disruption
End-User Insights
- Embedded Engineering Organizations are Slow to Adopt AI Assistants, but Change is Imminent
- AI Usage Improves Project Schedule Adherence
- Embedded Engineers Using AI-generated Code Demonstrate Strong Software Stack Preferences
- Engineers Use AI for Similar Tasks Across Organization Types
About the Authors
List of Exhibits:
- Exhibit 1: Global Revenue of Copilots & Code Generation Tools & Related Services Segmented by Tool Type
- Exhibit 2: Percentage of Global Revenue from Copilots & Code Generation Tools & Related Services Segmented by Tool Type
- Exhibit 3: Current Concerns About AI-generated Software Code
- Exhibit 4: Global Revenue of Copilots & Code Generation Tools & Related Services Segmented by Geographic Region
- Exhibit 5: Percentage of Global Revenue from Copilots & Code Generation Tools & Related Services Segmented by Geographic Region
- Exhibit 6: Amount of Trust in AI-generated Software Code Segmented by Vertical Market
- Exhibit 7: Global Revenue of Copilots & Code Generation Tools & Related Services Segmented by Vertical Market
- Exhibit 8: Percentage of Global Revenue from Copilots & Code Generation Tools & Related Services Segmented by Vertical Market
- Exhibit 9: 2024 Percentage of Global Revenue from Copilots & Code Generation Tools & Related Services Segmented by Leading Vendors
- Exhibit 10: 2025 Estimated Market Share of Global Revenue from Copilots & Code Generation Tools & Related Services Segmented by Leading Vendors:
- Exhibit 11: Consideration/Use of AI-generated Software/Code (e.g., Use of Copilot and/or Prompt-based Code Creation)
- Exhibit 12: Expected Changes in Use of AI-generated Software in the Next Three Years
- Exhibit 13: Current Project's Schedule Adherence Segmented by AI-generated Code Usage
- Exhibit 14: Embedded Software Stack Components Required on Current/Most Recent Project Segmented by AI-generated Code Usage
IoT & Embedded Engineering Survey (Partial list):
- Exhibit 1: Primary Role Within Company/Organization
- Exhibit 2: Respondent's Organization's Primary Industry
- Exhibit 3: Total Number of Employees at Respondent's Organization
- Exhibit 4: Primary Region of Residence
- Exhibit 5: Primary Country of Residence
- Exhibit 6: Type of Most Current or Recent Project
- Exhibit 7: Involvement with Engineering of an Embedded/Edge, Enterprise/IT, HPC, AI/ML, or Mobile/System Device or Solution
- Exhibit 8: Type of Purchase by Respondent's Organization
- Exhibit 9: Primary Industry Classification of Project
- Exhibit 10: Type of Aerospace & Defense Application for Most Recent Project
- Exhibit 11: Type of Automotive In-Vehicle Application for Most Recent Project
- Exhibit 12: Type of Communications & Networking Application for Most Recent Project
- Exhibit 13: Type of Consumer Electronics Application for Most Recent Project
- Exhibit 14: Type of Digital Security Application for Most Recent Project
- Exhibit 15: Type of Digital Signage Application for Most Recent Project
- Exhibit 16: Type of Energy and Utilities Application for Most Recent Project
- Exhibit 17: Type of Gaming Application for Most Recent Project
- Exhibit 18: Type of Industrial Automation Application for Most Recent Project
- Exhibit 19: Type of Media & Broadcasting Application for Most Recent Project
- Exhibit 20: Type of Medical Device Application for Most Current Project
- Exhibit 21: Type of Mobile Phone
- Exhibit 22: Type of Office/Business Automation Application for Most Recent Project



















