
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1891233
소프트웨어 정의 차량(SDV)의 도입(2026년)Software-defined Vehicles Adoption Report 2026 |
||||||
샘플 미리보기
자동차 산업은 하드웨어 중심의 설계에서 소프트웨어 우선의 접근 방식으로 전환하고 있으며, 차량 아키텍처, 개발 프로세스, 운전자 경험을 근본적으로 변화시키고 있습니다. 소프트웨어 정의 차량(SDV)으로의 전환은 지속적인 기능 업데이트, 중앙 집중식 컴퓨팅, 구독형 서비스를 통한 새로운 수익화 모델을 가능하게 합니다. 그러나 조직 구조의 복잡성, 사이버 보안 위험, 다중 시스템 소프트웨어 스택의 통합 등의 문제도 발생하고 있습니다.
본 보고서에서는 SDV의 현황을 종합적으로 분석하고, 주요 OEM 및 티어1 공급업체의 도입 전략을 상세히 설명합니다. 전기/전자(E/E) 아키텍처의 진화, 8계층 소프트웨어 스택의 구성, 개발에서 AI의 역할, 차량 보안을 규제하는 프레임워크 등 다양한 기술적, 전략적 관점에서 시장을 검토하고 있습니다.
본 보고서의 조사 결과는 2025년 초에 실시된 86명의 OEM 및 공급업체 자동차 업계 임원들을 대상으로 한 설문조사와 20여 명의 전문가들과의 심층 인터뷰를 바탕으로 작성되었습니다. 또한 AutoShanghai 2025 및 IAA Mobility 2025와 같은 주요 업계 행사에서 얻은 지식도 포함됩니다.
샘플 미리보기


보고서 개요
- 140페이지 분량의 보고서 : SDV 시장을 정의하는 도입 동향, 기술, 전략을 상세히 설명합니다.
- 시장 우선순위 데이터 : OEM의 45%가 SDV를 최우선 전략 과제로 꼽아, 자율주행과 전동화를 능가하는 것으로 나타났습니다.
- 재무 분석 : 주요 OEM들은 SDV 관련 지출의 21%를 소프트웨어에 할당하고, 거의 동일한 비율로 E/E 아키텍처에 투자하고 있습니다.
- 구역별 아키텍처 상세 분석 : 배선 간소화 및 컴퓨팅 자원의 집중화를 위해 많은 OEM이 구역형 E/E 아키텍처를 채택하고 있습니다.
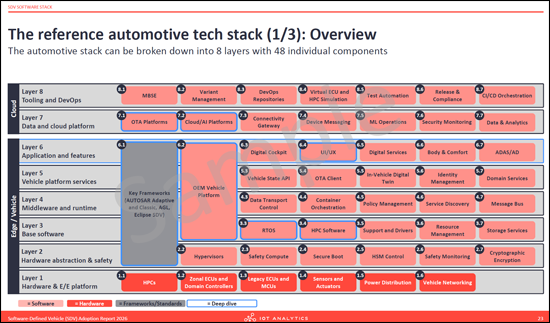
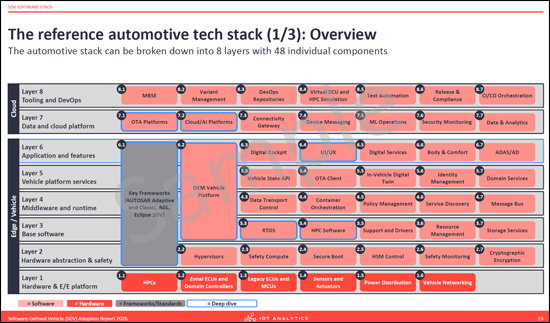
- 소프트웨어 스택 구조 분석 : 하드웨어 추상화 계층부터 클라우드 플랫폼까지 8층 48개 구성요소로 구성된 구조로 구성
- 벤더 및 OEM 동향 : Tesla, BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Nio, Nissan, AWS, Microsoft, NXP 등 주요 기업의 전략 프로파일링
샘플 미리보기

주요 분석 분야
- SDV 개요 : SDV는 차량 아키텍처, 클라우드 통합, 소프트웨어 중심 엔지니어링, 라이프사이클 관리의 4가지 차원에서 소프트웨어 우선 접근 방식으로 구축된 차량으로 정의합니다. 분산형 ECU에서 중앙집중형 컴퓨팅으로의 전환을 설명합니다.
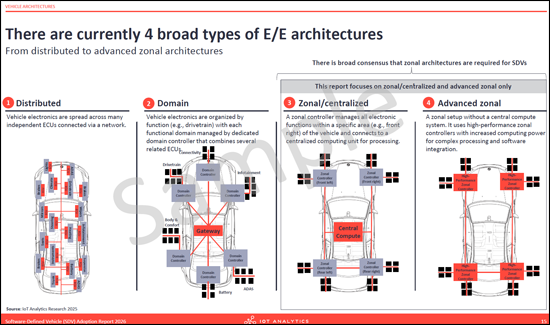
- 차량 아키텍처 : 도메인 기반에서 구역 기반 E/E 아키텍처로의 전환을 자세히 설명합니다. 무게 감소, 배선 간소화 등 존 설계의 장점을 분석하는 한편, 기술 격차, 높은 초기 비용 등의 장벽을 언급합니다.
- SDV 소프트웨어 스택 : 레퍼런스 자동차 기술 스택을 하드웨어 & E/E 플랫폼, 미들웨어, 애플리케이션 계층을 포함한 8개의 레이어로 분해합니다. AUTOSAR Adaptive, Eclipse SDV와 같은 주요 프레임워크를 평가하고, MB.OS, Tesla OS와 같은 차량 플랫폼을 자세히 살펴봅니다.
- AI의 역할과 도입 현황 : V 모델 개발 프로세스 전반에서 AI의 가치를 분석합니다. 데이터에 따르면, 압도적으로 많은 OEM 업체들이 소프트웨어 개발 및 검증에서 AI의 가장 큰 가치를 발견하고 있습니다. 코드 생성 및 요구 사양 엔지니어링에서 생성형 AI의 적용에 대해서도 다룹니다.
- 보안과 규제 : SDV의 확장된 공격 대상 영역을 검증하고, ECU 악용 및 OTA 취약점을 포함한 5가지 주요 공격 벡터를 식별합니다. ISO 21434 및 UN R155/R156과 같은 표준 준수 요건을 설명합니다.
- OEM 및 공급업체 도입 전략 : Tesla와 Nio와 같은 테크 네이티브 기업과 기존 기업의 노력을 대조합니다. 유럽 OEM들이 아시아태평양의 경쟁사들보다 훨씬 더 적극적으로 SDV를 우선시하고 있다는 점을 강조합니다.
- 트렌드와 과제 : 클라우드 네이티브 개발 파이프라인 채택, 소프트웨어 스택의 모듈화 등 거시적 트렌드를 파악합니다. 또한, 구독 모델에 대한 소비자의 반발과 소프트웨어 엔지니어링 인력 부족 등의 문제도 언급합니다.
게재 기업:
|
|
|
목차
제1장 주요 요약
제2장 소개
- 서론 : 장의 개요 및 중요 포인트
- 전통적인 자동차 산업은 세 가지 측면에서 압력을 받고 있다.
- 그 결과, OEM은 세 가지 주요 제품 전략에 투자하고 있다.
- IoT Analytics의 2025년 조사에 따르면 SDV가 가장 중요한 전략 과제임이 밝혀졌다.
- 유럽 OEM 및 공급업체, SDV 혁명의 최전선에 서 있다.
- SDV의 정의
- 제조사 및 업계 단체가 SDV를 정의하는 방법
- SDV에는 네 가지 주요 측면이 있다.
- 네 가지 측면은 각각 전체 자동차 개발 V 모델에서 별도의 역할을 수행
- SDV가 왜 그렇게 중요한가? 중요한 인용문
- SDV의 진화
- OEM은 매년 SDV에 투자하고 있으며, 그 대부분은 소프트웨어와 E/E 아키텍처에 투자하고 있다.
- 사례 : Mercedes-Benz의 소프트웨어 정의의 미래
- 전문가 시장 컨센서스 : 기술 네이티브 OEM은 SDV에서 분명히 앞서고 있다.
제3장 차량 아키텍처
- 차량 아키텍처 : 장 개요 및 핵심 포인트
- SDV 요구사항은 미래의 E/E 아키텍처를 변화시킬 것이다.
- 현재, E/E 아키텍처는 다양한 종류가 있다.
- 존 아키텍처 채택
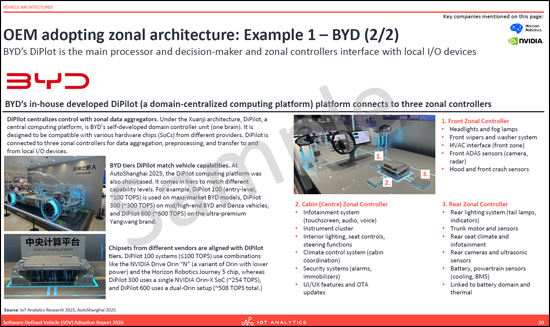
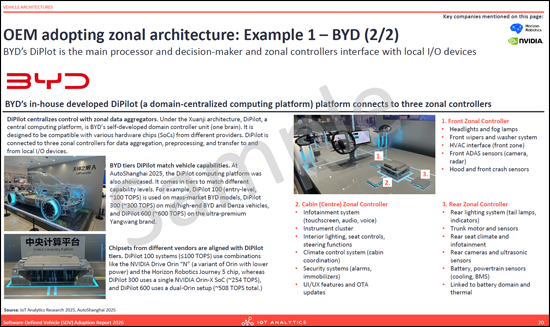
- 존 아키텍처를 채택한 OEM : 사례 1 - BYD
- 존 아키텍처를 채택한 OEM : 사례 2 - Tesla
- 존 아키텍처를 채택한 OEM : 사례 3 - Rivian
- 존 아키텍처를 채택한 공급업체 : 예 - NXP
- 존 아키텍처의 주요 장점
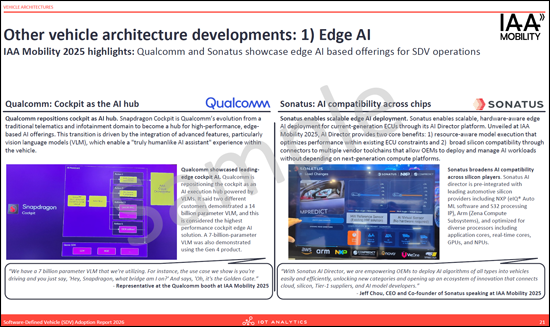
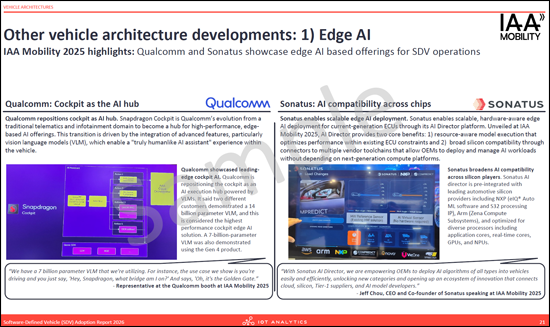
- 기타 차량 아키텍처 개발 : 1 - Edge AI
- 기타 차량 아키텍처 개발 : 2 - 하드웨어 가상화
제4장 SDV 소프트웨어 스택
- SDV 소프트웨어 스택 : 장 개요 및 핵심 포인트
- 레퍼런스 자동차 기술 스택
- 상세 분석 1 : 주요 프레임워크
- 상세 분석 2 : OEM 차량 플랫폼
- 상세 분석 3 : RTOS
- 상세 분석 4 : HPC 소프트웨어
- 상세 분석 5 : OTA 플랫폼
- 상세 분석 6 : 클라우드 플랫폼
- 상세 분석 7 : UI/UX
- 상세 분석 8 : 애플리케이션 및 기능 - SDV로 실현 가능한 것들
제5장 AI의 역할과 도입
- AI의 역할과 도입 : 장의 개요와 주요 포인트
- 자동차 개발에서 AI의 가치 창출 가능성
- 자세히 보기 : 존 아키텍처 개발에서 AI의 역할
- 차량 설계 및 차량 애플리케이션에서 AI의 역할
- 특정 차량 시스템을 구축할 때 AI의 역할
- AI를 활용한 주요 차량 기능
- 생성형 AI의 역할
제6장 보안과 규제의 역할
- 보안과 규제의 역할 : 장 개요 및 핵심 포인트
- SDV의 사이버 보안 리스크
- SDV V 모델에서 사이버 보안의 역할
- 전반적인 사이버 보안의 성숙도
- 주요 사이버 보안 주제에 대한 책임
- 자동차 벤더 보안 벤더 쇼케이스 1 : Upstream
- 자동차 벤더 보안 벤더 쇼케이스 2 : Critical Software
- 규칙
- OEM 및 공급업체 채용 전략 : 장의 개요 및 핵심 포인트
- OEM SDV 채택(10부)
- 공급업체 SDV 도입
제7장 동향과 과제
- 동향과 과제 : 장 개요 및 주요 포인트
- 동향
- 과제
- 기타 인사이트 : EW25 SDV 패널 토론의 주요 내용
제8장 조사 방법
제9장 IoT Analytics에 대하여
KSM 26.01.02A report detailing the adoption of software-defined vehicles, incl. deep-dive on the software stack, specific OEM and supplier adoption strategies, and key trends and challenges.
Sample preview
The automotive industry is transitioning from hardware-centric engineering to a software-first approach, fundamentally altering vehicle architecture, development processes, and the driver experience. This shift to Software-Defined Vehicles (SDVs) enables continuous feature updates, centralized computing, and new monetization models through subscription-based services. However, it also introduces complexities in organizational structure, cybersecurity risks, and the integration of multi-system software stacks.
The "Software-Defined Vehicle (SDV) Adoption Report 2026" provides a comprehensive analysis of the SDV landscape, detailing the adoption strategies of major OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers. It examines the market through multiple technical and strategic lenses: the evolution of electrical/electronic (E/E) architectures, the composition of the 8-layer software stack, the role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in development, and the regulatory frameworks governing vehicle security.
The findings in this report rely on a survey of 86 automotive executives from OEMs and suppliers, conducted in early 2025, alongside 20+ in-depth expert interviews. The research also incorporates insights from major industry events such as AutoShanghai 2025 and IAA Mobility 2025.
Sample preview


Report at a glance
- 140-page report: Detailing the adoption trends, technologies, and strategies defining the SDV market.
- Market prioritization data: Analysis indicates that 45% of OEMs classify SDVs as their top strategic priority, surpassing autonomous driving and electrification.
- Financial insights: Data details that leading OEMs allocate 21% of their SDV expenditure to software, with a nearly equal portion dedicated to electrical/electronic architectures.
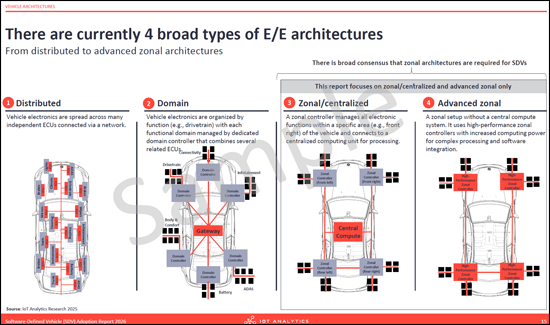
- Deep dive into Zonal Architectures: Examines the migration status, with a vast majority of OEMs currently adopting zonal E/E architectures to reduce wiring complexity and centralize compute power.
- Software stack breakdown: A structural analysis of the SDV software stack, identifying 8 layers and 48 components, from hardware abstraction to cloud platforms.
- Vendor and OEM landscape: Profiles strategies from key players including Tesla, BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Nio, Nissan, AWS, Microsoft, and NXP.
Sample preview

Key areas of analysis
- Introduction to SDVs: Defines the SDV as a vehicle built with a software-first approach across four dimensions: vehicle architecture, cloud integration, software-driven engineering, and lifecycle management. It outlines the shift from distributed ECUs to centralized computing.
- Vehicle architectures: Details the transition from domain-based to zonal E/E architectures. The section analyzes the benefits of zonal designs, such as weight reduction and simplified wiring, while addressing barriers like skill gaps and high upfront costs.
- The SDV software stack: Dissects the reference automotive tech stack into 8 layers, including the hardware & E/E platform, middleware, and application layers. It evaluates key frameworks such as AUTOSAR Adaptive and Eclipse SDV, and deep-dives into vehicle platforms like MB.OS and Tesla OS.
- Role and adoption of AI: Analyzes the value of AI across the V-model development process. Data indicates that the overwhelming majority of OEMs see the greatest value for AI in software development and validation. The section also covers Generative AI applications in code generation and requirements engineering.
- Security and regulations: Examines the expanded attack surface of SDVs, identifying five primary attack vectors including ECU exploitation and OTA vulnerabilities. It outlines compliance requirements with standards such as ISO 21434 and UN R155/R156.
- OEM and supplier adoption strategies: Contrasts the approaches of tech-native players like Tesla and Nio against traditional incumbents. It highlights that European OEMs prioritize SDVs significantly more aggressively than their APAC counterparts.
- Trends and challenges: Identifies macro trends such as the adoption of cloud-native development pipelines and the modularization of software stacks. It also addresses challenges like consumer pushback on subscription models and the shortage of software engineering talent.
A data-driven foundation for key business functions
- Strategy & corporate development: Align strategic roadmaps with the shift toward zonal architectures, which a vast majority of competitors are adopting, and assess investment priorities where 45% of OEMs classify SDVs as their top strategic goal.
- Product management: Inform feature roadmaps by analyzing the adoption of specific SDV capabilities; for instance, a significant majority of new vehicles sold in 2024 possessed Software-Over-The-Air (SOTA) capabilities.
- R&D & engineering leadership: Direct resource allocation based on industry priorities, noting that software accounts for the leading share of SDV budgets. Evaluate the utility of AI, as a clear majority of peers expect it to be critical for ADAS simulation.
- Market intelligence: Assess the competitive landscape by reviewing the platform strategies of major players like BMW, Stellantis, Nissan, and BYD, and understanding the friction points between OEMs and suppliers regarding "white-box" code sharing.
Key concepts defined
- Software-Defined Vehicle (SDV): An automobile engineered with a software-first approach, where core functions (control, connectivity, user experience) and development processes are primarily defined by software rather than hardware.
- Zonal Architecture: An E/E architecture that groups Electronic Control Units (ECUs) by their physical location (zones) within the vehicle rather than by function, connecting them to central computing units to simplify wiring and processing.
- Vehicle Platform: An end-to-end software ecosystem (e.g., MB.OS, VW.OS) that manages hardware, enables real-time control, supports OTA updates, and provides a development environment for applications.
- Over-the-Air (OTA): The capability to download and install software and firmware updates remotely, managing the lifecycle of vehicle software without physical dealership visits.
- High-Performance Computing (HPC): Centralized computing units within the vehicle that process complex, data-intensive workloads such as AI, ADAS, and cross-domain functions.
Questions answered:
- What is a software-defined vehicle (definition), and which stakeholders treat SDV as a strategic priority?
- Which components of the automotive technology stack are foundational to SDV development and operations?
- What types of zonal architecture are emerging, and what are its benefits and adoption challenges?
- How valuable is AI expected to be across SDV lifecycle?
- What are SDV cybersecurity risks and mitigation approaches?
- What are the SDV adoption strategies of OEMs and suppliers?
- What are the key trends and challenges in SDV adoption?
Companies mentioned:
A selection of companies mentioned in the report.
|
|
|
Table of Contents
1. Executive summary
- The insights in this report are based on 4 main research sources
- Executive summary (4 parts)
- Analyst opinion: 4 things that stood out in our research
2. Introduction
- Introduction: Chapter overview and key takeaways
- The traditional automotive industry is experiencing pressure on 3 fronts
- As a result, OEMs are investing in 3 key product strategies
- IoT Analytics' 2025 survey shows SDV is the top strategic priority
- European OEMs and suppliers are at the forefront of SDV revolution
- Definition of an SDV
- How manufacturers and industry associations define SDV
- There are 4 main dimensions of an SDV
- Each of the 4 dimensions plays a separate role across the automotive development V-model
- Why are SDVs so important? Key quotes
- Evolution of SDVs
- OEMs invest into SDVs each year with most spending on software and E/E architectures
- Case in point: Mercedes-Benz's software-defined future (3 parts)
- Expert market consensus: Tech-native OEMs are clearly ahead with SDVs
3. Vehicle architectures
- Vehicle architectures: Chapter overview and key takeaways
- SDV requirements change future E/E architectures
- There are currently broad types of E/E architectures
- Zonal architecture adoption (5 parts)
- OEM adopting zonal architecture: Example 1 - BYD (2 parts)
- OEM adopting zonal architecture: Example 2 - Tesla
- OEM adopting zonal architecture: Example 3 - Rivian
- Supplier adopting zonal architecture: Example - NXP (2 parts)
- Key benefits of zonal architecture
- Other vehicle architecture developments: 1 - Edge AI
- Other vehicle architecture developments: 2 - Hardware virtualization
4. The SDV software stack
- SDV Software stack: Chapter overview and key takeaways
- The reference automotive tech stack (3 parts)
- Deep dive 1: Key frameworks (2 parts)
- Deep dive 2: OEM Vehicle Platform (7 parts)
- Deep dive 3: RTOS (2 parts)
- Deep dive 4: HPC software (2 parts)
- Deep dive 5: OTA platforms (2 parts)
- Deep dive 6: Cloud platforms (6 parts)
- Deep dive 7: UI/UX (2 parts)
- Deep dive 8: Applications and features - What SDV enables
5. Role and adoption of AI
- Role and adoption of AI: Chapter overview and key takeaways
- AI's value creation potential in vehicle development
- Deep-dive: Role of AI in zonal architecture development
- The role of AI for vehicle design and vehicle applications
- Role of AI when building specific vehicle systems
- Key vehicle functions that make use of AI
- The role of generative AI
6. Role of security and regulations
- Role of security and regulations: Chapter overview and key takeaways
- Cybersecurity risks in SDVs (2 parts)
- The role of cybersecurity in the SDV V-Model
- Overall cybersecurity maturity
- Responsibility for key cybersecurity topics
- Automotive cybersecurity vendor showcase 1: Upstream
- Automotive cybersecurity vendor showcase 2: Critical Software
- Regulations (2 parts)
- OEM and supplier adoption strategies: Chapter overview and key takeaways
- OEM SDV adoption (10 parts)
- Supplier SDV adoption (4 parts)
7. Trends and challenges
- Trends and challenges: Chapter overview and key takeaways
- Trend 1 (3 parts)
- Trend 2
- Trend 3
- Trend 4
- Challenge 1 (2 parts)
- Challenge 2 (2 parts)
- Challenge 3 (3 parts)
- Other insights: Highlights from the EW25 SDV panel discussion
8. Methodology
- The insights in this report are based on 4 main research sources
- Complete list of survey questions (2 parts)
- Complete list of interview questions
- Respondent sampling overview (3 parts)
9. About IoT Analytics
- About IoT Analytics
- Other publications by IoT Analytics
- Information and contact



















