
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1794020
전기 소형 상용차 시장 : 차종별, 추진 방식별, GVWR별, 배터리 유형별, 배터리 용량별, 항속거리별, 최종 용도별, 지역별 - 예측(-2032년)Electric Light Commercial Vehicle Market by Vehicle Type (Pickup Truck, Van), Propulsion (BEV, PHEV), GVWR (< 6,000 lbs, and 6,001 to 10,000 lbs), Battery Type (LFP, NMC, Others), Battery Capacity, Range, End Use, And Region - Global Forecast to 2032 |
||||||
세계의 전기 소형 상용차 시장 규모는 2025년에 추정 244억 9,000만 달러를 기록하고, 2032년까지 1,166억 달러에 달할 것으로 예측되며, 2025-2032년에 CAGR로 25.0%의 성장이 전망됩니다.
| 조사 범위 | |
|---|---|
| 조사 대상 연도 | 2021-2032년 |
| 기준 연도 | 2024년 |
| 예측 기간 | 2025-2032년 |
| 단위 | 금액(10억 달러), 수량(1,000대) |
| 부문 | 차종, 항속거리, 배터리 유형, 배터리 용량, 추진력, 최종 용도, GVWR, 지역 |
| 대상 지역 | 중국, 아시아태평양(중국 제외), 유럽, 북미 |
이러한 급격한 확대는 배출가스 감축에 대한 규제 압력, E-Commerce의 성장으로 인한 도시 물류 수요 증가, 취득 비용 절감을 위한 정부 혜택에 기인합니다. 예를 들어, 미국과 캐나다에서는 엄격한 배출가스 규제(EPA 2027 기준 등), 강력한 구매 인센티브(미국 최대 4만 달러, 캐나다 iMHZEV 최대 14만 6,000달러), 주 및 준주별 리베이트가 전기 상용 밴과 픽업 트럭의 급속한 보급을 촉진하고 있습니다.
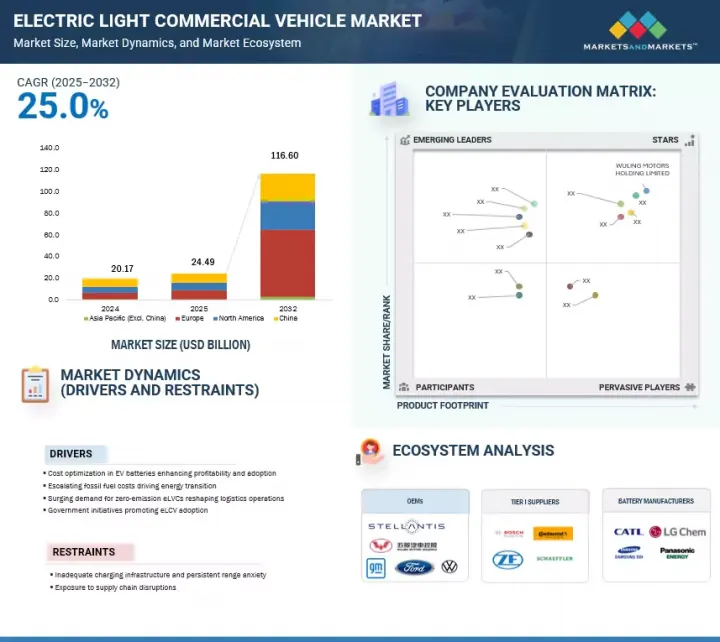
이는 E-Commerce의 성장으로 인한 도시 물류에 대한 수요 증가로 인해 전기 구동계로의 전환이 가속화되고 있기 때문이기도 합니다. 유럽은 여전히 독일, 프랑스, 영국, 네덜란드 등 국가가 주도하는 중요한 채택 국가이며, 중국은 강력한 국내 보조금과 수직적으로 통합된 EV 공급망의 혜택을 누리고 있습니다. 인도와 동남아시아에서는 각각 FAME-II와 같은 정부 제도와 상용차 수요 증가에 힘입어 채택이 가속화되고 있습니다. 배터리 화학(LFP/NMC)의 기술 발전, DC 급속 충전 인프라를 차량 보관소에 배치하고, 텔레매틱스와 차량 관리 시스템을 통합하여 e-LCV의 실현 가능성을 더욱 높이고 있습니다. Stellantis, Ford, Renault, Wuling Motors 등 주요 OEM의 생산 확대에 따라 시장은 틈새에서 주류로 이동하고 있으며, 2톤 미만의 미니 LCV와 도시 및 지역의 다양한 물류 수요에 대응하는 2-3.5톤의 배달용 밴으로 세분화되고 있습니다. 사이의 정확한 세분화가 이루어지고 있습니다.
"플러그인 하이브리드 전기자동차는 예측 기간 동안 배터리 전기자동차보다 더 빠르게 성장하는 추진력 부문이 될 것입니다."
전기 소형 상용차 시장의 플러그인 하이브리드 전기자동차 부문은 주로 충전 인프라가 안정적이지 않은 지역에서 운영의 유연성으로 인해 인기를 끌고 있습니다. 2025년 4월, 포드는 호주 최초의 플러그인 하이브리드 밴인 2025 포드 트랜짓 커스텀 PHEV(Ford Transit Custom PHEV)의 출시를 발표했습니다. PHEV 모델은 Trend LWB와 Sport SWB입니다. 이 플러그인 하이브리드 모델은 도시 저공해 지역에서는 전기로만 운행하고, 지방의 장거리 노선에서는 ICE를 백업으로 사용할 수 있는 이점을 제공합니다. 또한, 전기 소형 상용차의 주행거리 불안감 감소는 특히 충전 인프라가 확대되고 배터리 기술이 향상됨에 따라 차량 채택을 촉진하는 중요한 요인으로 작용하고 있습니다. 이 보증을 통해 물류 및 라스트 마일 배송 기업은 도시 및 반도시 지역에 eLCV를 혼란 없이 자신 있게 배치할 수 있습니다.
"50kWh 이하가 예측 기간 동안 큰 시장 점유율을 차지할 것입니다."
전기 소형 상용차 시장의 50kWh 이하 배터리 용량 부문은 주로 단거리 도시 내 물류에 최적화된 소형 배송 밴에 대한 수요 증가에 힘입어 성장세를 보이고 있습니다. 이 배터리 팩은 특히 하루 주행거리가 150km 미만이고, 잦은 스톱 앤 고(stop-and-go)를 반복하는 인구 밀집 지역에서 도시 차량에 비용 효율적인 솔루션을 제공합니다. BYD(중국)는 배터리 용량 43kWh의 T3 소형 전기 트럭을 제공하고 있습니다. Workhorse Group(미국)은 배터리 용량 50kWh의 전기 트럭 W-15를 제공하고 있습니다. 인도, 일본, 인도네시아 등의 국가에서는 Tata Ace EV, Suzuki Every EV와 같이 30-50kWh 미만의 배터리 팩을 장착한 단거리 물류 및 소규모 기업용으로 조정된 소형 eLCV의 채택이 증가하고 있습니다. 이 차량은 정부 지원 전기화 프로그램 및 도시 모빌리티 목표에 부합하며, 신흥 경제권의 상업용 차량 운영자에게 중요한 요소인 낮은 총소유비용과 제한된 충전 인프라에 대한 적합성을 제공합니다.
세계의 전기 소형 상용차 시장에 대해 조사 분석했으며, 주요 촉진요인과 억제요인, 경쟁 구도, 향후 동향 등의 정보를 전해드립니다.
목차
제1장 소개
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 중요한 인사이트
- 전기 소형 상용차 시장 기업에서 매력적인 기회
- 전기 소형 상용차 시장 : 차종별
- 전기 소형 상용차 시장 : GVWR별
- 전기 소형 상용차 시장 : 추진력별
- 전기 소형 상용차 시장 : 항속거리별
- 전기 소형 상용차 시장 : 배터리 유형별
- 전기 소형 상용차 시장 : 배터리 용량별
- 전기 소형 상용차 시장 : 용도별
- 전기 소형 상용차 시장 : 지역별
제5장 시장 개요
- 소개
- 시장 역학
- 성장 촉진요인
- 성장 억제요인
- 기회
- 과제
- 시장 역학의 영향
- 고객 비즈니스에 영향을 미치는 동향/혼란
- 가격 설정 분석
- 차종 평균판매가격 동향 : 주요 제조업체별
- 평균판매가격 동향 : 지역별(2022-2024년)
- 생태계 분석
- OEM
- 원재료 공급업체
- Tier 1 공급업체
- Tier 2 공급업체
- 부품 제조업체
- EV 충전 인프라 프로바이더
- 공급망 분석
- 규제 상황
- 규제 : 국가별
- 규제기관, 정부기관, 기타 조직
- 주요 회의와 이벤트(2025-2026년)
- 사례 연구 분석
- FEDEX의 지속 가능한 물류로의 도약
- SCOTTISH WATER의 전기 밴 도입 성공
- KENT COUNTY COUNCIL의 기업용 전기 밴 시범 도입
- 투자와 자금 조달 시나리오
- 특허 분석
- HS 코드(8702) : 전기 소형 상용차
- 전기 소형 상용차 시장 수입 시나리오
- 전기 소형 상용차 시장 수출 시나리오
- AI/생성형 AI의 영향
- 기술 분석
- 주요 기술
- 보완 기술
- 인접 기술
- 향후 자동차 발매, 주요 OEM의 투자, 전기화 목표에 관한 MNM의 견해
- 향후 차량 모델 발매
- OEM의 목표와 투자
- OEM의 eLCV 플랫폼 전략에 관한 인사이트
- 전기 픽업 트럭과 밴 배터리 교환에 관한 전략적 인사이트
- 전기 픽업 트럭과 밴 사업 사례 분석
- 플릿 소유·운영
- Fleet as a Service(FaaS)
- 플랫폼과 생태계의 제휴
- 종량 과금 모델
- 부품표
- 총소유비용
- 전기 소형 상용차의 주요 성능의 비교
- 항속거리/배터리 용량
- 항속거리와 최종 용도
- 배터리 용량과 최종 용도
- 출력과 충전 시간
- 주요 이해관계자와 구입 기준
제6장 전기 소형 상용차 시장 : 차종별
- 소개
- 픽업 트럭
- 밴
- 중요한 인사이트
제7장 전기 소형 상용차 시장 : 추진력별
- 소개
- 배터리 전기자동차
- 플러그인 하이브리드 전기자동차
- 중요한 인사이트
제8장 전기 소형 상용차 시장 : 배터리 용량별
- 소개
- 50 kWh 이하
- 50-100kWh
- 100-150kWh
- 중요한 인사이트
제9장 전기 소형 상용차 시장 : 배터리 유형별
- 소개
- 인산철리튬(LFP)
- 니켈 망간 코발트(NMC)
- 전고체 전지
- 기타
- 중요한 인사이트
제10장 전기 소형 상용차 시장 : 용도별
- 소개
- 라스트 마일 배송
- 필드 서비스
- 배송 서비스
- 주요 산업 분석
제11장 전기 소형 상용차 시장 : GVWR별
- 소개
- 6,000 파운드 미만
- 6,001-1만 파운드
- 중요한 인사이트
제12장 전기 소형 상용차 시장 : 차종별
- 소개
- 100마일 이하
- 100-200마일
- 200마일 이상
- 중요한 인사이트
제13장 전기 소형 상용차 시장 : 지역별
- 소개
- 중국
- 아시아태평양(중국 제외)
- 거시경제 전망
- 일본
- 인도
- 한국
- 유럽
- 거시경제 전망
- 프랑스
- 독일
- 스페인
- 오스트리아
- 노르웨이
- 스웨덴
- 네덜란드
- 영국
- 이탈리아
- 기타 유럽
- 북미
- 거시경제 전망
- 미국
- 캐나다
제14장 경쟁 구도
- 개요
- 주요 진출 기업의 전략/강점
- 시장 점유율 분석(2024년)
- 매출 분석(2020-2024년)
- 기업 평가와 재무 지표
- 브랜드/제품의 비교
- 기업 평가 매트릭스 : 주요 기업(2024년)
- 기업 평가 매트릭스 : 스타트업/중소기업(2024년)
- 경쟁 시나리오
제15장 기업 개요
- 주요 기업
- WULING MOTORS HOLDINGS LIMITED
- FORD MOTOR COMPANY
- GENERAL MOTORS
- STELLANTIS N.V.
- RENAULT GROUP
- TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION
- BYD COMPANY LTD.
- NISSAN MOTOR CO., LTD.
- IVECO GROUP N.V.
- FLEXIS
- RIVIAN
- FOTON INTERNATIONAL
- TATA MOTORS LIMITED
- MAXUS ELECTRIC VEHICLES AND VANS
- MITSUBISHI FUSO TRUCK AND BUS CORPORATION
- 기타 기업
- SWITCH MOBILITY
- EULER MOTORS
- TELO TRUCKS
- OMEGA SEIKI MOBILITY
- SLATE
- EVUM MOTORS
- ARRIVAL UK LTD.
- EKA MOBILITY
- NU RIDE INC.
- MULLEN AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
- EVAGE
- QUCEV
- KAIYUN MOTORS
제16장 MARKETSANDMARKETS에 의한 제안
- 중국, 전기 소형 상용차의 주요 시장으로 부상
- 6,001-10만 파운드 세그먼트는 예측 기간 동안 성장할 것으로 예상
- ADAS(첨단운전자보조시스템) 통합
- 결론
제17장 부록
KSM 25.08.27The electric light commercial vehicle market is estimated at USD 24.49 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 116.60 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of 25.0% from 2025 to 2032.
| Scope of the Report | |
|---|---|
| Years Considered for the Study | 2021-2032 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2032 |
| Units Considered | Value (USD Billion), Volume (Thousand Units) |
| Segments | Vehicle Type, Range, Battery Type, Battery Capacity, Propulsion, End Use, GVWR, and Region |
| Regions covered | China, Asia Pacific (excl. China), Europe, and North America |
This rapid expansion is driven by regulatory pressure to cut emissions, rising urban logistics demand due to e-commerce growth, and favorable government incentives that reduce acquisition costs. For instance, in the US and Canada, rapid adoption of electric commercial vans and pickups is driven by strict emission norms (e.g., EPA 2027 standards) and strong purchase incentives up to USD 40,000 in the US and up to USD 146,000 in Canada (iMHZEV), with additional state and provincial rebates.
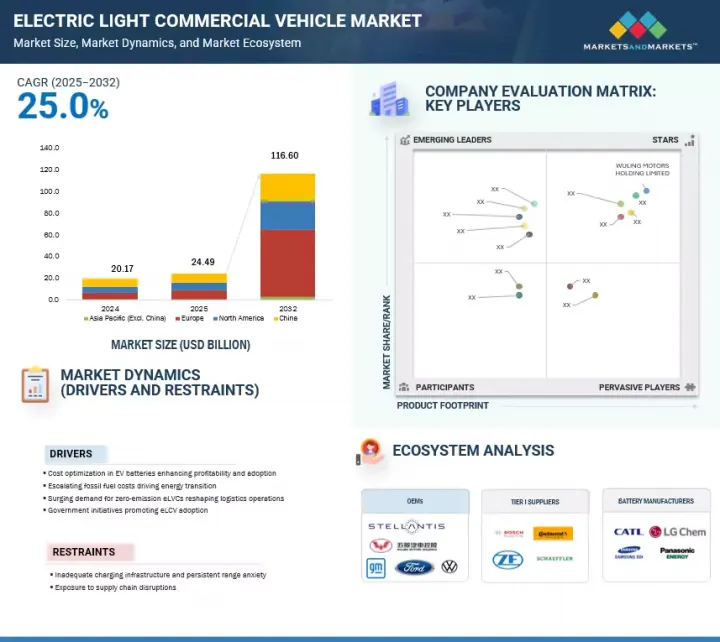
This is further supported by rising urban logistics demand due to e-commerce growth, accelerating the shift to electric drivetrains. Europe remains a key adopter, led by countries like Germany, France, the UK, and the Netherlands, while China benefits from strong domestic subsidies and vertically integrated EV supply chains. In India and Southeast Asia, adoption is gaining momentum, supported by government schemes like FAME-II and increasing commercial fleet demand, respectively. Technological advancements in battery chemistries (LFP/NMC), deployment of DC fast-charging infrastructure at fleet depots, and integration of telematics and fleet management systems further enhance the viability of e-LCVs. With major OEMs such as Stellantis, Ford, Renault, and Wuling Motors scaling production, the market is transitioning from niche to mainstream, with a precise segmentation emerging between sub-2-ton mini-LCVs and 2-3.5-ton delivery vans for diverse urban and regional logistics needs.
"Plug-in hybrid electric vehicle to be faster-growing propulsion segment than battery electric vehicle segment during forecast period"
The plug-in hybrid electric vehicle segment of the electric light commercial vehicle market is gaining traction primarily due to its operational flexibility in regions with inconsistent charging infrastructure. In April 2025, Ford announced the launch of Australia's first plug-in hybrid van, the 2025 Ford Transit Custom PHEV, arriving in October alongside its full-electric sibling. The PHEV models are Trend LWB and Sport SWB. This plug-in hybrid model offers fleets the benefit of electric-only operation in urban low-emission zones, while retaining ICE backup for extended rural routes. Additionally, lower range anxiety in electric light commercial vehicles is a key driver for fleet adoption, especially as charging infrastructure expands and battery technologies improve. This assurance enables logistics and last-mile delivery companies to deploy eLCVs across urban and semi-urban routes without disruption, confidently.
"Up to 50 kWh to hold significant market share during forecast period"
The up to 50 kWh battery capacity segment of the electric light commercial vehicle market is primarily driven by the growing demand for compact delivery vans optimized for short-distance, intra-city logistics. These battery packs offer a cost-effective solution for urban fleets, especially in densely populated regions where daily routes are under 150 km and frequent stop-and-go driving is common. BYD (China) offers T3 light-duty electric trucks with a battery capacity of 43 kWh. The offerings of Workhorse Group (US) include its electric truck W-15 with a battery capacity of 50 kWh. Countries like India, Japan, and Indonesia are witnessing increased adoption of compact eLCVs such as Tata Ace EV and Suzuki Every EV, equipped with battery packs under 30-50 kWh, tailored for short-haul logistics and small business use. These vehicles align with government-supported electrification programs and urban mobility goals, offering lower total cost of ownership and compatibility with limited charging infrastructure, factors critical to commercial fleet operators in emerging economies.
"North America to hold second-largest market share during forecast period"
North America is home to renowned OEMs that specialize in producing high-quality and high-performance vehicles, driving the electric light commercial vehicle market. These manufacturers, including Ford Motor Company (US), GMC (US), and General Motors (US), are increasingly focusing on developing faster, cleaner, and more efficient electric light commercial vehicles. In North America, governments at both the federal and state levels are offering incentives to promote the adoption of electric vehicles, including electric light commercial vehicles. For instance, under the US Federal Commercial Clean Vehicle Credit (IRC 45W), businesses can receive up to USD 7,500 for light commercial EVs, and state programs like California's HVIP offer up to USD 60,000 per vehicle for zero-emission vans and trucks, with tiered reductions for large fleets. These incentives include tax credits, rebates, grants, and infrastructure investments. For instance, the US federal government's investments in charging infrastructure and tax incentives for EV purchases have stimulated growth in the electric light commercial vehicle market. The expansion of charging infrastructure is critical for the widespread adoption of electric light commercial vehicles. In North America, there has been significant investment in charging networks, including fast-charging stations along major transportation routes and in urban areas. For instance, in January 2024, the US government invested USD 623 million in charging infrastructure. In February 2024, the first public 500 kW charging station for North America was unveiled at Mercedes-Benz USA Headquarters in Sandy Springs, Georgia.
Breakup of Primaries:
In-depth interviews were conducted with CEOs, marketing directors, other innovation and technology directors, and executives from various key organizations operating in this market.
- By Company Type: OEMs- 35%, Tier I- 41%, and Tier II & III- 24%
- By Designation: CXOs - 60%, Managers - 10%, and Executives- 30%
- By Region: China-20%, Asia Pacific (excl. China)-34%, Europe-23%, North America-18%
The electric light commercial vehicle market is dominated by major players, including Wuling Motors Holdings Limited (China), Ford Motor Company (US), General Motors (US), Stellantis NV (Netherlands), and Renault (France).
The study includes an in-depth competitive analysis of these key players in the electric light commercial vehicle market, with their company profiles, recent developments, and key market strategies.
Research Coverage:
This research report categorizes the electric light commercial vehicle market by vehicle type (pickup truck and van), propulsion (battery electric vehicle and plug-in hybrid electric vehicle), by battery type (LFP, NMC, solid-state, and others), battery capacity (up to 50 kWh, 50 to 100 kWh, and 100 to 150 kWh), range (up to 100 miles, 100 to 200 miles, and above 200 miles), by GVWR (Below 6,000 lbs and 6,001 to 10,000 lbs), end use (last-mile delivery, field services, and distribution services), and region (China, Asia Pacific (excl. China), Europe, and North America). The scope of the report covers detailed information regarding the major factors, such as drivers, restraints, challenges, and opportunities, influencing the growth of the market. A detailed analysis of the key industry players provided insights into their business overviews, solutions & services, key strategies, contracts, partnerships, agreements, product & service launches, mergers & acquisitions, and recent developments associated with the electric light commercial vehicle market. Competitive analysis of upcoming startups in the electric light commercial vehicle market ecosystem has been covered in this report.
Reasons to Buy this Report
The report will help the market leaders/new entrants in this market with information on the closest approximations of the revenue numbers for the overall electric light commercial vehicle market and the subsegments. This report will also help stakeholders understand the competitive landscape and gain more insights to position their businesses better and plan suitable go-to-market strategies. It will help stakeholders understand the pulse of the market and provide them with information on key market drivers, restraints, challenges, and opportunities.
The report provides insights into the following pointers:
- Analysis of key drivers (cost optimization in EV batteries enhancing profitability and adoption, Escalating fossil fuel costs driving energy transition, Surging demand for zero-emission eLVCs reshaping logistics operations, government initiatives promoting eLCV adoption), restraints (inadequate charging infrastructure and persistent range anxiety hindering market adoption, exposure to supply chain disruptions), opportunities (battery leasing and mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) models, development of wireless EV charging technology for on-the-go charging), and challenges (lack of standardization in charging protocols, low availability of lithium for EV batteries) influencing the growth of the electric light commercial vehicle market
- Product Development/Innovation: Detailed insights into upcoming technologies and research & development activities in the electric light commercial vehicle market
- Market Development: Comprehensive information about lucrative markets (the report analyses the electric light commercial vehicle market across varied regions)
- Market Diversification: Exhaustive information about new products & services, untapped geographies, recent developments, and investments in the electric light commercial vehicle market
Competitive Assessment: In-depth assessment of market shares, growth strategies, and service offerings of leading players, such as Wuling Motors Holdings Limited. (China), Ford Motor Company (US), General Motors (US), Stellantis NV (Netherlands), and Renault (France), in the electric light commercial vehicle market
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 STUDY OBJECTIVES
- 1.2 MARKET DEFINITION
- 1.3 STUDY SCOPE
- 1.3.1 MARKETS COVERED AND REGIONAL SCOPE
- 1.3.2 INCLUSIONS AND EXCLUSIONS
- 1.3.3 YEARS CONSIDERED
- 1.4 CURRENCY CONSIDERED
- 1.4.1 UNITS CONSIDERED
- 1.5 STAKEHOLDERS
- 1.6 SUMMARY OF CHANGES
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 RESEARCH DATA
- 2.1.1 SECONDARY DATA
- 2.1.1.1 List of key secondary sources
- 2.1.1.2 Key data from secondary sources
- 2.1.2 PRIMARY DATA
- 2.1.2.1 Primary interviews: demand and supply sides
- 2.1.2.2 Primary interview participants
- 2.1.2.3 Objectives of primary research
- 2.1.1 SECONDARY DATA
- 2.2 MARKET SIZE ESTIMATION
- 2.2.1 BOTTOM-UP APPROACH
- 2.2.2 TOP-DOWN APPROACH
- 2.3 DATA TRIANGULATION
- 2.4 FACTOR ANALYSIS
- 2.4.1 DEMAND- AND SUPPLY-SIDE FACTOR ANALYSIS
- 2.5 RESEARCH ASSUMPTIONS
- 2.6 RESEARCH LIMITATIONS
- 2.7 RISK ANALYSIS
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 PREMIUM INSIGHTS
- 4.1 ATTRACTIVE OPPORTUNITIES FOR PLAYERS IN ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET
- 4.2 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE
- 4.3 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY GVWR
- 4.4 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY PROPULSION
- 4.5 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY RANGE
- 4.6 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY BATTERY TYPE
- 4.7 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY BATTERY CAPACITY
- 4.8 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY END USE
- 4.9 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY REGION
5 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 5.1 INTRODUCTION
- 5.2 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.2.1 DRIVERS
- 5.2.1.1 Cost optimization in EV batteries enhancing profitability and adoption
- 5.2.1.2 Escalating fossil fuel costs driving energy transition
- 5.2.1.3 Surging demand for zero-emission eLCVs reshaping logistics operations
- 5.2.1.4 Government initiatives promoting eLCV adoption
- 5.2.2 RESTRAINTS
- 5.2.2.1 Inadequate charging infrastructure and persistent range anxiety hindering market adoption
- 5.2.2.2 Exposure to supply chain disruptions
- 5.2.3 OPPORTUNITIES
- 5.2.3.1 Battery leasing and mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) models
- 5.2.3.2 Development of wireless EV charging technology for on-the-go charging
- 5.2.4 CHALLENGES
- 5.2.4.1 Lack of standardization in charging protocols
- 5.2.4.2 Low availability of lithium for EV batteries
- 5.2.5 IMPACT OF MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.2.1 DRIVERS
- 5.3 TRENDS/DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMER BUSINESS
- 5.4 PRICING ANALYSIS
- 5.4.1 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE TREND FOR VEHICLE TYPES, BY KEY PLAYERS, 2024 (USD)
- 5.4.2 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE TREND, BY REGION, 2022-2024
- 5.5 ECOSYSTEM ANALYSIS
- 5.5.1 OEMS
- 5.5.2 RAW MATERIAL SUPPLIERS
- 5.5.3 TIER I SUPPLIERS
- 5.5.4 TIER II SUPPLIERS
- 5.5.5 COMPONENT MANUFACTURERS
- 5.5.6 EV CHARGING INFRASTRUCTURE PROVIDERS
- 5.6 SUPPLY CHAIN ANALYSIS
- 5.7 REGULATORY LANDSCAPE
- 5.7.1 COUNTRY-WISE REGULATIONS
- 5.7.1.1 Netherlands
- 5.7.1.2 Germany
- 5.7.1.3 France
- 5.7.1.4 UK
- 5.7.1.5 China
- 5.7.1.6 US
- 5.7.2 REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS
- 5.7.1 COUNTRY-WISE REGULATIONS
- 5.8 KEY CONFERENCES AND EVENTS, 2025-2026
- 5.9 CASE STUDY ANALYSIS
- 5.9.1 FEDEX'S LEAP INTO SUSTAINABLE LOGISTICS
- 5.9.2 SCOTTISH WATER'S SUCCESSFUL ADOPTION OF ELECTRIC VANS
- 5.9.3 ELECTRIC VAN TRIAL FOR BUSINESSES BY KENT COUNTY COUNCIL
- 5.10 INVESTMENT AND FUNDING SCENARIO
- 5.11 PATENT ANALYSIS
- 5.11.1 INTRODUCTION
- 5.12 HS CODE (8702): ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE
- 5.12.1 IMPORT SCENARIO OF ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET
- 5.12.2 EXPORT SCENARIO OF ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET
- 5.13 IMPACT OF AI/GEN AI
- 5.14 TECHNOLOGY ANALYSIS
- 5.14.1 KEY TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.14.1.1 Development in wireless charging technology
- 5.14.1.2 Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) integration
- 5.14.2 COMPLEMENTARY TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.14.2.1 Development in solid-state batteries
- 5.14.2.2 Advanced fleet telematics systems
- 5.14.3 ADJACENT TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.14.3.1 Multi-motor configurations
- 5.14.1 KEY TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.15 MNM INSIGHTS ON UPCOMING VEHICLE LAUNCHES, KEY OEM INVESTMENTS, AND TARGET FOR ELECTRIFICATION
- 5.15.1 UPCOMING VEHICLE MODEL LAUNCHES
- 5.15.2 OEM TARGETS AND INVESTMENT
- 5.16 INSIGHTS INTO OEMS' STRATEGIES FOR ELCV PLATFORMS
- 5.17 STRATEGIC INSIGHTS INTO BATTERY SWAPPING FOR ELECTRIC PICKUP TRUCKS AND VANS
- 5.18 BUSINESS CASE ANALYSIS FOR ELECTRIC PICKUP TRUCKS AND VANS
- 5.18.1 FLEET OWNERSHIP & OPERATIONS
- 5.18.2 FLEET-AS-A-SERVICE (FAAS)
- 5.18.3 PLATFORM AND ECOSYSTEM COLLABORATION
- 5.18.4 PAY-PER-USE MODEL
- 5.19 BILL OF MATERIALS
- 5.20 TOTAL COST OF OWNERSHIP
- 5.21 KEY PERFORMANCE COMPARISON FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLES
- 5.21.1 RANGE/BATTERY CAPACITY
- 5.21.2 RANGE VS. END USE
- 5.21.3 BATTERY CAPACITY VS. END USE
- 5.21.4 POWER VS. CHARGING DURATION
- 5.22 KEY STAKEHOLDERS AND BUYING CRITERIA
- 5.22.1 KEY STAKEHOLDERS IN BUYING PROCESS
- 5.22.2 BUYING CRITERIA
6 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE
- 6.1 INTRODUCTION
- 6.2 PICKUP TRUCK
- 6.2.1 RISING DEMAND FOR DUAL-PURPOSE UTILITY VEHICLES TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 6.3 VAN
- 6.3.1 LOWER TOTAL COST OF OWNERSHIP TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 6.3.2 CARGO VAN
- 6.3.3 PASSENGER VAN
- 6.4 KEY PRIMARY INSIGHTS
7 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY PROPULSION
- 7.1 INTRODUCTION
- 7.2 BATTERY ELECTRIC VEHICLE
- 7.2.1 LOWER TOTAL COST OF OWNERSHIP THAN ICE AND HYBRID VEHICLES TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 7.3 PLUG-IN HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLE
- 7.3.1 LOWER RANGE ANXIETY AND OPERATIONAL FLEXIBILITY TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 7.4 PRIMARY INSIGHTS
8 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY BATTERY CAPACITY
- 8.1 INTRODUCTION
- 8.2 UP TO 50 KWH
- 8.2.1 INCREASING ADOPTION OF COMPACT DELIVERY VANS TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 8.3 50 TO 100 KWH
- 8.3.1 SUITABILITY FOR MID-RANGE LOGISTICS AND URBAN-SUBURBAN DELIVERY OPERATIONS TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 8.4 100 TO 150 KWH
- 8.4.1 HIGH PAYLOAD APPLICATIONS TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 8.5 PRIMARY INSIGHTS
9 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY BATTERY TYPE
- 9.1 INTRODUCTION
- 9.2 LITHIUM IRON PHOSPHATE (LFP)
- 9.2.1 HIGH ENERGY DENSITY AND FAST-CHARGING CAPABILITIES TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 9.3 NICKEL MANGANESE COBALT (NMC)
- 9.3.1 LONG DRIVING RANGES FOR LOGISTICS AND DELIVERY TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 9.4 SOLID-STATE
- 9.4.1 LONGER LIFECYCLE THAN CONVENTIONAL LITHIUM-ION BATTERIES TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 9.5 OTHERS
- 9.6 PRIMARY INSIGHTS
10 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY END USE
- 10.1 INTRODUCTION
- 10.2 LAST-MILE DELIVERY
- 10.2.1 RISING DEMAND FOR VEHICLE ELECTRIFICATION IN E-COMMERCE TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 10.3 FIELD SERVICES
- 10.3.1 INCREASING DEMAND FOR GREEN MOBILITY IN FIELD SERVICES TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 10.4 DISTRIBUTION SERVICES
- 10.4.1 INCREASING RELIANCE ON DELIVERY SERVICES TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 10.5 KEY INDUSTRY INSIGHTS
11 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY GVWR
- 11.1 INTRODUCTION
- 11.2 BELOW 6,000 LBS
- 11.2.1 GROWING DEMAND FOR LAST-MILE DELIVERY IN URBAN AREAS TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 11.3 6,001-10,000 LBS
- 11.3.1 GROWING DEMAND FOR OPTIMAL LOAD-CARRYING CAPACITY DRIVE GROWTH
- 11.4 PRIMARY INSIGHTS
12 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY RANGE
- 12.1 INTRODUCTION
- 12.2 UP TO 100 MILES
- 12.2.1 INCREASING DEMAND FROM MICRO-MOBILITY LOGISTICS TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 12.3 100 TO 200 MILES
- 12.3.1 OPERATIONAL FLEXIBILITY AND COST-EFFECTIVENESS TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 12.4 ABOVE 200 MILES
- 12.4.1 INCREASING DEMAND FOR ZERO-EMISSION CARGO VANS IN EUROPE TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 12.5 PRIMARY INSIGHTS
13 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY REGION
- 13.1 INTRODUCTION
- 13.2 CHINA
- 13.2.1 RAPID ROLLOUT OF COST-EFFECTIVE ELCVS TO DRIVE MARKET
- 13.2.2 MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 13.3 ASIA PACIFIC (EXCL. CHINA)
- 13.3.1 MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 13.3.2 JAPAN
- 13.3.2.1 Government-led decarbonization and urban logistics innovation to drive growth
- 13.3.3 INDIA
- 13.3.3.1 Urban emission norms and government push toward clean mobility to drive growth
- 13.3.4 SOUTH KOREA
- 13.3.4.1 Targeted fleet electrification initiatives to drive growth
- 13.4 EUROPE
- 13.4.1 MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 13.4.2 FRANCE
- 13.4.2.1 Growth in e-commerce and parcel delivery to drive market
- 13.4.3 GERMANY
- 13.4.3.1 Commercial charging infrastructure development to drive growth
- 13.4.4 SPAIN
- 13.4.4.1 Government-led electrification targets and subsidies to drive growth
- 13.4.5 AUSTRIA
- 13.4.5.1 Increasing deployment of fast-charging hubs near industrial parks and logistic centers to drive growth
- 13.4.6 NORWAY
- 13.4.6.1 Zero-emission commercial transport policies to drive growth
- 13.4.7 SWEDEN
- 13.4.7.1 Government-backed green transport incentives to drive growth
- 13.4.8 NETHERLANDS
- 13.4.8.1 Stringent legislation to drive growth
- 13.4.9 UK
- 13.4.9.1 ZEV mandate to drive growth
- 13.4.10 ITALY
- 13.4.10.1 Integration of smart mobility solutions in commercial fleets to drive growth
- 13.4.11 REST OF EUROPE
- 13.5 NORTH AMERICA
- 13.5.1 MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 13.5.2 US
- 13.5.2.1 Rising adoption of electric pickup trucks to drive growth
- 13.5.3 CANADA
- 13.5.3.1 Government plans to electrify transit to drive growth
14 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 14.1 OVERVIEW
- 14.2 KEY PLAYER STRATEGIES/RIGHT TO WIN
- 14.3 MARKET SHARE ANALYSIS, 2024
- 14.4 REVENUE ANALYSIS, 2020-2024
- 14.5 COMPANY VALUATION AND FINANCIAL METRICS
- 14.5.1 COMPANY VALUATION
- 14.5.2 FINANCIAL METRICS
- 14.6 BRAND/PRODUCT COMPARISON
- 14.7 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: KEY PLAYERS, 2024
- 14.7.1 STARS
- 14.7.2 EMERGING LEADERS
- 14.7.3 PERVASIVE PLAYERS
- 14.7.4 PARTICIPANTS
- 14.7.5 COMPANY FOOTPRINT
- 14.7.5.1 Company footprint
- 14.7.5.2 Region footprint
- 14.7.5.3 Vehicle type footprint
- 14.8 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: STARTUPS/SMES, 2024
- 14.8.1 PROGRESSIVE COMPANIES
- 14.8.2 RESPONSIVE COMPANIES
- 14.8.3 DYNAMIC COMPANIES
- 14.8.4 STARTING BLOCKS
- 14.8.5 COMPETITIVE BENCHMARKING
- 14.8.5.1 List of startups/SMEs
- 14.8.5.2 Competitive benchmarking of startups/SMEs
- 14.9 COMPETITIVE SCENARIO
- 14.9.1 PRODUCT LAUNCHES
- 14.9.2 DEALS
- 14.9.3 EXPANSIONS
- 14.9.4 OTHER DEVELOPMENTS
15 COMPANY PROFILES
- 15.1 KEY PLAYERS
- 15.1.1 WULING MOTORS HOLDINGS LIMITED
- 15.1.1.1 Business overview
- 15.1.1.2 Products offered
- 15.1.1.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.1.3.1 Product launches
- 15.1.1.3.2 Deals
- 15.1.1.4 MnM view
- 15.1.1.4.1 Key strengths
- 15.1.1.4.2 Strategic choices
- 15.1.1.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 15.1.2 FORD MOTOR COMPANY
- 15.1.2.1 Business overview
- 15.1.2.2 Products offered
- 15.1.2.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.2.3.1 Product launches
- 15.1.2.3.2 Deals
- 15.1.2.3.3 Expansions
- 15.1.2.3.4 Other developments
- 15.1.2.4 MnM view
- 15.1.2.4.1 Key strengths
- 15.1.2.4.2 Strategic choices
- 15.1.2.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 15.1.3 GENERAL MOTORS
- 15.1.3.1 Business overview
- 15.1.3.2 Chevrolet BrightDrop
- 15.1.3.3 Products offered
- 15.1.3.4 Recent developments
- 15.1.3.4.1 Deals
- 15.1.3.5 MnM view
- 15.1.3.5.1 Key strengths
- 15.1.3.5.2 Strategic choices
- 15.1.3.5.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 15.1.4 STELLANTIS N.V.
- 15.1.4.1 Business overview
- 15.1.4.2 Peugeot
- 15.1.4.3 Citroen
- 15.1.4.4 Fiat Professional
- 15.1.4.5 Vauxhall
- 15.1.4.6 Ram
- 15.1.4.7 Products offered
- 15.1.4.8 Recent developments
- 15.1.4.8.1 Product launches
- 15.1.4.8.2 Deals
- 15.1.4.9 MnM view
- 15.1.4.9.1 Key strengths
- 15.1.4.9.2 Strategic choices
- 15.1.4.9.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 15.1.5 RENAULT GROUP
- 15.1.5.1 Business overview
- 15.1.5.2 Products offered
- 15.1.5.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.5.3.1 Product developments
- 15.1.5.3.2 Deals
- 15.1.5.4 MnM view
- 15.1.5.4.1 Key strengths
- 15.1.5.4.2 Strategic choices
- 15.1.5.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 15.1.6 TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION
- 15.1.6.1 Business overview
- 15.1.6.2 Products offered
- 15.1.6.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.6.3.1 Deals
- 15.1.6.3.2 Other developments
- 15.1.7 BYD COMPANY LTD.
- 15.1.7.1 Business overview
- 15.1.7.2 Products offered
- 15.1.7.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.7.3.1 Product launches
- 15.1.7.3.2 Deals
- 15.1.7.3.3 Expansions
- 15.1.8 NISSAN MOTOR CO., LTD.
- 15.1.8.1 Business overview
- 15.1.8.2 Products offered
- 15.1.8.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.8.3.1 Product launches
- 15.1.8.3.2 Deals
- 15.1.9 IVECO GROUP N.V.
- 15.1.9.1 Business overview
- 15.1.9.2 Products offered
- 15.1.9.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.9.3.1 Product launches
- 15.1.9.3.2 Deals
- 15.1.10 FLEXIS
- 15.1.10.1 Business overview
- 15.1.10.2 Products offered
- 15.1.10.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.10.3.1 Deals
- 15.1.11 RIVIAN
- 15.1.11.1 Business overview
- 15.1.11.2 Products offered
- 15.1.11.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.11.3.1 Product enhancements/launches
- 15.1.11.3.2 Deals
- 15.1.11.3.3 Other developments
- 15.1.12 FOTON INTERNATIONAL
- 15.1.12.1 Business overview
- 15.1.12.2 Products offered
- 15.1.12.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.12.3.1 Product launches
- 15.1.12.3.2 Deals
- 15.1.12.3.3 Other developments
- 15.1.13 TATA MOTORS LIMITED
- 15.1.13.1 Business overview
- 15.1.13.2 Products offered
- 15.1.13.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.13.3.1 Product launches
- 15.1.13.3.2 Deals
- 15.1.14 MAXUS ELECTRIC VEHICLES AND VANS
- 15.1.14.1 Business overview
- 15.1.14.2 Products offered
- 15.1.14.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.14.3.1 Product launches
- 15.1.15 MITSUBISHI FUSO TRUCK AND BUS CORPORATION
- 15.1.15.1 Business overview
- 15.1.15.2 Products offered
- 15.1.15.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.15.3.1 Deals
- 15.1.15.3.2 Other developments
- 15.1.1 WULING MOTORS HOLDINGS LIMITED
- 15.2 OTHER PLAYERS
- 15.2.1 SWITCH MOBILITY
- 15.2.2 EULER MOTORS
- 15.2.3 TELO TRUCKS
- 15.2.4 OMEGA SEIKI MOBILITY
- 15.2.5 SLATE
- 15.2.6 EVUM MOTORS
- 15.2.7 ARRIVAL UK LTD.
- 15.2.8 EKA MOBILITY
- 15.2.9 NU RIDE INC.
- 15.2.10 MULLEN AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
- 15.2.11 EVAGE
- 15.2.12 QUCEV
- 15.2.13 KAIYUN MOTORS
16 RECOMMENDATIONS BY MARKETSANDMARKETS
- 16.1 CHINA TO BE PROMINENT MARKET FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLES
- 16.2 6,001 TO 10,000 LBS SEGMENT TO WITNESS GROWTH DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- 16.3 INTEGRATION OF ADVANCED DRIVER ASSISTANCE SYSTEMS
- 16.4 CONCLUSION
17 APPENDIX
- 17.1 KEY INSIGHTS OF INDUSTRY EXPERTS
- 17.2 DISCUSSION GUIDE
- 17.3 KNOWLEDGESTORE: MARKETSANDMARKETS' SUBSCRIPTION PORTAL
- 17.4 CUSTOMIZATION OPTIONS
- 17.4.1 COMPANY PROFILES
- 17.4.1.1 Profiling of Additional Market Players (Up to 5)
- 17.4.2 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY PROPULSION, AT COUNTRY LEVEL
- 17.4.3 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY GVWR, AT COUNTRY LEVEL
- 17.4.1 COMPANY PROFILES
- 17.5 RELATED REPORTS
- 17.6 AUTHOR DETAILS



















