
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1823726
데이터센터용 전력 시장 예측(-2030년) : 전기 솔루션별, 데이터센터 규모별, 데이터센터 유형별Data Center Power Market by Electrical Solution, Data Center Size, Data Center Type - Global Forecast to 2030 |
||||||
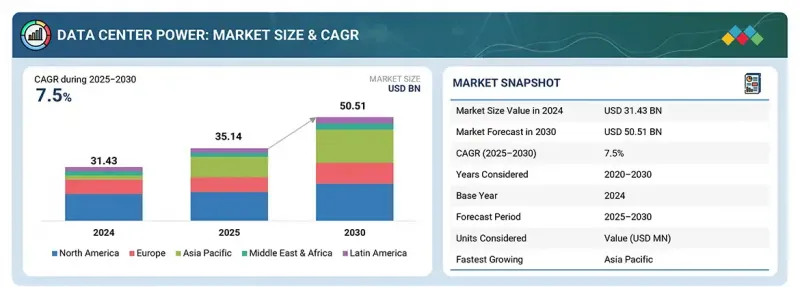
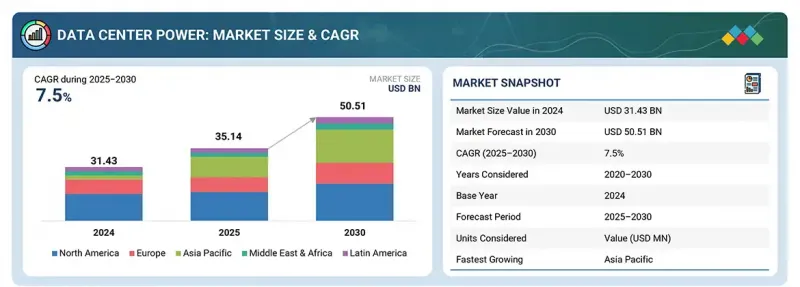
세계의 데이터센터용 전력 시장 규모는 2025년 351억 4,000만 달러에서 2030년까지 505억 1,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예측되며, 예측 기간에 CAGR로 7.5%의 성장이 전망됩니다.
| 조사 범위 | |
|---|---|
| 조사 대상 연도 | 2020-2030년 |
| 기준연도 | 2024년 |
| 예측 기간 | 2025-2030년 |
| 단위 | 100만 달러/10억 달러 |
| 부문 | 컴포넌트, Tier 유형, 데이터센터 규모(전력 용량), 데이터센터 유형, 업계 |
| 대상 지역 | 북미, 유럽, 아시아태평양, 중동 및 아프리카, 라틴아메리카 |
지속가능성 목표 증가와 에너지 정책의 지원으로 전 세계에서 첨단 데이터센터용 전력 시스템 도입이 가속화되고 있습니다. 사업자들은 배출량 감소, 효율성 향상, 가동시간 확보를 위해 AI를 활용한 전력 관리, 재생에너지와의 통합, 그리드 인터랙티브 솔루션에 대한 투자를 진행하고 있습니다. 이러한 발전은 확장성, 운영 탄력성, 친환경 표준 준수를 강화합니다.
그러나 많은 데이터센터가 효율성과 유연성을 제한하는 레거시 시스템으로 운영되고 있으므로 기존 전력 인프라에 대한 의존도는 여전히 억제요인으로 작용하고 있습니다. 최신 지능형 전력 아키텍처로 전환하기 위해서는 막대한 자본, 숙련된 전문 지식, 통합 작업이 필요하며, 비용과 복잡성은 데이터센터 전력 시장 성장에 큰 걸림돌로 작용하고 있습니다.
"산업별로는 통신 부문이 2025년 가장 큰 시장 점유율을 차지할 것으로 추정됩니다. "
통신 데이터센터는 모바일 네트워크, 인터넷 서비스, VoIP 플랫폼, 클라우드 통신 시스템을 지원하며 세계 연결성의 중추를 형성하고 있습니다. 전력이 끊기면 네트워크 성능 저하, 서비스 중단, 5G 기지국 등 중요 인프라에 영향을 미쳐 서비스 중단 및 고객 불만을 초래할 수 있습니다. 공급업체는 UPS 시스템, PDU, 현장 발전기, 배터리 에너지 저장을 제공하여 이러한 고 수요 워크로드를 위한 지속적 이고 안정적인 전력을 보장합니다.
다중 배전 경로를 갖춘 이중화된 내결함성 전력 아키텍처는 고밀도 네트워크 운영의 가동 시간을 유지하고, 다양한 지역에 걸쳐 원활한 연결성을 보장합니다. 실시간 모니터링, 예지보전, 에너지 관리 플랫폼이 전력 소비를 최적화하고 다운타임을 방지하여 운영 비용을 절감합니다. 모듈식 확장형 전력 솔루션을 통해 통신 데이터센터는 지속적인 운영에 영향을 주지 않고 가입자 수 증가, IoT 트래픽, 엣지 컴퓨팅 배포에 대응할 수 있도록 용량을 빠르게 확장할 수 있습니다.
지능형 부하 분산 및 최적화된 에너지 공급은 민감한 네트워크 장비를 보호하고 중단없는 데이터 흐름을 지원하며 대기 시간을 최소화합니다. 탄력적이고 고성능의 효율적으로 관리되는 전력 인프라를 제공하는 벤더는 통신 사업자가 지속적인 서비스를 유지하고, SLA 요건을 충족하며, 운영의 신뢰성을 높일 수 있도록 지원합니다. 이러한 솔루션은 통신 데이터센터에 전력을 공급하고 안정적인 연결성, 고가용성, 효율적인 네트워크 운영을 보장하기 위한 견고한 기반을 형성합니다.
"계층별로는 Tier IV 부문이 예측 기간 중 가장 높은 CAGR로 성장할 것으로 예측됩니다. "
Tier IV 데이터센터는 최고 수준의 전력 안정성과 내결함성을 갖춘 데이터센터로, 중단이 허용되지 않는 미션 크리티컬한 워크로드를 지원하도록 설계되었습니다. 완전 이중화된 이중화 전원 시스템을 통해 UPS와 PDU에서 발전기 및 에너지 저장장치에 이르기까지 모든 컴포넌트가 다중 장애 발생 시에도 계속 작동할 수 있습니다. 이 설계는 중단 없는 전력 공급을 보장하고, 중요한 IT 인프라에 대한 위험을 최소화하며, 어떤 상황에서도 비즈니스 연속성을 보호합니다.
Tier IV는 솔루션 프로바이더에게 여러 개의 독립적인 전력 경로, 이중화 냉각 시스템, 강력한 모니터링 플랫폼을 통합하기 위한 치밀한 계획과 정확한 배포를 요구합니다. 구성 요소는 지속적인 작동을 유지하기 위해 신중하게 동기화해야 하며, 고급 전력 관리 소프트웨어는 실시간 가시성, 예측 분석, 잠재적 이상에 대한 자동 대응을 제공합니다.
세계의 데이터센터용 전력 시장에 대해 조사분석했으며, 주요 촉진요인과 억제요인, 경쟁 구도, 향후 동향 등의 정보를 제공하고 있습니다.
목차
제1장 서론
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 개요
제4장 중요 인사이트
- 데이터센터용 전력 시장의 개요
- 데이터센터용 전력 시장 : 컴포넌트별
- 데이터센터용 전력 시장 : 데이터센터 유형별
- 데이터센터용 전력 시장 : 기업별
- 데이터센터용 전력 시장 : 지역의 시나리오
제5장 시장 개요와 산업 동향
- 서론
- 시장 역학
- 촉진요인
- 억제요인
- 기회
- 과제
- 사례 연구 분석
- 에코시스템
- 공급망 분석
- 무역 분석
- 가격결정 분석
- 솔루션 프로바이더의 평균 판매 가격 : 지역별(2025년)
- 솔루션 프로바이더의 가격 지표 : 솔루션별(2025년)
- 특허 분석
- 기술 분석
- 주요 기술
- 보완 기술
- 인접 기술
- 규제 상황
- 규제기관, 정부기관, 기타 조직
- 규제 : 지역별
- 규제의 영향과 산업 표준
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 주요 이해관계자와 구입 기준
- 구입 기준
- 주요 컨퍼런스와 이벤트(2025-2026년)
- 고객 비즈니스에 영향을 미치는 동향/혼란
- 투자와 자금조달 시나리오
- 데이터센터용 전력 시장에 대한 AI/생성형 AI의 영향
- 사례 연구
- 벤더의 구상
- 2025년 미국 관세의 영향 - 개요
- 서론
- 주요 관세율
- 가격의 영향 분석
- 국가/지역에 대한 영향
제6장 데이터센터용 전력 시장 : 컴포넌트별
- 서론
- 전기 솔루션
- UPS(Uninterruptible Power Supplies) 시스템
- 전력 분배 유닛(PDU)
- 온사이트 발전·에너지 저장
- 전력 관리 소프트웨어·DCIM
- 기타 전기 솔루션(배선 인프라, 개폐기, 버스웨이)
- 서비스
- 설계·컨설팅
- 통합·배포
- 지원·정비
제7장 데이터센터용 전력 시장 : Tier 유형별
- 서론
- Tier I·II
- Tier III
- Tier IV
제8장 데이터센터용 전력 시장 : 데이터센터 규모별(전력 용량)
- 서론
- 소규모 데이터센터(1MW 미만)
- 중규모 데이터센터(1MW-5MW)
- 대규모 데이터센터(5MW-10MW)
- 대규모 데이터센터(10MW-100MW)
- 대규모 데이터센터(100MW 초과)
제9장 데이터센터용 전력 시장 : 데이터센터 유형별
- 서론
- 코로케이션 데이터센터
- 클라우드/하이퍼스케일 데이터센터
- 기업
제10장 데이터센터용 전력 시장 : 업계별
- 서론
- BFSI
- 정부·공공 부문
- 의료·생명과학
- 제조
- 소매·E-Commerce
- 통신
- 기술·소프트웨어
- 기타 업계(교육, 연구, 에너지·유틸리티)
제11장 데이터센터용 전력 시장 : 지역별
- 서론
- 북미
- 북미의 데이터센터용 전력 시장 촉진요인
- 북미의 거시경제 전망
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 유럽
- 유럽의 데이터센터용 전력 시장 촉진요인
- 유럽의 거시경제 전망
- 영국
- 독일
- 프랑스
- 이탈리아
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 아시아태평양의 데이터센터용 전력 시장 촉진요인
- 아시아태평양의 거시경제 전망
- 중국
- 일본
- 인도
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 중동 및 아프리카의 데이터센터용 전력 시장 촉진요인
- 중동 및 아프리카의 거시경제 전망
- GCC
- 남아프리카공화국
- 기타 중동 및 아프리카
- 라틴아메리카
- 라틴아메리카의 데이터센터용 전력 시장 촉진요인
- 라틴아메리카의 거시경제 전망
- 브라질
- 멕시코
- 기타 라틴아메리카
제12장 경쟁 구도
- 서론
- 주요 참여 기업의 전략/강점
- 매출 분석
- 시장 점유율 분석(2024년)
- 브랜드/제품 비교
- 기업 평가 매트릭스 : 주요 기업(2024년)(IT 인프라)
- 기업 평가 매트릭스 : 스타트업/중소기업(2024년)
- 주요 벤더의 기업의 평가와 재무 지표
- 경쟁 시나리오와 동향
제13장 기업 개요
- 서론
- 주요 기업
- SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC
- ABB
- EATON
- DELTA ELECTRONICS
- VERTIV
- HUAWEI
- LEGRAND
- TOSHIBA
- SIEMENS
- MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
- 기타 기업
- KEHUA TECH
- RITTAL
- SOCOMEC
- CYBER POWER SYSTEM
- ANORD MARDIX
- CUMMINS
- ROSENBERGER OSI
- BELDEN
- PANDUIT
- AEG POWER SOLUTIONS
- RIELLO UPS
- ROLLS-ROYCE
- ZINCFIVE
- 42U
- NVENT
제14장 인접 시장/관련 시장
- 서론
- 관련 시장
- 제한 사항
- 데이터센터 솔루션 시장
- 모듈러 데이터센터 시장
제15장 부록
KSA 25.10.02The global data center power market is expected to grow from USD 35.14 billion in 2025 to USD 50.51 billion by 2030 at a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.5% during the forecast period.
| Scope of the Report | |
|---|---|
| Years Considered for the Study | 2020-2030 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2030 |
| Units Considered | Value (USD Million/Billion) |
| Segments | Component, Tier Type, Data Center Size (Power Capacity), Data Center Type, Enterprise Vertical |
| Regions covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, the Middle East & Africa, and Latin America |
Rising sustainability targets and supportive energy policies are accelerating the adoption of advanced data center power systems worldwide. Operators are investing in AI-driven power management, renewable integration, and grid-interactive solutions to reduce emissions, improve efficiency, and ensure uptime. These advancements enhance scalability, operational resilience, and compliance with green standards.
However, reliance on traditional power infrastructure remains a restraint, as many data centers still operate with legacy systems that limit efficiency and flexibility. Transitioning to modern, intelligent power architectures demands significant capital, skilled expertise, and integration efforts, making cost and complexity major hurdles in the growth of the data center power market.
"Based on enterprise vertical, the telecommunications segment is estimated to hold the largest market share in 2025"
Telecommunications data centers form the backbone of global connectivity, supporting mobile networks, internet services, VoIP platforms, and cloud communication systems. Any disruption in power can degrade network performance, interrupt services, or impact critical infrastructure such as 5G base stations, leading to service outages and customer dissatisfaction. Vendors provide UPS systems, PDUs, on-site generators, and battery energy storage to ensure continuous, reliable electricity for these high-demand workloads.
Redundant and fault-tolerant power architectures with multiple distribution paths maintain uptime for high-density network operations, ensuring seamless connectivity across diverse geographies. Real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and energy management platforms optimize electricity consumption, prevent downtime, and reduce operational costs. Modular and scalable power solutions allow telecommunications data centers to expand capacity rapidly to accommodate growing subscriber bases, IoT traffic, and edge computing deployments without affecting ongoing operations.
Intelligent load balancing and optimized energy delivery safeguard sensitive networking equipment, supporting uninterrupted data flow and minimizing latency. Vendors supplying resilient, high-performance, and efficiently managed power infrastructure enable telecommunications providers to sustain continuous service, meet SLA requirements, and enhance operational reliability. These solutions form a robust foundation for powering telecom data centers, ensuring reliable connectivity, high availability, and efficient network operations.
"Based on tier type, the tier IV segment is expected to grow at the highest CAGR during the forecast period"
Tier IV data centers represent the highest standard of power reliability and fault tolerance, designed to support mission-critical workloads that cannot afford any interruption. Fully redundant and dual-powered systems ensure that every component-from UPS and PDUs to generators and energy storage-can continue functioning even in the event of multiple failures. This design guarantees uninterrupted power delivery, minimizing risk to critical IT infrastructure and protecting business continuity under all circumstances.
For solution providers, Tier IV demands meticulous planning and precise deployment to integrate multiple independent power paths, redundant cooling systems, and robust monitoring platforms. Components must be carefully synchronized to maintain continuous operation, while advanced power management software delivers real-time visibility, predictive analytics, and automated responses to potential anomalies.
Scalability and future readiness are essential, as Tier IV facilities often need to accommodate rapidly growing workloads without compromising fault tolerance. Energy efficiency is enhanced through load balancing, peak shaving, and renewable energy integration, reducing operational costs while maintaining resilience.
By delivering uncompromised uptime and optimized performance, Tier IV data centers provide a foundation for the most demanding applications and services. Vendors supporting this tier enable organizations to achieve the ultimate in operational reliability, energy efficiency, and scalable, future-proof power infrastructure.
"North America will lead in the market share, while Asia Pacific emerges as the fastest-growing market during the forecast period"
North America is the largest market for data center power solutions, supported by the concentration of hyperscale facilities, cloud service providers, and colocation operators. The US and Canada are witnessing heavy investments in renewable integration, battery energy storage, and AI-driven power management to meet surging energy demand and sustainability goals. Strong regulatory support, advanced digital infrastructure, and continuous expansion of hyperscale campuses further strengthen the region's leadership.
In contrast, Asia Pacific represents the fastest-growing data center power market, with rapid capacity expansion in countries like China, India, Singapore, and Australia. Explosive growth in cloud adoption, 5G rollouts, and digital transformation initiatives are fueling demand for scalable, energy-efficient, and reliable power solutions. Government-backed green energy programs, increasing investments by global tech firms, and rising colocation activity are accelerating adoption, positioning APAC as a high-growth hub for data center power technologies.
Breakdown of primaries
Chief Executive Officers (CEOs), directors of innovation and technology, system integrators, and executives from several significant data center power market companies were interviewed to gain insights into this market.
- By Company: Tier I: 40%, Tier II: 25%, and Tier III: 35%
- By Designation: C-Level Executives: 45%, Director Level: 30%, and Others: 25%
- By Region: North America: 30%, Europe: 20%, Asia Pacific: 25%, Rest of the World: 15%
Some of the significant data center power market vendors are Schneider Electric (France), Vertiv (US), ABB (Switzerland), Eaton (Ireland), Delta Electronics (Taiwan), Huawei (China), Legrand (France), Toshiba (Japan), Siemens (Germany), Mitsubishi Electric (Japan), Kehua Tech (China), Rittal (Germany), Socomec (France), Cyber Power Systems (US), Anord Mardix (Ireland), Cummins (US), Rosenberger OSI (Germany), Belden (US), Panduit (US), AEG Power Solutions (Netherlands), Riello UPS (Italy), Rolls-Royce (UK), ZincFive (US), 42U (US), and nVent (US).
Research Coverage
The market report covered the data center power market across segments. We estimated the market size and growth potential for many segments based on electrical solution, service, data center tier type, data center size (power capacity), data center type, enterprise vertical, and region. It contains a thorough competition analysis of the major market participants, information about their businesses, essential observations about their product and service offerings, current trends, and critical market strategies.
Reasons to buy this report:
This research provides the most accurate revenue estimates for the entire data center power industry and its subsegments, benefiting both established leaders and new entrants. Stakeholders will gain valuable insights into the competitive landscape, enabling them to better position their companies and develop effective go-to-market strategies. The report outlines key market drivers, constraints, opportunities, and challenges, helping industry players understand the current state of the market.
The report provides insights into the following pointers:
- Analysis of key drivers (high-performance computing driving ultra-dense power requirements), restraints (water scarcity and localized resource risks restrain data center growth), opportunities (geothermal energy enhances sustainable and reliable power for data centers), and challenges (power challenges threatening data center growth), influencing the growth of the data center power market
- Product Development/Innovation: Comprehensive analysis of emerging technologies, R&D initiatives, and new service and product introductions in the data center power market
- Market Development: In-depth details regarding profitable markets, examining the global data center power market
- Market Diversification: Comprehensive details regarding recent advancements, investments, unexplored regions, and new solutions and services
- Competitive Assessment: Thorough analysis of the market shares, expansion plans, and offerings of the top competitors in the data center power industry, such as Schneider Electric (France), Vertiv (US), ABB (Switzerland), Eaton (Ireland), Delta Electronics (Taiwan), Huawei (China), Legrand (France), Toshiba (Japan), Siemens (Germany), Mitsubishi Electric (Japan), Kehua Tech (China), Rittal (Germany), Socomec (France), Cyber Power Systems (US), Anord Mardix (Ireland), Cummins (US), Rosenberger OSI (Germany), Belden (US), Panduit (US), AEG Power Solutions (Netherlands), Riello UPS (Italy), Rolls-Royce (UK), ZincFive (US), 42U (US), and nVent (US).
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 STUDY OBJECTIVES
- 1.2 MARKET DEFINITION
- 1.3 STUDY SCOPE
- 1.3.1 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 1.3.2 INCLUSIONS AND EXCLUSIONS
- 1.3.3 YEARS CONSIDERED
- 1.3.4 CURRENCY CONSIDERED
- 1.4 STAKEHOLDERS
- 1.5 SUMMARY OF CHANGES
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 RESEARCH APPROACH
- 2.1.1 SECONDARY DATA
- 2.1.1.1 Key data from secondary sources
- 2.1.2 PRIMARY DATA
- 2.1.2.1 Key data from primary sources
- 2.1.2.2 Breakup of primary profiles
- 2.1.2.3 Key industry insights
- 2.1.1 SECONDARY DATA
- 2.2 MARKET BREAKUP AND DATA TRIANGULATION
- 2.3 MARKET SIZE ESTIMATION
- 2.3.1 TOP-DOWN APPROACH
- 2.3.2 BOTTOM-UP APPROACH
- 2.3.3 MARKET ESTIMATION APPROACHES
- 2.4 MARKET FORECAST
- 2.5 RESEARCH ASSUMPTIONS
- 2.6 RESEARCH LIMITATIONS
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 PREMIUM INSIGHTS
- 4.1 OVERVIEW OF DATA CENTER POWER MARKET
- 4.2 DATA CENTER POWER MARKET, BY COMPONENT
- 4.3 DATA CENTER POWER MARKET, BY DATA CENTER TYPE
- 4.4 DATA CENTER POWER MARKET, BY ENTERPRISE VERTICAL
- 4.5 DATA CENTER POWER MARKET: REGIONAL SCENARIO
5 MARKET OVERVIEW AND INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 5.1 INTRODUCTION
- 5.2 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.2.1 DRIVERS
- 5.2.1.1 Rise in data centers worldwide
- 5.2.1.2 High-performance computing driving ultra-dense power requirements
- 5.2.1.3 Rising AI workloads escalating energy consumption and grid pressure
- 5.2.1.4 Growing need for power resilience and guaranteed uptime
- 5.2.2 RESTRAINTS
- 5.2.2.1 Water scarcity and localized resource risks restrain data center growth
- 5.2.3 OPPORTUNITIES
- 5.2.3.1 Geothermal energy enhances sustainable and reliable power for data centers
- 5.2.3.2 Nuclear energy drives high-capacity, low-emission power solutions for data centers
- 5.2.4 CHALLENGES
- 5.2.4.1 Power challenges threatening data center growth
- 5.2.1 DRIVERS
- 5.3 CASE STUDY ANALYSIS
- 5.3.1 ABB'S MODULAR UPS SOLUTION EMPOWERED FICOLO'S UNDERGROUND DATA CENTER EXPANSION
- 5.3.2 CONVERGE ICT SOLUTIONS EXPANDED ITS DATA CENTER WITH HUAWEI SMARTLI UPS
- 5.3.3 CZECH ICT LEADER UPGRADED DATA CENTER POWER WITH ABB'S CONCEPTPOWER DPA 500 UPS
- 5.3.4 POWERING UP WITH VEGETABLE OILS
- 5.3.5 HITACHI ENERGY PROVIDED POWER STRUCTURE FOR TURKIYE'S MOST ADVANCED DATA CENTER
- 5.4 ECOSYSTEM
- 5.5 SUPPLY CHAIN ANALYSIS
- 5.6 TRADE ANALYSIS
- 5.7 PRICING ANALYSIS
- 5.7.1 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE OF SOLUTION PROVIDERS, BY REGION, 2025
- 5.7.2 INDICATIVE PRICING OF SOLUTION PROVIDERS, BY SOLUTION, 2025
- 5.8 PATENT ANALYSIS
- 5.8.1 LIST OF MAJOR PATENTS
- 5.9 TECHNOLOGY ANALYSIS
- 5.9.1 KEY TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.9.1.1 Silicon carbide (SiC) & gallium nitride (GaN) semiconductors
- 5.9.1.2 Solid-state circuit breakers (SSCBs)
- 5.9.1.3 Nuclear small modular reactors (SMRs)
- 5.9.2 COMPLEMENTARY TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.9.2.1 Digital twin
- 5.9.2.2 Energy management platforms (DCIM, EMS)
- 5.9.2.3 Remote monitoring & gateways
- 5.9.3 ADJACENT TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.9.3.1 Microgrids & demand response
- 5.9.3.2 Grid-interactive UPS/Energy-as-a-service models
- 5.9.1 KEY TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.10 REGULATORY LANDSCAPE
- 5.10.1 REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS
- 5.10.2 REGULATIONS BASED ON REGION
- 5.10.2.1 North America
- 5.10.2.2 Europe
- 5.10.2.3 Asia Pacific
- 5.10.2.4 Middle East & South Africa
- 5.10.2.5 Latin America
- 5.10.3 REGULATORY IMPLICATIONS AND INDUSTRY STANDARDS
- 5.10.3.1 General data protection regulation
- 5.10.3.2 SEC Rule 17a-4
- 5.10.3.3 ISO/IEC 27001
- 5.10.3.4 System and organization controls 2 type II
- 5.10.3.5 Financial industry regulatory authority
- 5.10.3.6 Freedom of information act
- 5.10.3.7 Health insurance portability and accountability act
- 5.11 PORTER'S FIVE FORCES ANALYSIS
- 5.11.1 THREAT OF NEW ENTRANTS
- 5.11.2 THREAT OF SUBSTITUTES
- 5.11.3 BARGAINING POWER OF SUPPLIERS
- 5.11.4 BARGAINING POWER OF BUYERS
- 5.11.5 INTENSITY OF COMPETITIVE RIVALRY
- 5.12 KEY STAKEHOLDERS AND BUYING CRITERIA
- 5.13 BUYING CRITERIA
- 5.14 KEY CONFERENCES AND EVENTS, 2025-2026
- 5.15 TRENDS/DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMER BUSINESS
- 5.16 INVESTMENT & FUNDING SCENARIO
- 5.17 IMPACT OF AI/GEN AI ON DATA CENTER POWER MARKET
- 5.17.1 CASE STUDY
- 5.17.1.1 Compass and Schneider Electric utilized AI to transform data center maintenance
- 5.17.2 VENDOR INITIATIVES
- 5.17.2.1 Enhancing data center reliability with AI-powered predictive maintenance
- 5.17.1 CASE STUDY
- 5.18 IMPACT OF 2025 US TARIFF - OVERVIEW
- 5.18.1 INTRODUCTION
- 5.18.2 KEY TARIFF RATES
- 5.18.3 PRICE IMPACT ANALYSIS
- 5.18.4 IMPACT ON COUNTRY/REGION
- 5.18.4.1 North America
- 5.18.4.1.1 United States
- 5.18.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.18.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.18.4.2 Europe
- 5.18.4.2.1 Germany
- 5.18.4.2.2 France
- 5.18.4.3 APAC
- 5.18.4.3.1 China
- 5.18.4.3.2 India
- 5.18.4.3.3 Australia
- 5.18.4.1 North America
6 DATA CENTER POWER MARKET, BY COMPONENT
- 6.1 INTRODUCTION
- 6.1.1 COMPONENT: DATA CENTER POWER MARKET DRIVERS
- 6.2 ELECTRICAL SOLUTIONS
- 6.2.1 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS) SYSTEMS
- 6.2.1.1 Ensuring Uninterrupted Operations with UPS Systems
- 6.2.1.2 By type
- 6.2.1.2.1 Modular UPS
- 6.2.1.2.2 Monolithic UPS
- 6.2.1.3 By technology
- 6.2.1.3.1 Double Conversion
- 6.2.1.3.2 Line-interactive
- 6.2.1.3.3 Standby
- 6.2.2 POWER DISTRIBUTION UNITS (PDUS)
- 6.2.2.1 Reducing Downtime Risks with Intelligent PDUs
- 6.2.2.2 Intelligent PDUs
- 6.2.2.3 Metered PDUs
- 6.2.2.4 Basic PDUs
- 6.2.3 ON-SITE POWER GENERATION & ENERGY STORAGE
- 6.2.3.1 Turning Grid Instability into Reliability with On-site Power Systems
- 6.2.3.2 Generators
- 6.2.3.2.1 Maintaining Operations under Grid Failure with Generators
- 6.2.3.2.2 Diesel
- 6.2.3.2.3 Gas
- 6.2.3.3 Battery energy storage system (BESS)
- 6.2.3.3.1 Storing Energy for Instant Backup and Cost Optimization
- 6.2.3.3.2 Lithium-ion
- 6.2.3.3.3 Lead Acid
- 6.2.4 POWER MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE & DCIM
- 6.2.4.1 Turning Real-time Insights into Reliable Data Center Power Performance
- 6.2.5 OTHER ELECTRICAL SOLUTIONS (CABLING INFRASTRUCTURE, SWITCHGEARS, BUSWAYS)
- 6.2.1 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS) SYSTEMS
- 6.3 SERVICES
- 6.3.1 DESIGN & CONSULTING
- 6.3.1.1 Building Optimized Power Strategies for Long-term Reliability
- 6.3.2 INTEGRATION & DEPLOYMENT
- 6.3.2.1 Transforming Power Designs into Seamless Data Center Operations
- 6.3.3 SUPPORT & MAINTENANCE
- 6.3.3.1 Sustaining Reliable Performance Through Proactive Support and Maintenance
- 6.3.1 DESIGN & CONSULTING
7 DATA CENTER POWER MARKET, BY TIER TYPE
- 7.1 INTRODUCTION
- 7.1.1 TIER TYPE: DATA CENTER POWER MARKET DRIVERS
- 7.2 TIER I & II
- 7.2.1 ENABLING AFFORDABLE BACKUP AND BASIC POWER CONTINUITY
- 7.3 TIER III
- 7.3.1 DELIVERING REDUNDANT AND RESILIENT POWER FOR CRITICAL WORKLOADS
- 7.4 TIER IV
- 7.4.1 MAXIMIZING POWER RESILIENCE WITH TIER IV DATA CENTER ARCHITECTURE
8 DATA CENTER POWER MARKET, BY DATA CENTER SIZE (POWER CAPACITY)
- 8.1 INTRODUCTION
- 8.1.1 DATA CENTER SIZE (POWER CAPACITY): DATA CENTER POWER MARKET DRIVERS
- 8.2 SMALL-SIZED DATA CENTER (LESS THAN 1 MW)
- 8.2.1 ENABLING RELIABLE LOCALIZED OPERATIONS IN SUB-1 MW FACILITIES
- 8.3 MID-SIZED DATA CENTER (1 MW TO 5 MW)
- 8.3.1 BALANCING EFFICIENCY AND RELIABILITY IN MID-SIZED DATA CENTERS
- 8.4 LARGE DATA CENTER (5 MW TO 10 MW)
- 8.4.1 DELIVERING HIGH-DENSITY, RELIABLE POWER IN LARGE DATA CENTERS
- 8.5 MEGA-SIZED DATA CENTER (10 MW TO 100 MW)
- 8.5.1 POWERING HIGH-IMPACT OPERATIONS WITH MEGA-SIZED DATA CENTERS
- 8.6 MASSIVE DATA CENTER (OVER 100 MW)
- 8.6.1 ENABLING HYPERSCALE POWER AND RESILIENCE IN MASSIVE DATA CENTERS
9 DATA CENTER POWER MARKET, BY DATA CENTER TYPE
- 9.1 INTRODUCTION
- 9.1.1 DATA CENTER TYPE: DATA CENTER POWER MARKET DRIVERS
- 9.2 COLOCATION DATA CENTERS
- 9.2.1 DELIVERING RELIABLE MULTI-TENANT POWER TO COLOCATION DATA CENTERS
- 9.2.2 COLOCATION DATA CENTERS: USE CASES
- 9.2.2.1 Multi-tenant Uptime Assurance
- 9.2.2.2 Scalable client deployment
- 9.2.2.3 Shared energy optimization
- 9.3 CLOUD/HYPERSCALE DATA CENTERS
- 9.3.1 POWERING SCALABLE AND RESILIENT HYPERSCALE CLOUD INFRASTRUCTURE
- 9.3.2 CLOUD/HYPERSCALE DATA CENTERS: USE CASES
- 9.3.2.1 High-density Load Management
- 9.3.2.2 Global Scalability and Redundancy
- 9.3.2.3 Sustainable energy integration
- 9.4 ENTERPRISES
- 9.4.1 OPTIMIZING POWER CONTINUITY FOR CRITICAL ENTERPRISE WORKLOADS
- 9.4.2 ENTERPRISES: USE CASES
- 9.4.2.1 Business-critical Application Continuity
- 9.4.2.2 Incremental scalability
- 9.4.2.3 Operational cost management
10 DATA CENTER POWER MARKET, BY ENTERPRISE VERTICAL
- 10.1 INTRODUCTION
- 10.1.1 ENTERPRISE VERTICAL: DATA CENTER POWER MARKET DRIVERS
- 10.2 BFSI
- 10.2.1 ENSURING UNINTERRUPTED POWER FOR CRITICAL FINANCIAL OPERATIONS
- 10.2.2 BFSI: USE CASES
- 10.2.2.1 Real-time Transaction Continuity
- 10.2.2.2 Fraud detection analytics
- 10.2.2.3 Regulatory reporting & compliance
- 10.3 GOVERNMENT & PUBLIC SECTOR
- 10.3.1 ENSURING CONTINUOUS POWER FOR CRITICAL GOVERNMENT SERVICES AND PUBLIC SAFETY
- 10.3.2 GOVERNMENT & PUBLIC SECTOR: USE CASES
- 10.3.2.1 Citizen services continuity
- 10.3.2.2 Secure data storage
- 10.3.2.3 Emergency response systems
- 10.4 HEALTHCARE & LIFE SCIENCES
- 10.4.1 CONTINUOUS OPERATION FOR EHR SYSTEMS AND IMAGING WORKLOADS
- 10.4.2 HEALTHCARE & LIFE SCIENCES: USE CASES
- 10.4.2.1 Electronic health record access
- 10.4.2.2 Medical imaging & diagnostics
- 10.4.2.3 Clinical research & trials
- 10.5 MANUFACTURING
- 10.5.1 POWERING SMART FACTORIES AND INDUSTRIAL AUTOMATION WITH RELIABLE DATA CENTER INFRASTRUCTURE
- 10.5.2 MANUFACTURING: USE CASES
- 10.5.2.1 Industrial IoT Operations
- 10.5.2.2 Production automation
- 10.5.2.3 Supply chain data analytics
- 10.6 RETAIL & E-COMMERCE
- 10.6.1 POWERING SEAMLESS ONLINE TRANSACTIONS AND RETAIL OPERATIONS WITH RELIABLE DATA CENTER INFRASTRUCTURE
- 10.6.2 RETAIL & E-COMMERCE: USE CASES
- 10.6.2.1 Online transaction uptime
- 10.6.2.2 Inventory & fulfillment systems
- 10.6.2.3 Customer data analytics
- 10.7 TELECOMMUNICATIONS
- 10.7.1 ENABLING UNINTERRUPTED NETWORK OPERATIONS AND CONNECTIVITY THROUGH ROBUST DATA CENTER POWER
- 10.7.2 TELECOMMUNICATIONS: USE CASE
- 10.7.2.1 Network operations centers
- 10.7.2.2 IoT & Edge Computing
- 10.7.2.3 Telecom billing & customer management
- 10.8 TECHNOLOGY & SOFTWARE
- 10.8.1 POWERING HIGH-PERFORMANCE COMPUTING AND SOFTWARE SERVICES WITH RELIABLE DATA CENTER INFRASTRUCTURE
- 10.8.2 TECHNOLOGY & SOFTWARE: USE CASES
- 10.8.2.1 Cloud platform uptime
- 10.8.2.2 Software development pipelines
- 10.8.2.3 AI/ML workloads
- 10.9 OTHER ENTERPRISE VERTICALS (EDUCATION, RESEARCH, ENERGY & UTILITIES)
11 DATA CENTER POWER MARKET, BY REGION
- 11.1 INTRODUCTION
- 11.2 NORTH AMERICA
- 11.2.1 NORTH AMERICA: DATA CENTER POWER MARKET DRIVERS
- 11.2.2 NORTH AMERICA: MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 11.2.3 US
- 11.2.3.1 Surging Energy Demand from Hyperscale and AI Expansion
- 11.2.4 CANADA
- 11.2.4.1 Sustainable Growth and Clean Energy Integration in Canada's Data Center Power Market
- 11.3 EUROPE
- 11.3.1 EUROPE: DATA CENTER POWER MARKET DRIVERS
- 11.3.2 EUROPE: MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 11.3.3 UK
- 11.3.3.1 Frontier-Ethos Partnership Targets 5 GW of Colocated Capacity in UK
- 11.3.4 GERMANY
- 11.3.4.1 Rising Energy Needs of Germany's Data Center Industry
- 11.3.5 FRANCE
- 11.3.5.1 Franco-Emirati investment highlights France's AI data center expansion
- 11.3.6 ITALY
- 11.3.6.1 Regulatory Reforms and Legislative Support for Expansion
- 11.3.7 REST OF EUROPE
- 11.4 ASIA PACIFIC
- 11.4.1 ASIA PACIFIC: DATA CENTER POWER MARKET DRIVERS
- 11.4.2 ASIA PACIFIC: MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 11.4.3 CHINA
- 11.4.3.1 Powering Sustainable Growth in China's Data Center Market
- 11.4.4 JAPAN
- 11.4.4.1 Public-Private Collaboration to Align Data Centers with Renewables
- 11.4.5 INDIA
- 11.4.5.1 Sustainability and Carbon Reduction in India's Data Center Industry
- 11.4.6 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC
- 11.5 MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA
- 11.5.1 MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA: DATA CENTER POWER MARKET DRIVERS
- 11.5.2 MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA: MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 11.5.3 GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL
- 11.5.3.1 High-density PDUs and Backup Solutions Strengthen GCC Data Center Reliability
- 11.5.3.2 KSA
- 11.5.3.3 UAE
- 11.5.3.4 Rest of GCC
- 11.5.4 SOUTH AFRICA
- 11.5.4.1 Integrating Renewable Energy into Data Center Power Infrastructure
- 11.5.5 REST OF MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA
- 11.6 LATIN AMERICA
- 11.6.1 LATIN AMERICA: DATA CENTER POWER MARKET DRIVERS
- 11.6.2 LATIN AMERICA: MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 11.6.3 BRAZIL
- 11.6.3.1 Optimizing Energy Consumption with Smart Power Solutions
- 11.6.4 MEXICO
- 11.6.4.1 Scalable and Sustainable Power Solutions in Mexican Data Centers
- 11.6.5 REST OF LATIN AMERICA
12 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 12.1 INTRODUCTION
- 12.2 KEY PLAYERS' STRATEGIES/RIGHT TO WIN
- 12.3 REVENUE ANALYSIS
- 12.4 MARKET SHARE ANALYSIS, 2024
- 12.5 BRAND/PRODUCT COMPARISON
- 12.6 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: KEY PLAYERS, 2024 (IT INFRASTRUCTURE)
- 12.6.1 STARS
- 12.6.2 EMERGING LEADERS
- 12.6.3 PERVASIVE PLAYERS
- 12.6.4 PARTICIPANTS
- 12.6.5 COMPANY FOOTPRINT: KEY PLAYERS, 2024
- 12.6.5.1 Company footprint
- 12.6.5.2 Region footprint
- 12.6.5.3 Component footprint
- 12.6.5.4 Data center type footprint
- 12.7 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: STARTUPS/SMES, 2024
- 12.7.1 PROGRESSIVE COMPANIES
- 12.7.2 RESPONSIVE COMPANIES
- 12.7.3 DYNAMIC COMPANIES
- 12.7.4 STARTING BLOCKS
- 12.7.5 COMPETITIVE BENCHMARKING: STARTUP/SMES, 2024
- 12.7.5.1 Detailed list of key startups/SMEs
- 12.7.5.2 Competitive benchmarking of startups/SMEs
- 12.8 COMPANY VALUATION AND FINANCIAL METRICS OF KEY VENDORS
- 12.8.1 COMPANY VALUATION OF KEY VENDORS
- 12.8.2 FINANCIAL METRICS OF KEY VENDORS
- 12.9 COMPETITIVE SCENARIO AND TRENDS
- 12.9.1 PRODUCT LAUNCHES
- 12.9.2 DEALS
13 COMPANY PROFILES
- 13.1 INTRODUCTION
- 13.2 MAJOR PLAYERS
- 13.2.1 SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC
- 13.2.1.1 Business overview
- 13.2.1.2 Products/solutions/services offered
- 13.2.1.3 Recent developments
- 13.2.1.3.1 Product launches and enhancements
- 13.2.1.3.2 Deals
- 13.2.1.4 MnM view
- 13.2.1.4.1 Right to win
- 13.2.1.4.2 Strategic choices
- 13.2.1.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 13.2.2 ABB
- 13.2.2.1 Business overview
- 13.2.2.2 Products/solutions/services offered
- 13.2.2.3 Recent developments
- 13.2.2.3.1 Product launches and enhancements
- 13.2.2.3.2 Deals
- 13.2.2.4 MnM view
- 13.2.2.4.1 Right to win
- 13.2.2.4.2 Strategic choices
- 13.2.2.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 13.2.3 EATON
- 13.2.3.1 Business overview
- 13.2.3.2 Products/solutions/services offered
- 13.2.3.3 Recent developments
- 13.2.3.3.1 Product launches
- 13.2.3.3.2 Deals
- 13.2.3.4 MnM view
- 13.2.3.4.1 Right to win
- 13.2.3.4.2 Strategic choices
- 13.2.3.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 13.2.4 DELTA ELECTRONICS
- 13.2.4.1 Business overview
- 13.2.4.2 Products/solutions/services offered
- 13.2.4.3 Recent developments
- 13.2.4.3.1 Product launches
- 13.2.4.3.2 Deals
- 13.2.4.4 MnM view
- 13.2.4.4.1 Right to win
- 13.2.4.4.2 Strategic choices
- 13.2.4.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 13.2.5 VERTIV
- 13.2.5.1 Business overview
- 13.2.5.2 Products/solutions/services offered
- 13.2.5.3 Recent developments
- 13.2.5.3.1 Product launches and enhancements
- 13.2.5.3.2 Deals
- 13.2.5.4 MnM view
- 13.2.5.4.1 Right to win
- 13.2.5.4.2 Strategic choices
- 13.2.5.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 13.2.6 HUAWEI
- 13.2.6.1 Business overview
- 13.2.6.2 Products/solutions/services offered
- 13.2.6.3 Recent developments
- 13.2.6.3.1 Product launches and enhancements
- 13.2.6.3.2 Deals
- 13.2.7 LEGRAND
- 13.2.7.1 Business overview
- 13.2.7.2 Products/solutions/services offered
- 13.2.7.3 Recent developments
- 13.2.7.3.1 Product launches and enhancements
- 13.2.7.3.2 Deals
- 13.2.8 TOSHIBA
- 13.2.8.1 Business overview
- 13.2.8.2 Products/solutions/services offered
- 13.2.8.3 Recent developments
- 13.2.8.3.1 Product launches and enhancements
- 13.2.9 SIEMENS
- 13.2.9.1 Business overview
- 13.2.9.2 Products/solutions/services offered
- 13.2.9.3 Recent developments
- 13.2.9.3.1 Deals
- 13.2.10 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
- 13.2.10.1 Business overview
- 13.2.10.2 Products/solutions/services offered
- 13.2.10.3 Recent developments
- 13.2.10.3.1 Deals
- 13.2.1 SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC
- 13.3 OTHER PLAYERS
- 13.3.1 KEHUA TECH
- 13.3.2 RITTAL
- 13.3.3 SOCOMEC
- 13.3.4 CYBER POWER SYSTEM
- 13.3.5 ANORD MARDIX
- 13.3.6 CUMMINS
- 13.3.7 ROSENBERGER OSI
- 13.3.8 BELDEN
- 13.3.9 PANDUIT
- 13.3.10 AEG POWER SOLUTIONS
- 13.3.11 RIELLO UPS
- 13.3.12 ROLLS-ROYCE
- 13.3.13 ZINCFIVE
- 13.3.14 42U
- 13.3.15 NVENT
14 ADJACENT/RELATED MARKETS
- 14.1 INTRODUCTION
- 14.1.1 RELATED MARKETS
- 14.1.2 LIMITATIONS
- 14.2 DATA CENTER SOLUTIONS MARKET
- 14.3 MODULAR DATA CENTER MARKET
15 APPENDIX
- 15.1 DISCUSSION GUIDE
- 15.2 CUSTOMIZATION OPTIONS
- 15.3 RELATED REPORTS
- 15.4 AUTHOR DETAILS



















