
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1906294
Fab 자동화 시장 : 제공 제품별, 자동화층별, 웨이퍼 사이즈별, 전개 유형별, Fab 타입별, 최종사용자별, 지역별 - 예측(-2032년)Fab Automation Market By Offering (Harfware, Software), Wafer Size, End User - Global Forecast to 2032 |
||||||
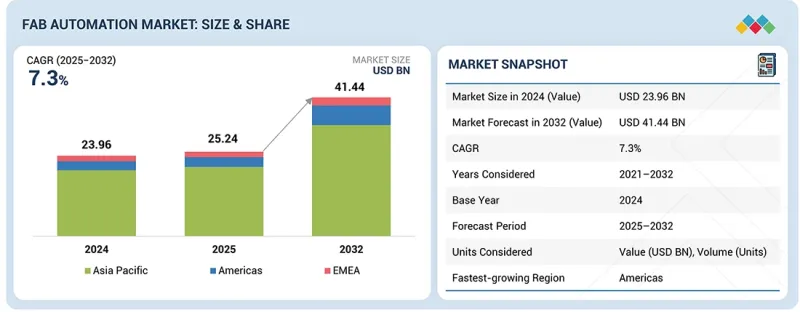
Fab 자동화 시장 규모는 2025년에 252억 4,000만 달러, 2032년까지 414억 4,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며, 2025-2032년 CAGR 7.3%를 보일 전망입니다.
반도체 제조의 복잡성 증가와 전 세계적으로 높은 수율, 사이클 타임 단축, 운영의 일관성 향상을 위한 노력으로 인해 예측 기간 동안 시장은 크게 성장할 것으로 예측됩니다.
| 조사 범위 | |
|---|---|
| 조사 대상 기간 | 2020-2032년 |
| 기준 연도 | 2024년 |
| 예측 기간 | 2025-2032년 |
| 대상 단위 | 금액(10억 달러) |
| 부문 | 제공 제품별, 자동화층별, 웨이퍼 사이즈별, 전개 유형별, Fab 타입별, 최종사용자별, 지역별 |
| 대상 지역 | 북미, 유럽, 아시아태평양, 기타 지역 |
300mm 생산능력 확대, 첨단 노드 생산, 이기종 통합의 진전으로 자동 자재 이송 시스템(AMHS), 로봇, 제조 실행 시스템(MES), 고급공정제어(APC)(APC), 수율 관리 소프트웨어(YMS), AI를 활용한 분석 솔루션의 도입이 가속화되고 있습니다. 도입이 가속화되고 있습니다. 이러한 솔루션을 통해 팹은 정밀한 재료 처리, 실시간 공정 최적화, 예지보전을 실현하고 초청정 제조 표준을 준수할 수 있습니다. 신규 그린필드 공장에 대한 대규모 투자, 정부의 반도체 산업 지원책, AI, 5G, 차량용 전장, 고성능 컴퓨팅을 위한 칩 수요 증가가 성장을 뒷받침할 것입니다. 그러나 높은 도입 비용, 통합의 복잡성, 숙련된 기술자 확보가 문제점으로 작용할 수 있습니다. 자동화 생태계 전반의 상호운용성 강화, 모듈형 도입, 파트너십 구축은 장기적인 시장 확대를 지속하기 위해 필수적입니다.

팹 자동화 시장에서 2025년부터 2032년까지 아웃소싱 반도체 조립 및 테스트(OSAT) 제공업체 부문이 가장 높은 CAGR을 나타낼 것으로 예측됩니다. 이는 첨단 패키징, 이기종 통합, 칩렛 기반 아키텍처의 급속한 성장에 힘입은 것입니다. OSAT 시설에서는 웨이퍼 레벨 패키징(WLP), 팬아웃 기술, 2.5D/3D 스태킹, 고급 테스트 작업과 같은 복잡한 공정을 지원하기 위해 고정밀, 무공해, 고처리량 자동화 솔루션에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있습니다. 증가하는 디바이스의 복잡성과 줄어드는 공차를 관리하기 위해 OSAT 기업들은 자동 자재 이송 시스템(AMHS), 로봇 공학, 스마트 검사 시스템, 제조 실행 시스템(MES), 고급 공정 제어(APC), AI 지원 분석을 도입하여 수율 향상, 운영 변동성 감소, 전체 패키징 워크플로우의 추적성을 유지합니다. 패키징 및 테스트 워크플로우 전반의 추적성 유지를 위해 노력하고 있습니다. AI, HPC, 자동차 전장, 5G 용도의 확대로 인해 OSAT 고객들은 더 빠른 사이클 타임, 확장 가능한 생산, 높은 신뢰성을 요구하고 있습니다. 패키징이 반도체 성능의 중요한 차별화 요소로 떠오르면서 OSAT 기업들은 디지털 전환, 자동화 업그레이드, 클린룸 최적화에 대한 투자를 가속화하고 있습니다. 아웃소싱 증가 추세, 고급 패키징에 대한 수요, 비용 효율적인 대량 생산의 필요성이 결합되어 OSAT 공급업체는 세계 팹 자동화 시장에서 매우 중요하고 빠르게 성장하는 최종 사용자 부문으로 자리매김하고 있습니다.
반도체 제조 능력의 급속한 확대와 고처리량 및 오염 제어 생산 환경에 대한 수요 증가로 인해 하드웨어 부문은 2032년까지 팹 자동화 시장에서 가장 큰 점유율을 차지할 것으로 예측됩니다. 팹이 첨단 노드 및 300mm 라인을 확장함에 따라 자동 자재 이송 시스템(AMHS), 로봇, 웨이퍼 핸들링 장비, 환경 제어 시스템, 전력 및 유틸리티 자동화 시스템, 통신 및 네트워크 하드웨어를 포함한 견고한 하드웨어에 대한 수요는 계속 증가하고 있습니다. 계속 증가하고 있습니다. 이러한 시스템은 자동화 팹의 물리적 기반을 형성하고, 정밀한 웨이퍼 운송, 안정적인 클린룸 환경 유지, 중단 없는 유틸리티 관리, 안정적인 장비 연결성을 실현합니다. AI, HPC, 자동차 전장, 5G 용도를 중심으로 로직, 메모리, 첨단 패키징 생산이 급증하면서 자동화 하드웨어에 대한 투자가 더욱 가속화되고 있습니다. 아시아태평양, 미국, 유럽의 신규 공장(그린필드)에서는 수율 안정성 확보, 사이클 타임 단축, 운영 탄력성 강화를 위해 엔드투엔드 자동화 인프라 구축에 대한 우선순위가 높아지고 있습니다. 또한, 기존 공장의 현대화를 통해 차세대 로봇, AMHS(자동 컨베이어 시스템) 업그레이드, 고도화된 오염 관리 시스템 도입을 추진하고 있습니다. 반도체 공정이 복잡해지고 처리량 요구사항이 증가함에 따라, 하드웨어는 앞으로도 세계 팹 자동화 분야에서 가장 많은 투자가 이뤄지는 분야로 남을 것입니다.
미국 지역은 첨단 반도체 제조에 대한 대규모 투자, 기존 팹의 현대화, 국내 칩 생산 강화를 위한 정부의 새로운 노력에 힘입어 2025년부터 2032년까지 팹 자동화 시장에서 가장 높은 CAGR을 나타낼 것으로 예측됩니다. 미국 및 기타 미국 국가들로 구성된 이 지역에서는 최첨단 로직, 메모리, 이기종 통합 기술을 지원하기 위한 여러 그린필드 및 브라운필드 프로젝트가 추진되고 있습니다. 신규 팹에서는 고처리량, 무공해, 에너지 절약형 운영이 강조되면서 자동 자재 이송 시스템(AMHS), 로봇공학, 환경 제어 시스템, 첨단 계측 장비, 공장 통신 인프라에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있습니다. 미국은 IDM, 파운드리, OSAT의 대규모 설비투자와 더불어 자동화, 디지털 전환, 노동력 최적화를 우선시하는 국가 반도체 정책에 따른 특혜 조치로 지역 성장을 견인하고 있습니다. 10nm 이하 공정과 EUV 지원 공정의 채택이 확대되면서 정밀 핸들링 장비와 지능형 자동화 플랫폼의 필요성이 더욱 가속화되고 있습니다. 한편, 다른 미국 국가들은 백엔드 조립, 테스트 및 패키징 역량을 확장하고 있으며, 확장 가능하고 비용 효율적인 자동화 솔루션에 대한 추가 수요를 창출하고 있습니다. 강력한 정책적 지원, 반도체 소비량 증가, 대규모 생산능력 확장과 함께 미주 대륙은 차세대 팹 자동화의 고성장 거점으로서 입지를 다지고 있습니다.
팹 자동화 시장에서 세계적으로 큰 존재감을 보이는 주요 기업으로는 Daifuku(일본), Murata Machinery(일본), Atlas Copco(스웨덴), Rorze Automation(일본), Ebara(일본) 등을 들 수 있습니다.
조사 범위
본 보고서에서는 팹 자동화 시장을 제공 형태, 배포 유형, 웨이퍼 크기, 최종 사용자, 지역별로 세분화하여 시장 규모를 예측했습니다. 또한 시장 성장에 영향을 미치는 촉진요인, 저해요인, 기회, 과제를 종합적으로 분석합니다. 질적, 양적 측면 모두에서 시장을 포괄하고 있습니다.
본 보고서 구매 이유:
이 보고서는 시장 리더와 신규 시장 진출기업에게 전체 팹 자동화 시장 및 관련 부문의 예상 수익에 대한 정보를 제공합니다. 이를 통해 이해관계자들은 경쟁 구도를 이해하고, 시장에서의 입지를 강화하거나 효과적인 시장 진출 전략을 수립하는 데 도움이 되는 귀중한 통찰력을 얻을 수 있습니다. 또한, 주요 시장 성장 촉진요인, 억제요인, 기회, 과제에 대한 정보를 제공하고 시장 동향을 파악하는 데 도움이 될 것입니다.
이 보고서는 다음 사항에 대한 통찰력을 제공합니다.
- 주요 촉진요인 분석(고처리량 자동화가 필요한 첨단 노드 및 EUV 지원 제조 확대, 300mm 팹 생산 능력의 급격한 성장, 로직, 메모리, 첨단 패키징의 공정 복잡성 증가, AI/ML 기반 예측 분석 및 디지털 트윈 플랫폼 채택 증가, 그린필드 공장 건설을 촉진하는 정부 인센티브, 높은 설비 투자 비용, 레거시 하드웨어 및 차세대 자동화 하드웨어의 상호운용성 제한, 성숙된 자동화 하드웨어 및 통합을 위한 높은 자본 비용) 그린필드 공장 건설을 촉진하는 정부 인센티브), 제약 요인(자동화 하드웨어 및 통합을 위한 고가의 설비 투자, 레거시 시스템과 차세대 시스템 간의 상호운용성 제한, 숙련된 자동화 및 소프트웨어 전문가 부족, 벤더 집중에 따른 설비 리드타임의 장기화), 기회(2. 기회(2.5D/3D 패키징 및 이기종 통합을 위한 첨단 자동화 도입, 자율 AI 지원 팹의 등장, 미국, 아시아, 유럽의 신규 팹의 대규모 자동화 수요, 모듈형 AMHS(자동 자재 이송 시스템) 및 협동 로봇 도입, 에너지 효율 및 에너지 효율 및 클린룸 효율을 중시하는 지속가능성 중심의 자동화 솔루션), 과제(엄격한 초청정 제조 요건으로 인한 오염 및 신뢰성 리스크 증가, 여러 벤더의 MES, APC, YMS, AMHS 에코시스템 간의 통합 복잡성, 높은 웨이퍼 양산 및 EUV 공정 민감도에서의 자동화 성능 유지, 반도체 장비 공급망 유지, 반도체 장비 공급망에 영향을 미치는 지정학적 혼란, 생산에 영향을 주지 않는 기존 공장 현대화의 높은 복잡성과 비용)
- 제품 개발/혁신 : 팹 자동화 시장에서의 신제품 출시, 확장, 계약, 제휴, 인수 등의 전략과 향후 기술 동향 및 R&D 활동에 대한 심층적인 통찰력을 제공합니다.
- 시장 개발: 수익성 높은 시장에 대한 종합적인 정보 - 이 보고서는 다양한 지역의 팹 자동화 시장을 분석합니다.
- 시장 다각화 : 팹 자동화 시장의 신제품, 미개척 지역, 최근 동향, 투자에 대한 종합적인 정보를 제공합니다.
- 주요 기업 - Daifuku(일본),Murata Machinery(일본),Atlas Copco(스웨덴),Rorze Automation(일본),Ebara(일본),FANUC(일본),Kawasaki Heavy Industries(일본),Hirata Corporation(일본),Yaskawa(일본),KUKA AG(독일) 시장 점유율, 성장전략, 제품 제공에 대한 상세한 평가
자주 묻는 질문
목차
제1장 서론
제2장 주요 요약
제3장 프리미엄 인사이트
제4장 시장 개요
- 시장 역학
- 연결된 시장과 분야간 기회
- Tier1/2/3 기업의 전략적 움직임
- 시장 역학
제5장 업계 동향
- Porter의 Five Forces 분석
- 거시경제 지표
- 밸류체인 분석
- 생태계 분석
- 가격 분석
- 무역 분석
- 2026년-2027년 주요 컨퍼런스 및 이벤트
- 고객의 비즈니스에 영향을 미치는 동향/파괴적 변화
- 투자 및 자금조달 시나리오, 2021-2025년
- 사례 연구 분석
- 2025년 미국 관세의 영향 Fab 자동화 시장
제6장 기술 진보, AI 별 영향, 특허, 혁신, 향후 응용
- 주요 신기술
- 보완적 기술
- 인접 기술
- 기술 및 제품 로드맵
- 특허 분석
- AI가 Fab 자동화 시장에 미치는 영향
제7장 규제 상황
- 규제기관, 정부기관 및 기타 조직
- 업계표준
- 세미 스탠다드(GEM, GEM300, E84, E87, EDA/인터페이스 A)
- ISO 클린룸 및 환경 관리 규격(ISO 14644 시리즈)
- ISO 10218 &IEC 61508-로봇 안전성과 기능 안전 규격
- 제조 장비 통신을 위한 OPC UA
- ANSI/ISA-95-제조 통합 규격
- SEMI S2-환경/건강/안전(EHS) 규격
제8장 고객 상황과 구매 행동
- 의사결정 프로세스
- 주요 이해관계자와 구입 기준
- 채택 장벽과 내부 과제
- 다양한 최종사용자의 미충족 요구
제9장 Fab 자동화 시장(제공 제품별)
- 하드웨어
- 소프트웨어
- 서비스
제10장 Fab 자동화 시장(자동화층 별)
- 자재관리 자동화
- 설비 자동화
- 프로세스 자동화
- 공장 자동화 소프트웨어
- AI/애널리틱스 자동화
제11장 Fab 자동화 시장(웨이퍼 사이즈별)
- 150mm 미만
- 200mm
- 300mm
제12장 Fab 자동화 시장(전개 유형별)
- GREENFIELD FABS
- BROWNFIELD FABS
제13장 Fab 자동화 시장(Fab 타입 별)
- ADVANCED NODE FABS (<=7 NM)
- MAINSTREAM NODE FABS (10-28 NM)
- MATURE NODE FABS (28-90 NM)
- LEGACY NODE FABS (>90 NM)
제14장 Fab 자동화 시장(자동화 레벨별)
- 완전자동화
- 반자동
제15장 Fab 자동화 시장(최종사용자별)
- 통합 디바이스 제조업체
- 주조소
- 아웃소싱 반도체 조립 및 테스트 프로바이더
- RESEARCH FAB
제16장 Fab 자동화 시장(지역별)
- 아메리카
- 미국
- 기타
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 한국
- 대만
- 인도
- 기타
- EMEA
- 유럽
- 중동 및 아프리카
제17장 경쟁 구도
- 개요
- 주요 시장 진출기업의 전략/강점, 2021년 1월-2025년 10월
- 시장 점유율 분석, 2024년
- 매출 분석, 2021년-2024년
- 기업 평가와 재무 지표
- 브랜드/제품 비교
- 기업 평가 매트릭스 : 주요 시장 진출기업, 2024년
- 기업 평가 매트릭스 : 스타트업/중소기업, 2024년
- 경쟁 시나리오
제18장 기업 개요
- 주요 시장 진출기업
- DAIFUKU CO., LTD.
- MURATA MACHINERY
- EBARA CORPORATION
- RORZE CORPORATION
- FANUC
- HIRATA CORPORATION
- KUKA AG
- YASKAWA ELECTRIC CORPORATION
- KAWASAKI HEAVY INDUSTRIES
- 기타 기업
- ATLAS COPCO
- THIRA-UTECH
- DAIHEN CORPORATION
- BROOKS AUTOMATION
- MIRLE AUTOMATION
- SYNUS TECH
- SHINKO ELECTRIC INDUSTRIES
- MEETFUTURE
- 파브 MATICS
- TAIYO INC.
- SINEVA
- CASTEC INTERNATIONAL
- SYSTEMA GMBH
- KYOWA ELECTRIC & INSTRUMENT
- AMHS TECHNOLOGIES
- ATS AUTOMATION
- NIDEC CORPORATION
- GENMARK AUTOMATION
- JEL CORPORATION
- KENSINGTON LABS
- SIEMENS
- ROCKWELL AUTOMATION
- 최종사용자
- FOUNDRIES
- IDM FIRMS
- OSAT COMPANIES
제19장 조사 방법
제20장 부록
LSH 26.01.22The fab automation market is projected to reach USD 25.24 billion in 2025 and USD 41.44 billion by 2032, registering a CAGR of 7.3% between 2025 and 2032. The market is projected to witness substantial growth during the forecast period, driven by the increasing complexity of semiconductor manufacturing and the global push toward higher yields, faster cycle times, and greater operational consistency.
| Scope of the Report | |
|---|---|
| Years Considered for the Study | 2020-2032 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2032 |
| Units Considered | Value (USD Billion) |
| Segments | By Offering, Deployment Type, Wafer Size, End User and Region |
| Regions covered | North America, Europe, APAC, RoW |
Expanding 300 mm capacity, advanced-node production, and heterogeneous integration are accelerating the adoption of automated material handling systems (AMHS), robotics, manufacturing execution systems (MES), advanced process control (APC), yield management software (YMS), and AI-enabled analytics. These solutions enable fabs to achieve precision handling, real-time process optimization, and predictive maintenance, ensuring compliance with ultra-clean manufacturing standards. Growth is further supported by large-scale investments in new greenfield fabs, government semiconductor incentives, and the rising demand for chips powering AI, 5G, automotive electronics, and high-performance computing. However, high implementation costs, integration complexity, and the need for skilled technical resources may present operational challenges. Strengthening interoperability, modular deployments, and partnerships across the automation ecosystem will be essential to sustaining long-term market expansion.
"By end user, the outsourced semiconductor assembly & test (OSAT) providers segment is expected to register the highest CAGR between 2025 and 2032."
The outsourced semiconductor assembly and test (OSAT) providers segment is expected to register the highest CAGR in the fab automation market between 2025 and 2032, driven by the rapid growth of advanced packaging, heterogeneous integration, and chiplet-based architectures. OSAT facilities are experiencing rising demand for high-precision, contamination-free, and high-throughput automation solutions to support complex processes such as wafer-level packaging (WLP), fan-out technologies, 2.5D/3D stacking, and advanced test operations. To manage increasing device complexity and shrinking tolerances, OSATs are deploying Automated Material Handling Systems (AMHS), robotics, smart inspection systems, Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), Advanced Process Control (APC), and AI-enabled analytics to enhance yield, reduce operational variability, and maintain traceability across packaging and test workflows. The expansion of AI, HPC, automotive electronics, and 5G applications is further driving OSAT customers to demand faster cycle times, scalable production, and higher reliability. As packaging becomes a critical differentiator in semiconductor performance, OSATs are accelerating investments in digital transformation, automation upgrades, and cleanroom optimization. The combination of rising outsourcing trends, advanced packaging demand, and the need for cost-efficient, high-volume production positions OSAT providers as a pivotal and fast-growing end-user segment in the global fab automation market.
"Based on offering, the hardware segment is projected to account for the largest market share in 2032."
The hardware segment is projected to account for the largest share of the fab automation market by 2032, driven by the rapid expansion of semiconductor manufacturing capacity and the increasing demand for high-throughput, contamination-controlled production environments. As fabs scale advanced-node and 300mm lines, demand for robust hardware, including automated material handling systems (AMHS), robotics, wafer-handling equipment, environmental control systems, power and utility automation systems, and communication and networking hardware, continues to rise. These systems form the physical backbone of automated fabs, enabling precise wafer transport, maintaining stable cleanroom conditions, ensuring uninterrupted utility management, and ensuring reliable equipment connectivity. The surge in logic, memory, and advanced packaging production driven by AI, HPC, automotive electronics, and 5G applications is further accelerating investments in automation hardware. Greenfield fabs in the Asia Pacific, the US, and Europe are increasingly prioritizing end-to-end automated infrastructure to ensure yield consistency, reduce cycle time, and enhance operational resilience. Additionally, the modernization of brownfield facilities is boosting the adoption of next-generation robotics, AMHS upgrades, and advanced contamination control systems. As semiconductor processes become more complex and throughput requirements rise, hardware will remain the foundational and most heavily invested offering within the global fab automation landscape.
"The Americas region is projected to exhibit the highest CAGR from 2025 to 2032."
The Americas region is projected to exhibit the highest CAGR in the fab automation market from 2025 to 2032, driven by substantial investments in advanced semiconductor manufacturing, modernization of existing fabs, and renewed government focus on strengthening domestic chip production. The region, comprising the US and the Rest of the Americas, is advancing multiple greenfield and brownfield projects aimed at supporting leading-edge logic, memory, and heterogeneous integration technologies. As new fabs emphasize high-throughput, contamination-free, and energy-efficient operations, demand is rising for automated material handling systems (AMHS), robotics, environmental control systems, advanced metrology hardware, and factory communication infrastructure. The US leads regional growth, fueled by substantial capital expenditure from IDMs, foundries, and OSATs, alongside incentives under national semiconductor policies that prioritize automation, digital transformation, and workforce optimization. Increasing adoption of sub-10 nm and EUV-enabled processes is further accelerating the need for precision handling equipment and intelligent automation platforms. Meanwhile, countries in the Rest of the Americas are expanding backend assembly, test, and packaging capabilities, creating additional demand for scalable, cost-efficient automation solutions. Collectively, strong policy support, rising semiconductor consumption, and large-scale capacity expansion position the Americas as a high-growth hub for next-generation fab automation.
The break-up of the profile of primary participants in the fab automation market-
- By Company Type: Tier 1 - 35%, Tier 2 - 45%, Tier 3 - 20%
- By Designation: C-level Executives - 40%, Directors - 30%, Others - 30%
- By Region: Americas - 40%, EMEA - 25%, Asia Pacific - 35%
Note: Other designations include sales, marketing, and product managers.
The three tiers of the companies are based on their total revenues as of 2024: Tier 1: >USD 1 billion, Tier 2: USD 500 million-1 billion, and Tier 3: USD 500 million.
The major players in the fab automation market with a significant global presence include Daifuku (Japan), Murata Machinery (Japan), Atlas Copco (Sweden), Rorze Automation (Japan), and Ebara (Japan).
Research Coverage
The report segments the fab automation market and forecasts its size by offering, deployment type, wafer size, end user, and region. It also comprehensively reviews the drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges that influence market growth. The report encompasses both qualitative and quantitative aspects of the market.
Reasons to Buy the Report:
The report will help the market leaders/new entrants with information on the closest approximate revenues for the overall fab automation market and related segments. This report will help stakeholders understand the competitive landscape and gain valuable insights to strengthen their market position and develop effective go-to-market strategies. The report also helps stakeholders understand the pulse of the market, providing them with information on key market drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges.
The report provides insights into the following pointers:
- Analysis of key drivers (expansion of advanced-node and EUV-enabled manufacturing requiring high-throughput automation; rapid growth in 300 mm fab capacity; rising process complexity across logic, memory, and advanced packaging; increasing adoption of AI/ML-driven predictive analytics and digital-twin platforms; government incentives accelerating greenfield fab construction), restraints (high capital expenditure for automation hardware and integration; limited interoperability between legacy and next-generation systems; shortages of skilled automation and software specialists; extended equipment lead times due to vendor concentration), opportunities (deployment of advanced automation for 2.5D/3D packaging and heterogeneous integration; emergence of autonomous, AI-enabled fabs; large-scale automation demand from new fabs in the US, Asia, and Europe; adoption of modular AMHS and collaborative robotics; sustainability-focused automation solutions for energy and cleanroom efficiency), and challenges (stringent ultra-clean manufacturing requirements increasing contamination and reliability risks; integration complexity across multi-vendor MES, APC, YMS, and AMHS ecosystems; maintaining automation performance at high wafer volumes and EUV process sensitivities; geopolitical disruptions affecting semiconductor equipment supply chains; high complexity and cost of modernizing brownfield fabs without production impact)
- Product Development/Innovation: Detailed insights on upcoming technologies, research & development activities, and strategies such as new product launches, expansions, contracts, partnerships, and acquisitions in the fab automation market
- Market Development: Comprehensive information about lucrative markets-the report analyses the fab automation market across varied regions
- Market Diversification: Exhaustive information about new products, untapped geographies, recent developments, and investments in the fab automation market
- Competitive Assessment: In-depth assessment of market shares, growth strategies, and product offerings of leading players, including Daifuku (Japan), Murata Machinery (Japan), Atlas Copco (Sweden), Rorze Automation (Japan), Ebara (Japan), FANUC (Japan), Kawasaki Heavy Industries (Japan), Hirata Corporation (Japan), Yaskawa (Japan), and KUKA AG (Germany).
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 STUDY OBJECTIVES
- 1.2 MARKET DEFINITION
- 1.3 STUDY SCOPE
- 1.3.1 MARKETS COVERED AND REGIONAL SCOPE
- 1.3.2 YEARS CONSIDERED
- 1.3.3 INCLUSIONS AND EXCLUSIONS
- 1.4 CURRENCY CONSIDERED
- 1.5 UNITS CONSIDERED
- 1.6 STAKEHOLDERS
2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- 2.1 MARKET HIGHLIGHTS AND KEY INSIGHTS
- 2.2 KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS: MAPPING OF STRATEGIC DEVELOPMENTS
- 2.3 DISRUPTIVE TRENDS IN FAB AUTOMATION MARKET
- 2.4 HIGH-GROWTH SEGMENTS
- 2.5 REGIONAL SNAPSHOT: MARKET SIZE, GROWTH RATE, AND FORECAST
3 PREMIUM INSIGHTS
- 3.1 ATTRACTIVE OPPORTUNITIES FOR PLAYERS IN FAB AUTOMATION MARKET
- 3.2 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING
- 3.3 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY WAFER SIZE
- 3.4 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT TYPE
- 3.5 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY END USER
- 3.6 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION
- 3.7 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY COUNTRY
4 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 4.1 INTRODUCTION
- 4.2 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.2.1 DRIVERS
- 4.2.1.1 Rising demand for high-throughput, high-yield semiconductor manufacturing across AI, HPC, automotive, and 5G applications
- 4.2.1.2 Expansion of advanced-node fabs requiring deep automation to sustain process stability
- 4.2.1.3 Increasing adoption of AMHS, robotics, and contamination-free transport to reduce human intervention
- 4.2.1.4 Increasing integration of MES, APC, YMS, and ECS platforms to enhance real-time process control and production efficiency
- 4.2.1.5 Government-backed investments and incentive programs accelerating greenfield fabs and capacity expansion
- 4.2.2 RESTRAINTS
- 4.2.2.1 High capital investment requirements for full fab automation deployment, particularly in brownfield facilities
- 4.2.2.2 Interoperability challenges between legacy tools and modern automation systems
- 4.2.2.3 Limited availability of skilled automation engineers for system integration and fab-level optimization
- 4.2.2.4 Supply chain constraints for automation components and cleanroom systems, resulting in extended deployment timelines
- 4.2.3 OPPORTUNITIES
- 4.2.3.1 AI/ML-driven automation enabling predictive maintenance, intelligent scheduling, and yield enhancement
- 4.2.3.2 Rising automation demand in OSAT facilities driven by advanced packaging and throughput requirements
- 4.2.3.3 Expansion of 300 mm fabs and modernization of 200 mm facilities, driving long-term automation upgrade cycles
- 4.2.3.4 Growing adoption of digital twins and simulation platforms to optimize fab workflows and equipment layouts
- 4.2.4 CHALLENGES
- 4.2.4.1 Complex coordination and orchestration across multi-layer automation architectures in large semiconductor fabs
- 4.2.4.2 Ensuring real-time, low-latency communication across distributed automation networks under heavy data loads
- 4.2.4.3 Ensuring ultra-clean automated handling as device geometries shrink and contamination sensitivity intensifies
- 4.2.4.4 Long deployment and integration timelines create operational risks in upgrading automation within running fabs
- 4.2.1 DRIVERS
- 4.3 INTERCONNECTED MARKETS AND CROSS-SECTOR OPPORTUNITIES
- 4.3.1 INTERCONNECTED MARKETS
- 4.3.2 CROSS-SECTOR OPPORTUNITIES
- 4.4 STRATEGIC MOVES BY TIER 1/2/3 PLAYERS
- 4.4.1 MARKET DYNAMICS
5 INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 5.1 INTRODUCTION
- 5.2 PORTER'S FIVE FORCES ANALYSIS
- 5.2.1 THREAT OF NEW ENTRANTS
- 5.2.2 THREAT OF SUBSTITUTES
- 5.2.3 BARGAINING POWER OF SUPPLIERS
- 5.2.4 BARGAINING POWER OF BUYERS
- 5.2.5 INTENSITY OF COMPETITIVE RIVALRY
- 5.3 MACROECONOMIC INDICATORS
- 5.3.1 INTRODUCTION
- 5.3.2 GDP TRENDS AND FORECAST
- 5.3.3 TRENDS IN MANUFACTURING & INDUSTRIAL AUTOMATION INDUSTRY
- 5.3.4 TRENDS IN SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING INDUSTRY
- 5.4 VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS
- 5.5 ECOSYSTEM ANALYSIS
- 5.6 PRICING ANALYSIS
- 5.6.1 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE OF KEY PLAYERS, BY OFFERING, 2024
- 5.6.2 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE, BY REGION, 2021-2024
- 5.7 TRADE ANALYSIS
- 5.7.1 IMPORT SCENARIO (HS CODE 8479)
- 5.7.2 EXPORT SCENARIO (HS CODE 8479)
- 5.8 KEY CONFERENCES AND EVENTS, 2026-2027
- 5.9 TRENDS/DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMER BUSINESSES
- 5.10 INVESTMENT AND FUNDING SCENARIO, 2021-2025
- 5.11 CASE STUDY ANALYSIS
- 5.11.1 TSMC'S CLEANROOM THROUGHPUT IMPROVEMENT WITH DAIFUKU'S NEO-AMHS PLATFORM
- 5.11.2 SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS' AUTOMATION UPGRADE USING MURATA MACHINERY'S WAFER-HANDLING ROBOTICS
- 5.11.3 GLOBALFOUNDRIES' APC/YMS TRANSFORMATION WITH APPLIED MATERIALS AUTOMATION SOFTWARE SOLUTIONS
- 5.12 IMPACT OF 2025 US TARIFF - FAB AUTOMATION MARKET
- 5.12.1 KEY TARIFF RATES
- 5.12.2 PRICE IMPACT ANALYSIS
- 5.12.3 IMPACT ON COUNTRIES/REGIONS
- 5.12.3.1 US
- 5.12.3.2 Europe
- 5.12.3.3 Asia Pacific
- 5.12.4 IMPACT ON END USERS
6 TECHNOLOGICAL ADVANCEMENTS, AI-DRIVEN IMPACT, PATENTS, INNOVATIONS, AND FUTURE APPLICATIONS
- 6.1 KEY EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES
- 6.1.1 AI-DRIVEN ADVANCED PROCESS CONTROL (APC) & PREDICTIVE AUTOMATION
- 6.1.2 MODULAR & COLLABORATIVE AMHS PLATFORMS
- 6.1.3 DIGITAL TWIN & VIRTUAL FAB SIMULATION PLATFORMS
- 6.2 COMPLEMENTARY TECHNOLOGIES
- 6.2.1 EDGE COMPUTING & REAL-TIME DATA INFRASTRUCTURE
- 6.2.2 HIGH-PRECISION CLEANROOM ENVIRONMENTAL CONTROL & MONITORING SYSTEMS
- 6.2.3 SECURE FAB COMMUNICATION NETWORKS & INDUSTRIAL IOT CONNECTIVITY
- 6.3 ADJACENT TECHNOLOGIES
- 6.3.1 ADVANCED PACKAGING & HETEROGENEOUS INTEGRATION AUTOMATION
- 6.3.2 SEMICONDUCTOR MATERIALS DELIVERY & CHEMICAL MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
- 6.4 TECHNOLOGY/PRODUCT ROADMAP
- 6.4.1 SHORT-TERM (2025-2027): AUTOMATION MODERNIZATION & AI-AUGMENTED OPERATIONS
- 6.4.2 MID-TERM (2027-2030): HYPER-AUTOMATION & ADVANCED PACKAGING INTEGRATION
- 6.4.3 LONG-TERM (2030-2035+): AUTONOMOUS FABS & SYSTEM-LEVEL CONVERGENCE
- 6.5 PATENT ANALYSIS
- 6.6 IMPACT OF AI ON FAB AUTOMATION MARKET
- 6.6.1 TOP USE CASES AND MARKET POTENTIAL
- 6.6.2 BEST PRACTICES IN FAB AUTOMATION MARKET
- 6.6.3 CASE STUDIES OF AI IMPLEMENTATION IN FAB AUTOMATION MARKET
- 6.6.4 INTERCONNECTED ADJACENT ECOSYSTEM AND IMPACT ON MARKET PLAYERS
- 6.6.5 CLIENTS' READINESS TO ADOPT GENERATIVE AI IN FAB AUTOMATION MARKET
7 REGULATORY LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 INTRODUCTION
- 7.1.1 REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS
- 7.2 INDUSTRY STANDARDS
- 7.2.1 SEMI STANDARDS (GEM, GEM300, E84, E87, EDA/INTERFACE A)
- 7.2.2 ISO CLEANROOM & ENVIRONMENTAL CONTROL STANDARDS (ISO 14644 SERIES)
- 7.2.3 ISO 10218 & IEC 61508 - ROBOTICS SAFETY & FUNCTIONAL SAFETY STANDARDS
- 7.2.4 OPC UA FOR FAB EQUIPMENT COMMUNICATION
- 7.2.5 ANSI/ISA-95 - MANUFACTURING INTEGRATION STANDARD
- 7.2.6 SEMI S2 - ENVIRONMENTAL, HEALTH & SAFETY (EHS) STANDARD
8 CUSTOMER LANDSCAPE AND BUYER BEHAVIOR
- 8.1 DECISION-MAKING PROCESS
- 8.2 KEY STAKEHOLDERS AND BUYING CRITERIA
- 8.2.1 KEY STAKEHOLDERS IN BUYING PROCESS
- 8.2.2 BUYING CRITERIA
- 8.3 ADOPTION BARRIERS AND INTERNAL CHALLENGES
- 8.4 UNMET NEEDS FROM VARIOUS END USERS
9 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING
- 9.1 INTRODUCTION
- 9.2 HARDWARE
- 9.2.1 AUTOMATED MATERIAL HANDLING SYSTEMS
- 9.2.1.1 AI-orchestrated throughput growth to fuel AMHS demand in fab automation
- 9.2.2 ROBOTICS & HANDLING EQUIPMENT
- 9.2.2.1 AI-enabled precision and vision integration to drive demand
- 9.2.3 ENVIRONMENTAL CONTROL SYSTEMS
- 9.2.3.1 Humidity and AMC control to increase demand for advanced environmental control systems
- 9.2.4 POWER & UTILITY AUTOMATION SYSTEMS
- 9.2.4.1 Power quality and energy-efficiency mandates to accelerate adoption of utility & power automation systems in fabs
- 9.2.5 COMMUNICATION & NETWORKING HARDWARE
- 9.2.5.1 Low-latency, deterministic connectivity requirements to drive market
- 9.2.1 AUTOMATED MATERIAL HANDLING SYSTEMS
- 9.3 SOFTWARE
- 9.3.1 MANUFACTURING EXECUTION SYSTEMS
- 9.3.1.1 Model-driven traceability and real-time dispatch to accelerate adoption
- 9.3.2 EQUIPMENT CONTROL SOFTWARE
- 9.3.2.1 Real-time tool-state coordination and recipe enforcement to drive adoption
- 9.3.3 ADVANCED PROCESS CONTROL
- 9.3.3.1 Shrinking process windows and high-mix production to drive APC integration
- 9.3.4 YIELD MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE
- 9.3.4.1 Defect density reduction and multi-source data fusion to increase adoption
- 9.3.5 AI/ML & PREDICTIVE ANALYTICS PLATFORMS
- 9.3.5.1 Predictive maintenance and lot-flow optimization to accelerate AI/ML deployment
- 9.3.6 SIMULATION & DIGITAL TWIN SOFTWARE
- 9.3.6.1 Capacity planning and virtual process optimization to expand digital twin usage
- 9.3.7 MIDDLEWARE & COMMUNICATION PROTOCOL SOFTWARE
- 9.3.7.1 Interoperability requirements and multi-vendor tool integration to fuel middleware adoption
- 9.3.1 MANUFACTURING EXECUTION SYSTEMS
- 9.4 SERVICES
- 9.4.1 PROFESSIONAL SERVICES
- 9.4.1.1 System integration complexity and node migration timelines to increase demand
- 9.4.2 MANAGED SERVICES
- 9.4.2.1 Predictive maintenance and 24/7 operational assurance to accelerate managed services adoption
- 9.4.1 PROFESSIONAL SERVICES
10 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY AUTOMATION LAYER
- 10.1 INTRODUCTION
- 10.2 MATERIAL HANDLING AUTOMATION
- 10.3 EQUIPMENT AUTOMATION
- 10.4 PROCESS AUTOMATION
- 10.5 FACTORY AUTOMATION SOFTWARE
- 10.6 AI/ANALYTICS AUTOMATION
11 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY WAFER SIZE
- 11.1 INTRODUCTION
- 11.2 <150 MM
- 11.2.1 INCREASED SPECIALTY-DEVICE PRODUCTION TO DRIVE ADOPTION
- 11.3 200 MM
- 11.3.1 GROWTH IN POWER AND ANALOG DEVICES TO INCREASE DEMAND
- 11.4 300 MM
- 11.4.1 ADVANCED PACKAGING DEMAND AND HIGH-VOLUME TEST REQUIREMENTS TO DRIVE MARKET
12 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT TYPE
- 12.1 INTRODUCTION
- 12.2 GREENFIELD FABS
- 12.2.1 ADVANCED NODE CAPACITY EXPANSION AND HIGH-THROUGHPUT MANUFACTURING REQUIREMENTS TO DRIVE MARKET
- 12.3 BROWNFIELD FABS
- 12.3.1 RETROFIT INVESTMENTS AND LEGACY-ASSET UTILIZATION TO SUPPORT MARKET GROWTH
13 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY FAB TYPE
- 13.1 INTRODUCTION
- 13.2 ADVANCED NODE FABS (<=7 NM)
- 13.3 MAINSTREAM NODE FABS (10-28 NM)
- 13.4 MATURE NODE FABS (28-90 NM)
- 13.5 LEGACY NODE FABS (>90 NM)
14 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY AUTOMATION LEVEL
- 14.1 INTRODUCTION
- 14.2 FULLY AUTOMATED
- 14.3 SEMI-AUTOMATED
15 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY END USER
- 15.1 INTRODUCTION
- 15.2 INTEGRATED DEVICE MANUFACTURERS
- 15.2.1 COMPLEX PRODUCT PORTFOLIOS AND MULTI-FAB MANUFACTURING COORDINATION TO DRIVE MARKET
- 15.3 FOUNDRIES
- 15.3.1 HIGH-MIX PRODUCTION LOADS AND ADVANCED-NODE CAPACITY REQUIREMENTS TO PROPEL MARKET
- 15.4 OUTSOURCED SEMICONDUCTOR ASSEMBLY & TEST PROVIDERS
- 15.4.1 ADVANCED PACKAGING DEMAND AND HIGH-VOLUME TEST REQUIREMENTS TO DRIVE MARKET
- 15.5 RESEARCH FABS
- 15.5.1 HIGH-ACCURACY EXPERIMENTATION AND ACCELERATED PROTOTYPING DEMAND TO DRIVE MARKET
16 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION
- 16.1 INTRODUCTION
- 16.2 AMERICAS
- 16.2.1 US
- 16.2.1.1 Federal incentives and advanced-node capacity expansion to drive adoption
- 16.2.2 REST OF AMERICAS
- 16.2.1 US
- 16.3 ASIA PACIFIC
- 16.3.1 CHINA
- 16.3.1.1 China's 300 mm expansion and localized automation ecosystem to drive market
- 16.3.2 JAPAN
- 16.3.2.1 Government subsidies and new 300 mm fab investments to accelerate demand
- 16.3.3 SOUTH KOREA
- 16.3.3.1 Memory-led capacity expansion and mega-cluster investments to accelerate demand
- 16.3.4 TAIWAN
- 16.3.4.1 Advanced-node expansion and foundry-led manufacturing growth to drive automation
- 16.3.5 INDIA
- 16.3.5.1 Government-backed fab expansion and growing domestic demand to drive adoption
- 16.3.6 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC
- 16.3.1 CHINA
- 16.4 EMEA
- 16.4.1 EUROPE
- 16.4.1.1 Advanced-node investments and power-semiconductor expansion to drive market
- 16.4.2 MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA
- 16.4.2.1 Government-led technology initiatives and emerging electronics manufacturing to support market growth
- 16.4.1 EUROPE
17 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 17.1 OVERVIEW
- 17.2 KEY PLAYER STRATEGIES/RIGHT TO WIN, JANUARY 2021-OCTOBER 2025
- 17.3 MARKET SHARE ANALYSIS, 2024
- 17.4 REVENUE ANALYSIS, 2021-2024
- 17.5 COMPANY VALUATION AND FINANCIAL METRICS
- 17.6 BRAND/PRODUCT COMPARISON
- 17.7 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: KEY PLAYERS, 2024
- 17.7.1 STARS
- 17.7.2 EMERGING LEADERS
- 17.7.3 PERVASIVE PLAYERS
- 17.7.4 PARTICIPANTS
- 17.7.5 COMPANY FOOTPRINT: KEY PLAYERS, 2024
- 17.7.5.1 Company footprint
- 17.7.5.2 Region footprint
- 17.7.5.3 Offering footprint
- 17.7.5.4 Wafer size footprint
- 17.7.5.5 Deployment type footprint
- 17.7.5.6 End user footprint
- 17.8 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: STARTUPS/SMES, 2024
- 17.8.1 PROGRESSIVE COMPANIES
- 17.8.2 RESPONSIVE COMPANIES
- 17.8.3 DYNAMIC COMPANIES
- 17.8.4 STARTING BLOCKS
- 17.8.5 COMPETITIVE BENCHMARKING: STARTUPS/SMES, 2024
- 17.8.5.1 Detailed list of key startups/SMEs
- 17.8.5.2 Competitive benchmarking of key startups/SMEs
- 17.9 COMPETITIVE SCENARIO
- 17.9.1 PRODUCT LAUNCHES
- 17.9.2 EXPANSIONS
18 COMPANY PROFILES
- 18.1 INTRODUCTION
- 18.2 KEY PLAYERS
- 18.2.1 DAIFUKU CO., LTD.
- 18.2.1.1 Business overview
- 18.2.1.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 18.2.1.3 Recent developments
- 18.2.1.3.1 Expansions
- 18.2.1.4 MnM view
- 18.2.1.4.1 Key strengths
- 18.2.1.4.2 Strategic choices
- 18.2.1.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 18.2.2 MURATA MACHINERY
- 18.2.2.1 Business overview
- 18.2.2.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 18.2.2.3 MnM view
- 18.2.2.3.1 Key strengths
- 18.2.2.3.2 Strategic choices
- 18.2.2.3.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 18.2.3 EBARA CORPORATION
- 18.2.3.1 Business overview
- 18.2.3.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 18.2.3.3 MnM view
- 18.2.3.3.1 Key strengths
- 18.2.3.3.2 Strategic choices
- 18.2.3.3.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 18.2.4 RORZE CORPORATION
- 18.2.4.1 Business overview
- 18.2.4.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 18.2.4.3 MnM view
- 18.2.4.3.1 Key strengths
- 18.2.4.3.2 Strategic choices
- 18.2.4.3.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 18.2.5 FANUC
- 18.2.5.1 Business overview
- 18.2.5.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 18.2.5.3 MnM view
- 18.2.5.3.1 Key strengths
- 18.2.5.3.2 Strategic choices
- 18.2.5.3.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 18.2.6 HIRATA CORPORATION
- 18.2.6.1 Business overview
- 18.2.6.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 18.2.7 KUKA AG
- 18.2.7.1 Business overview
- 18.2.7.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 18.2.8 YASKAWA ELECTRIC CORPORATION
- 18.2.8.1 Business overview
- 18.2.8.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 18.2.9 KAWASAKI HEAVY INDUSTRIES
- 18.2.9.1 Business overview
- 18.2.9.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 18.2.1 DAIFUKU CO., LTD.
- 18.3 OTHER PLAYERS
- 18.3.1 ATLAS COPCO
- 18.3.2 THIRA-UTECH
- 18.3.3 DAIHEN CORPORATION
- 18.3.4 BROOKS AUTOMATION
- 18.3.5 MIRLE AUTOMATION
- 18.3.6 SYNUS TECH
- 18.3.7 SHINKO ELECTRIC INDUSTRIES
- 18.3.8 MEETFUTURE
- 18.3.9 FABMATICS
- 18.3.10 TAIYO INC.
- 18.3.11 SINEVA
- 18.3.12 CASTEC INTERNATIONAL
- 18.3.13 SYSTEMA GMBH
- 18.3.14 KYOWA ELECTRIC & INSTRUMENT
- 18.3.15 AMHS TECHNOLOGIES
- 18.3.16 ATS AUTOMATION
- 18.3.17 NIDEC CORPORATION
- 18.3.18 GENMARK AUTOMATION
- 18.3.19 JEL CORPORATION
- 18.3.20 KENSINGTON LABS
- 18.3.21 SIEMENS
- 18.3.22 ROCKWELL AUTOMATION
- 18.4 END USERS
- 18.4.1 FOUNDRIES
- 18.4.1.1 Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited
- 18.4.1.2 Samsung
- 18.4.1.3 GlobalFoundries
- 18.4.1.4 SMIC
- 18.4.1.5 United Microelectronics Corporation
- 18.4.2 IDM FIRMS
- 18.4.2.1 Intel Corporation
- 18.4.2.2 Texas Instruments Incorporated
- 18.4.2.3 Infineon Technologies AG
- 18.4.3 OSAT COMPANIES
- 18.4.3.1 ASE Technology Holding Co., Ltd.
- 18.4.3.2 Amkor Technology
- 18.4.1 FOUNDRIES
19 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 19.1 RESEARCH DATA
- 19.1.1 SECONDARY AND PRIMARY RESEARCH
- 19.1.2 SECONDARY DATA
- 19.1.2.1 List of key secondary sources
- 19.1.2.2 Key data from secondary sources
- 19.1.3 PRIMARY DATA
- 19.1.3.1 List of primary interview participants
- 19.1.3.2 Breakdown of primaries
- 19.1.3.3 Key data from primary sources
- 19.1.3.4 Key industry insights
- 19.2 MARKET SIZE ESTIMATION
- 19.2.1 BOTTOM-UP APPROACH
- 19.2.2 TOP-DOWN APPROACH
- 19.3 DATA TRIANGULATION
- 19.4 RESEARCH ASSUMPTIONS
- 19.5 RESEARCH LIMITATIONS AND RISK ASSESSMENT
20 APPENDIX
- 20.1 INSIGHTS FROM INDUSTRY EXPERTS
- 20.2 DISCUSSION GUIDE
- 20.3 KNOWLEDGESTORE: MARKETSANDMARKETS' SUBSCRIPTION PORTAL
- 20.4 CUSTOMIZATION OPTIONS
- 20.5 RELATED REPORTS
- 20.6 AUTHOR DETAILS



















