
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1432979
세계 체외진단(IVD)용 실험실 자동화 시장 : 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 성장 예측(2024년-2029년)Lab Automation For In-Vitro Diagnostics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029) |
||||||
체외진단(IVD)용 실험실 자동화 시장 규모는 2024년에 57억 5,000만 달러로 추계되고, 2029년에는 78억 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며, 예측 기간 중(2024-2029년)의 복합 연간 성장률(CAGR) 6.30%로 성장할 전망입니다.

팬데믹에 의한 검사 증가나 신속하고 정확하고 실수가 없는 진단을 제공하기 위한 실험실용 자동 체외 진단 시스템의 개발이 시장 성장의 요인으로 생각됩니다.
주요 하이라이트
- 실험실 자동화는 시료 처리 장치를 사용하여 임상 연구를 수행하는 것입니다. 이 절차는 생산성을 높이고 시간주기를 단축하기 위해 새로운 기술을 개발하기 위해 수행됩니다. 체외진단제는 검사실, 클리닉, 교육기관, 진단센터, 개인집 등 다양한 환경에서 사용되고 있습니다.
- In-Vitro 진단용 의약품(IVD) 제품 포트폴리오에는 임상 화학 및 면역 측정, 소변 검사, 포인트 오브 케어 검사, 환자 자체 검사 장치 등을 지원하는 장치가 포함됩니다. 시장은 IVD(체외진단제) 제품을 도입하는 대기업 증가로 확대되고 있습니다.
- 실험실 자동화는 특히 In-Vitro 진단용 의약품 개발에 흔히 사용되고 있습니다. 전례없는 규모로 체외 진단의 생산성과 처리량 향상에 기술이 기여했습니다. 게다가 In-Vitro 진단용 의약품 시장은 진단 검사 정보를 보완하는 인지적 머신러닝 기능과 빅데이터와 여러 장비 시스템 간의 원활한 연결을 가능하게 하는 기술로부터 혜택을 누릴 것으로 예상됩니다. 이러한 기술 진보의 결과, 자동화 솔루션 수요가 높아질 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 제약 업계에서 R&D 활동 증가와 식품 안전을 위한 공정 자동화에 대한 수요 증가는 In-Vitro 진단용 의약품 시장에서 실험실 자동화의 성장을 가속하고 있습니다. 헬스케어 산업에서 워크플로우의 표준화와 엄격한 규제관리의 결과로 이러한 시스템의 채용이 증가하고 있는 것이 In-Vitro 진단용 랩 자동화 시장의 성장에 영향을 미치고 있습니다.
- 첨단 기술에 대한 많은 투자와 제품 및 부가가치 서비스를 통한 비즈니스 모델의 변화가 시장의 추진력이 될 것으로 예상됩니다. 또한 기존 질병의 급속한 확산과 새로운 질병의 발견으로 조기 치료와 진단에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있습니다. 이로 인해 임상 진단 애플리케이션의 비율이 증가하고 실험실 자동화 솔루션을 채택하는 데 박차가 걸릴 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 체외 진단 장치의 자동화를 통해 의료 진단 업계는 잠재적인 오류를 크게 줄이고 감염 탐지, 병리학 진단, 질병 예방, 약물 치료 모니터링을 보다 정확하게 수행할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 유행성(세계적 유행) 발생 시에는 로봇 공학을 이용하여 감염에 대한 노출을 줄이고, 약이나 식품을 배급하고, 생체 사인을 평가하고, 국경 관리를 촉진하고, 소독을 자동화한다 수 있습니다.
- 또한, 실험실 워크플로우에 AI 및 분석 도구를 통합함으로써 실험실 자동화 시장의 수익 기회가 확대됩니다. 그러나 숙련된 검사 전문가의 부족과 분석 실험실의 기술 통합의 제한된 실현 가능성은 체외 진단 실험실 자동화 시장의 과제와 방해가 될 것으로 보입니다.
- COVID-19 팬데믹의 지속적인 시장 영향과 소비자 수요 증가는 분자진단에 기인합니다. 예를 들어, 인플루엔자와 COVID-19는 구별하기 어려운 증상을 가지고 있습니다. 또한 COVID-19의 유행에 따라 일부 지역에서는 바이러스를 검출하기 위한 검사 건수가 증가하고 있어 실험실 자동화 기술이 필요합니다.
체외진단(IVD)용 실험실 자동화 시장 동향
로봇암 채용이 시장 성장을 도와
- 체외 진단(IVD)은 질병 진단 및 치료 정책 결정에 중요한 정보를 제공함으로써 건강 관리 시스템에 필수적입니다. 로봇 수술의 범위, 개복 수술에서 복강경 수술로의 전환, 복잡한 로봇 의료 절차 전문 지식을 가진 외과 의사 수요는 모두 확대됩니다.
- 임상 진단 및 체외 진단(IVD) 시장은 개별 피펫팅 작업 및 기타 유형의 수동 작업이 아닌 강화된 액체 취급 로봇 솔루션을 포함한 현재 자동화 및 로봇 공학의 진보로 이익을 얻고 있습니다. 로봇 초음파는 수술실, 원격 진료소, 우주 등 다양한 환경에서 테스트되었습니다.
- 로봇 팔은 유연성, 효율적인 공간 활용, 실험실 주변기기와의 원활한 통합을 필요로 하는 용도을 위해 실험실에서의 사용이 증가하고 있습니다. 암 프로그래밍이 쉽기 때문에 채용은 시간이 지남에 따라 증가하고 있습니다. 그 결과, 연구실의 자동화에 로봇 암이 채용되게 되어, 시장이 견인되게 됩니다.
- 실험실에서 로봇 공학의 가장 일반적인 용도는 노동 요건을 줄이고 생산성을 높이기 위한 기계 조작 및 픽앤플레이스입니다. 그러나 모듈형 기기의 진보로 소규모 실험실에서도 자동화의 장점을 누릴 수 있게 되었습니다. 다양한 공급업체의 지원으로 모든 규모의 실험실이 로봇을 통한 실험실 자동화의 많은 장점을 빠르게 실현하고 있습니다.
- 기술의 진보와 결과에 대한 요구가 증가함에 따라, 실험실은 점점 더 자동화 시스템을 활용하고 있습니다. 정확도, 데이터 관리 능력 향상, 반복 감소, 궁극적으로 인적 개입 감소로 실험실 자동화가 보다 흔해지고 처리 능력과 정확도가 높아집니다. 예를 들어, 혈액 샘플을 선별하는 로봇 암은 안전성을 확보하면서 병원의 진단센터 직원의 작업 부담을 경감합니다.
- 또한 IoT 지원 시스템은 다양한 센서에 대한 서버 제어 및 모니터링을 제공하고 추가 하드웨어 인터페이스 모듈을 처리하도록 쉽게 구성할 수 있습니다. 로봇에 설치된 센서나 디바이스에 탑재된 센서는 데이터 수집 및 클라우드 서버 및 기타 디바이스와의 통신을 지원할 수 있습니다. 또한 연구소는 IoT를 통해 정확하고 변경되지 않은 데이터를 제공하면서 높은 보안 수준에서 데이터를 유지할 수 있습니다.
북미가 가장 큰 시장 점유율을 차지
- 북미는 주요 제약회사의 존재와 창약,게놈 분야에 대한 투자의 급증으로 인-비트로 진단용 실험실 자동화 시장을 독점하고 있습니다. 한편, 미국은 신기술 개발 증가, 급속한 인구 증가, 지속적인 기술 진보로 예측 기간 동안 큰 성장률이 예상됩니다.
- 북미는 수년간 임상 연구의 선두 주자입니다. Pfizer, 노바티스, 흑소 스미스크라인, J&J, 노바티스 등이 이 지역에 본사를 둔 대형 제약 기업입니다. 게다가 이 지역에는 의약품 개발 업무 수탁 기관(CRO)이 가장 집중하고 있습니다. 중요한 CRO로는 실험실 기업의 미국 홀딩스, IQVIA, 시네오스 헬스, 팔렉셀 인터내셔널 등이 있습니다.
- 정부 자금 이용 가능, FDA 규제 엄격, 유전자 질환 및 암 스크리닝에서 분자진단의 이용이 확대되고 있으며, 이 지역의 주요 기업 대부분이 이 지역에서 활동하고 있습니다. 따라서 이 지역은 큰 시장 점유율을 차지할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 또한 수술 건수 증가와 다양한 만성 질환의 만연이 임상 진단 업계에서의 자동화 수요의 원동력이 되고 있습니다. 미국 정형외과학회(AAOS)는 2030년까지 미국에서 약 300만 건의 인공 슬관절 전치환술이 실시될 것으로 예측했습니다. 이러한 질병 및 기타 만성 질환의 진단을 위해서는 시료 채취가 필요하며, 이는 검토 중인 시장 수요를 높이고 있습니다.
- 게다가 우수한 기술에 대한 접근성 증가, 실험실 자동화에 대한 수요 증가, 미국의 유전 질환 및 암 스크리닝을 위한 분자진단의 확대는 모두 북미 시장 수요를 끌어올릴 수 있습니다. 보스턴에 본사를 둔 Laboratory-as-a-Service(LaaS)의 리더인 SmartLabs는 보스턴과 베이 지역에서 SmartLabs의 고급 인재 확보 외에도 2022년 8월에 동시에서 최초의 시설을 개설할 계획 를 발표하고 있어, 2025년의 완성시에는 동시에서 가장 저명한 생명과학 연구,생산 스페이스가 될 전망입니다.
- 또한 COVID-19의 유행에 따라 이 지역에서는 바이러스를 검출하기 위한 검사 건수가 증가했습니다. 2022년 2월 미국 정부는 COVID-19의 대유행에 의해 진단되지 않게 된 증례를 발견하기 위해 암 검진의 진찰률을 높이는 '캔서 문샷'을 시작했습니다. 정부는 조기발견,조기치료에 의해 향후 25년간암에 의한 사망자 수를 반감시키는 방침으로 이에 따라 암 In-Vitro 진단용 의약품 수요가 높아집니다.
- 헬스케어 플랜과 공급자를 위한 인공지능 및 케어 매니지먼트 솔루션의 선두 제공업체인 Diagnostic Robotics사는 오늘 StageOne 투자자가 주도하는 4,500만 달러의 시리즈 B 자금 조달 라운드의 완료를 발표했습니다. 이러한 투자는 의료 실험실에서 자동화 솔루션의 사용을 촉진합니다.
체외진단(IVD)용 실험실 자동화 산업 개요
체외진단(IVD)용 실험실 자동화 시장은 통합 시장입니다. 실험실 인프라를 구축하기 위한 진입 비용은 여전히 높기 때문에 시장을 독점하는 기업은 소수의 대기업뿐입니다. 게다가 이 시장은 이미 통합이 순환하고 있습니다. Cognex, Roche Holding AG, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Abbott Laboratories 등이 대표적인 예입니다. 이 업계에서는 혁신적인 제품 출시와 전략적 계약을 통한 시장 지배가 계속되고 있습니다.
2022년 1월, In-Vitro 진단용 의약품의 세계 리더인 후지 레비오는 널리 사용되는 INNO-LIA 점수 분석의 자동 처리를 위한 폐쇄 시스템인 RoboBlot 장비의 상업적 출시를 발표했습니다. 이 시스템은 사전 프로그래밍된 검사 프로토콜을 통해 시료의 첨가로부터 스트립 처리, 이미지 캡처, 결과 해석을 자동화하고, 필요에 따라 검사 정보 시스템(LIS)과의 통신을 자동화합니다.
2022년 2월, 개별 작업을 위한 로봇 팔의 개발로 시작된 오토마타는 처음부터 끝까지 실험실의 전체 프로세스를 자동화하기 위해 5,000만 달러를 조달했습니다. 이 라운드는 Octopus Ventures가 주도하여 Hummingbird, Latitude Ventures, ABB Technology Ventures, Isomer Capital, In-Q-Tel 등이 참가했습니다. 이 회사는 부분 자동화에서 완전 자동화로의 전환이 상당한 시간 절약과 처리량 향상으로 이어질 것이라고 생각합니다.
기타 혜택:
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트,지원
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 역학
- 시장 개요
- 업계의 매력도 - Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계의 강도
- 업계 밸류체인 분석
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 실험실 자동화 시스템의 유연성과 적응성
- IoT에 의한 랩의 디지털 전환
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 중소 실험실에 의한 도입률의 지연
- 숙련된 검사 전문가의 부족
- COVID-19의 업계에 대한 영향 평가
제5장 시장 세분화
- 장치별
- 자동 플레이트 핸들러
- 자동 리퀴드 핸들러
- 로봇 암
- 자동 보관,검색 시스템
- 분석장치
- 최종 사용자별
- 아카데믹
- 연구기관
- 기타 최종 사용자
- 지역별
- 북미
- 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 라틴아메리카
- 중동 및 아프리카
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 기업 프로파일
- Cognex Corporation
- Roche Holding AG
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- Danaher Corporation
- Agilent Technologies Inc.
- Abbott Laboratories
- PerkinElmer Inc.
- Tecan Group Ltd
- Becton, Dickinson and Company
- Siemens Healthineers AG
제7장 투자 분석
제8장 시장 기회와 앞으로의 동향
BJH 24.03.04The Lab Automation For In-Vitro Diagnostics Market size is estimated at USD 5.75 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 7.80 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 6.30% during the forecast period (2024-2029).
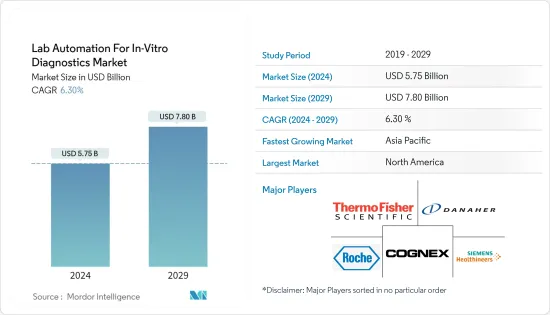
The increase in testing due to the pandemic and the development of automated in-vitro diagnostic systems for labs to provide quick, precise, and error-free diagnoses can be attributed to market growth.
Key Highlights
- Lab automation is the process of using specimen-processing equipment to conduct clinical research. This procedure is carried out in order to develop new technology in order to increase productivity and decrease time cycles. In-vitro diagnostics is used in various settings, including laboratories, clinics, educational institutions, diagnostic centers, and private homes.
- The IVD product portfolio includes devices that aid clinical chemistry and immunoassays, urinalysis, point-of-care testing, and patient self-testing devices. The market is expanding as a result of significant players introducing an increasing number of IVD (in vitro diagnostics) products.
- Lab automation is becoming more common, particularly in the development of IVD medical devices. On an unprecedented scale, technology is assisting in increasing the productivity and throughput of in vitro diagnostics. Furthermore, the IVD market is expected to benefit from cognitive machine-learning capabilities and Big Data to supplement diagnostic test information and technologies to enable seamless connectivity between multiple instrument systems. Automation solutions will be in high demand as a result of such technological advancements.
- The increase in R&D activities in the pharmaceutical industries and the increase in demand for process automation for food safety are driving the growth of lab automation for the in-vitro diagnostics market. The increased adoption of these systems as a result of workflow standardization and stringent regulatory control in the healthcare industry influences the growth of lab automation for the in-vitro diagnostics market.
- Significant investments in advanced technologies and business model transformation, driven by products and value-added services, are expected to propel the market. Furthermore, the rapid spread of existing diseases and the discovery of new diseases increase the demand for early treatment and diagnosis. This is expected to increase the rate of clinical diagnostic applications, fueling the adoption of lab automation solutions.
- Automating in-vitro diagnostic devices allows the healthcare diagnostic industry to drastically reduce potential errors, detect infection, diagnose medical conditions, prevent disease, and monitor drug therapies more accurately. For example, in pandemic outbreaks, robotics can be used to reduce infection exposure, distribute medications and food, assess vital signs, promote border control, and automate disinfection.
- Furthermore, incorporating AI and analytical tools into laboratory workflows expands the lab automation market's profitable opportunities. However, a lack of skilled laboratory professionals and the limited feasibility of technology integration in analytical labs will challenge and hinder the in-vitro diagnostics lab automation market.
- The COVID-19 pandemic's continued market impact and increased consumer demand can be attributed to molecular diagnostics. Flu and COVID-19, for example, have symptoms that are difficult to distinguish. Furthermore, with the outbreak of COVID-19, several regions have seen an increase in the number of tests performed to detect the virus, necessitating lab automation technologies.
Lab Automation For In-Vitro Diagnostics Market Trends
Adoption of Robotics Arms Aids the Market Growth
- In-vitro diagnostics (IVD) has become indispensable in the healthcare system by providing critical information to diagnose diseases and guide therapeutic decisions. The scope of robotic surgery, the transition from open to laparoscopic surgery, and the demand for surgeons with expertise in complex robotic medical procedures will all expand.
- Clinical diagnostics and in vitro diagnostic (IVD) markets benefit from current advancements in automation and robotics, such as enhanced liquid handling robot solutions rather than individual pipetting chores or other types of manual handling. Robotic ultrasound has been tested in various settings, including operating rooms, remote clinics, and space.
- Robotic arms are increasingly used in research laboratories for applications requiring flexibility, efficient space utilization, and seamless integration of lab peripherals. Adoption has grown over time due to the ease with which the arms can be programmed. As a result, the market will be driven by the increased adoption of robotic arms for lab automation.
- The most common application of robotics in laboratories is machine tending or pick and place to reduce labor requirements and increase productivity. However, thanks to advancements in modular equipment, even small laboratories can reap the benefits of automation. With the assistance of various vendors, laboratories of all sizes are quickly realizing the many advantages of robotic laboratory automation.
- Because of technological advancements and increased demand for results, laboratories are increasingly utilizing automated systems. Because of its precision, improved data management capabilities, reduced repetitiveness, and eventually less human intervention, lab automation is becoming more popular, resulting in higher throughput and accuracy. For example, a robot arm for sorting blood samples reduces hospital diagnostic center personnel's workload while ensuring safety.
- Moreover, IoT-enabled systems provide server control and monitoring of various sensors and can be easily configured to handle additional hardware interface modules. Sensors installed in robots and loaded onto devices may aid data collection and communication with cloud servers and other devices. Furthermore, laboratories can maintain data with high levels of security while providing accurate and unaltered data via IoT.
North America to Hold the Largest Market Share
- North America dominates the lab automation for the in-vitro diagnostics market due to the presence of large pharmaceutical companies and the rapid increase in investment in the drug discovery and genomics sectors. The United States, on the other hand, is expected to have a significant growth rate during the forecast period due to the increased development of novel technologies, rapid population growth, and continuous technological advancements.
- North America has been a leader in clinical research for many years. Pfizer, Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline, J&J, and Novartis are among the major pharmaceutical companies headquartered in this region. In addition, the area has the greatest concentration of contract research organizations (CROs). Some significant CROs are Laboratory Corp. of America Holdings, IQVIA, Syneos Health, and Parexel International Corp.
- Because of the availability of government funds, stringent FDA regulations, the growing use of molecular diagnostics in genetic disorders and cancer screening, and most of the major players in this region, the region is expected to account for a major market share.
- Additionally, the growing number of surgeries and the prevalence of various chronic diseases drive demand for automation in the clinical diagnostics industry. The American Orthopedic Surgeons (AAOS) predicts that approximately 3.0 million total knee arthroplasty surgeries will be performed in the United States by 2030. The diagnosis of these and other chronic conditions necessitates sample collection, which increases demand for the market under consideration.
- Moreover, increased access to superior technologies, increased demand for laboratory automation, and the expansion of molecular diagnostics for genetic disorders and cancer screening in the United States may all boost market demand in North America. SmartLabs, a Boston-based Laboratory-as-a-Service (LaaS) leader, announced plans to open its first facility in the city in August 2022, in addition to SmartLabs' advanced resourcing in Boston and the Bay Area, which is expected to become the city's most prominent life sciences research and production space upon completion in 2025.
- Furthermore, with the outbreak of COVID-19, the region saw an increase in the number of tests performed to detect the virus. In February 2022, the American government launched the Cancer Moonshot to increase cancer screening rates to find cases that had gone undiagnosed due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The government intends to cut cancer deaths by half in the next 25 years through early detection and treatment, which will increase demand for cancer IVD tests.
- Diagnostic Robotics, a leading provider of Artificial Intelligence and Care Management solutions for Healthcare plans and providers, today announced the closing of a USD 45M Series B funding round led by StageOne investors, which will help to drive vastly improved care management for members in July 2022. Such investments will encourage the use of automation solutions in medical laboratories.
Lab Automation For In-Vitro Diagnostics Industry Overview
Lab automation for the in-vitro diagnostics market is a consolidated market. The entry cost for setting up lab infrastructure remains high, and hence, only a few major players dominate the market. Moreover, this market has undergone a round of consolidation already. The major players in this market are Cognex Corporation, Roche Holding AG, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., and Abbott Laboratories. Market domination through innovative product launches and strategic agreements continues across this industry.
In January 2022, Fujirebio, a global leader in IVD testing, announced the commercial launch of the RoboBlot instrument, a closed system for the automated processing of the widely used INNO-LIA Score assays. The system's preprogrammed test protocols automate sample addition to strip processing, image capture, and result interpretation, as well as laboratory information system (LIS) communication where applicable.
In February 2022, Automata, which began by developing a robotic arm for individual tasks, raised USD 50 million to automate entire lab processes from beginning to end. Octopus Ventures led the round, which included Hummingbird, Latitude Ventures, ABB Technology Ventures, Isomer Capital, In-Q-Tel, and others. The company believes transitioning from partial to full automation will result in significant time savings and increased throughput.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.2.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.2.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.2.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.2.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.2.6 Industry Value Chain Analysis
- 4.3 Market Drivers
- 4.3.1 Flexibility and Adaptability of Lab Automation Systems
- 4.3.2 Digital Transformation for Laboratories with IoT
- 4.4 Market Restraints
- 4.4.1 Slow Adoption Rates by Small and Medium Laboratories
- 4.4.2 Lack of Skilled Laboratory Professionals
- 4.5 Assessment of COVID-19 Impact on the Industry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Equipment
- 5.1.1 Automated Plate Handler
- 5.1.2 Automated Liquid Handler
- 5.1.3 Robotic Arm
- 5.1.4 Automated Storage and Retrieval System
- 5.1.5 Analyzer
- 5.2 By End User
- 5.2.1 Academic
- 5.2.2 Laboratory
- 5.2.3 Other End Users
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 North America
- 5.3.2 Europe
- 5.3.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.4 Latin America
- 5.3.5 Middle-East and Africa
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Company Profiles
- 6.1.1 Cognex Corporation
- 6.1.2 Roche Holding AG
- 6.1.3 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- 6.1.4 Danaher Corporation
- 6.1.5 Agilent Technologies Inc.
- 6.1.6 Abbott Laboratories
- 6.1.7 PerkinElmer Inc.
- 6.1.8 Tecan Group Ltd
- 6.1.9 Becton, Dickinson and Company
- 6.1.10 Siemens Healthineers AG

















