|
시장보고서
상품코드
1441484
일본의 통신 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2024-2029년)Japan Telecom - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029) |
||||||
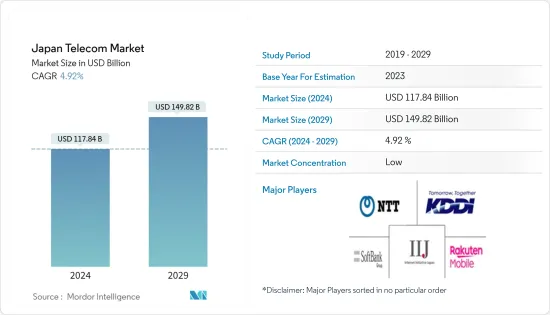
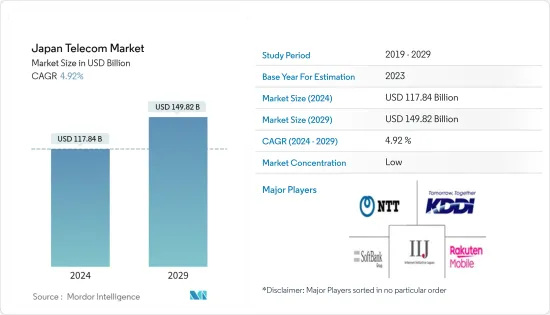
일본의 통신 시장 규모는 2024년 1,178억 4,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 추정됩니다. 2029년까지 1,498억 2,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예상되며, 예측 기간(2024-2029년) 동안 4.92%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)을 나타낼 것으로 예상됩니다.
일본은 사람들이 항상 연결될 수 있는 고도로 발달된 인프라를 갖추고 있습니다. 일본은 높은 인터넷 보급률과 더불어 스마트폰의 인기 상승을 반영하여 상당한 모바일 인터넷 사용자층을 보유하고 있습니다. 스마트폰의 보급률은 높은 편이며, 향후 몇 년동안 더 많은 사람들이 스마트폰을 사용할 것으로 예상됩니다.
주요 하이라이트
- 일본에서는 모바일 분야의 경쟁 촉진과 이용자 보호를 목적으로 2019년 10월 전기통신사업법이 개정되었습니다. 이후 이용자 부담 경감을 위해 휴대전화 요금 인하에 대한 논의가 진행되어 왔습니다. 총무성은 공정하고 경쟁력 있는 모바일 시장 형성을 통한 휴대폰 요금 인하를 위한 행동계획을 발표했습니다. 2021년 3월까지 모든 이동통신사가 새로운 저가 브랜드와 요금제를 도입하고, 그 중 일부는 20GB의 데이터를 제공하는 요금제를 도입하기로 했습니다.
- 6G 통신이 그 잠재력을 최대한 발휘하려면 10년이 걸릴 수 있지만, 일본은 이미 독자적인 국내 네트워크와 기술 기반을 구축하고 있습니다. 일본 정부는 초고속 통신 개발 촉진에 수십억 달러를 투자할 계획입니다. 일본 장비 제조업체인 NEC와 후지쯔, 핀란드 장비 제조업체인 노키아는 2030년까지 6G 서비스 상용화를 목표로 새로운 이동통신 기술 실험을 실시할 계획을 발표했습니다.
- 인터넷 덕분에 시스템과 프로토콜이 계속 진화했지만, 모바일 네트워크의 발전은 오랫동안 폐쇄적인 문화와 독점적인 기술로 인해 제약을 받아왔습니다. 모바일 네트워크가 다양한 분야에 필수적인 인프라가 되려면, 모바일 네트워크는 즉석에서 변경 및 동적 설정을 제공할 수 있어야 합니다. RESTful(Representational State Transfer) 용도 프로그래밍 인터페이스(API)를 통합함으로써 소프트뱅크는 소비자의 요구를 충족하고 보다 편리한 서비스를 제공하기 위해 네트워크를 조정하고 변경할 수 있습니다.
- 코로나19의 확산은 일본 경제에 큰 영향을 미쳤습니다. 팬데믹 기간과 팬데믹 이후 국가의 회복력을 강화하기 위해서는 디지털 기술의 도입이 필수적이었습니다. 기술 용도는 고객과의 연락, 디지털 비즈니스 운영, 비즈니스 운영 재개, 물류 병목 현상을 완화하는 기술 도입을 지원함으로써 기업과 직원들이 코로나19의 경제적 영향을 관리할 수 있도록 돕고 있습니다. 46조 8,000억 엔(미화 4,340억 달러)에 달하는 일본의 디지털 기회의 69%는 기업과 직원들이 전염병이 경제에 미치는 영향을 관리할 수 있도록 지원하는 기술에서 창출될 수 있는 것으로 추정되고 있습니다.
일본의 통신시장 동향
5G의 전개
- GSMA의 보고서에 따르면 일본은 통신 사업자가 신호등 위에 5G 기지국을 설치할 수 있도록 허용하여 전국적인 5G 배포가 가속화되고 있습니다. 작은 셀이 배치되고 네트워크 밀도가 증가함에 따라 21 개의 더 큰 용량의 이용 사례가 번창 할 수 있습니다. 일본의 연결 보급률은 2021년 153%에서 2022년 154%로 증가할 것으로 예상됩니다. 스마트폰 보급률은 2021년 71%에서 2025년 81%로 증가할 것으로 예상됩니다. 또한 일본의 가입자 보급률도 87에서 87로 상승할 것으로 예상됩니다. 2021 년%에서 2025년88%까지.
- 아이폰 12와 13의 가격 인하와 매장에서의 가용성을 고려하면 일본 내 5G 도입 전망은 더욱 유망해 보입니다. 최근 일본 정부는 NTT 도코모, KDDI au, 소프트뱅크, 그리고 최근 진출한 라쿠텐 모바일 등 일본 3대 이동통신 사업자에게 5G 주파수 대역을 허가했습니다. 향후 몇 년동안 이들 일본의 통신사 4곳은 기지국, 서버, 광섬유 등 자본 프로젝트에 140억 달러 이상을 투자할 것으로 예상됩니다. 피치(Fitch) 조사에 따르면, 2026년까지 5G가 4G를 제치고 일본의 주요 휴대폰 기술로 자리 잡을 것이며, 2029년까지 4G 가입자는 약 4,500만 명, 5G 가입자는 1억 5,100만 명 이상이 될 것으로 예상했습니다.
- 현지 보도에 따르면 일본의 통신사 NTT 도코모는 경쟁사들도 마찬가지로 5G의 전국적인 보급 속도를 높일 계획이라고 합니다. 이 기사는 NTT 도코모가 2024년3 월까지 일본 인구의 80%보다 더 많은 90%에게 서비스를 제공 할 계획이며, 2022년 9월NTT 도코모는 세계 최초의 상용 5G 독립형(SA) 네트워크를 보유하고 있다고 주장했습니다. 이를 통해 스마트폰은 5G NR 듀얼 커넥션으로 알려진 미드밴드(6GHz 이하) 주파수와 밀리미터파 주파수를 동시에 사용할 수 있게 됩니다. 이번 발표는 무선 기술 회사인 퀄컴과 함께 진행되었으며, 퀄컴은 자사의 Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 플랫폼이 탑재된 스마트폰이 새로운 네트워크의 최대 속도를 활용할 수 있다는 점을 강조하고자 했습니다.
- 일본 고객은 삼성, 소니, 샤프, 후지쯔, 구글의 하이엔드 스마트폰을 포함한 다양한 밀리미터파 기기와 이 기술에 대한 통신사의 큰 모멘텀을 이용할 수 있습니다. 하위 계층을 포함한 다른 OEM 업체들도 향후 몇 달 내에 일본에 밀리미터파 스마트폰을 출시할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 소프트뱅크는 2022년 5월, 일본 전국에 MEC 서버를 구축하기 시작했으며, 관동 지역에 5G MEC(멀티 액세스 엣지 컴퓨팅) 사이트를 구축할 것을 선언했습니다. 'SoftBank 5G MEC'는 5G SA(5G Stand Alone) 상용 서비스를 이용하여 저지연, 고품질(저지터), 안전한 서비스 경험을 제공합니다. 소프트뱅크는 다양한 비즈니스의 디지털 전환(Digital Transformation, DX)을 추진하고 디지털 트윈(Digital Twin)*2을 실현함으로써, Beyond 5G의 미래 디지털 플랫폼 제공업체로서 사회적 과제에 대응하고 산업 발전을 도모할 것으로 기대됩니다.
디지털 전환을 위한 노력
- 디지털 전환은 코로나19 위기로 인해 가장 눈에 띄게 가속화된 트렌드(DX) 중 하나입니다. 이 갑작스러운 변화는 비즈니스와 조직의 운영을 개선하고 사람들의 삶에 광범위한 긍정적인 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다. 국제전기통신연합(ITU)의 조사에 따르면 2020년 전 세계 대도시 지역에서 인터넷에 접속할 수 있는 인구는 76%인 반면, 지방에서는 39%에 불과했습니다. 일본은 인간과 지속가능성을 중시하는 '새로운 자본주의 형태'를 만들겠다는 높은 목표를 세우고, DX를 성장과 분배의 선순환을 위한 노력의 중요한 요소로 삼고 있습니다.
- 지방의 민간기업은 당장 수익성을 달성하기 어려울 수 있지만, 지방 정부나 부처와 협력하면 참신한 아이디어를 실현할 수 있습니다. 또한, 디지털화는 일본에서는 물론 지방에서도 새로운 것이 아닙니다. 총무성의 지역 IoT 추진 연구소 프로젝트는 2016년에 시작된 이래로 일본 전국 105개 지역의 연구소를 선정하여 가장 우수한 새로운 IoT 솔루션과 기업을 시상하고, 지역 프로젝트와 벤처의 번영과 이륙을 지원하기 위해 멘토를 파견하고 있습니다.
- 일본의 대기업들은 다른 조직의 기술, 개념, 자산 및 자원을 활용하여 혁신을 촉진하기 위해 오픈 이노베이션 컨퍼런스와 비즈니스 콘테스트를 개최하고 있습니다. 일본에서는 오픈 이노베이션이 아직 기타 국가에 비해 덜 보급되어 있지만, 일본 대기업에서는 오픈 이노베이션이 보편화되어 성장하고 있습니다. 최근 몇 년동안 다양한 분야에서 오픈 이노베이션의 노력과 비즈니스 콘테스트가 많이 개최되고 있습니다. 예를 들어, 통신 분야의 NTT데이터 오픈 이노베이션을 들 수 있습니다.
- 이나시는 2020년 8월,월이용료를 지불하는 주민을 대상으로 전국 최초로 드론을 이용한 쇼핑 서비스인 '서로 응원하는 쇼핑 서비스'를 도입했습니다. 이 서비스는 케이블TV를 통해 제공되며 통신사 KDDI 주식회사와 협력하여 개발되었습니다. 고객은 TV 리모컨을 이용해 주문하고 케이블 요금을 지불할 수 있습니다. 이 지역은 산간지역이라 일반 TV 방송의 전파가 잘 닿지 않아 시에서 각 가정에 케이블TV를 제공한 결과, 케이블TV 보급률이 거의 100%에 육박하고 있습니다.
- 지방의 민간 기업은 당장 수익성을 달성하기 어려울 수 있지만, 지방 정부나 부처와 협력하면 참신한 아이디어가 실현될 수 있습니다. 또한, 디지털화는 일본에서는 비록 지방이라 할지라도 새로운 것이 아닙니다. 일본 경제산업성(METI)의 보고서에 따르면, 총무성의 지역 IoT 추진 연구소 프로젝트는 2016년에 시작된 이래로 일본 전국 105개 지역 연구소를 선정하여 가장 우수한 새로운 IoT 솔루션과 우수한 솔루션을 시상해 왔습니다고 합니다. 기업에 지도자를 파견하여 지역 프로젝트와 벤처의 번영과 발전을 지원합니다.
일본의 통신산업 개요
일본의 통신 시장은 본질적으로 매우 세분화되어 있습니다. 주요 기업으로는 일본전신전화 주식회사, KDDI 주식회사, 소프트뱅크 그룹 주식회사, 라쿠텐 모바일 주식회사, 인터넷 이니셔티브 주식회사 등을 들 수 있습니다. 이 시장에는 다른 인터넷 서비스 제공업체(ISP), MVNO, 유선 전화 회사도 있습니다. 일부 일본의 통신사들은 국제적으로 매우 경쟁력이 있으며, 세계 통신 분야에서 강력한 입지를 구축하고 있습니다.
- 2022년 1월, NTT 커뮤니케이션즈(NTT Com)는 스마트 데이터 플랫폼에서 통합 운영(SDPF)을 갖춘 에지 컴퓨팅 솔루션인 'SDPF Edge'를 즉시 출시한다고 발표했습니다. 주로 제조 부문에 서비스를 제공하는 새로운 SDPF Edge 서비스의 도움으로 기업은 대량의 생산 데이터를 처리하고 품질 관리를 유지하며 더 빠르고 저렴하게 선택할 수 있습니다.
- KDDI는 2022년 2월, 삼성 및 후지쯔와 함께 가상화 무선 액세스 네트워크(vRAN)를 활용한 세계 최초의 5G 독립형 오픈 RAN 사이트가 가나가와현 가와사키시에서 온라인에 접속한다고 발표했습니다. Open RAN과 vRAN을 통해 5G SA를 상용화한 최초의 사례입니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장의 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 인사이트
- 시장 개요
- 업계 생태계 분석
- 업계의 매력 - Porter의 Five Forces 분석
- 공급 기업의 교섭력
- 소비자의 교섭력
- 신규 진출업체의 위협
- 대체 제품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁도
- 신형 코로나바이러스(COVID-19)가 업계 에코시스템에 미치는 영향
- 국내 규제 상황
제5장 시장 역학
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 접속성에 근거한 시장 분석(상세한 동향 분석을 포함한 커버리지)
- 고정 네트워크
- 브로드밴드(케이블 모뎀, 유선 섬유, 유선 DSL, 고정 Wi-Fi), ADSL/VDSL, FTTP/B, 케이블 모뎀, FWA, 5G FWA 동향
- 협대역
- 모바일 네트워크
- 스마트폰 및 모바일 보급
- 모바일 브로드밴드
- 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G 접속
- 스마트홈, IoT, M2M 접속
- 고정 네트워크
- 통신탑 분석(격자탑, 지선탑, 모노폴탑, 스텔스탑 등, 다양한 유형 탑 상세한 동향 분석 포함)
제6장 시장 세분화
- 서비스별 세분화(서비스 부문 전체 사용자당 평균수익, 2020년-2027년 기간 각 부문 시장 규모라고 추정 및 상세한 동향 분석을 포함한 범위)
- 음성 서비스
- 유선
- 무선
- 데이터 및 메시징 서비스(인터넷 및 휴대폰 데이터 패키지, 패키지 할인을 포함한 범위)
- OTT 및 유료 TV 서비스
- 음성 서비스
제7장 경쟁 구도
- 기업 개요
- Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation
- KDDI Corporation
- SoftBank Group Corp.
- Rakuten Mobile, Inc.
- Internet Initiative Japan, Inc.
- JSAT Corporation
- TOKAI Communications Corporation
- Wowow Inc.
- Internet Initiative Japan, Inc.
- Z Holdings Corporation
제8장 투자 분석
제9장 시장 기회와 향후 동향
LSH 24.03.14The Japan Telecom Market size is estimated at USD 117.84 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 149.82 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 4.92% during the forecast period (2024-2029).
Japan has a highly developed infrastructure that allows its people to be constantly connected. Along with having a high internet penetration rate, Japan has a sizable mobile internet user base, which reflects the rising popularity of smartphones. Though the smartphone adoption rate is strong, more individuals are anticipated to utilize smartphones in the years to come.
Key Highlights
- In Japan, the Telecommunications Business Law was changed in October 2019 to encourage competition in the mobile sector and safeguard users. Since then, there have been conversations about reducing mobile phone fees to lessen the load on users. The Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications unveiled an action plan to lower mobile phone costs by creating a fair and competitive mobile market. By March 2021, all MNO companies introduced new, less-priced brands and pricing schemes, some of which included 20 GB of data.
- It might take a decade for 6G telecommunications to reach its full potential, but Japan is already establishing its own domestic network and technology foundation. The Japanese government plans to invest billions of dollars in promoting the development of ultra-high-speed communication. Japanese equipment manufacturers NEC and Fujitsu, as well as Finnish equipment manufacturer Nokia, announced plans to conduct experimental trials of new mobile communications technologies for the targeted commercial launch of 6G services by 2030.
- Though system and protocol evolution continued due to the Internet, the development of mobile networks was constrained by closed cultures and proprietary technologies for a very long time. Mobile networks must be able to offer modification and dynamic set up on the spot to be essential infrastructure for many different sectors. By integrating RESTful (Representational State Transfer) application programming interfaces (APIs), SoftBank tailors and modifies its network to meet the needs of consumers and offer more convenient services.
- The COVID-19 outbreak significantly impacted the Japanese economy. The adoption of digital technology was essential for the nation to become more resilient during and after the pandemic. Technology applications can help businesses and their employees manage the financial effects of COVID-19 by assisting them in contacting clients and conducting business digitally, restarting business operations, and implementing technologies that reduce logistical bottlenecks. A sizable 69% of Japan's digital opportunity, valued at JPY 46.8 trillion (USD 434 billion), was thought to be sourced from technology that assists companies and employees in managing the effects of the pandemic on the economy.
Japan Telecom Market Trends
5G Rollouts
- According to a GSMA report, Japan allows operators to mount 5G base stations atop traffic signals, accelerating 5G deployments nationwide. 21 higher-capacity use cases can flourish when tiny cells are put into place, and network density is raised. The connection penetration in Japan is expected to rise from 153% in 2021 to 154% in 2022. The projected increase in smartphone adoption rate is from 71% in 2021 to 81% in 2025. Subscriber penetration in Japan is also expected to rise from 87% in 2021 to 88% in 2025.
- Given the price reductions and the availability of the iPhone 12 and 13 in stores, the prospects for 5G adoption in the nation seem more promising. Recently, the Japanese government granted the 5G spectrum to the country's top three mobile providers, NTT Docomo, KDDI au, Softbank, and a recent entrant, Rakuten Mobile. Over the following years, these four Japanese carriers are anticipated to invest more than USD 14 billion in capital projects, including base stations, servers, and fiber optics. According to Fitch Research, by 2026, 5G will overtake 4G as the primary cellular technology in Japan, and by 2029 there will be around 45 million 4G subscribers and more than 151 million 5G subscribers.
- According to the local press, Japanese carrier, NTT Docomo, plans to quicken the speed of its 5G rollout nationwide while competitors do the same. The same article claims that NTT Docomo plans to provide coverage to 90% of the Japanese population, up from its earlier target of 80%, by March 2024. In September 2022 NTT Docomo claimed to have the world's first commercial 5G Standalone (SA) network that enables smartphones to simultaneously use mid-band (sub-6 GHz) and mmWave frequencies, known as 5G NR Dual Connectivity. The announcement was made with wireless technology company Qualcomm, which was keen to showcase that smartphones powered by its Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 platform can exploit the full speed of the new network.
- Japanese customers have access to a wide range of mmWave devices, including high-end smartphones from Samsung, Sony, Sharp, Fujitsu, and Google, and significant carrier momentum for the technology. Other OEMs, including those from lower tiers, are expected to introduce mmWave smartphones in Japan in the coming months.
- In May 2022, SoftBank Corp. declared beginning the statewide deployment of MEC servers in Japan and launching a 5G MEC (Multi-access Edge Computing) site in the Kanto area. Using 5G SA (5G Stand Alone) commercial services, SoftBank 5G MEC offers low-latency, high-quality (low-jitter), and highly secure service experience. By encouraging the digital transformation (DX) of various businesses and achieving Digital Twin*2, SoftBank is expected to address societal concerns and advance the industry as a digital platform provider in the Beyond 5G future.
Digital Transformation Initiatives
- Digital transformation is one of the trends that the COVID-19 crisis has most visibly hastened (DX). This abrupt change can improve business and organization operations and have a wide range of positive effects on people's lives. In metropolitan regions throughout the world, 76% of people had internet access in 2020, compared to 39% in rural areas, according to research by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). With the lofty objective of creating a "New Form of Capitalism" that would be both people- and sustainability-focused, Japan has positioned DX as a key component of its initiatives for a virtuous cycle of growth and distribution.
- Private businesses in rural locations may find it difficult to reach profitability quickly, but collaboration with regional authorities and ministries may be able to make novel ideas workable. Additionally, digitalization is nothing new in Japan, not even in rural regions. Since its inception in 2016, the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communication's Local IoT Acceleration Laboratories project has recognized labs in 105 areas around Japan, awarded the finest new IoT solutions and enterprises, and sent mentors to help regional projects and ventures flourish and take off.
- Large Japanese firms host Open Innovation conferences and business competitions to foster innovation by employing other organizations' technology, concepts, assets, and resources. Open innovation is still not as prevalent in Japan as it is in other countries, but it is becoming more common among major Japanese corporations, and it is growing. Over the past several years, numerous open innovation initiatives and business competitions have been held in various sectors. For example, NTTData Open Innovation for the telecom sector.
- Ina City introduced a "Mutual Support Shopping Service" in August 2020, which is Japan's first drone-delivered shopping service for residents who pay a monthly subscription fee. The service is delivered via cable TV and was developed in collaboration with the telecom company KDDI Corp. Customers can use the TV remote control to place orders and pay their cable bill. As a result of the city providing cable TV to households due to poor signal reception for standard television broadcasts due to the area's mountainous terrain, cable TV has almost 100% penetration.
- Private businesses in rural locations may find it difficult to reach profitability quickly, but collaboration with regional authorities and ministries may make novel ideas workable. Additionally, digitalization is nothing new in Japan, not even in rural areas. As per the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI) report, since its inception in 2016, the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communication's Local IoT Acceleration Laboratories project has recognized labs in 105 regions around Japan, awarded the finest new IoT solutions and enterprises, and sent mentors to help regional projects and ventures flourish and take off.
Japan Telecom Industry Overview
The Japanese telecom market is highly fragmented in nature. Some major players in the market include Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation, KDDI Corporation., SoftBank Group Corp., Rakuten Mobile, Inc, and Internet Initiative Japan, Inc. The market also hosts other Internet service providers (ISPs), MVNOs, and fixed-line service providers. Some Japanese telecommunication companies are very competitive internationally and hold strong ground in the global telecom space.
- In January 2022, on its Smart Data Platform, NTT Communications Corporation (NTT Com) announced the immediate launch of "SDPF Edge," an edge-computing solution with integrated operations (SDPF). With the help of the new SDPF Edge service, which primarily serves the manufacturing sector, companies may process massive volumes of production data to maintain quality control and make choices more quickly and inexpensively.
- In February 2022, KDDI, along with Samsung and Fujitsu, announced the world's first 5G Standalone Open RAN site, powered by a virtualized Radio Access Network (vRAN), will go online in Kawasaki, Kanagawa. With Open RAN and vRAN, this happened to be the first commercial deployment of 5G SA.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Industry Ecosystem Analysis
- 4.3 Industry Attractiveness-Porter's Five Force Analysis
- 4.3.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.3.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.3.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.3.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.3.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.4 Impact of COVID-19 on the Industry Ecosystem
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape in the Country
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 5G Device Penetration and Accelerated Expansion of Market
- 5.1.2 Continuation of Remote Work
- 5.2 Market Restrains
- 5.2.1 Concerns on Competition
- 5.3 Analysis of the Market based on Connectivity (Coverage to include In-depth Trend Analysis)
- 5.3.1 Fixed Network
- 5.3.1.1 Broadband (Cable modem, wireline-fiber, wireline DSL, fixed Wi-Fi ), Trends regarding ADSL/VDSL, FTTP/B, cable modem, FWA, and 5G FWA )
- 5.3.1.2 Narrowband
- 5.3.2 Mobile Network
- 5.3.2.1 Smartphone and Mobile Penetration
- 5.3.2.2 Mobile Broadband
- 5.3.2.3 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G connections
- 5.3.2.4 Smart Home, IoT, and M2M connections
- 5.3.1 Fixed Network
- 5.4 Analysis of Telecom Towers (Coverage to include in-depth trend analysis of various types of towers, like, lattice, guyed, monopole, and stealth towers)
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 Segmentation by Services (Coverage to include Average Revenue Per User for the overall Services segment, Market size and Estimates for each segment for the period of 2020-2027 and in-depth Trend Analysis)
- 6.1.1 Voice Services
- 6.1.1.1 Wired
- 6.1.1.2 Wireless
- 6.1.2 Data and Messaging Services (Coverage to include Internet & Handset Data packages, Package Discounts)
- 6.1.3 OTT and Pay-tv Services
- 6.1.1 Voice Services
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Company Profiles
- 7.1.1 Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation
- 7.1.2 KDDI Corporation
- 7.1.3 SoftBank Group Corp.
- 7.1.4 Rakuten Mobile, Inc.
- 7.1.5 Internet Initiative Japan, Inc.
- 7.1.6 JSAT Corporation
- 7.1.7 TOKAI Communications Corporation
- 7.1.8 Wowow Inc.
- 7.1.9 Internet Initiative Japan, Inc.
- 7.1.10 Z Holdings Corporation