
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1444104
고분자 전해질 연료전지(PEMFC) : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2024-2029년)Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029) |
||||||
PEMFC(고분자 전해질 연료전지) 시장 규모는 2024년 35억 8,000만 달러로 추정되며, 2029년까지 83억 4,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예상되며, 예측 기간(2024-2029년) 동안 18.43%의 CAGR로 성장할 것으로 예상됩니다.
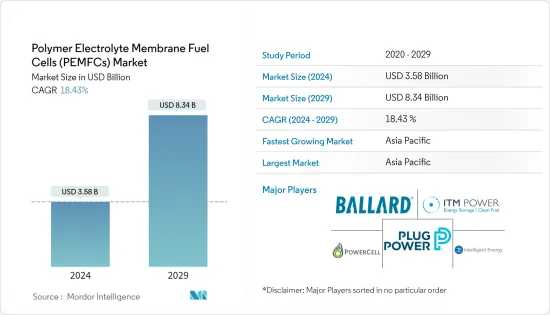
2020년 COVID-19가 시장에 부정적인 영향을 미쳤지만, COVID-19가 유행하기 전의 수준에 도달했습니다.
주요 하이라이트
- 시장을 이끄는 주요 요인은 연료전지 분야의 연구 개발(R&D) 활동이 증가함에 따라 높은 출력 밀도, 연료 보급 시간 단축, 저장 내구성 연장, 수명 연장 등 여러 가지 기술적 이점을 제공하는 PEMFC의 사이클이 리튬이온 배터리와 같은 대체 연료전지보다 우수합니다. 대체 연료전지보다 우수합니다. 이는 PEMFC 탑재 차량의 채택을 촉진하고 있으며, 예측 기간 동안 시장을 주도할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 그러나 현재 PEMFC 기술의 높은 비용과 시장에서 다른 실행 가능한 에너지 시스템의 가용성은 예측 기간 동안 시장 성장을 저해할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 연료전지 내 백금의 비율을 줄이고 최종 비용을 절감하는 등 PEMFC의 기술 발전은 예측 기간 동안 시장에 몇 가지 기회를 창출할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 2022년 세계 PEMFC 시장은 아시아태평양이 독점하고 있으며, 중국이 큰 점유율을 차지하고 있습니다. 이러한 성장의 주요 요인은 중국, 일본 등 각국 정부가 청정 에너지 사용을 촉진하기 위해 시작한 정책입니다.
PEMFC 시장 동향
정부의 노력과 민간 투자 증가가 시장을 견인할 것으로 예상
- PEMFC 시장은 지난 2년 동안 주요 시장에서의 정부 이니셔티브 도입과 민간 부문의 투자 지원 증가로 인해 크게 성장했습니다.
- 2013년 정부 이니셔티브인 캘리포니아 주 에너지 위원회의 대체 및 재생 가능 연료 및 차량 기술 프로그램은 최초의 100개 소매 수소 스테이션에 공동 자금을 지원할 수 있는 장기적인 권한을 부여했습니다. 이는 민간 부문의 연료전지 시장에 대한 투자를 촉진했습니다.
- 캘리포니아 연료전지 파트너십은 2030년까지 1,000개의 수소충전소 네트워크와 최대 100만 대의 연료전지 자동차를 보유하는 것을 목표로 하고 있습니다.
- 2022년 2월 프로젝트에서 고온 PEMFC(HT-PEMFC)가 효과적인 열 차단을 통해 대형 차량 및 기타 대규모 모빌리티 애플리케이션의 전기화를 위한 매력적인 솔루션을 제공한다는 것을 보여주었습니다.
- 연료전지 중 가장 널리 보급된 연료전지는 PEM형입니다. 유럽의 연료전지 도입 목표에 중요한 역할을 하며 PEMFC 시장을 주도할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 2022년 2월, 로스알라모스 국립연구소의 과학자들은 더 높은 온도에서 작동하는 새로운 고분자 연료전지를 개발했습니다.
- 또한, 연료전지 기반 차량에 대한 수요가 전 세계적으로 증가하고 있습니다. 북한과 미국은 연료전지 기반 자동차 재고에서 세계를 선도하는 국가입니다. 2021년 북한과 미국은 전 세계 연료전지 자동차 재고의 38%와 24%를 각각 차지했습니다.
- 따라서 이러한 정부의 노력과 투자는 예측 기간 동안 시장을 주도할 수 있습니다. 따라서 위의 요인으로 인해 정부의 노력과 PEMFC 기술에 대한 민간 투자 증가는 예측 기간 동안 시장을 주도할 것으로 예상됩니다.
아시아태평양이 시장을 독점할 것으로 예상
- 아시아태평양은 중국, 일본, 한국 등 각국 정부의 청정에너지 이용에 유리한 정책으로 인해 PEMFC의 유망한 지역 시장 중 하나입니다.
- 중국은 국가 및 지방 정부의 유리한 보조금과 지방 정부의 장려 프로그램, 주로 수소차 보급을 촉진하기 위한 국가 및 지방 정부의 장려 프로그램을 배경으로 중국의 수소 연료전지 산업이 탄력을 받고 있으며, PEMFC의 잠재력이 가장 높은 것으로 여겨집니다.
- 중국에는 잠재적으로 큰 시장이있을뿐만 아니라 PEMFC를 제조하는 많은 국내 기업이 있습니다. 따라서 국가 수요와 국내 공급이 존재하여 시장 성장을 더욱 촉진합니다. 또한 중국 기업들은 국내외 시장에 공급하기 위해 2022년까지 전해조 생산 능력을 1.5-2.5기가와트까지 늘리려고 합니다.
- 한편, 중국은 연간 10만-20만 톤의 재생가능 수소를 생산하고 2025년까지 5만 대의 수소연료 자동차를 보유할 계획을 세우고 있습니다. 중국은 현재 세계 최대의 연료전지 트럭 및 버스 시장이며, 세계 3위의 연료전지 시장입니다.
- 최근 인도 과학자들은 효율적인 절차를 통해 연료전지용 백금 기반 전극 촉매를 독자적으로 개발했습니다. 이 전극 촉매는 상용 전극 촉매와 동등한 특성을 보여 연료전지 스택 성능의 수명을 연장할 수 있었습니다.
- 따라서 위의 요인으로 인해 아시아태평양이 예측 기간 동안 시장을 장악할 것으로 예상됩니다.
PEMFC 산업 개요
세계 PEMFC 시장의 주요 기업들이 통합되었습니다. 주요 기업으로는 Ballard Power Systems, Plug Power Inc., ITM Power PLC, PowerCell Wednesday AB, Intelligent Energy Limited 등이 있습니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식의 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사 범위
- 시장 정의
- 조사 가정
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 개요
- 서론
- 2027년까지 시장 규모와 수요 예측(10억 달러)
- 최근의 동향과 발전
- 연구개발 상황
- 정부 정책과 규제
- 시장 역학
- 성장 촉진요인
- 성장 억제요인
- 공급망 분석
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 공급 기업의 교섭력
- 소비자의 협상력
- 신규 참여업체의 위협
- 대체 제품과 서비스의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 강도
제5장 시장 세분화
- 지역별
- 북미
- 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 세계 기타 지역
제6장 경쟁 상황
- 인수합병, 합작투자, 협업 및 계약
- 유력 기업이 채용한 전략
- 기업 개요
- Cummins Inc.
- Bramble Energy
- Toshiba Corporation
- Ballard Power Systems
- Plug Power Inc.
- ITM Power PLC
- Powercell Sweden AB
- Intelligent Energy Limited
제7장 시장 기회와 향후 동향
ksm 24.03.14The Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells Market size is estimated at USD 3.58 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 8.34 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 18.43% during the forecast period (2024-2029).
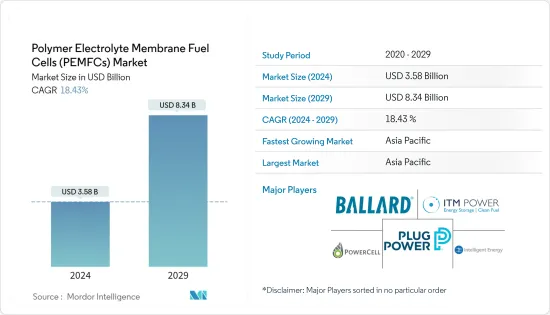
Though COVID-19 negatively impacted the market in 2020, it has reached pre-pandemic levels.
Key Highlights
- Major factors driving the market are increasing research & development (R&D) activities in the field of fuel cells, which has led to several technological advantages, such as high power density, less time to refuel, more extended storage durability, and more number of life-cycles of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells over its alternatives, such as Li-ion battery. This has been driving the adoption of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell-powered vehicles and is thus expected to drive the market during the forecast period.
- However, the current high cost of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell technology and the availability of other viable energy systems in the market is expected to hinder the market growth during the forecast period.
- The technological advancements in PEMFCs, such as reducing the share of platinum in the fuel cell, which in turn decreases its final cost, are expected to create several opportunities in the market during the forecast period.
- The Asia-Pacific dominated the global polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells market in 2022, with China holding a significant share. The major factors attributing to the growth are the policies initiated by various governments in countries such as China and Japan to drive the use of clean energy.
PEM Fuel Cells Market Trends
Government Initiatives and Growing Private Investments are Expected to Drive the Market
- The PEM fuel cell market witnessed significant growth in the last two years, mainly due to the introduction of government initiatives in key markets and increasing investment support from the private sector.
- The Californian Energy Commission's Alternative and Renewable Fuel and Vehicle Technology Program, a government initiative in 2013, established long-term authority to co-fund the first 100 retail hydrogen stations. This encouraged the private sector to invest in the fuel cell market.
- The Californian Fuel Cell Partnership aims for a network of 1,000 hydrogen stations and a fuel cell vehicle population of up to 1,000,000 vehicles by 2030. The target reflects the input and consensus of more than 40 partners, including fuel cell technology companies, automakers, energy companies, government agencies and non-governmental organizations, and universities.
- In February 2022, a project showed that high-temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells (HT-PEMFCs) offer an attractive solution to electrify heavy-duty vehicles and other large-scale mobility applications due to effective heat rejection.
- Moreover, multiple institutions, including LANL (Katie Lim), Sandia National Labs (Cy Fujimoto), Korea Institute of Science and Technology (Jiyoon Jung), University of New Mexico (Ivana Gonzales), University of Connecticut (Jasna Jankovic), and Toyota Research Institute of North America (Zhendong Hu and Hongfei Jia) were involved in this project.
- Among fuel cells, the PEM type is the most popular one. It is expected to play a crucial role in Europe's target for fuel cell deployment and drive the PEM fuel cells market.
- In February 2022, scientists of the Los Alamos National Laboratory developed a new polymer fuel cell that operates at higher temperatures. The long-standing issue of overheating, one of the biggest technical obstacles to using medium- and heavy-duty fuel cells in vehicles, such as trucks and buses, was resolved by a new high-temperature polymer fuel cell that operates at 80-160 degrees Celsius and has a higher rated power density than cutting-edge fuel cells.
- Furthermore, there is a rise in fuel cell-based vehicle demand worldwide. North Korea and the United States are the leading countries in the world in terms of stock of fuel cell-based vehicles. In 2021, North Korea and the United States had 38% and 24% of world fuel cell-based vehicle stock, respectively.
- Hence, such government initiatives and investments are likely to propel the market during the forecast period. Therefore, owing to the abovementioned factors, government initiatives and growing private investments in PEMFC technology are expected to drive the market during the forecast period.
The Asia-Pacific is Expected to Dominate the Market
- The Asia-Pacific is one of the promising regional markets for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells due to favorable government policies for clean energy usage in countries such as China, Japan, and South Korea.
- China is considered to have the highest potential for PEMFC as the hydrogen fuel cell industry in the country has been gaining traction on the back of favorable national and provincial government subsidies and incentive programs from local authorities, mainly to encourage the uptake of hydrogen vehicles to cut pollution.
- Along with the potentially large market, China has numerous domestic enterprises that manufacture PEMFC. Hence, the country's demand and domestic supply are present, further bolstering the growth of the market. Moreover, Chinese companies seek to build their electrolyzer manufacturing capacity to 1.5-2.5 GW in 2022 to supply domestic and overseas markets.
- Meanwhile, China has plans to manufacture 100,000 to 200,000 tonnes of renewable hydrogen annually and have a fleet of 50,000 hydrogen-fueled vehicles by 2025. China is currently the world's largest market for fuel-cell trucks and buses and the third-largest for fuel-cell electric vehicles (FCEVs).
- Recently, Indian Scientists have indigenously developed platinum-based electrocatalysts for fuel cells through an efficient procedure. This electrocatalyst showed comparable properties to the commercially available electrocatalyst and could enhance the lifetime of the fuel cell stack performance.
- Therefore, owing to the abovementioned factors, the Asia-Pacific is expected to dominate the market during the forecast period.
PEM Fuel Cells Industry Overview
The key players in the global polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells market are consolidated. Some of the major players in the market (in no particular order) are Ballard Power Systems, Plug Power Inc., ITM Power PLC, PowerCell Sweden AB, and Intelligent Energy Limited, among others.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Scope of the Study
- 1.2 Market Definition
- 1.3 Study Assumptions
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Market Size and Demand Forecast in USD billion, until 2027
- 4.3 Recent Trends and Developments
- 4.4 Research and Development Status
- 4.5 Government Policies and Regulations
- 4.6 Market Dynamics
- 4.6.1 Drivers
- 4.6.2 Restraints
- 4.7 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.8 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.8.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.8.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.8.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.8.4 Threat of Substitute Products and Services
- 4.8.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Geography
- 5.1.1 North America
- 5.1.2 Europe
- 5.1.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.1.4 Rest of the World
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Mergers and Acquisitions, Joint Ventures, Collaborations, and Agreements
- 6.2 Strategies Adopted by Leading Players
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 Cummins Inc.
- 6.3.2 Bramble Energy
- 6.3.3 Toshiba Corporation
- 6.3.4 Ballard Power Systems
- 6.3.5 Plug Power Inc.
- 6.3.6 ITM Power PLC
- 6.3.7 Powercell Sweden AB
- 6.3.8 Intelligent Energy Limited



















