
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1521589
그린 빌딩 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2024-2029년)Green Buildings - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029) |
||||||
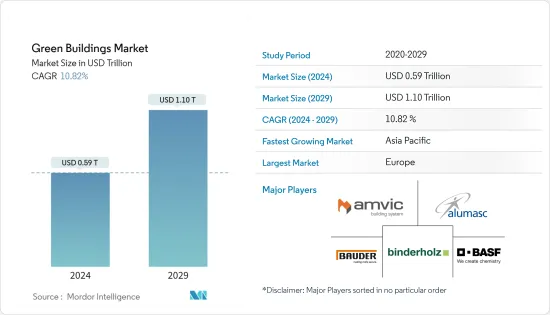
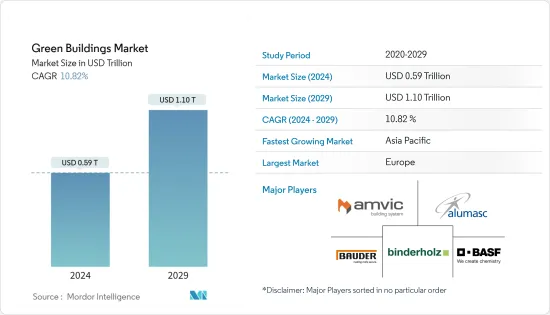
그린 빌딩 시장 규모는 2024년 5,900억 달러로 추정되며, 2029년에는 1조 1,000억 달러에 달할 것으로 예상되며, 예측 기간(2024-2029년) 동안 10.82%의 CAGR을 기록할 것으로 예상됩니다.
주요 하이라이트
- 그린 빌딩 시장은 환경 친화적이고 지속가능한 건물을 건설하고 운영하는 것을 말합니다. 이러한 건물은 환경에 미치는 영향을 최소화하고, 거주자의 건강과 복지를 증진하며, 자원을 절약할 수 있도록 설계됩니다.
- 그린 빌딩은 에너지 효율이 높은 조명, HVAC 시스템, 태양광 패널과 같은 재생에너지원, 효율적인 물 관리 시스템, 재활용 및 지속가능한 재료, 실내 공기 환경 개선 등 다양한 기능과 기술을 통합하고 있습니다.
- 환경문제에 대한 인식이 높아지고 탄소배출량 감축에 대한 요구가 높아지면서 최근 그린 빌딩 시장이 급성장하고 있습니다. 많은 국가들이 그린 빌딩물 건설을 장려하는 정책과 정책을 도입하여 LEED(Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design), BREEAM(Building Research Institute Environmental Assessment Method) 등의 인센티브와 인증을 제공하고 있습니다.
- 그린 빌딩의 장점은 다양합니다. 에너지 소비 감소, 운영 비용 절감, 물 사용량 감소, 거주자의 편안함과 생산성 향상, 더 건강하고 지속가능한 미래에 대한 기여 등 여러 가지가 있습니다.
- 그린 빌딩 시장은 상업시설뿐만 아니라 주택, 교육시설, 의료, 정부기관 등의 건물도 포함됩니다. 기업, 조직, 개인들이 적극적으로 그린 빌딩을 채택하고 있으며, 이는 전 세계적인 운동이 되고 있습니다.
그린 빌딩 시장 동향
상업 부문의 지속가능한 건물에 대한 투자 증가와 수요 증가
지속가능한 건물에 대한 기업 수요는 많은 세계 시장에서 오피스 시장의 역동성을 주도할 것으로 예상됩니다. 향후 몇 년 동안 뉴욕, 파리, 싱가포르 등 세계 최대 오피스 시장 20곳(뉴욕, 파리, 싱가포르 등)은 저탄소화 수요의 34%만 충족할 수 있을 것으로 예상되며, 이는 현재 3평방미터당 1평방미터의 수요를 충족할 수 있는 수준입니다.
지속가능한 건물은 입주자들의 건물에 대한 관점도 바꾸고 있습니다. JLL의 2023년 거래 사례에 따르면, 전 세계 다양한 오피스 시장 부문에서 인증받은 건물은 여전히 건전한 임대료 프리미엄을 달성하고 있지만, 그 상황은 변화하고 있습니다. 변화하고 있습니다.
임차인들은 친환경 인증 외에도 환경 성과 지표(에너지 원단위, 전기화율 등)를 점점 더 중요하게 여기고 있습니다. 예를 들어, JLL의 2020년 거래 사례에 따르면, 런던과 파리의 고급 프라임 오피스 공간은 이 부문의 경기 둔화에도 불구하고 올해 사상 최고 수준의 임대료를 기록했습니다.
견조한 성장세를 보이고 있는 아시아태평양
아시아태평양의 그린 빌딩 시장은 예측 기간 동안 급성장할 것으로 예상됩니다. 이는 지속가능한 건축 관행에 대한 정부 지원 증가, 기후 변화에 대한 관심 증가, 녹색 건축의 이점에 대한 인식 증가 등 다양한 요인에 기인합니다.
아시아태평양은 그린 빌딩 시장에서 괄목할 만한 성장세를 보이고 있습니다. 이 지역에는 중국, 인도, 일본, 싱가포르, 호주 등이 포함됩니다. 이들 국가는 환경 문제를 해결하고 에너지 효율을 높이기 위해 지속가능한 건축 관행을 적극적으로 추진하고 있습니다.
이 지역 최대 경제대국 중 하나인 중국은 그린 빌딩을 추진하기 위해 많은 노력을 기울여왔습니다. 중국 정부는 에너지 효율이 높은 건설을 장려하는 규제와 정책을 시행하고 있으며, 그린 빌딩 개발에 대한 야심찬 목표를 설정하고 있습니다. 최근 중국에서는 에코시티와 지속가능한 도시 개발 이니셔티브를 포함한 그린 빌딩 프로젝트가 급증하고 있습니다.
또 다른 주요 지역 플레이어인 인도도 그린 빌딩 분야에서 큰 진전을 이루고 있습니다. 인도그린 빌딩협의회(IGBC)는 그린 빌딩을 장려하고 지속가능한 프로젝트를 인증하는 데 힘쓰고 있습니다. 인도의 많은 도시들이 그린 빌딩 규범과 규제를 채택하고 있으며, 상업 및 주거 분야 모두에서 그린 빌딩에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있습니다.
일본은 건축 및 건설 산업에 지속가능한 관행을 도입한 오랜 역사를 가지고 있습니다. 일본은 에너지 효율이 높은 기술의 선두주자이며, 지속가능성을 촉진하기 위해 엄격한 건축 기준을 도입했습니다. 일본 정부는 친환경 건축물의 도입을 장려하기 위해 다양한 인센티브와 인증을 도입하고 있습니다.
혁신적인 도시 계획으로 유명한 싱가포르는 아시아태평양에서 그린 빌딩을 위한 노력의 최전선에 서 있습니다. 건축건설청(BCA)은 에너지 효율과 지속가능성에 대한 야심찬 목표를 세웠으며, 그린마크 제도와 같은 그린 빌딩 인증은 널리 인정받고 있습니다.
광활한 경관과 다양한 기후를 가진 호주는 환경에 미치는 영향을 줄이기 위해 지속가능한 건축 방식에 중점을 두고 있습니다. 호주그린 빌딩협회(GBCA)는 그린 빌딩 표준을 보급하는 데 주력하고 있으며, 호주의 많은 도시들이 그린 빌딩 정책과 규정을 채택하고 있습니다.
전체적으로 아시아태평양의 그린 빌딩 시장은 정부의 노력, 환경 인식의 증가, 에너지 효율에 대한 요구로 인해 크게 성장하고 있습니다. 이 지역에서는 그린 빌딩 프로젝트, 인증, 지속가능한 도시개발에 대한 노력이 증가하고 있습니다.
또한 아시아태평양은 인구가 급증하고 가처분 소득이 증가함에 따라 그린 빌딩에 대한 수요도 증가할 것으로 예상되며, 2023년 아시아 인구는 47억 명, 2050년에는 88억 명에 달할 것으로 예상됩니다. 이에 따라 아시아의 도시화는 예측 기간 동안 지속될 것으로 예상됩니다.
그린 빌딩 산업 개요
지속가능성과 에너지 효율의 중요성을 인식하는 국가와 기업이 늘어남에 따라 그린 빌딩 시장의 경쟁은 더욱 치열해지고 있습니다. 이 시장에는 여러 주요 업체들이 등장했으며, 각 업체들은 그린 빌딩에 대한 수요 증가에 대응할 수 있는 독자적인 솔루션과 서비스를 제공하고 있습니다.
시장의 주요 기업 중 하나는 건설 산업입니다. 많은 건설회사들이 친환경 건축 관행을 받아들이고 지속가능한 설계 원칙을 프로젝트에 적용하고 있습니다. 이러한 기업들은 건축가, 엔지니어 및 기타 전문가들과 긴밀히 협력하여 건축물이 최고 수준의 지속가능성 기준을 충족할 수 있도록 합니다.
이 시장의 주요 기업으로는 Amvik Systems, Alumasc Group PLC, BASF SE, Binderholz Gmbh, Bauder Limited 등이 있습니다.
기타 혜택:
- 엑셀 형식의 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 소개
- 조사 가정과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
- 분석 방법
- 조사 단계
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 인사이트
- 현재 시장 시나리오
- 기술 동향
- 그린 빌딩 산업 공급망/밸류체인 분석에 관한 인사이트
- 프리패브 건축 산업에서 사용되는 다양한 구조에 관한 개요
- 그린 빌딩 산업 비용 구조 분석
- COVID-19의 영향
제5장 시장 역학
- 성장 촉진요인
- 건설의 에너지 효율
- 유연성과 맞춤형 옵션
- 성장 억제요인
- 건설에 적절한 토지 한정된 입수 가능성
- 기존 건설에 비해 품질이 낮다
- 기회
- 다양한 부문의 수요
- 에너지 효율적 건설
- 업계의 매력 - Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 공급 기업의 교섭력
- 소비자/구매자의 교섭력
- 신규 참여업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업 간의 경쟁 강도
제6장 시장 세분화
- 제품별
- 익스테리어 제품
- 인테리어 제품
- 기타 제품(빌딩 시스템, 솔라 시스템 등)
- 최종사용자별
- 주택
- 오피스
- 소매
- 시설
- 기타 최종사용자
- 지역별
- 아시아태평양
- 북미
- 유럽
- 남미
- 중동 및 아프리카
제7장 경쟁 상황
- 기업 개요
- Amvik Systems
- Alumasc Group PLC
- BASF SE
- Binderholz Gmbh
- Bauder Limited
- Interface Inc.
- Forbo International SA
- Owens Corning SA
- CEMEX
- Kingspan Group PLC*
- 기타 기업
제8장 시장 전망
제9장 부록
ksm 24.08.01The Green Buildings Market size is estimated at USD 0.59 trillion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 1.10 trillion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 10.82% during the forecast period (2024-2029).
Key Highlights
- The green buildings market refers to constructing and operating environmentally friendly and sustainable buildings. These buildings are designed to minimize their environmental impact, promote the health and well-being of occupants, and conserve resources.
- Green buildings incorporate various features and technologies such as energy-efficient lighting and HVAC systems, renewable energy sources like solar panels, efficient water management systems, recycled and sustainable materials, and improved indoor air quality.
- The market for green buildings has been growing rapidly in recent years due to increased awareness of environmental issues and the desire to reduce carbon emissions. Many countries have introduced policies and regulations to encourage the construction of green buildings, offering incentives and certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) or BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method).
- The benefits of green buildings are numerous. They help reduce energy consumption, lower operating costs, decrease water usage, improve occupant comfort and productivity, and contribute to a healthier and more sustainable future.
- The green buildings market is not limited to commercial buildings but includes residential, educational, healthcare, and government buildings. It has become a global movement, with companies, organizations, and individuals actively adopting green building practices.
Green Buildings Market Trends
Increasing investment and rise in demand for sustainable buildings in the commercial segment
Corporate demand for sustainable buildings is expected to drive office market dynamics in many global markets. Across 20 of the world's largest office markets (New York, Paris, Singapore, etc.) in the next few years, only 34% of low-carbon demand is expected to be met, one square meter for every three square meters currently in demand.
Sustainable buildings are also changing the way occupiers view them. Green certifications have traditionally been the hallmark of sustainable buildings, and tenants are willing to pay for them. JLL's 2023 transaction evidence shows that certified buildings are still achieving healthy rental premiums across various global office market segments, but the landscape is changing.
Tenants increasingly look for environmental performance indicators (e.g., energy intensity, electrification, etc.) in addition to green credentials. For example, JLL's 2020 transaction evidence shows that high-quality prime office spaces in London and Paris are reaching record rental heights this year, even as the sector slows down.
Asia-Pacific is growing at a steady pace
The Asia-Pacific green buildings market is expected to grow rapidly during the forecast period. This is due to various factors, such as the increasing government support for sustainable building practices, growing concerns about climate change, and increasing awareness of the benefits of green buildings.
The Asia-Pacific region has been witnessing significant growth in the green building market. The region includes China, India, Japan, Singapore, and Australia. These countries have actively promoted sustainable building practices to address environmental concerns and encourage energy efficiency.
China, one of the region's largest economies, has made substantial efforts to promote green buildings. The government has implemented policies and regulations to encourage energy-efficient construction and has set ambitious targets for green building development. In recent years, China has seen a surge in green building projects, including eco-cities and sustainable urban development initiatives.
India, another major regional player, has also made strides in the green building sector. The Indian Green Building Council (IGBC) has been instrumental in promoting green building practices and certifying sustainable projects. Many cities in India have adopted green building codes and regulations, and there is a growing demand for green buildings in both the commercial and residential sectors.
Japan has a long history of incorporating sustainable practices in its architecture and construction industry. The country has been a leader in energy-efficient technologies and has implemented strict building standards to promote sustainability. The Japanese government has introduced various incentives and certifications to encourage green building adoption.
Singapore, known for its innovative urban planning, has been at the forefront of green building initiatives in the Asia-Pacific region. The Building and Construction Authority (BCA) has set ambitious targets for energy efficiency and sustainability, and green building certifications such as the Green Mark scheme are widely recognized.
Australia, with its vast landscapes and diverse climate, has been focusing on sustainable building practices to reduce its environmental impact. The Green Building Council of Australia (GBCA) has been instrumental in promoting green building standards, and many Australian cities have adopted green building policies and regulations.
Overall, the Asia-Pacific green building market is experiencing significant growth, driven by government initiatives, increasing environmental awareness, and the desire for energy efficiency. The region is witnessing a rise in green building projects, certifications, and sustainable urban development initiatives.
The demand for green buildings in Asia-Pacific is also expected to grow due to its rapidly growing population and rising disposable income. In 2023, Asia had a population of 4.7 billion, which is expected to reach 8.8 billion people by 2050. As a result, Asia's urbanization is expected to continue during the forecast period.
Green Buildings Industry Overview
The green building market has become increasingly competitive as more countries and companies recognize the importance of sustainability and energy efficiency. Several key players have emerged in this market, each offering unique solutions and services to meet the growing demand for green buildings.
One of the major players in the market is the construction industry. Many construction companies have embraced green building practices and incorporated sustainable design principles into their projects. These companies often work closely with architects, engineers, and other professionals to ensure their buildings meet the highest sustainability standards.
Some of the major players in the market include Amvik Systems, Alumasc Group PLC, BASF SE, Binderholz Gmbh, and Bauder Limited.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definitions
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 Analysis Methodology
- 2.2 Research Phases
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Technological Trends
- 4.3 Insights on Supply Chain/Value Chain Analysis of the Green Buildings Industry
- 4.4 Brief on Different Structures Used in the Prefabricated Buildings Industry
- 4.5 Cost Structure Analysis of the Green Buildings Industry
- 4.6 Impact of COVID 19
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Drivers
- 5.1.1 Energy Efficiency in Construction
- 5.1.2 Flexibility and Customization Options
- 5.2 Restraints
- 5.2.1 Limited Availability of Suitable Land for Construction
- 5.2.2 Lower Quality Compared to Traditional Construction
- 5.3 Opportunitites
- 5.3.1 Demand Across Various Sectors
- 5.3.2 Energy Efficient Construction
- 5.4 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 5.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 5.4.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers/Buyers
- 5.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 5.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 5.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Product
- 6.1.1 Exterior Products
- 6.1.2 Interior products
- 6.1.3 Other Products (Building Systems, Solar Systems, etc.)
- 6.2 By End User
- 6.2.1 Residential
- 6.2.2 Office
- 6.2.3 Retail
- 6.2.4 Institutional
- 6.2.5 Other End Users
- 6.3 By Geography
- 6.3.1 Asia-Pacific
- 6.3.2 North America
- 6.3.3 Europe
- 6.3.4 South America
- 6.3.5 Middle East and Africa
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Overview (Market Concentration and Major Players)
- 7.2 Company Profiles
- 7.2.1 Amvik Systems
- 7.2.2 Alumasc Group PLC
- 7.2.3 BASF SE
- 7.2.4 Binderholz Gmbh
- 7.2.5 Bauder Limited
- 7.2.6 Interface Inc.
- 7.2.7 Forbo International SA
- 7.2.8 Owens Corning SA
- 7.2.9 CEMEX
- 7.2.10 Kingspan Group PLC*
- 7.3 Other Companies



















