
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1636191
인도의 EPCM(설계, 조달, 건설 및 관리) 시장 전망 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향과 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)India Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management (EPCM) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
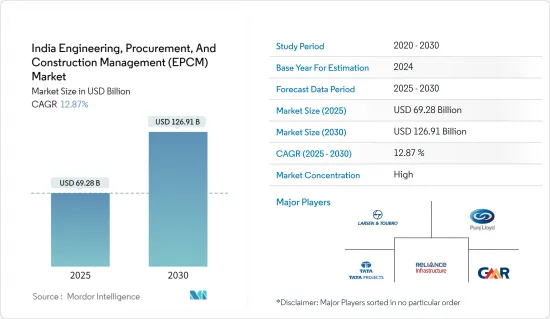
인도의 EPCM(설계, 조달, 건설 및 관리) 시장 규모는 2025년에 692억 8,000만 달러로 추정되며, 예측기간(2025-2030년)의 연평균 성장율(CAGR)은 12.87%로, 2030년에는 1,269억 1,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예측됩니다.
주요 하이라이트
- 인도의 EPC(설계, 조달 및 건설)시장은 이 시장은 다양한 산업에 걸쳐 다양한 트렌드, 도전 과제, 기회를 제공합니다. 인도의 EPC 시장은 야심찬 인프라 청사진과 산업 발전에 힘입어 탄탄하게 성장해 왔습니다. 정부의 추진력과 민간 투자에 힘입어 시장의 연평균 성장률(CAGR)은 향후 몇 년 동안 활기를 유지할 것으로 보입니다. 도로 건설, 철도망 현대화, 스마트 시티 미션과 같은 지원를 위한 바라트말라 프로젝트에 주목할 만한 투자가 이루어지고 있습니다. 또한 태양광, 풍력 등 재생 에너지 프로젝트가 눈에 띄게 급증하고 있습니다.
- 또, 화력발전소, 수력발전소, 원자력발전소의 개발 및 확장, 송전 네트워크도 진행되고 있습니다. 스마트 시티 미션, AMRUT, 바라트말라와 같은 주요 지원는 인프라 성장에 대한 인도의 노력을 강조합니다. 또한 인도의 급속한 산업화와 도시화로 인해 인프라 개선에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있습니다. 마지막으로 FDI 정책의 자유화로 인해 최첨단 건설 기술과 프로젝트 관리 도구를 도입하고 있는 국제적인 EPC 업체들이 인도로 유입되고 있습니다.
인도의 EPCM(설계, 조달, 건설 및 관리) 시장 동향
인프라 개발이 EPC 서비스 수요 주도
인도 정부는 스마트 시티 미션, 고속도로를 위한 바라트말라 파리요자나, 항만을 위한 사가르말라 프로젝트 등 야심찬 인프라 프로그램에 착수했습니다. 스마트 시티 미션은 핵심 인프라를 개선하고, 높은 삶의 질을 보장하며, 깨끗하고 지속 가능한 환경을 조성하고, '스마트' 솔루션을 구현하여 도시의 수준을 높이는 것을 목표로 합니다. 지속 가능하고 포용적인 성장을 강조하는 이 미션은 다른 도시를 안내할 수 있는 복제 가능한 모델을 만드는 것을 목표로 소규모 지역에 초점을 맞추고 있습니다. 이 지원는 개별 도시를 변화시키는 것뿐만 아니라 더 스마트한 도심을 향한 전국적인 움직임을 촉진하기 위한 것입니다.
이러한 노력은 인프라 개발에 대한 인도의 노력을 강조하며 EPCM 서비스에 상당한 기회를 제시합니다. 도시화가 급증하면서 메트로 철도 시스템부터 공항, 스마트 시티 프로젝트에 이르기까지 도시 인프라를 업그레이드해야 할 필요성이 커지고 있습니다. 이와 함께 제조업 강화를 목표로 하는 '메이크 인 인디아' 캠페인이 새로운 공장 및 산업 시설 건설에 박차를 가하면서 EPCM 서비스에 대한 수요를 더욱 촉진하고 있습니다.
'메이크 인 인디아'의 글로벌 출범은 인도가 제조업에 새롭게 집중하는 계기가 되었습니다. 이 지원의 주요 목표는 인도를 글로벌 제조업을 위한 최고의 선택지로 자리매김하는 것입니다. 인도 정부는 출범 이후 제조, 디자인, 혁신, 스타트업을 강화하기 위해 수많은 개혁을 주도해 왔습니다. 전 세계적으로 침체된 경제 환경 속에서도 인도는 7.5%의 성장률을 기록하며 가장 빠르게 성장하는 경제로 부상했고, 그 속도는 계속 빨라지고 있습니다. 이러한 성장의 원동력에는 '메이크 인 인디아', '디지털 인디아', '100대 스마트 시티', '스킬 인디아' 등의 지원가 중추적인 역할을 하고 있습니다.
'메이크 인 인디아'는 특히 인도를 세계 공급망에 통합하는 것을 목표로 하고 있으며 인도 기업이 세계 무대에서 활약할 필요성을 강조하고 있습니다. 인도는 경제를 크게 자유화하고 국방, 철도, 건설, 보험, 연금기금, 의료기기 등의 분야를 외국 직접투자(FDI)에 개방했습니다. 이 움직임은 인도를 세계에서 가장 개방적인 경제 중 하나로 자리매김했습니다. 비즈니스 환경을 더욱 강화하기 위해 인도 정부는 비즈니스의 용이성을 개선하는 것을 우선시하고 있습니다. 규제를 간소화하고 비즈니스가 쉬운 환경을 조성하는 데 중점을 둡니다. 기술을 활용하여 정부는 14개의 서비스를 eBiz 포털에 통합하여 다양한 정부 기관의 클리어런스를 간소화합니다. 메이크업 인디아의 효과는 이미 나타났습니다.
전반적으로 인도는 경제 지표의 상승, 외국 투자 증가, 제조업의 확대 등 '메이크 인 인디아'의 구체적인 성과를 목격하고 있습니다. Smart Cities Mission, Bharatmala Pariyojana, Sagarmala Project, Make in India의 협력적인 노력으로 인도의 인프라가 재구성되고 있습니다. 이 야심찬 의제는 도시 및 산업 역량을 강화하고 엔지니어링, 조달 및 건설 관리 서비스를 위한 중요한 길을 열어줍니다. 인도의 글로벌 공급망 통합이 심화되고 비즈니스 환경을 개선하기 위한 노력이 계속되면서 인도는 중추적인 제조 및 인프라 허브로 부상하여 지속적인 경제 성장과 발전을 위한 발판을 마련하고 있습니다.
인도의 에너지 및 유틸리티 부문, 투자 및 지원 증가로 수요가 급증
인도는 여전히 불안정한 전력망으로 인해 인구의 상당수가 인터넷에 연결되지 않은 채 매일 정전 사태에 직면하고 있습니다. 인도의 전력 부문은 다양한 에너지원으로 전 세계적으로 두각을 나타내고 있습니다. 인도는 석탄, 천연가스, 석유, 원자력과 같은 전통적인 방식과 풍력, 태양광, 수력, 도시 폐기물, 바이오매스와 같은 새로운 옵션을 활용하고 있습니다. 인도 정부는 청정 에너지로의 전환을 위한 노력에 힘입어 대대적인 산업 개편을 주도하고 있습니다. 여기에는 인프라를 개선하고 풍력 및 태양광 발전과 같은 친환경 에너지에 대한 투자를 확대하는 것이 포함됩니다.
인도 정부는 민간 투자의 중추적인 역할을 인식하고 이 부문을 강화하기 위해 여러 가지 인센티브 제도를 시행하고 있습니다. 인도는 야심찬 목표를 설정하여 10년 말까지 탄소 배출량을 45% 감축하고, 2030년까지 전력의 50%를 재생에너지로 조달하며, 궁극적으로 2070년까지 탄소 중립을 달성하는 것을 목표로 하고 있습니다. 이러한 목표와 인도의 견고하고 지속적인 경제 성장은 에너지 기업에게 유리한 전망을 제시합니다.
인도의 2030년 비전에는 500GW의 청정 에너지 용량이 포함되며, 그중 상당 부분인 280GW가 태양광 발전에서 생산됩니다. 2023년 2월 기준 인도의 총 발전 용량은 412.21GW로, 이 중 약 100GW가 청정 에너지원에 의한 것입니다. 특히 인도는 중국에 이어 아시아에서 두 번째로 높은 풍력 발전 용량을 자랑합니다. 또한 세계에서 다섯 번째로 빠르게 성장하는 태양광 에너지 시장이자 가장 비용 효율적인 태양광 발전 생산국이라는 타이틀을 보유하고 있습니다.
전 세계적으로도 인도는 재생 에너지 발전량에서 4위를 차지하고 있습니다. 인도 정부는 혁신을 촉진하고 에너지 부문의 규모를 확대하기 위해 향후 5년간 420억 달러에 달하는 막대한 예산을 배정했습니다. 에너지 환경을 개선하기 위한 인도의 노력은 세계은행의 2019년 비즈니스 용이성 - 전기 공급 조사에서 89.4점이라는 인상적인 점수를 받은 것에서도 잘 드러납니다. 이 점수는 전력망 연결의 용이성, 공급 안정성, 관세 투명성, 전기 요금 등을 평가한 것입니다. 참고로 덴마크는 이보다 약간 높은 90.2점을 받았습니다.
앞으로 인도는 해상풍력발전의 야심적인 계획을 내세우고 2022년까지 5GW, 2030년까지 30GW의 프로젝트 설립을 목표로 하고 있습니다. Grid Connected Solar Rooftop Program은 2022년까지 옥상 태양광 발전(RTS) 프로젝트에서 40GW의 용량을 달성하는 것을 목표로 했습니다. 주요 초점은 신에너지와 신재생에너지의 도입을 강화하기 위한 연구개발 및 실증(RD&D)입니다. 신재생에너지부(MNRE)는 에너지기술, 재료, 현지생산능력 향상을 위한 연구개발을 적극 추진하고 있습니다.
전반적으로 인도의 전력 분야는 큰 변화를 맞이하고 있으며 다양한 에너지 믹스와 청정에너지에 대한 주목할만한 집중이 이루어 지고 있습니다. 이러한 변화는 상당한 인프라 개선에 박차를 가하고 있으며 상당한 투자를 이끌어내고 있습니다. 탄소 배출량을 줄이고, 재생 에너지 용량을 늘리고, 궁극적으로 탄소 중립을 달성하겠다는 명확한 목표가 있는 인도는 에너지 기업들에게 매력적인 시장으로 떠오르고 있습니다. 혁신을 촉진하고 부문별 성장을 촉진하는 관대한 자금 지원과 지원 정책 등 인도 정부의 적극적인 조치는 이러한 매력을 더욱 강화했습니다. 인도는 에너지 환경을 강화하고 더 많은 재생 에너지를 수용하면서 지속 가능한 에너지 분야의 글로벌 선두주자로서의 입지를 공고히 하고 있습니다. 이는 시민들에게 더욱 안정적인 전력 공급을 약속하고 전 세계 환경 목표에 대한 인도의 노력을 강조합니다
인도의 EPCM(설계, 조달, 건설 및 관리) 산업 개요
인도의 EPCM(설계, 조달, 건설 및 관리) 시장은 다수의 기업을 보유한 단편적인 상황입니다. 유력 기업은 존재하고 시장은 세분화되어 있으며, 특히 전문 분야와 지역 시장에서는 많은 중소기업이 적극적으로 진입하고 있습니다. 이 분야에서 유명한 기업으로는 Larsen&Tubro(L&T), Tata Projects Limited, Punj Lloyd Group, Reliance Infrastructure Limited, GMR Group 등이 있습니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 성과
- 조사의 전제
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 역학
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 신재생에너지 프로젝트
- 정부의 대처
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 규제와 관료적 장애물
- 건설자재 비용 상승
- 시장 기회
- 스마트 인프라 기술 채용
- 밸류체인, 서플라이체인 분석
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자, 소비자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계의 강도
- PESTLE 분석
- 시장에서의 혁신의 통찰
제5장 시장 세분화
- 서비스별
- 설계
- 조달
- 건설
- 기타 서비스
- 섹터별
- 주택 산업, 인프라(운수), 에너지 및 유틸리티
- 산업
- 인프라(운수)
- 에너지 및 유틸리티
제6장 경쟁 구도
- Market Concetration Overview
- 기업 프로파일
- Larsen & Toubro(L&T)
- Tata Projects Limited
- Punj Lloyd Group
- Reliance Infrastructure Limited
- GMR Group
- Afcons Infrastructure Limited
- Hindustan Construction Company(HCC)
- NCC Limited(Nagarjuna Construction Company)
- IVRCL Limited
- KEC International
- Gammon India Limited
- Simplex Infrastructures Limited
- Rays Power Infra Limited
- Megha Engineering & Infrastructures Ltd
- Salasar Techno Engineering Ltd(STEL)
제7장 향후의 동향
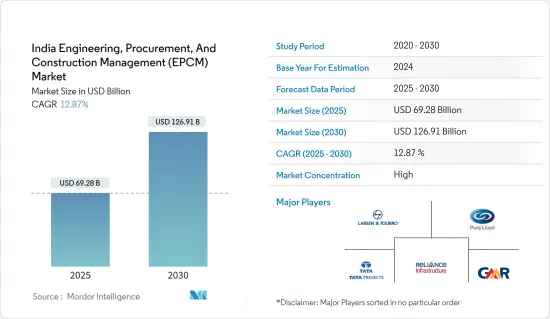
HBR 25.02.10The India Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management Market size is estimated at USD 69.28 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 126.91 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 12.87% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Key Highlights
- India's engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) market is pivotal in the nation's infrastructure landscape. This market presents a spectrum of trends, challenges, and opportunities spanning diverse industries. India's EPC market has grown robustly and is fueled by ambitious infrastructure blueprints and industrial advancements. Bolstered by governmental impetus and private investments, the market's compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is poised to maintain its vigor in the coming years. Noteworthy investments are channeled into the Bharatmala project for road construction, the modernization of the railway network, and initiatives like the Smart Cities Mission. In addition, there is a notable surge in renewable energy projects, spanning solar, wind, and other avenues.
- The nation is also witnessing the development and expansion of thermal, hydroelectric, and nuclear power plants alongside a bolstered power transmission network. Key initiatives such as the Smart Cities Mission, AMRUT, and Bharatmala underscore India's commitment to infrastructure growth. Furthermore, the nation's rapid industrialization and urbanization fuel an escalating demand for enhanced infrastructure. Lastly, the liberalization of FDI policies is drawing in international EPC players, who are also embracing cutting-edge construction technologies and project management tools.
India Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management (EPCM) Market Trends
Infrastructure Development Driving Demand For EPC Services
The Indian government has embarked on ambitious infrastructure programs, notably the Smart Cities Mission, Bharatmala Pariyojana for highways, and the Sagarmala Project for ports. The Smart Cities Mission aims to elevate cities by enhancing core infrastructure, ensuring a high quality of life, fostering a clean and sustainable environment, and implementing 'Smart' Solutions. Emphasizing sustainable and inclusive growth, the mission focuses on compact areas, aiming to create a replicable model to guide other cities. This initiative is not just about transforming individual cities but about catalyzing a nationwide movement toward smarter urban centers.
These initiatives underscore India's commitment to infrastructure development, presenting significant opportunities for EPCM services. With urbanization surging, there is a critical need for upgraded urban infrastructure, from metro rail systems to airports and smart city projects. In tandem, the "Make in India" campaign, aimed at bolstering manufacturing, is spurring the construction of new plants and industrial facilities, further driving the demand for EPCM services.
The global launch of the "Make in India" initiative marked India's renewed focus on manufacturing. The primary goal of this initiative is to position India as the top choice for global manufacturing. Since its inception, the Indian government has spearheaded numerous reforms to bolster manufacturing, design, innovation, and startups. Amidst a globally subdued economic landscape, India has emerged as the fastest-growing economy, boasting a growth rate of 7.5% that continues to accelerate. Initiatives like "Make in India," "Digital India," "100 Smart Cities," and "Skill India" have played a pivotal role in driving this growth.
"Make in India" specifically targets integrating India into the global supply chain, emphasizing the need for Indian companies to excel on a global stage. India has significantly liberalized its economy, opening sectors like defense, railways, construction, insurance, pension funds, and medical devices to foreign direct investment (FDI). This move has positioned India as one of the most open economies worldwide. To further enhance the business environment, the Indian government has prioritized improving the ease of doing business. The focus is on simplifying regulations to foster a conducive environment for businesses. Leveraging technology, the government has integrated 14 services into the eBiz portal, streamlining clearances from various government agencies. The impact of "Make in India" is already evident.
Overall, India is witnessing tangible outcomes from its "Make in India" initiative, with economic indicators on the rise, foreign investments increasing, and the manufacturing sector expanding. The concerted efforts of the Smart Cities Mission, Bharatmala Pariyojana, Sagarmala Project, and Make in India are reshaping India's infrastructure. This ambitious agenda bolsters urban and industrial capabilities and opens up significant avenues for engineering, procurement, and construction management services. With India's deepening integration into global supply chains and ongoing efforts to improve its business environment, the nation is on track to emerge as a pivotal manufacturing and infrastructure hub, setting the stage for sustained economic growth and development.
India's Energy And Utilities Segment Experiencing Surge in Demand, Driven by Increased Investments and Initiatives
India still grapples with an unreliable power grid, leaving a significant portion of its populace unconnected and facing daily power outages. The country's power sector stands out globally for its diverse energy sources. India harnesses traditional avenues like coal, natural gas, oil, and nuclear power alongside newer options such as wind, solar, hydropower, municipal waste, and biomass. Driven by a commitment to transition to clean energy, the Indian government is spearheading a substantial industry overhaul. This includes revamping infrastructure and channeling investments into green energy, notably wind and solar power.
Recognizing the pivotal role of private investment, the Indian government has rolled out several incentive schemes to bolster the sector. Setting ambitious targets, India aims to slash carbon emissions by 45% by the end of the decade, source 50% of its electricity from renewables by 2030, and ultimately achieve carbon neutrality by 2070. These targets and India's robust and consistent economic growth present lucrative prospects for energy companies.
India's vision for 2030 includes a 500 GW clean energy capacity, with a significant 280 GW from solar power. As of February 2023, India's total generation capacity stood at 412.21 GW, with approximately 100 GW attributed to clean sources. Notably, India boasts the second-highest wind power capacity in Asia, trailing only China. It also holds the title of the world's fifth-fastest-growing solar energy market and the most cost-efficient producer of solar power.
On the global stage, India ranks fourth in renewable energy generation. The government has earmarked a substantial USD 42 billion over the next five years to foster innovation and scale up the energy sector. India's commitment to enhancing its energy landscape is underscored by its impressive score of 89.4 in the World Bank's 2019 Ease of Doing Business - Getting Electricity survey. This score evaluates the ease of connecting to the grid, supply reliability, tariff transparency, and electricity pricing. For context, Denmark secured a slightly higher score of 90.2.
Looking ahead, India has laid out ambitious plans for offshore wind energy, aiming to establish 5 GW of projects by 2022 and a substantial 30 GW by 2030. The "Grid Connected Solar Rooftop Program" is set on achieving a 40 GW capacity for rooftop solar (RTS) projects by 2022. The key focus is on research, development, and demonstration (RD&D) to bolster the adoption of new and renewable energy. The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) actively promotes R&D to advance energy technologies, materials, and local production capabilities.
Overall, India's power sector is undergoing a significant transformation, a diverse energy mix, and a notable focus on clean energy. This shift is spurring substantial infrastructure enhancements and drawing in considerable investments. With clear targets to slash carbon emissions, ramp up renewable energy capacity, and ultimately achieve carbon neutrality, India emerges as an attractive prospect for energy firms. The government's proactive steps bolstered this appeal, such as generous funding and supportive policies, which nurture innovation and foster sectoral growth. As India fortifies its energy landscape and embraces more renewables, the country is on track to cement its position as a global frontrunner in sustainable energy. This promises a more dependable power supply for its citizens and underscores India's commitment to worldwide environmental objectives.
India Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management (EPCM) Industry Overview
The Indian engineering, procurement, and construction management (EPCM) market features a fragmented landscape, hosting numerous players. Although dominant players exist, the market is fragmented, with many small to mid-sized companies actively participating, especially in specialized sectors or regional markets. Prominent entities in this sector include Larsen & Toubro (L&T), Tata Projects Limited, Punj Lloyd Group, Reliance Infrastructure Limited, and GMR Group.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Deliverables
- 1.2 Study Assumptions
- 1.3 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Renewable Energy Projects
- 4.2.2 Government Initiatives
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Regulatory and Bureaucratic Hurdles
- 4.3.2 Increase in Cost of Construction Material
- 4.4 Market Opportunities
- 4.4.1 Adoption of Smart Infrastructure Technologies
- 4.5 Value Chain/Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.7 PESTLE Analysis
- 4.8 Insights into Technology Innovation in the Market
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Service
- 5.1.1 Engineering
- 5.1.2 Procurement
- 5.1.3 Construction
- 5.1.4 Other Services
- 5.2 By Sectors
- 5.2.1 Residential Industrial, Infrastructure (Transportation), and Energy and Utilities
- 5.2.2 Industrial
- 5.2.3 Infrastructure (Transportation)
- 5.2.4 Energy and Utilities
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concetration Overview
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 Larsen & Toubro (L&T)
- 6.2.2 Tata Projects Limited
- 6.2.3 Punj Lloyd Group
- 6.2.4 Reliance Infrastructure Limited
- 6.2.5 GMR Group
- 6.2.6 Afcons Infrastructure Limited
- 6.2.7 Hindustan Construction Company (HCC)
- 6.2.8 NCC Limited (Nagarjuna Construction Company)
- 6.2.9 IVRCL Limited
- 6.2.10 KEC International
- 6.2.11 Gammon India Limited
- 6.2.12 Simplex Infrastructures Limited
- 6.2.13 Rays Power Infra Limited
- 6.2.14 Megha Engineering & Infrastructures Ltd
- 6.2.15 Salasar Techno Engineering Ltd (STEL)




















