
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1637883
중국의 발전 시장 : 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)China Power - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
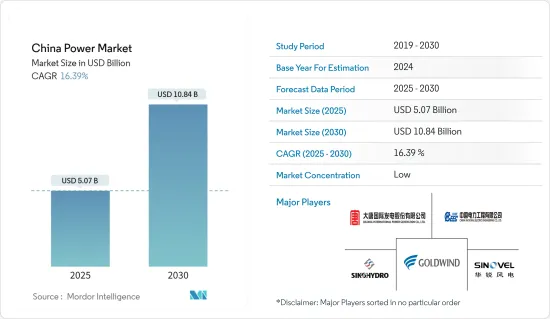
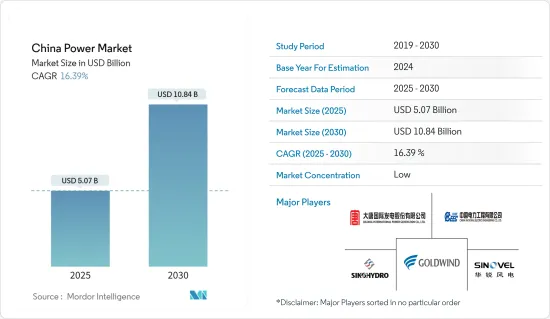
중국의 발전 시장 규모는 2025년에 50억 7,000만 달러, 2030년에는 108억 4,000만 달러로 추정되며, 예측 기간 중(2025-2030년) CAGR은 16.39%에 달할 것으로 예측됩니다.
주요 하이라이트
- 중기적으로는 향후 투자 증가나 제조업의 성장 등의 요인이 예측기간 중 중국의 발전시장을 견인할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 한편, 중국의 발전량의 대부분을 차지하는 석탄 기반 발전소의 단계적 폐지는 발전 시장의 성장을 방해할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 중국 정부는 2030년까지 신재생에너지 도입량을 1200GW까지 늘릴 것이라고 발표했습니다. 이것은 예측 기간 동안 중국의 발전 시장에 몇 가지 기회를 가져올 것으로 예상됩니다.
중국의 발전 시장 동향
신재생에너지 부문이 시장을 독점할 전망
- 중국 정부는 보조금, 감세, 규제 등 다양한 시책과 인센티브를 통해 신재생에너지 개발을 적극 추진하고 있습니다. 이러한 정부의 지원은 신재생에너지 부문의 성장을 뒷받침하고 앞으로도 계속될 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 게다가 중국은 에너지 수요를 충족시키기 위해 수입 화석 연료에 크게 의존하고 있습니다. 따라서 가격 변동이나 공급 중단의 영향을 받기 쉽습니다. 신재생에너지에 투자함으로써 중국은 외국 에너지원에 대한 의존도를 줄이고 에너지 안보를 높일 수 있습니다.
- 게다가 신재생에너지 비용은 최근 급격히 떨어지고 있으며, 화석연료와의 경쟁은 점점 치열해지고 있습니다. 경우에 따라 재생 가능 에너지는 이미 석탄 화력 발전소보다 저렴합니다. 이 비용 경쟁은 에너지 비용 절감을 목표로 하는 중국에서 재생 가능 에너지를 매력적인 선택으로 삼고 있습니다.
- 2022년 중국의 재생 가능 에너지 발전량은 약 1367TWh였습니다. 2021년에 비해 19% 증가. 예측 기간 동안에도 유사한 경향이 지속될 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 예를 들어 2022년 3월 중국 정부는 고비사막 등 사막지대에 450GW의 태양광·풍력발전용량을 건설할 의향이라고 발표했습니다. 현재 약 100GW의 태양광 발전 용량이 이미 건설 중입니다.
- 국가에너지국(NEA)에 따르면 중국은 2022년에 3,260만 kW의 육상 풍력 발전 용량을 연결하여 총 설비 용량을 3억 3,398만 kW로 끌어올립니다. 게다가 중국의 육상풍력발전시장은 국내시장용과 국제수출을 위한 주요 부품과 재료의 요구가 높아지고 있으며, 향후 수년간 안정된 성장이 예상되고 있습니다. 또한 중국에서는 발전량의 70% 가까이가 화력 발전입니다. 화력발전으로 인한 공해가 증가하는 가운데, 이 나라는 발전에서 보다 깨끗하고 재생 가능한 전원의 비율을 늘리는 데 주력하고 있습니다.
향후 투자계획 증가가 시장을 견인
- 세계 2위 경제대국인 중국의 에너지 수요는 경제개발 목표를 달성하기 위해 급성장했습니다. 인구 증가, 도시화, 공업화가 이 수요에 공헌해, 발전 능력의 필요성이 높아지고 있습니다.
- 2022년 중국의 총 발전량은 8,848.7TWh로 2021년 대비 약 3.6% 증가했습니다. 이 추세는 중국이 재생가능 에너지 용량을 늘릴수록 계속될 것으로 예상됩니다. 이것이 발전 능력 증가를 돕는 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 게다가 세계원자력협회에 따르면 중국은 현재 55기의 가동 중인 원자로를 가지고 있으며, 22기가 건설 중이거나 개발 중입니다. 중국 정부는 석탄 화력 발전소에 의한 오염에 대한 우려도 있으며, 에너지 수요를 충족시키기 위해 장기적으로 폐쇄 사이클 원자력의 이용을 늘리는 것을 목표로하고 있습니다.
- 2022년 4월, 중국 국무원은 6기의 신규 원자력발전소 건설을 허가하고 Sanmen, Haiyang, Lufeng의 각 원자력발전소 부지 내에 2기의 원자로를 추가 건설할 계획을 나타냈습니다. 건설이 승인된 것은 Sanmen의 3호기와 4호기, Haiyang의 3호기와 4호기, Lufeng의 5호기와 6호기입니다. 이러한 움직임으로 중국의 원자력 발전 설비 용량은 2025년까지 70GWe로 증가할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 또한 러시아 우크라이나 전쟁과 같은 최근 지정학적 동향으로 중국 정부는 에너지 안보 강화에 중점을 둡니다. 러시아와 우크라이나 전쟁과 같은 최근 지정학적 움직임으로 중국 정부는 에너지 안보 강화에 중점을 둡니다. 석유 및 가스 공급은 세계적으로 영향을 받았으며 중국의 발전 부문도 영향을 받았습니다.
- 중국은 발전 부문의 다른 부문 업그레이드에도 많은 투자를 하고 있습니다. 여기에는 재생 가능한 발전을 소규모 발전 사업에서 수요 센터로 수송하기 위한 주요 HVDC와 UHVDC 프로젝트에 있어서의 송전과 배전 인프라, 송전망을 안정시키면서 잉여 재생 가능 에너지 발전을 저장하기 위해 배터리 저장 용량을 포함합니다.
- 예를 들어, 2022년 7월에 Baihetan-Jiangsu 800kV 초고압(UHV) 직류 송전 프로젝트가 상업 운전을 시작했는데, 이는 대규모 서쪽에서 동쪽으로의 송전 계획에서 주요 프로젝트 중 하나입니다. 이러한 개발은 대규모 태양광 공원에서 배전하는 데 도움이 될 것으로 기대됩니다.
- 따라서 위와 같은 점에서 중국 정부는 이 나라의 에너지 부문에 대한 투자를 늘리고 이 나라의 발전 시장을 확대할 것으로 기대됩니다.
중국의 발전 산업 개요
중국의 발전 시장은 세분화되어 있습니다. 이 시장의 주요 기업(순부동)에는 Datang International Power Generation Company Limited, China National Electric Engineering, Xinjiang Goldwind Science & Technology, Sinohydro Corporation, Sinovel Wind Group 등이 포함됩니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사 범위
- 시장의 정의
- 조사의 전제
제2장 주요 요약
제3장 조사 방법
제4장 시장 개요
- 소개
- 중국의 발전량과 2028년까지의 예측(단위:테라와트)
- 최근 동향과 개발
- 정부의 규제와 시책
- 시장 역학
- 성장 촉진요인
- 신재생에너지 부문에 대한 투자 증가
- 제조업 성장에 따른 발전 수요 증가
- 억제요인
- 석탄발전소의 단계적 폐지 증가
- 성장 촉진요인
- 공급망 분석
- PESTLE 분석
제5장 시장 세분화
- 발전원
- 화력
- 수력 발전
- 원자력
- 신재생에너지
- 기타 발전원
- 송배전(T&D)
제6장 경쟁 구도
- M&A, 합작사업, 제휴, 협정
- 주요 기업의 전략
- 기업 프로파일
- Datang International Power Generation Company Limited
- China National Electric Engineering Co. Ltd
- Xinjiang Goldwind Science & Technology Co. Ltd
- Sinohydro Corporation
- Sinovel Wind Group Co. Ltd.
- Wuxi Suntech Power Co. Ltd.
- China Yangtze Power Co., Ltd.
- China National Electric Wire & Cable I/E Corp.
- State Grid Corporation of China
- Shandong energy group co. Ltd.
제7장 시장 기회와 앞으로의 동향
- 재생 가능 에너지 발전을 지원하는 정부 목표의 존재
The China Power Market size is estimated at USD 5.07 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 10.84 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 16.39% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Key Highlights
- Over the medium term, factors such as the increasing upcoming investments and the growing manufacturing sector will likely drive the Chinese power market during the forecast period.
- On the other hand, phasing out coal-based power plants, which account for a major share of power generation in China, is expected to hinder the growth of the power market.
- Nevertheless, the Chinese government announced increasing its installation of renewable energy sources to 1200 GW by 2030. It will likely create several opportunities for the Chinese power market in the forecast period.
China Power Market Trends
The Renewable Energy Segment Expected to Dominate the Market
- The Chinese government actively promoted renewable energy development through various policies and incentives, such as subsidies, tax breaks, and regulations. This government support helped to drive growth in the renewable energy sector and is expected to continue in the coming years.
- Moreover, China heavily relies on imported fossil fuels to meet its energy needs. It makes the country vulnerable to price fluctuations and supply disruptions. By investing in renewable energy, China can reduce its dependence on foreign energy sources and increase its energy security.
- Additionally, the cost of renewable energy has decreased rapidly in recent years, making it increasingly competitive with fossil fuels. In some cases, renewable energy is already cheaper than coal-fired power plants. This cost competitiveness makes renewable energy an attractive option for China, which aims to reduce its energy costs.
- In 2022, the electricity generated through renewable energy in China was around 1367 TWh. It is an increase of 19% compared to 2021. A similar trend is expected to be followed during the forecasted period.
- For instance, in March 2022, it was announced by the Chinese government that they intend to construct solar and wind power generation capacity of 450 GW in desert regions such as the Gobi desert. Currently, around 100 GW of solar power capacity is already under construction.
- According to the National Energy Administration (NEA), China connected 32.6 GW of onshore wind capacity in 2022, boosting its total installations to 333.98 GW. Further, the Chinese onshore wind market is expected to grow steadily in the coming years, with rising needs for key components and materials for the national market and international exports. Besides, in China, nearly 70% of the electricity produced is from thermal energy sources. With increasing pollution from thermal sources, the country focuses on increasing the share of cleaner and renewable sources in power generation.
Increasing Upcoming Investment Plans to Drive the Market
- As the world's second-largest economy, China's energy demand grew rapidly to meet its economic development goals. A growing population, urbanization, and industrialization contributed to this demand, increasing the need for electricity generation capacity.
- In 2022, the total electricity generated in China was 8848.7 TWh, an increase of almost 3.6% compared to 2021. This trend is expected to continue as China increases its renewable energy capacity. It will aid in increasing electricity generation capacity.
- Moreover, according to the World Nuclear Association, China currently contains 55 operational nuclear power reactors, with 22 more under construction or development. The Chinese government aims to increase its use of closed-cycle nuclear power in the long term to meet its energy demands, partly due to concerns over the pollution caused by coal-fired power plants.
- In April 2022, China's State Council gave the green light to construct six new nuclear power plants, with plans to build two additional reactors at the Sanmen, Haiyang, and Lufeng nuclear power plant sites. The approved construction involves units 3 and 4 at Sanmen, 3 and 4 at Haiyang, and 5 and 6 at Lufeng. This move is expected to increase China's installed nuclear-generating capacity to 70 GWe by 2025.
- Additionally, the Chinese government shifted its focus on increasing energy security due to recent geopolitical developments like the Russia-Ukraine war. It affected the oil and gas supply globally and China's electricity sector, as the country heavily relies on imported fossil fuels for power generation.
- China is also investing heavily in upgrading other segments of its power sector. It includes transmission and distribution infrastructure in major HVDC and UHVDC projects for transporting renewable electricity from small utility-scale energy projects to demand centers and battery storage capacity to store excess renewable generation while stabilizing the grid.
- For instance, in July 2022, the Baihetan-Jiangsu 800 kV ultra-high-voltage (UHV) direct current power transmission project entered commercial operation, one of the key projects in the larger West-to-East power transmission program. Such developments are expected to help the electricity distribution from utility-scale solar parks.
- Therefore, due to the points mentioned above, the government of China is expected to increase investment in the country's energy sector, which will increase the country's power market.
China Power Industry Overview
The Chinese power market is fragmented. The key players in the market (in no particular order) include Datang International Power Generation Company Limited, China National Electric Engineering Co. Ltd, Xinjiang Goldwind Science & Technology Co. Ltd, Sinohydro Corporation, and Sinovel Wind Group Co. Ltd, among others.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Scope of the Study
- 1.2 Market Definition
- 1.3 Study Assumptions
2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
4 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 China Power Generation and Forecast, in Terawatt, till 2028
- 4.3 Recent Trends and Developments
- 4.4 Government Policies and Regulations
- 4.5 Market Dynamics
- 4.5.1 Drivers
- 4.5.1.1 Increasing Upcoming Investments in Renewable Energy Sector
- 4.5.1.2 Growing Manufacturing Sector Increases Demand For Power
- 4.5.2 Restraints
- 4.5.2.1 Rising Phase Out of Coal-based Power Plants
- 4.5.1 Drivers
- 4.6 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.7 PESTLE Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Power Generation Source
- 5.1.1 Thermal
- 5.1.2 Hydroelectric
- 5.1.3 Nuclear
- 5.1.4 Renewable
- 5.1.5 Other Power Generation Sources
- 5.2 Power Transmission and Distribution (T&D)
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Mergers and Acquisitions, Joint Ventures, Collaborations, and Agreements
- 6.2 Strategies Adopted by Leading Players
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 Datang International Power Generation Company Limited
- 6.3.2 China National Electric Engineering Co. Ltd
- 6.3.3 Xinjiang Goldwind Science & Technology Co. Ltd
- 6.3.4 Sinohydro Corporation
- 6.3.5 Sinovel Wind Group Co. Ltd.
- 6.3.6 Wuxi Suntech Power Co. Ltd.
- 6.3.7 China Yangtze Power Co., Ltd.
- 6.3.8 China National Electric Wire & Cable I/E Corp.
- 6.3.9 State Grid Corporation of China
- 6.3.10 Shandong energy group co. Ltd.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS
- 7.1 Presence of Government Targets to Support Renewable Energy Generation



















