
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1639525
M2M 연결 - 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)M2M Connections - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
M2M 연결 시장 규모는 2025년 400억 달러로 추정되며, 예측 기간(2025-2030년) 동안 7.24%의 CAGR로 2030년에는 567억 3,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예상됩니다.
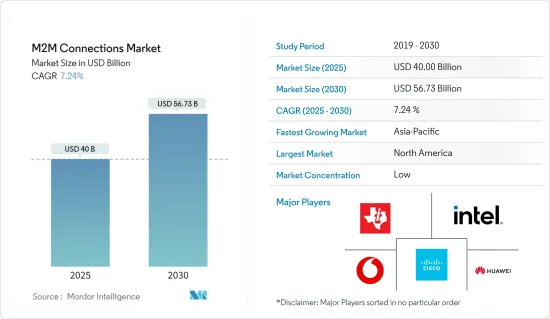
이 산업은 인터넷 이용률의 증가와 규제 환경의 개선으로 인해 예측 기간 동안 성장할 것으로 예상됩니다. 또한, 이종 산업 간 M2M 연결이 증가하고 4G/LTE 및 Bluetooth Smart/BLE와 같은 새로운 통신 기술의 사용이 증가함에 따라 예측 기간 동안 시장이 확대될 것으로 예상됩니다.
주요 하이라이트
- M2M 연결은 지난 수십 년 동안 전 세계 인터넷과 IP 네트워크 시스템의 발전과 함께 변화해 왔습니다. Cisco Systems Inc.에 따르면, 2023년 말까지 M2M 연결 수는 전 세계적으로 147억 개에 달할 것으로 예상되며, 2018-2023년 연결 수의 연평균 성장률은 19%에 달할 것으로 예측됩니다.
- 인간의 개입과 작업 관련 활동을 줄이는 것은 기계 간 통신의 본질적인 장점 중 하나입니다. 자동화된 데이터 수집을 통해 기계 제어 시스템은 이전에는 사람이 개입하여 수행하던 수많은 작업을 수행할 수 있게 되었습니다. 작업자나 기술자는 인간과의 상호작용이 필요한 더 가치 있는 작업을 수행할 수 있게 됩니다.
- 인도와 같은 신흥국들은 M2M의 중요성을 인식하고 있으며, 이에 따라 M2M의 보급 확대에 폭넓게 집중하고 있습니다. 또한, 2022년 2월 인도 정부는 M2M/사물인터넷(IoT)은 세계에서 가장 빠르게 발전하는 기술 중 하나이며 사회, 기업, 소비자에게 풍부하고 유리한 잠재력을 제공한다고 밝혔습니다. 정부의 이니셔티브는 M2M(Machine-to-Machine) 산업의 이용 확대와 기술 혁신을 장려하고 있습니다.
- 머신투머신(M2M) 커넥티비티 시장은 네트워크 커버리지 확대, 무선 통신의 발전, 급속한 디지털화, 산업화, R&D 활동, 투자 급증, 다양한 산업 분야에서의 M2M 커넥티비티 증가에 대한 수요 증가로 인해 긍정적인 영향을 받고 있습니다. 예측 기간 동안 머신투머신(M2M) 커넥티비티 시장에 진입하는 기업들은 커넥티드카 및 스마트 시티에 대한 수요 증가와 시스템 통합업체와의 전략적 파트너십을 통해 혜택을 누릴 수 있을 것으로 보입니다.
- 그러나 프라이버시 및 보안 문제, 복잡한 애플리케이션 개발 등이 이 산업의 지속적인 확장을 저해하는 주요 요인으로 작용하고 있습니다. 또한, 확장성의 부족과 높은 배송 비용으로 인해 시장 성장을 어렵게 만들고 있습니다.
- COVID-19는 M2M 비즈니스에 긍정적인 영향을 미쳤고, 원격 모니터링 및 조작 도구에 대한 수요가 급증하면서 M2M 기술 및 솔루션에 대한 요구가 높아졌습니다. 또한, 이러한 솔루션은 의사와 간호사가 혼자 치료받는 환자를 돌보는 데 도움이 되었습니다.
기계 간 연결 시장 동향
인터넷 이용 확대가 시장 성장을 견인할 것으로 예상
- 인터넷은 주로 종량제가 아닌 고속 연결의 보급으로 근무시간과 근무지의 유연성을 높여주고 있습니다. 모바일 인터넷 기기를 포함한 다양한 방법으로 어디서든 인터넷에 접속할 수 있습니다. 휴대폰, 데이터 카드, 휴대용 게임기, 휴대폰 라우터 등을 통해 사용자는 무선으로 인터넷에 접속할 수 있습니다.
- Speedtest에 따르면 2023년 4월 현재 카타르의 평균 모바일 인터넷 연결 속도는 약 190Mbps로 세계에서 가장 빠른 것으로 나타났습니다. 그 뒤를 이어 아랍에미리트와 마카오가 뒤를 이었으며, 이들 국가는 모두 평균 평균 속도가 170Mbps를 초과하는 것으로 나타났습니다.
- 인터넷과 무선 기술 표준의 향상으로 난방 장비, 전기 계량기, 인터넷에 연결된 소비자 전자제품과 같은 일용품에 텔레메트리의 활용이 확대되고 있습니다. 이전에는 텔레메트리는 제조업, 엔지니어링, 순수 과학 분야에서만 사용되었습니다.
- 기계 간(M2M) 연결에 대한 전 세계적인 관심과 인터넷 사용의 확대는 M2M 연결 시장의 성장을 촉진하는 두 가지 주요 이유입니다. 기계 간(M2M) 연결은 4G/LTE 셀 기술의 보급과 5G 기술의 등장에 의해 더욱 영향을 받을 것입니다.
- ITU에 따르면, 2022년에는 유럽의 인터넷 보급률이 전 세계 모든 지역 중 가장 두드러져 2009년 60% 미만에서 최근 자료가 입수 가능한 해에 89%까지 상승할 것으로 예상됩니다. 인터넷 이용률이 가장 낮은 지역은 아프리카로 40%에 불과했습니다. 같은 해 기준 전 세계 인터넷 접속자 수 기준으로 약 49억 명이 인터넷을 이용하고 있는 것으로 추정됩니다.
- 또한 각국 정부는 인터넷 연결 기술을 확장하고 M2M 연결을 확대하기 위한 새로운 전략을 적극적으로 추진하고 있습니다. 예를 들어, 2022년 11월 유럽의회와 유럽연합(EU) 회원국 관계자들은 위성 인터넷 인프라를 구축하기 위한 60억 유로(61억 8,000만 달러) 규모의 협정 체결이 임박했다고 발표했습니다. 유럽연합 집행위원회는 우주를 통한 연결은 현대 디지털 환경에서 EU의 회복력을 위한 전략적 자산이라고 밝혔습니다. 이는 EU의 경제, 디지털 리더십, 기술 독립성, 경쟁, 사회 발전을 뒷받침하는 것입니다.
북미가 큰 비중을 차지할 것으로 예상
- 이 지역에는 AT&T, Verizon, Cisco를 비롯한 유명 통신 사업자들이 기반을 두고 있으며, 기술 혁신에 대응하기 위해 인프라를 확장하고 개선하기 위해 지속적으로 투자하고 있습니다. 예측 기간 동안 M2M 연결의 채택이 가속화될 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 5G의 등장은 예측 기간 동안 M2M 연결의 성장을 촉진할 것으로 예상되며, M2M 통신의 목적은 다양한 애플리케이션, 낮은 지연, 빠른 속도, 방대한 대역폭을 가진 5G 기술로 성공적으로 해결될 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 자율주행차는 5G 기술을 사용하여 최소한의 대기 시간과 우수한 신뢰성으로 연결됩니다. 또한, QoS가 보장된 네트워킹 기술이 5G 시스템에 의해 제공될 것입니다.
- 또한, 북미의 5G 연결 수(IoT 제외)는 2021년 14%에서 2025년 2억 8,000만 개로 증가하여 전체 모바일 연결 수의 64%를 차지할 것으로 예상됩니다. 캐나다는 그때쯤이면 일본에 이어 4위가 될 것으로 예상되며, 미국의 5G 도입률은 한국에 이어 세계 2위가 될 것입니다.
- 이 부문에서는 여러 주요 기업들이 조사개발, 전략적 제휴, M&A를 통해 기술을 향상시키고 있습니다. 이로 인해 예측 기간 동안 이 지역에서 M2M 연결의 사용이 증가할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 예를 들어, 2022년 12월 캘리포니아에 본사를 둔 사물인터넷(IoT) 및 M2M(Machine-to-Machine) 통신 업체인 Aeris Communications는 Ericsson의 IoT 가속기 및 커넥티드 비히클 클라우드 사업부 인수 계획을 발표했습니다. 이번 계약으로 Aeris와 Ericsson의 IoT 플랫폼은 전 세계 190개국에서 1억 개 이상의 IoT 기기를 연결할 수 있을 것으로 예상됩니다. 또한, 양사의 합병으로 인해 IoT 시장 전체가 급성장할 것으로 예상되며, 4G와 5G의 수요에 IoT가 상당 부분 포함되어 확대될 것으로 예상됩니다.
M2M 연결 산업 개요
M2M 커넥티비티 시장은 경쟁이 치열하고 대규모 제조업체와 소규모 제조업체가 모두 존재하는 것이 특징입니다. 이들 기업들은 생산능력을 높이고 확대되는 시장 수요를 충족시키기 위해 연구개발에 투자하고 있습니다. 북미와 유럽과 같은 기존 시장에서는 경쟁이 더 치열합니다. 생산 및 서비스 확대, 인수합병 증가, 기술 발전 등 다양한 변수의 결과로 이 시장에서의 경쟁 정도는 향후 몇 년 동안 계속 증가할 것으로 보입니다.
- 2022년 5월 - C-DOT와 보다폰 아이디어 리미티드(Vodafone Idea Limited)는 oneM2M의 요구 사항을 충족하기 위해 다른 솔루션 제공업체의 앱과 장치를 평가하고, 구현의 어려움을 해결하기 위해 공동 인증을 부여하기 위해 비독점적으로 협력하고 협력하기로 합의했습니다. 인도 통신부(DOT)와 텔레매틱스 개발 센터(C-DoT)는 인도용 머신 투 머신(M2M) 및 사물인터넷(IoT) 솔루션 협력을 위한 양해각서에 서명했습니다.
- 2022년 2월 - T-Mobile과 Deutsche Telekom AG가 IoT 연결, 플랫폼 관리 및 지원을 위한 기업용 솔루션인 T-IoT를 출시합니다. 모든 국제 연결에 대응할 수 있습니다. 기업들이 이 솔루션을 이용하는 이유는 IoT가 산업을 변화시키고 5G 시대를 준비하는 데 도움이 된다는 것을 알고 있기 때문입니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식의 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 소개
- 조사 가정과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 인사이트
- 시장 개요
- 산업 밸류체인 분석
- 산업의 매력 - Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 공급 기업의 교섭력
- 구매자/소비자의 협상력
- 신규 참여업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업 간의 경쟁 강도
- COVID-19의 시장에 대한 영향 평가
제5장 시장 역학
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 용도 확대 텔레매틱스
- 인터넷 이용 확대
- 모바일 접속수 증가
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 프라이버시와 보안 문제
- 표준화의 결여
제6장 시장 세분화
- 연결 유형별
- 유선
- 무선
- 기술
- 셀룰러 접속
- 저전력 광역(LPWA)
- 단거리
- MAN
- 광역 고정
- 위성
- 최종 이용 산업
- 소매업
- 은행·금융기관
- 통신·IT 산업
- 의료
- 자동차 산업
- 석유 및 가스
- 운송
- 기타
- 지역
- 북미
- 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 라틴아메리카
- 중동 및 아프리카
제7장 경쟁 구도
- 기업 개요
- Vodafone Group
- Texas Instruments Incorporated
- VMWare Inc.
- AT&T Inc.
- Duetsche Telecom AG
- Siera Wireless
- China Mobile Ltd.
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- Intel Corporation
- Gemalto NV(Thales Group)
- Telefonica SA
- Telit Communications
제8장 투자 분석
제9장 시장 전망
ksm 25.02.10The M2M Connections Market size is estimated at USD 40.00 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 56.73 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 7.24% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
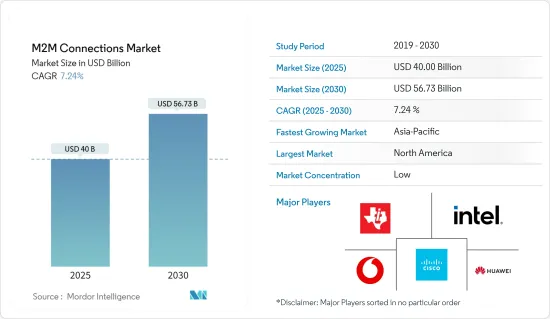
The industry is anticipated to grow over the forecast period due to rising internet usage and a supportive regulatory environment. Also, the market is expected to grow during the forecast period because more M2M connections are being made between different types of businesses and because more new communication technologies like 4G/LTE and Bluetooth Smart/BLE are being used.
Key Highlights
- M2M connections have changed over the past few decades as the global Internet and IP network systems have grown. This has made it easier and more effective to communicate over long distances and between many devices. According to Cisco Systems, by the end of 2023, there will be 14.7 billion M2M connections globally. The forecasted compound annual growth rate of connections from 2018 to 2023 is 19 percent.
- Reducing human involvement and task-related activities is one of the essential benefits of machine-to-machine communication. Due to automated data collection, mechanical machine control systems can now do numerous duties that were formerly done by human intervention. Operators and technicians are freed up to perform higher-value tasks that require human interaction.
- Developing countries like India have identified the importance of M2M and are, therefore, focusing extensively on the increased penetration of M2M. Moreover, in February 2022, the government of India stated that M2M/Internet of Things (IoT) is one of the most rapidly developing technologies worldwide, offering a wealth of advantageous potential for society, businesses, and consumers. The government initiative encourages greater use and innovation in the machine-to-machine (M2M) industry.
- The market for machine-to-machine (M2M) connections is positively impacted by increased demand for expanded network coverage, wireless communication advancements, rapid digitization, industrialization, R&D activities, a surge in investment, and a rise in M2M connections among different industry verticals. During the period of the forecast, those in the machine-to-machine (M2M) connections market would also benefit from the growing demand for connected vehicles and smart cities, as well as from strategic partnerships with system integrators.
- However, issues with privacy and security and complex application development are a few of the primary factors hindering the industry under study from continuing to expand. Also, the lack of scalability and high delivery costs are making it hard to grow the market.
- The COVID-19 pandemic positively impacted the M2M business due to a sudden requirement for remote monitoring and operating tools, leading to increasing requests for M2M technology and solutions. Moreover, these solutions helped doctors and nurses keep an eye on patients who were being treated alone.
Machine to Machine Connections Market Trends
Growing Usage of Internet is Expected to Drive the Market Growth
- The Internet provides more flexibility in terms of working hours and location, due mainly to the proliferation of unmetered high-speed connections. Many methods, including mobile Internet devices, may be used to access the Internet anywhere. Users can access the Internet wirelessly using mobile phones, data cards, portable gaming consoles, and cellular routers.
- According to Speedtest, as of April 2023, Qatar had the fastest average mobile internet connections globally, nearly 190 Mbps. The United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Macau followed, with each of these countries registering average median speeds above 170 Mbps.
- Telemetry usage in daily items like heating units, electric meters, and internet-connected appliances has grown because of the Internet and better wireless technology standards. Previously, telemetry was only used in manufacturing, engineering, and pure science.
- The global focus on machine-to-machine (M2M) connections and the expansion of internet usage are the two main reasons promoting the market's growth for M2M connections. Machine-to-machine (M2M) connections are affected even more by the spread of 4G/LTE cell technologies and the coming of 5G technology.
- According to the ITU, Europe had the most significant internet penetration rate among all world regions in 2022, increasing from just under 60% in 2009 to 89% in the most recent year for which data was available. The lowest internet usage rate, at 40%, was found in Africa. Around 4.9 billion people were reportedly online as of the same year, based on total global internet access.
- Furthermore, governments are actively pursuing new strategies for broadening internet connectivity technologies, thereby increasing M2M connectivity. For instance, in November 2022, officials from the European Parliament and member states of the European Union (EU) announced that they were close to concluding a EUR 6 billion (USD 6.18 billion) agreement to launch a satellite internet infrastructure. The European Commission stated that space-based connectivity is a strategic asset for the resilience of the EU in the modern digital environment. It supports the development of its economy, digital leadership, technical independence, competitiveness, and society.
North America is Expected to Hold Significant Share
- Some of the prominent telecom sector firms are based in the area, including AT&T, Verizon, Cisco, and many more, who are constantly investing in expanding and improving their infrastructure in order to stay up with technological breakthroughs. Over the projected period, it is anticipated to accelerate the adoption of M2M connections.
- The advent of 5G is expected to fuel the growth of M2M connections over the forecast period. M2M communication objectives may be successfully addressed by 5G technology, which has a wide variety of applications, low latency, greater speed, and enormous bandwidth. As an illustration, autonomous cars will use 5G technology to connect with minimal latency and great dependability. Moreover, networking technologies with assured QoS can be offered by the 5G system.
- Furthermore, the number of 5G connections (excluding IoT) in North America will increase from 14% in 2021 to 280 million by 2025, making up 64% of all mobile connections. Canada is expected to rank fourth behind Japan by then, with the United States having the world's second-highest 5G adoption rate, trailing only South Korea.
- Several big companies in the area have been able to improve the technology through research and development, strategic alliances, and mergers and acquisitions. This is expected to increase the use of M2M connections in the area during the projection period.
- For instance, in December 2022, Aeris Communications, a California-based Internet of Things and machine-to-machine (IoT and M2M) communications provider, announced plans to acquire Ericsson's IoT Accelerator and Connected Vehicle Cloud businesses. The agreement is expected to enable Aeris and Ericsson's IoT platforms to link over 100 million IoT devices worldwide in 190 different countries. Additionally, the loT market will grow faster overall owing to the two businesses' merger. The demand for 4G and 5G will include a significant and expanding portion of IoT.
Machine to Machine Connections Industry Overview
The market for M2M connections is highly competitive and distinguished by the abundance of both large- and small-scale manufacturers. These businesses have been investing in R&D to increase their production capacity and satisfy the expanding market demand. In established markets like North America and Europe, competition is more intense. The degree of rivalry in this market will continue to increase over the coming years as a result of a variety of variables, including rising production and service extensions, an increase in acquisitions, and technical advancements.
- May 2022 - C-DOT and Vodafone Idea Limited have agreed to cooperate and work on a non-exclusive basis to evaluate apps and devices from different solution providers to meet oneM2M requirements and to give joint certifications to solve these difficulties in the implementation. The Department of Telecommunications (DOT) and the Center for Development of Telematics (C-DoT) signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) to work together on machine-to-machine (M2M) and Internet of Things (IoT) solutions for India.
- February 2022 - T-Mobile and Deutsche Telekom AG will introduce T-IoT, a corporate solution for IoT connection, platform administration, and support. Businesses using T-IoT can handle all of their international connections because it will be accessible in 188 locations and on 383 networks globally. The firms use the solution because they know that IoT can change their industries and help them get ready for the 5G era.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Industry Value Chain Analysis
- 4.3 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.3.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.3.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.3.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.3.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.3.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.4 Assessment of the Impact of COVID-19 on the Market
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Augmenting Applications Telematics
- 5.1.2 Growing Usage of Internet
- 5.1.3 Increasing Number of Mobile Connections
- 5.2 Market Restraints
- 5.2.1 Privacy and Security Issues
- 5.2.2 Lack of Standardization
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Connection Type
- 6.1.1 Wired
- 6.1.2 Wireless
- 6.2 Technology
- 6.2.1 Cellular Connections
- 6.2.2 Low Power Wide Area (LPWA)
- 6.2.3 Short Range
- 6.2.4 MAN
- 6.2.5 Wide Area Fixed
- 6.2.6 Satellite
- 6.3 End User Industry
- 6.3.1 Retail Sector
- 6.3.2 Banking and Financial Institution
- 6.3.3 Telecom and IT Industry
- 6.3.4 Healthcare
- 6.3.5 Automotive
- 6.3.6 Oil & Gas
- 6.3.7 Transportation
- 6.3.8 Other End User Industries
- 6.4 Geography
- 6.4.1 North America
- 6.4.2 Europe
- 6.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 6.4.4 Latin America
- 6.4.5 Middle East and Africa
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Company Profiles
- 7.1.1 Vodafone Group
- 7.1.2 Texas Instruments Incorporated
- 7.1.3 VMWare Inc.
- 7.1.4 AT&T Inc.
- 7.1.5 Duetsche Telecom AG
- 7.1.6 Siera Wireless
- 7.1.7 China Mobile Ltd.
- 7.1.8 Cisco Systems, Inc.
- 7.1.9 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- 7.1.10 Intel Corporation
- 7.1.11 Gemalto NV(Thales Group)
- 7.1.12 Telefonica SA
- 7.1.13 Telit Communications



















