
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1907226
토탈 실험실 자동화 : 시장 점유율 분석, 업계 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2026-2031년)Total Lab Automation - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
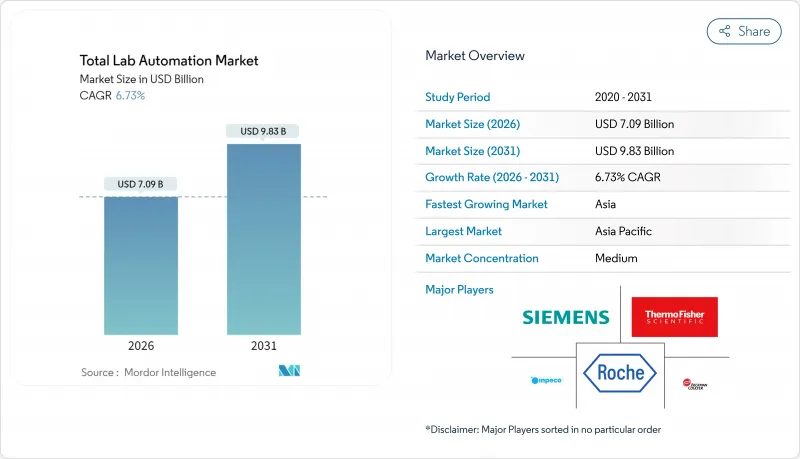
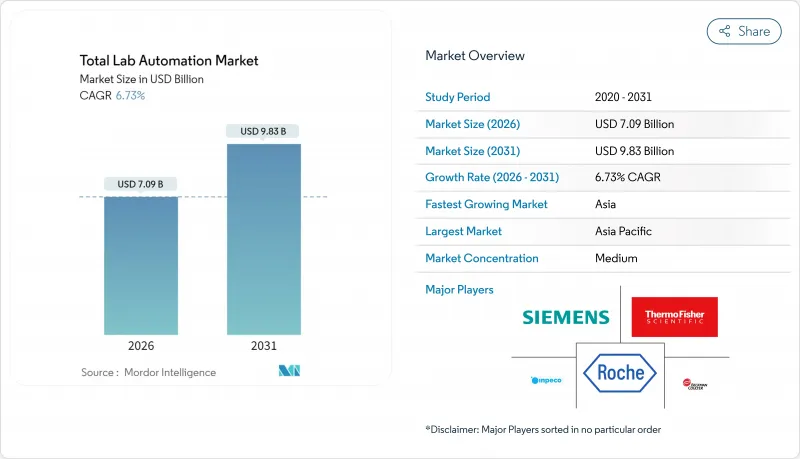
토탈 실험실 자동화 시장은 2025년 66억 5,000만 달러에서 2026년에는 70억 9,000만 달러로 성장해 2026년부터 2031년에 걸쳐 CAGR 6.73%를 나타낼 전망입니다. 2031년까지 98억 3,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예상됩니다.
이 확대는 창약에서 높은 처리량 스크리닝의 급증, 진단 검사량 증가, 임상·연구 현장에서의 에러 최소화의 중요성 증가에 의해 추진되고 있습니다. 로봇 공학, 인공지능, 클라우드 연결성이 완벽하게 통합된 플랫폼에 융합하여 실험실은 워크플로우 최적화, 장비 고장 예측, 대규모 데이터 세트의 실시간 분석이 가능해졌습니다. 모듈 설계로의 전환으로 소규모 시설에서도 완전한 '아일랜드' 시스템을 도입하지 않고 자동화를 도입할 수 있게 되어, 협동 로봇의 보급에 의해 대상 유저층이 확대되고 있습니다. 정밀의료에 대한 관심의 높아짐, 규제 프레임워크의 엄격화, 세포 및 유전자 치료 제조의 급속한 스케일 업도, 토탈 실험실 자동화 시장 전체에 있어서 기기의 업그레이드나 신규 도입을 가속시키고 있습니다.
세계의 토탈 실험실 자동화 시장 동향과 인사이트
다운타임 최소화를 위한 AI 탑재 예지 보전 통합
현재는 수천 개의 데이터 포인트에 걸친 온도, 압력, 진동 및 모터 부하를 사전 능동적으로 분석하여 고장 몇 시간 전에 이상을 감지합니다. 높은 처리량 임상 실험실에서는 이러한 알고리즘을 액체 처리기 및 트럭 시스템에 통합한 결과 예정되지 않은 정지가 최대 30% 감소하고 자산 수명이 15-20% 연장되었다고 보고되었습니다. 서비스 콜 감소, 시약 폐기량 감소, 스케줄 예측 가능성 향상 등으로 자산 이용률이 직접적으로 향상됩니다. 공급업체의 대시보드는 모바일 알림을 통해 기술자에게 정보를 제공하여 수 시간이 아닌 몇 분 안에 많은 응답을 완료합니다. 북미에서는 이러한 성과가 투자 회수 기간을 단축하고 다음 자동화 업그레이드의 강력한 재무적 근거가 되고 있습니다.
임상 진단 분야에서 EU IVDR 주도 업그레이드주기
유럽에서 IVDD에서 IVDR로의 전환에 따라 문서화, 추적성, 성능 실증 요건이 강화되어 검사실에서는 노후화된 시스템을 전체 공정을 기록하는 자동화 솔루션으로 갱신하는 움직임이 가속화되고 있습니다. 미들웨어가 컴플라이언스 보고서를 자동으로 생성하므로 수동 문서 작성 및 감사 위험이 줄어듭니다. 각 공급업체는 바코드 튜브를 클라우드 리포지토리에 연결하는 분석 장비용 트랙을 제공하여 전 분석, 분석 및 후 분석의 각 단계에서 데이터 무결성을 보장합니다. 2028년의 마이그레이션 기한이 다가오고 있는 가운데 독일, 프랑스, 영국에서는 이 규제에 준거한 차세대 플랫폼의 도입이 조달 파이프라인에 잇달아 가세하고 있습니다. 컴플라이언스를 지원하는 하드웨어 소프트웨어를 추구하는 움직임은 실험실 자동화 시장 전반에 걸친 단기 수요를 이끌고 있습니다.
진정한 TLA 아일랜드에는 7자리 설비 투자와 장기 ROI가
전 분석 단계, 코어 랩 및 후 분석 단계를 통합하는 종합적인 아일랜드는 종종 100만 달러를 크게 초과하는 비용이 소요되며 설치에는 9개월 이상이 소요됩니다. 소규모 병원이나 대학 연구소에서는 연간 검사 건수가 적은 경우 이 지출의 정당화가 어렵습니다. 자금 조달 패키지와 시료별 과금 모델이 등장하고 있지만, 많은 지역에서는 여전히 한정적입니다. 예산이 승인된 경우에도 긴 검증 기간과 중복 계획으로 수익 창출이 지연됩니다. 이 상황은 종합 검사 자동화 시장에서 가장 통합된 형식의 단기 보급을 억제합니다.
부문 분석
자동 액체 핸들러는 최대 수익 점유율을 창출했으며 2025년에는 실험실 자동화 시장 전체의 31.45%를 차지했습니다. 그 정밀한 흡인·분주 기능은 진단, 창약, 학술 연구에 있어서 어세이의 신뢰성을 지지하고 있습니다. 첨단 모델은 압력식 레벨 감지와 교차 오염 검사 기능을 갖추고 있어, 하이 스루풋 플랫폼의 핵심으로서의 지위를 강화하고 있습니다. 정밀의료 프로그램의 샘플 수가 증가함에 따라 고속 데크 구성 및 온덱 배양에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있으며,이 카테고리는 종합적인 실험실 자동화 시장을 계속 이끌고 있습니다.
로봇 암은 기본 규모야말로 작은 것, 하드웨어 라인 중 가장 빠른 8.54%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)로 확대 중입니다. 컴팩트한 6축 설계로 바이오 세이프티 캐비닛에 설치할 수 있어 인큐베이터, 이미저, 원심분리기간에 플레이트를 비접촉으로 전달합니다. 새로운 그리퍼 기술은 크라이오바이알이나 세포 배양 플라스크의 취급을 가능하게 하고, 적용 범위를 확대하고 있습니다. 협동 모델에서는 기술자가 수동으로 동작을 가르칠 수 있으므로 프로그래밍 부담을 줄일 수 있습니다. 유연성 향상과 가격 저하로 중규모 실험실 도입이 촉진되어 실험실 자동화 시장 전체의 성장에 박차가 가해지고 있습니다.
2025년 시점에서 LIMS(Labs Information Management System)는 소프트웨어 계층의 실험실 자동화 시장 전체의 37.20%를 차지했습니다. 운영의 핵심 역할을 하는 현대적인 플랫폼은 시료 등록, 증거 관리, 장비 일정 관리, 규제 보고를 관리합니다. 최근 릴리스에는 병목 현상을 지적하고 레시피 조정을 제안하는 AI 모듈이 통합되어 LIMS를 수동 데이터베이스에서 실시간 최적화 엔진으로 변환하고 있습니다. 통합 API는 병원의 전자 기록 및 제조 실행 시스템과 직접 협력하여 LIMS를 디지털 헬스 인프라의 핵심 노드로 자리잡고 있습니다.
과학 데이터 관리 시스템(SDMS)은 9.85%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)로 가장 빠른 성장을 나타낼 전망입니다. 폭발적으로 증가하는 멀티오믹스 데이터 세트 외에도 이미징 및 고 컨텐츠 스크리닝은 스프레드시트 기반 아카이브 용량을 초과합니다. SDMS 솔루션은 자동화된 메타데이터 획득, 버전 관리, 감사 추적을 활용하여 규제 당국과 연구 재현성 요구 사항을 모두 충족합니다. 머신러닝 확장 기능을 통해 생크로마토그램과 유전자 발현 매트릭스에서 몇 분 안에 발견을 추출할 수 있어 의사 결정까지의 시간을 크게 단축할 수 있습니다. 클라우드 스토리지 비용이 지속적으로 감소함에 따라 구독형 SDMS의 도입은 실험실 자동화 시장 전반에 걸쳐 견조한 추풍이 될 전망입니다.
실험실 자동화 시장 보고서는 업계를 다음 부문으로 분류합니다. 장비 유형(자동 액체 처리기 등), 자동화 범위(분석 전 자동화 등), 소프트웨어(실험실 정보 관리 시스템 등), 용도(예 : 창약, 유전체학 등), 최종 사용자(제약 및 생명공학 회사 등), 지역으로 분류됩니다. 시장 예측은 금액 기준(달러)으로 제공됩니다.
지역별 분석
북미는 2025년에 실험실 자동화 시장 전체의 40.35%를 차지했습니다. 이것은 풍부한 임상 연구 예산, 대규모 참조 실험실의 존재, AI 예측 유지 보수의 조기 도입을 지원합니다. 벤더가 제공하는 현장 분석 지원은 가치 창출까지의 시간을 단축합니다. 의료 네트워크 간의 실시간 데이터 교환을 촉진하는 연방 정부의 이니셔티브도 도입을 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 캐나다의 정밀 종양학 추진과 멕시코의 민간 병원 부문 확대가 시너지 효과를 가져오고 지역 수익을 더욱 밀어 올리고 있습니다.
유럽은 두 번째로, 그 성장은 IVDR 전환에 의해 형성됩니다. 이 규제 전환으로 실험실은 데이터 수집과 추적성의 현대화를 촉구하고 있습니다. 독일, 영국, 프랑스가 도입을 주도하고 여러 병원에 서비스를 제공하는 중앙 집중식 코어 랩 허브에 자동화 통합이 진행되고 있습니다. 관민연계의 유전체 프로그램에서는 표준화된 검체처리가 요구되어 바이오뱅킹 자동화에 새로운 활기가 가져오고 있습니다. 동유럽 국가들은 유럽 구조 기금을 활용하여 대륙의 데이터 거버넌스 규칙을 준수하기 위해 레거시 미들웨어의 대체를 진행하고 있으며, 지역 전체의 실험실 자동화 시장에의 침투를 확대하고 있습니다.
아시아태평양은 가장 성장하는 지역이며 2031년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 7.72%를 기록할 전망입니다. 중국의 스마트 병원 구상에는 로봇 도입의 의무화가 포함되어 있으며 국내 생산과 구미 공급업체와의 합작 사업을 촉진하고 있습니다. 일본에서는 제한된 도시 시설에 적합한 공간 절약형 로봇 기술이 중시되고 있습니다. 한편 한국에서는 정부 보조금을 배경으로 높은 처리량형 백신 연구개발이 가속화되고 있습니다. 인도에서는 세계의 CRO(의약품 개발 수탁기관)의 투자와 표준화된 워크플로우를 요구하는 주 수준의 보건 계획 연구소라는 두 가지 촉진요인을 볼 수 있습니다. 지역 공급망이 성숙함에 따라 비용 효율적인 플랫폼이 동남아시아의 신흥 경제권 전체에서 점유율을 확대될 전망입니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 애널리스트 지원(3개월간)
자주 묻는 질문
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사 전제조건 및 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 다운타임 최소화를 위한 AI 탑재 예지보전의 통합
- EU IVDR을 기반으로 한 임상 진단 분야의 업그레이드 주기
- 세포 및 유전자 치료 제조에 있어서 고스루풋 품질 관리의 필요성
- 분산형 및 가상 임상시험 마이크로랩의 출현
- 바이오뱅크의 급증에 따른 초저온 자동화 스토리지 수요 증가
- 정부 자금에 의한 스마트 병원의 정비(GCC 국가 및 중국)
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 진정한 TLA 아일랜드의 7자리 설비 투자액과 장기간의 투자 회수 기간
- 차세대 분석 장치와의 레거시 미들웨어 상호 운용성의 갭
- 사이버 보안 및 데이터 주권 규정 준수 부담
- 정밀 메카트로닉스 부품에 있어서공급 체인의 변동성
- 가치/공급망 분석
- 규제 또는 기술적 전망
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 경쟁 기업 간 경쟁 관계
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 기기별
- 자동 액체 처리 장치
- 로봇 팔
- 자동 저장 및 검색 시스템
- 임상 화학 및 면역 분석기
- 자동 플레이트 핸들러
- 소프트웨어별
- 실험실 정보 관리 시스템(LIMS)
- 과학 데이터 관리 시스템(SDMS)
- 전자 실험 노트(ELN)
- 실험실 정보 시스템(LIS)
- 크로마토그래피 데이터 시스템(CDS)
- 자동화 범위별
- 분석 전 자동화
- 분석 및 코어랩 자동화
- 분석 후 자동화
- 토탈 실험실 자동화 아일랜드
- 용도별
- 임상 진단
- 유전체학
- 신약 개발
- 단백질체학 및 대사체학
- 바이오뱅크 및 샘플 관리
- 최종 사용자별
- 제약 및 바이오테크놀러지 기업
- 계약 연구 및 제조 기관(CRO/CDMO)
- 병원 및 진단 참조 실험실
- 학술 및 정부 기관
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 이탈리아
- 스페인
- 기타 유럽
- 중동
- GCC
- 튀르키예
- 기타 중동
- 아프리카
- 남아프리카
- 나이지리아
- 기타 아프리카
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 인도
- 한국
- 동남아시아
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- Danaher Corp.(Beckman Coulter)
- Roche Diagnostics International AG
- Siemens Healthineers AG
- Abbott Laboratories
- Tecan Group Ltd.
- Agilent Technologies Inc.
- PerkinElmer Inc.(Revvity)
- Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc.
- QIAGEN NV
- Inpeco SA
- Hamilton Company
- Hudson Robotics Inc.
- SPT Labtech Ltd.
- Swisslog Healthcare AG
- BD(Kiestra)
- LabVantage Solutions Inc.
- LabWare Inc.
- Opentrons Labworks Inc.
- Perceptive Automation LLC
- Yaskawa Electric Corp.
- Eppendorf SE
- Formulatrix Inc.
- Biosero Inc.
- Tecan Genomics Inc.
제7장 시장 기회와 향후 전망
KTH 26.01.20The total lab automation market is expected to grow from USD 6.65 billion in 2025 to USD 7.09 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 9.83 billion by 2031 at 6.73% CAGR over 2026-2031.
This expansion is propelled by the surge in high-throughput screening for drug discovery, escalating diagnostic test volumes, and the growing priority of error minimization in clinical and research settings. Robotics, artificial intelligence, and cloud connectivity now converge in fully integrated platforms that allow laboratories to optimize workflows, predict equipment failures, and analyze large datasets in real time. The shift toward modular designs helps smaller facilities embrace automation without committing to full "islands," while the spread of collaborative robots widens the addressable user base. Growing interest in precision medicine, stricter regulatory frameworks, and the rapid scale-up of cell and gene therapy manufacturing are also accelerating equipment upgrades and new installations across the total lab automation market.
Global Total Lab Automation Market Trends and Insights
Integration of AI-Enabled Predictive Maintenance to Minimise Downtime
Proactive analytics now monitor temperature, pressure, vibration, and motor load across thousands of data points, spotting anomalies hours before failure. High-throughput clinical labs report up to 30% fewer unscheduled stoppages and 15-20% longer asset life after embedding these algorithms into liquid handlers and track systems. Service calls drop, reagent waste falls, and scheduling becomes more predictable, directly raising asset utilization. Vendor dashboards keep technicians informed via mobile alerts, allowing many interventions to be completed in minutes rather than hours. In North America, these gains shorten ROI cycles, making a stronger financial case for the next wave of automation upgrades.
EU IVDR-Driven Upgrade Cycle in Clinical Diagnostics
Europe's shift from the IVDD to IVDR has tightened documentation, traceability, and performance evidence requirements, spurring laboratories to replace aging systems with automated solutions that log every step. Middleware now auto-generates compliance reports, reducing manual paperwork and audit risk. Vendors answer with analyzer tracks that link bar-coded tubes to cloud repositories, ensuring data integrity across pre-analytical, analytical, and post-analytical phases. As the 2028 transition milestones draw closer, procurement pipelines in Germany, France, and the United Kingdom are filling with next-generation platforms certified under the regulation. The scramble for compliant hardware and software drives short-term demand across the total lab automation market.
Seven-Figure CAPEX and Lengthy ROI for True TLA Islands
Comprehensive islands that unite pre-analytical, core-lab, and post-analytical stages often cost well above USD 1 million, and installation stretches past nine months. Smaller hospitals and academic labs struggle to justify outlays when annual test counts remain modest. Financing packages and pay-per-sample models are emerging but remain limited in many regions. Where budgets are approved, lengthy validation and redundancy planning delay revenue realization. This dynamic tempers near-term penetration of the most integrated formats within the total lab automation market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- High-Throughput QC Needs for Cell & Gene-Therapy Manufacturing
- Emergence of Decentralised & Virtual Clinical Trial Micro-Labs
- Legacy Middleware Interoperability Gaps with Next-Gen Analyzers
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Automated liquid handlers generated the largest revenue slice, securing 31.45% of total lab automation market share in 2025. Their precise aspiration and dispensing functions underpin assay reliability across diagnostics, drug discovery, and academic research. Advanced models feature pressure-based level sensing and cross-contamination checks, reinforcing their position at the heart of high-throughput platforms. As sample counts rise in precision medicine programs, demand for faster deck configurations and on-deck incubation grows, keeping this category firmly in front of the broader total lab automation market.
Robotic arms, while a smaller base, are expanding at an 8.54% CAGR, the quickest rate among hardware lines. Compact, six-axis designs now mount inside biosafety cabinets, handing off plates between incubators, imagers, and centrifuges without human touch. New gripper technologies handle cryo-vials and cell-culture flasks, widening their scope. Collaborative variants allow technicians to teach motions manually, reducing programming overhead. Greater flexibility and falling prices together unlock adoption in mid-volume labs, adding momentum to the overall total lab automation market growth.
LIMS accounted for 37.20% of total lab automation market size in the software layer during 2025. Acting as an operational backbone, modern platforms manage sample accessioning, chain of custody, instrument scheduling, and regulatory reporting. Recent releases embed AI modules that flag bottlenecks and recommend recipe tweaks, transforming LIMS into real-time optimization engines rather than passive databases. Integration APIs now link directly to hospital electronic records and manufacturing execution systems, positioning LIMS as a central node in digital health infrastructure.
Scientific data management systems posted the fastest advance at 9.85% CAGR. Exploding multi-omics datasets, coupled with imaging and high-content screens, exceed the capacity of spreadsheet-based archives. SDMS solutions lever automated metadata capture, versioning, and audit trails that satisfy both regulators and research reproducibility mandates. Machine-learning extensions pull insights from raw chromatograms or gene-expression matrices in minutes, slashing time to decision. As cloud storage costs continue to fall, subscription-based SDMS uptake should remain a robust tailwind for the total lab automation market.
Lab Automation Market Report Segments the Industry Into Equipment Type (Automated Liquid Handlers, and More), Automation Scope (Pre-Analytical Automation, and More), Software (Laboratory Information Management System, and More), Application (Drug Discovery, Genomics, and More), End-User (Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology Companies and More) and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America held 40.35% of total lab automation market share in 2025, supported by deep clinical research budgets, large reference laboratories, and early uptake of AI predictive maintenance. Equipment vendors provide on-site analytics support, accelerating time to value. Federal initiatives encouraging real-time data exchange across care networks also reinforce adoption. Canada's push for precision oncology and Mexico's expanding private hospital sector add complementary tailwinds, lifting regional revenues further.
Europe ranks second, with growth shaped by the IVDR transition that forces laboratories to modernize data capture and traceability. Germany, the United Kingdom, and France spearhead installations, often integrating automation into centralized core-lab hubs that serve multiple hospitals. Public-private genomics programs call for standardized sample handling, breathing fresh life into biobanking automation. Eastern European nations, leveraging European structural funds, are now replacing legacy middleware to align with continental data-governance rules, broadening regional penetration of the total lab automation market.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing territory, posting a 7.72% CAGR through 2031. China's smart-hospital blueprints include mandated robotic tracks, spurring domestic production and joint ventures with Western suppliers. Japan emphasizes space-efficient robotics that fit cramped urban facilities, while South Korea accelerates high-throughput vaccine R&D supported by government subsidies. India sees a dual driver: global CRO investments and state-level health-scheme laboratories seeking standardized workflows. As regional supply chains mature, cost-effective platforms will likely capture incremental share across emerging Southeast Asian economies.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- Danaher Corp. (Beckman Coulter)
- Roche Diagnostics International AG
- Siemens Healthineers AG
- Abbott Laboratories
- Tecan Group Ltd.
- Agilent Technologies Inc.
- PerkinElmer Inc. (Revvity)
- Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc.
- QIAGEN N.V.
- Inpeco SA
- Hamilton Company
- Hudson Robotics Inc.
- SPT Labtech Ltd.
- Swisslog Healthcare AG
- BD (Kiestra)
- LabVantage Solutions Inc.
- LabWare Inc.
- Opentrons Labworks Inc.
- Perceptive Automation LLC
- Yaskawa Electric Corp.
- Eppendorf SE
- Formulatrix Inc.
- Biosero Inc.
- Tecan Genomics Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Integration of AI-Enabled Predictive Maintenance to Minimise Downtime
- 4.2.2 EU IVDR-Driven Upgrade Cycle in Clinical Diagnostics
- 4.2.3 High-Throughput QC Needs for Cell and Gene-Therapy Manufacturing
- 4.2.4 Emergence of Decentralised and Virtual Clinical Trial Micro-Labs
- 4.2.5 Rising Biobank Volumes Demanding Ultra-Cold Automated Storage
- 4.2.6 Government-Funded Smart-Hospital Build-outs (GCC and China)
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Seven-Figure CAPEX and Lengthy ROI for True TLA Islands
- 4.3.2 Legacy Middleware Interoperability Gaps with Next-Gen Analyzers
- 4.3.3 Cyber-Security and Data-Sovereignty Compliance Burden
- 4.3.4 Supply-Chain Volatility in Precision Mechatronics Components
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory or Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Competitive Rivalry
- 4.6.2 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.3 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.4 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.5 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Equipment Type
- 5.1.1 Automated Liquid Handlers
- 5.1.2 Robotic Arms
- 5.1.3 Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems
- 5.1.4 Clinical Chemistry and Immuno-Analyzers
- 5.1.5 Automated Plate Handlers
- 5.2 By Software
- 5.2.1 Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS)
- 5.2.2 Scientific Data Management Systems (SDMS)
- 5.2.3 Electronic Lab Notebooks (ELN)
- 5.2.4 Laboratory Information Systems (LIS)
- 5.2.5 Chromatography Data Systems (CDS)
- 5.3 By Automation Scope
- 5.3.1 Pre-Analytical Automation
- 5.3.2 Analytical / Core-Lab Automation
- 5.3.3 Post-Analytical Automation
- 5.3.4 Total Lab Automation (TLA) Islands
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Clinical Diagnostics
- 5.4.2 Genomics
- 5.4.3 Drug Discovery
- 5.4.4 Proteomics and Metabolomics
- 5.4.5 Biobank and Sample Management
- 5.5 By End-User
- 5.5.1 Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology Companies
- 5.5.2 Contract Research and Manufacturing Organizations (CROs / CDMOs)
- 5.5.3 Hospitals and Diagnostic Reference Labs
- 5.5.4 Academic and Government Institutes
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Argentina
- 5.6.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.3 Europe
- 5.6.3.1 Germany
- 5.6.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3.3 France
- 5.6.3.4 Italy
- 5.6.3.5 Spain
- 5.6.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.4 Middle East
- 5.6.4.1 GCC
- 5.6.4.2 Turkey
- 5.6.4.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.5 Africa
- 5.6.5.1 South Africa
- 5.6.5.2 Nigeria
- 5.6.5.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.6 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.6.1 China
- 5.6.6.2 Japan
- 5.6.6.3 India
- 5.6.6.4 South Korea
- 5.6.6.5 Southeast Asia
- 5.6.6.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- 6.4.2 Danaher Corp. (Beckman Coulter)
- 6.4.3 Roche Diagnostics International AG
- 6.4.4 Siemens Healthineers AG
- 6.4.5 Abbott Laboratories
- 6.4.6 Tecan Group Ltd.
- 6.4.7 Agilent Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.8 PerkinElmer Inc. (Revvity)
- 6.4.9 Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc.
- 6.4.10 QIAGEN N.V.
- 6.4.11 Inpeco SA
- 6.4.12 Hamilton Company
- 6.4.13 Hudson Robotics Inc.
- 6.4.14 SPT Labtech Ltd.
- 6.4.15 Swisslog Healthcare AG
- 6.4.16 BD (Kiestra)
- 6.4.17 LabVantage Solutions Inc.
- 6.4.18 LabWare Inc.
- 6.4.19 Opentrons Labworks Inc.
- 6.4.20 Perceptive Automation LLC
- 6.4.21 Yaskawa Electric Corp.
- 6.4.22 Eppendorf SE
- 6.4.23 Formulatrix Inc.
- 6.4.24 Biosero Inc.
- 6.4.25 Tecan Genomics Inc.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment

















