
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1685858
인도의 작물 보호 화학제품 시장(2025-2030년) : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계 및 성장 예측India Crop Protection Chemicals - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
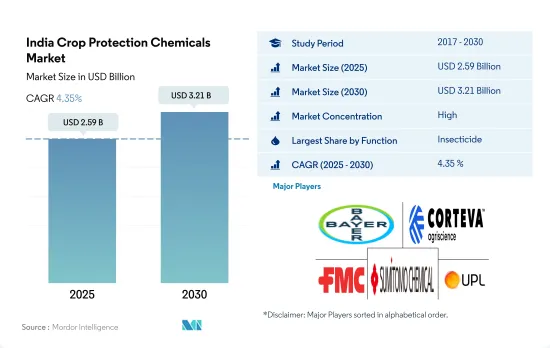
인도의 작물 보호 화학제품 시장 규모는 2025년에 25억 9,000만 달러로 추정되고, 2030년에는 32억 1,000만 달러에 이를 전망이며 예측 기간(2025-2030년) 동안 CAGR은 4.35%로 예측됩니다.
살충제 시장은 병해충 증가에 의해 견인
- 인도의 작물 보호 화학제품 시장은 오랜 세월에 걸쳐 일관된 성장을 이루었고, 2022년 시장 규모는 23억 달러에 달하였습니다.
- 가장 많이 사용되는 작물 보호 화학물질은 살충제로, 2022년 시장 점유율은 72.5%, 그 다음 제초제가 13.4%, 살균제가 8.9%였습니다. 이는 다양한 유형의 작물에 주는 경제적 손해에 기인하고 있습니다.
- 2022년에 살선충제의 점유율은 2.6%였습니다. 이러한 농약은 이 나라에서 재배되는 다양한 경제적으로 중요한 작물에 영향을 미치기 때문에 시장 성장의 여지가 큽니다. 예를 들어 쌀은 Meloidogyne graminicola의 영향을 받기 쉬우며 해충으로 인해 연간 2억 9,610만 달러의 경제 손실을 초래하고 있습니다.
- 마찬가지로, 인도의 코다그 주 북부에서는 300에이커에 이르는 약 40-45개의 농원이 연체 동물의 침입에 의해 큰 손실을 입고 있습니다.
- 국내에서의 병해충의 발생률 증가, 농작물의 생산성 향상의 필요성 등의 요인에 의해 시장은 예측 기간 중에 CAGR 4.6%를 나타낼 것으로 추정 및 예측됩니다.
인도 작물 보호 화학제품 시장 동향
주요 작물에서 다양한 병해충으로 인한 농작물 손실의 상당한 증가와 높은 생산성의 필요성이 헥타르 당 농약 소비에 기여
- 인도의 다양한 기후는 농업 부문이 다양한 작물을 재배하기 위한 호조건을 만들어 내고 있습니다. 그러나, 다양한 기후가 가져오는 혜택의 한편으로, 잡초, 해충, 균류에 의한 병해라고 하는 큰 과제에도 직면하고 있습니다. 이러한 과제에 의해 연간 작물의 손실은 증가하고 있습니다.
- 이러한 문제에 대처하기 위해, 농가는 농약에 점점 의지하고 있습니다.
- 잡초는 인도의 농업 부문에 큰 위협을 가져오고, 쌀, 밀, 옥수수 등 주요 작물에서 큰 손실을 가져오고 있습니다. 수작업에 의지하는 제초의 비용이 상승하면서 농가는 제초제에 의지하고 있습니다. 그러나, 제초제에 내성을 갖는 잡초의 출현이 문제가 되고 있어 헥타르 당 제초제 살포량이 증가할 가능성이 있습니다.
- 살충제의 헥타르 당 소비량은 지정된 기간 동안 일정했습니다. 살충제는 해충 제거 수단으로 부상해 왔습니다. 이러한 해충은 농업의 수량에 큰 위협을 가져오고, 작물의 대폭적인 손실로 이어집니다.
- 기타 요인으로서, 농업 활동 증가나 농작물 증산 요구가 국내의 1헥타르 당 살충제 소비량을 증가시키고 있습니다.
농업 부문과 농촌 경제 개선에 대한 정부의 지원이 가격에 미치는 영향
- 사이퍼메트린은 합성 피레스로이드계로, 벼룩 딱정벌레, 노린재, 바퀴벌레, 흰개미, 무당벌레, 전갈, 옐로우 재킷의 제거에 사용됩니다. 인도에서는 사이퍼메트린은 양배추, 밀, 면화, 쌀, 사탕수수, 가지, 해바라기, 오크라 등, 지정된 8가지 유형의 작물용으로 사용하기 위해 CIBRC에 의해 등록되었습니다.
- 아트라진은 인도의 옥수수와 벼농사에서 에키노크로아, 엘레우신속, 청비름 등의 활엽 잡초나 벼과 잡초의 방제에 널리 사용되는 제초제입니다. 이 제초제는 2022년에 1만 3,500달러로 평가되었습니다.
- 말라티온은 유기인계 살충제입니다. 2022년에는 1만 2,500달러로 평가되었습니다. CIBRC 가이드라인에서 말라티온은 수수, 완두콩, 피마자, 해바라기, 오크라, 가지, 콜리플라워, 무, 순무, 토마토, 사과, 망고에만 사용이 허용됩니다.
- 프로피네브는 접촉 살균제입니다. 2022년에는 1톤당 3,500달러로 평가되었습니다. 가지 끝 마름병, 벅아이 부패병, 노균병, 과실반점병, 갈색반점병, 협엽반점병 등 다양한 병해의 방제에 사용됩니다.
- 인도 정부는 농촌 경제의 부흥과 농가의 수입 증가를 위해 지속적으로 예산 지원을 실시했습니다.
인도 작물 보호 화학제품 산업의 개요
인도의 작물 보호 화학제품 시장은 상당히 통합되어 있으며 상위 5개 회사에서 74.59%를 차지합니다. 이 시장 주요 기업은 Bayer AG, Corteva Agriscience, FMC Corporation, Sumitomo Chemical Co. Ltd, UPL Limited입니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 주요 요약과 주요 조사 결과
제2장 보고서 제안
제3장 소개
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
- 조사 방법
제4장 주요 산업 동향
- 1헥타르 당 농약 소비량
- 유효 성분의 가격 분석
- 규제 프레임워크
- 인도
- 밸류체인과 유통채널 분석
제5장 시장 세분화
- 기능
- 살균제
- 제초제
- 살충제
- 연체동물 구제제
- 살선충제
- 살포 형태
- 약제 살포
- 잎면 살포
- 훈증
- 종자 처리
- 토양 처리
- 작물 유형
- 상업 작물
- 과일 및 야채
- 곡물
- 콩류 및 유지종자
- 잔디 및 관상용
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 주요 전략적 움직임
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 상황
- 기업 프로파일
- ADAMA Agricultural Solutions Ltd.
- BASF SE
- Bayer AG
- Corteva Agriscience
- FMC Corporation
- Gharda Chemicals Ltd
- PI Industries
- Sumitomo Chemical Co. Ltd
- Syngenta Group
- UPL Limited
제7장 CEO에 대한 주요 전략적 질문
제8장 부록
- 세계 개요
- 개요
- Porter's Five Forces 분석 프레임워크
- 세계의 밸류체인 분석
- 시장 역학(DROs)
- 정보원과 참고문헌
- 도표 일람
- 주요 인사이트
- 데이터 팩
- 용어집
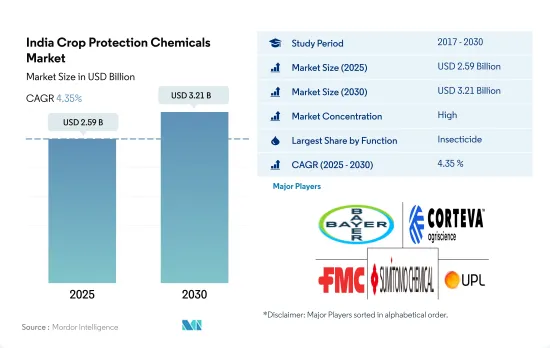
The India Crop Protection Chemicals Market size is estimated at 2.59 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 3.21 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 4.35% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
The market for pesticides is driven by increasing pest and disease incidence
- The Indian crop protection chemicals market experienced consistent growth over the years, with a market value of USD 2.3 billion in 2022, driven by factors such as increasing population, rising food demand, and the need to protect crops from pests, diseases, and weeds.
- Insecticides are the most used crop protection chemicals, with a market share of 72.5% in 2022, followed by herbicides and fungicides, with a market share of 13.4% and 8.9%, respectively. This is attributed to the economic damage that insect pests can cause in a variety of crop types. Aphids, leafhoppers, stem borers, and armyworms are the dominant insect pests that affect the production of major crops in India.
- Nematicides accounted for a share of 2.6% in 2022. Although the current market share is relatively less, these pesticides have higher scope for market growth as plant parasitic nematodes are known to cause an annual yield loss of 21.3% in India, which amounts to USD 1.58 billion annually, affecting various economically important crops grown in the country. For instance, rice (the most grown crop in India) is susceptible to root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola,leading to annual economic losses of 296.1 million.
- Similarly, around 40-45 plantations spanning 300 acres of land in the northern parts of Kodagu, India, have suffered significant losses due to mollusk infestations. However, the farmers in Kodagu have achieved a 90% reduction in the infestation by primarily utilizing molluscicides, which may result in market growth.
- Due to factors like increasing pest and disease incidence in the country and the need for higher crop productivity, the market is estimated to register a CAGR of 4.6% during the forecast period.
India Crop Protection Chemicals Market Trends
A significant increase in crop losses by various pests and diseases in major crops and the need for higher production contributed to the per-hectare pesticide consumption
- India's diverse climate creates favorable conditions for the agricultural sector to cultivate a wide range of crops. However, alongside the benefits of climatic diversity, the sector also faces significant challenges from weeds, insect pests, and fungal diseases. These challenges have resulted in substantial annual crop losses, with weeds accounting for 45% of the losses, insects for 35%, and fungal diseases for 20%.
- In response to these issues, farmers have increasingly relied on pesticides as their primary tool to combat crop losses. As a result, there has been limited change in the overall consumption of pesticides per hectare.
- Weeds pose a significant threat to the Indian agricultural sector, resulting in substantial losses for major crops such as rice, wheat, and maize. To mitigate these losses, farmers have increasingly relied on herbicides as manual weeding has become costlier due to labor shortages and rising wages. However, the emergence of herbicide-resistant weeds has become a concerning issue, leading to a potential escalation in the application of herbicides per hectare.
- The per-hectare consumption of insecticides has remained constant over the specified period. Insecticides have emerged as vital tools in enhancing crop production by combating the detrimental impact of insect pests, including stink bugs, loopers, armyworms, aphids, and whiteflies. These pests pose significant threats to agricultural yields, leading to substantial crop losses. To counter these sucking insect pests and boost their crop productivity, farmers are increasingly relying on the use of insecticides.
- Other factors like increased agricultural activities and the need for higher crop production are increasing per-hectare pesticide consumption in the country.
Influence of Government support for the improvement of the agriculture sector and the rural economy on prices
- Cypermethrin is a synthetic pyrethroid used to control flea beetles, boxelder bugs, cockroaches, termites, ladybugs, scorpions, and yellow jackets. It was priced at USD 21.0 thousand in 2022. In India, cypermethrin is registered by CIBRC for use in eight specified crops, such as cabbage, wheat, cotton, rice, sugarcane, brinjal, sunflower, and okra.
- Atrazine is an herbicide widely used for control of broadleaf and grassy weeds like Echinocloa, Elusine spp., and Amaranthus viridis in maize and rice crops in India. The herbicide was valued at USD 13.5 thousand in 2022. India is the largest importer of Atrazine technical in the world and imports majorly from China, Italy, and Israel.
- Malathion is an organophosphate insecticide. It was valued at USD 12.5 thousand in 2022. It is used to control aphids, thrips, mites, scales, borers, worms, leaf miners, fleas, grasshoppers, bugs, and maggots. As per guidelines of CIBRC, malathion is permitted to be used only in sorghum, pea, soybean, castor, sunflower, bhindi, brinjal, cauliflower, radish, turnip, tomato, apple, mango, and grape crops.
- Propineb is a contact fungicide. It was valued at USD 3.5 thousand per metric ton in 2022. It is used to control various diseases like scab early and late blight dieback, buckeye rot, downy mildew, fruit spots, and brown and narrow leaf spot diseases in apple, potato, chili, and tomato crops.
- The Government of India has been continuously providing budgetary support toward reviving the rural economy and increasing the farmers' income. Several measures and initiatives were proposed and announced during the FY22 budget for the improvement of the agriculture sector and the rural economy. This will further influence the prices of crop protection chemicals in the country.
India Crop Protection Chemicals Industry Overview
The India Crop Protection Chemicals Market is fairly consolidated, with the top five companies occupying 74.59%. The major players in this market are Bayer AG, Corteva Agriscience, FMC Corporation, Sumitomo Chemical Co. Ltd and UPL Limited (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Consumption Of Pesticide Per Hectare
- 4.2 Pricing Analysis For Active Ingredients
- 4.3 Regulatory Framework
- 4.3.1 India
- 4.4 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD and Volume, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Function
- 5.1.1 Fungicide
- 5.1.2 Herbicide
- 5.1.3 Insecticide
- 5.1.4 Molluscicide
- 5.1.5 Nematicide
- 5.2 Application Mode
- 5.2.1 Chemigation
- 5.2.2 Foliar
- 5.2.3 Fumigation
- 5.2.4 Seed Treatment
- 5.2.5 Soil Treatment
- 5.3 Crop Type
- 5.3.1 Commercial Crops
- 5.3.2 Fruits & Vegetables
- 5.3.3 Grains & Cereals
- 5.3.4 Pulses & Oilseeds
- 5.3.5 Turf & Ornamental
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and analysis of Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 ADAMA Agricultural Solutions Ltd.
- 6.4.2 BASF SE
- 6.4.3 Bayer AG
- 6.4.4 Corteva Agriscience
- 6.4.5 FMC Corporation
- 6.4.6 Gharda Chemicals Ltd
- 6.4.7 PI Industries
- 6.4.8 Sumitomo Chemical Co. Ltd
- 6.4.9 Syngenta Group
- 6.4.10 UPL Limited
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR CROP PROTECTION CHEMICALS CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms



















