
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1687233
웨어러블 관성 센서 시장 : 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Wearable Inertial Sensors - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
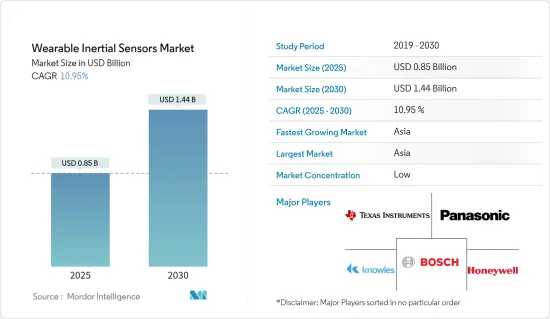
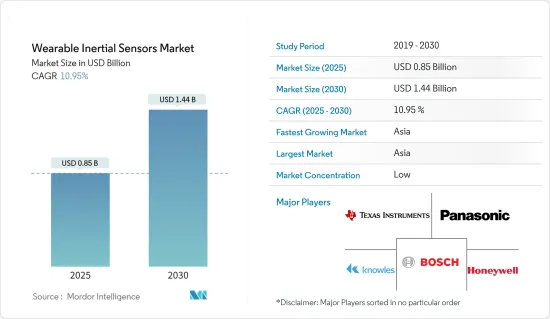
세계의 웨어러블 관성 센서 시장 규모는 2025년 8억 5,000만 달러로 추정되며, 예측 기간 중(2025-2030년) CAGR 10.95%로, 2030년에는 14억 4,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예측됩니다.
웨어러블 관성 센서는 관성 측정 유닛(IMU)으로도 알려져 있으며, 하나 이상의 가속도계, 자이로스코프 및 자력계를 사용하여 운동 관련 파라미터를 측정하도록 설계된 전자 장치입니다. 이 센서는 작고 가볍고 일상 활동 중에 움직임을 추적하기 위해 개인이 쉽게 장착 할 수 있습니다.
주요 하이라이트
- 자이로스코프, 가속도계, 지자기 센서를 포함한 웨어러블 관성 센서는 지난 10년간 크게 발전했습니다. 성능, 소형화, 비용 절감으로 웨어러블 관성 센서는 스마트폰과 스마트 워치 등 여러 일상생활 제품에 내장되어 있습니다.
- 웨어러블 관성 센서의 응용 분야는 다양합니다. 예를 들어, 소비자 시장에서는 활동 모니터링과 피트니스 트래킹이 널리 채택되고 있습니다. 웨어러블 관성 센서의 신호 데이터를 기반으로 한 다양한 의료 애플리케이션도 개발되었으며, 낙상 위험 평가, 낙상 감지, 파킨슨 병의 조기 발견 등이 있습니다. Parkinson's Foundation에 따르면 2016년 추정 파킨슨병 환자 수는 약 100만 명이었습니다. 이 수는 2030년까지 약 180만 명으로 증가할 것으로 예측됩니다. 이러한 개발은 조사 대상 시장 수요를 높이고 있습니다.
- 전 세계적으로 도시화가 진행됨에 따라 휴대성, 한 장치에 여러 기능, 컴팩트하고 타임 스케줄 등 소비자의 요구를 보다 잘 충족할 수 있는 고도로 미학적으로 매력적인 소비자용 전자제품에 대한 수요가 대폭 증가하고 있습니다. 또한 최근 몇 년동안 가처분 소득 증가와 디지털 솔루션 침투로 인해 세계적으로 상당한 수의 밀레니얼 세대가 스마트 워치를 포함한 다양한 유형의 웨어러블을 신속하게 채택하고 있습니다.
- Apple, Samsung, Fitbit 등 대부분의 웨어러블 디바이스 제공업체는 실시간으로 건강 상태를 업데이트하는 고급 건강 모니터링 기능을 통합하여 웨어러블이 노인층에서 더욱 채용되고 있습니다. 헬스케어 웨어러블에 대한 수요 증가를 고려해, 신규 진출기업은 혁신적인 솔루션을 발표함으로써 조사 대상 업계에서 지속적으로 존재감을 나타내고 있으며, 이것도 조사 대상 시장의 성장에 플러스의 영향을 주고 있습니다.
- 그러나 웨어러블 제품의 고비용과 첨단 지역 전체의 엄격한 규제 준수가 조사 시장의 과제가 되고 있습니다. 또한 세계 공통 표준 부족으로 인한 상호 운용성 우려도 조사 대상 시장의 성장을 억제하는 주요 요인 중 하나일 것으로 예상됩니다.
웨어러블 관성 센서 시장 동향
소비자 일렉트로닉스가 크게 성장
- 새로운 동향인 관성 웨어러블 센서 기술은 소비자 일렉트로닉스를 일상 활동에 통합하여 신체의 어느 부분에도 장착할 수 있는 기능으로 라이프 스타일의 변화에 대응합니다. 가전 산업에서의 웨어러블 관성 센서의 동향은 인터넷 연결 등의 요인에 의해 견인되고 있습니다. ITU에 따르면 세계 인터넷 사용자 수는 2023년 54억 명에 달했습니다.
- 센서, 특히 압력 센서 및 액티베이터의 진보와 소형화가 진행되고 있는 것도 가전 업계에서의 웨어러블 관성 센서 시장의 범위를 확대하고 있습니다. 센서의 생체 적합성이 높아짐에 따라 건강 관리 및 피트니스 활동에 대한 사용도 크게 증가하고 있습니다. 이로 인해 지난 몇 년동안 웨어러블 디바이스의 판매량이 크게 증가하고 있습니다. 시스코에 따르면 2020년 8억 3,500만대에서 2022년에는 11억 500만대가 되는 커넥티드 웨어러블 디바이스의 성장은 특히 건강 관리 용도에서 큰 기대를 받고 있습니다. 많은 기업들이 첨단 미세전기기계 시스템(MEMS)과 디지털 센서 개발에 투자하고 있으며, 그 크기는 더욱 축소되어 폭넓은 시장 응용을 커버하고 있습니다.
- 마이크로 전기 기계 센서(MEMS)와 가속도계는 전자 안정 제어 및 에어백 전개에 사용됩니다. 관성 측정 장치(IMU) 또는 IMU(MEMS 가속도계와 MEMS 자이로스코프를 조합한 것)는 기술의 진보에 따라 웨어러블용으로 개발되어, GPS이나 관성 측정 장치(IMU)(가속도계, 자이로스코프, 지자기계로 구성) 센서 등, 일상적으로 사용되고 있는 소비자용 전자 기기의 영향을 받아 따라서 피트니스 추적 웨어러블은 이러한 센서를 중심으로 전개됩니다.
- 예를 들어 Nintendo Switch Labo의 Joy-con은 가속도계와 자이로스코프에 기본 센서를 탑재하고 있습니다. Joy-con과 골판지를 조합하여 로봇과 같은 인공적인 웨어러블을 만들어 게임 기능에 응용합니다. 이것은 일반적으로 단순화된 커스텀 웨어러블 기술로 몰입형 경험을 함으로써 미래 세대(젊은 연령층만큼 기술에 친숙한)의 벽을 깨는 Nintendo의 방법입니다.
- 가속도계는 모션 센서로 웨어러블에 사용됩니다. 중력과 직선과 같은 가속도 브랜드는 그 센싱 능력을 보여줍니다. 한편, 측정 능력을 통해 측정 데이터를 다양한 목적으로 프로그래밍할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 달리기를 하는 사용자는 최고 속도의 출력과 가속도에 액세스할 수 있습니다. 또한 가속도계는 스마트 워치와 손목 밴드와 같이 수면 패턴을 추적할 수 있기 때문에 가전 분야에서 웨어러블 모션 센서 수요를 견인하고 있습니다.
아시아태평양이 시장을 독점
- 아시아태평양은 웨어러블 디바이스와 디지털 기술의 보급이 진행되고 소비자층이 두껍기 때문에 예측 기간 중에 현저한 성장이 예상됩니다. 이러한 전망을 고려하여 OEM 제조업체도 IMU(관성 측정 장치(IMU))나 MEMS 기술의 확대를 향해 상당한 지원을 실시해, 새롭게 개발된 제품의 보급을 강화하고 있습니다. 게다가 중국, 대만 등의 대두에 의한 일렉트로닉스 산업의 진화도 조사 대상 시장의 성장에 기여하고 있습니다.
- 웨어러블 관성 센서 시장은 중국에서 가장 큰 급성장 시장 중 하나가되었습니다. 스마트 워치, 피트니스 트래커, 가상현실(VR) 헤드셋, 모션 캡처 슈트는 모두 움직임과 방향을 감지할 수 있는 센서인 웨어러블 관성 센서를 사용합니다. 중국에서의 웨어러블 관성 센서 시장의 급성장은 이 나라가 웨어러블 기술을 받아들이고 있으며, 건강 지향의 인구가 확대되고 있는 것이 주된 요인이 되고 있습니다.
- 웨어러블 기술의 인기 증가와 건강과 피트니스를 측정하는 수요 증가는 모두 최근 인도의 웨어러블 관성 센서 시장의 거대한 상승에 기여하고 있습니다. 가속도계, 자이로스코프, 자력계 등의 웨어러블 관성 센서는 웨어러블 디바이스에 움직임과 방향에 대한 정보를 제공하는 데 필수적이며, 이 나라의 고객, 기업, 의료 전문가에게 인기가 있습니다.
- 기술적으로 숙련된 환경과 편의성과 혁신성을 중시하는 사회가 일본의 웨어러블 관성 센서 시장의 일관된 성장을 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 웨어러블 관성 센서는 헬스케어, 스포츠, 엔터테인먼트, 게임 산업 등 다양한 분야에서 이용되고 있습니다. 일반적인 건강 상태 모니터링 및 강화를 위한 관성 센서가 있는 웨어러블의 사용은 일본의 노인 인구와 건강과 웰빙에 대한 강한 관심으로 가속화되고 있습니다.
- 한국의 기술에 익숙한 인구와 웨어러블 기술에 대한 관심이 높아지면서 한국의 웨어러블 관성 센서 시장은 최근 급속히 확대되고 있습니다. 스마트 워치, 피트니스 밴드, 가상현실 헤드셋 및 기타 웨어러블 의료기기는 모두 웨어러블 관성 센서를 어느 정도 탑재하고 있습니다. 엔터테인먼트, 건강, 피트니스에 중점을 두고 첨단기술을 채택함으로써 한국 시장에서는 이러한 가제트 수요가 증가하고 있습니다.
- 기타 아시아태평양의 관성 센서 시장은 싱가포르, 호주, 말레이시아, 기타 아시아태평양에서 웨어러블 센서 수요를 감지하는 국가 등을 포함하여 피트니스 및 웰니스에 대한 관심 증가, 고령화 인구 증가, 기술과 헬스케어의 진보로 지난 몇 년간 꾸준히 증가
웨어러블 관성 센서 산업 개요
R&D 투자, 파트너십 및 제휴는 이 시장에서 활동하는 공급업체의 전략적 초점의 일부가 될 것으로 예상됩니다. 이 외에도 기술 혁신에 대한 투자와 전략적 제휴를 통한 시장 확대도이 시장에서 공급업체의 초점이 될 것으로 보입니다. 유통 채널과 고객층에 대한 액세스는 시장에서 사업을 전개하는 선도적 인 공급업체만큼 높습니다. 이 외에도 공급업체는 제휴 및 인수를 통해 시장에서의 능력 확대에 주력하는 경향이 있습니다. 전반적으로 경쟁업체 간의 적대관계는 높아질 것으로 예상됩니다. 시장의 주요 공급업체로는 Texas Instruments Incorporated, Panasonic Corporation, Bosch Sensortec GmbH, Knowles Electronics, Honeywell International Inc. 등이 있습니다.
2023년 1월, Quadric과 OSRAM은 가시광 및 적외광용 CMOS 센서의 최첨단 Mira 제품군과 쿼드릭의 최첨단 Chimera GPNPU 프로세서를 결합한 통합 감지 모듈을 개발하기 위한 협력 파트너십을 수립했습니다. 통합된 초저전력 모듈을 통해 웨어러블 기술로 새로운 유형의 스마트 감지를 사용할 수 있습니다.
Analog Devices는 2022년 12월 오레곤 건강과학대학(OHSU)과 공동으로 청소년의 정신건강 위기 증가에 대처하기 위해 중요한 정신건강 지표를 감지하는 스마트 워치를 개발했습니다. 세계 최초의 유일무이 프로젝트에 대한 협력과 마찬가지로 OHSU는 ADI의 혁신적인 기술과 제품을 활용하여 급증하는 세계 정신 위생 위기에 대처하여 사람들의 삶을 구하고 개선하고 풍요롭게 합니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트·지원
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 인사이트
- 시장 개요
- 업계의 매력도 - Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 소비자의 협상력
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계의 강도
- COVID-19와 거시 경제 동향의 업계에 대한 영향
- 기술 스냅샷
제5장 시장 역학
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 건강 의식의 고조
- 웨어러블 피트니스 모니터 수요 증가
- 급속한 기술의 진보
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 보안상의 우려
- 디바이스의 고비용
제6장 시장 세분화
- 제품 유형별
- 스마트 워치
- 피트니스 밴드/액티비티 트래커
- 스마트웨어
- 스포츠 기어
- 기타
- 최종 사용자별
- 헬스케어
- 스포츠 및 피트니스
- 가전
- 엔터테인먼트 미디어
- 정부 및 유틸리티
- 기타
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 아시아
- 중국
- 인도
- 일본
- 한국
- 호주 및 뉴질랜드
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 사우디아라비아
- 이스라엘
- 라틴아메리카
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 멕시코
- 북미
제7장 경쟁 구도
- 기업 프로파일
- Texas Instruments Incorporated
- Panasonic Corporation
- Bosch Sensortec GmbH
- Knowles Electronics
- Honeywell International Inc.
- TE Connectivity Ltd
- Analog Devices Inc
- General Electric Co.
- AMS osram AG
- STMicroelectronics NV
- Infineon Technologies AG
- NXP Semiconductors NV
- InvenSense, Inc.(TDK Corporation)
제8장 투자 분석
제9장 시장 기회와 앞으로의 동향
JHS 25.04.01The Wearable Inertial Sensors Market size is estimated at USD 0.85 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 1.44 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 10.95% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Wearable inertial sensors, also known as inertial measurement units (IMUs), are electronic devices designed to measure motion-related parameters using one or more accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers. These sensors are small, lightweight, and can be effortlessly worn by individuals to track their movements during daily activities.
Key Highlights
- Wearable inertial sensors, including gyroscopes, accelerometers, and magnetometers, have developed considerably during the last decade. Through performance, miniaturization, and cost drop, wearable inertial sensors have been integrated into several daily life products, such as smartphones and smartwatches.
- The fields of application of wearable inertial sensors are numerous. For instance, activity monitoring and fitness tracking are widely employed in the consumer market. Various medical applications based on signal data from wearable inertial sensors have been developed, including fall risk assessment, fall detection, and early identification of Parkinson's disease. According to the Parkinson's Foundation, in 2016, the estimated number of Parkinson's disease patients was around 1 million. This number is predicted to increase to approximately 1.8 million by 2030. Such developments raise the demand for the market studied.
- The rising urbanization across the globe has significantly driven the demand for advanced, aesthetically appealing consumer electronic products that can better serve the consumers' requirements, such as portability, multiple features in one device, and compact and time schedules. Moreover, in recent years, a sizable number of millennials globally has been quick to adopt wearables of different types, including smartwatches, owing to the increased disposable income and the growing penetration of digital solutions.
- Wearables are further witnessing a surge in adoption among the older age population, as most wearable device providers, including Apple, Samsung, and Fitbit, are integrating advanced health-monitoring features that keep them updated about their health status in real time. Considering the growing demand for healthcare wearables, new players are continuously marking their presence in the studied industry by launching innovative solutions, which are also positively impacting the growth of the market studied.
- However, the high cost of wearable products and stringent regulatory compliances across developed regions are challenging the studied market. Furthermore, interoperability concerns owing to the lack of common global standards are also anticipated to remain among the major factors restraining the growth of the studied market.
Wearable Inertial Sensors Market Trends
Consumer Electronics to Witness Significant Growth
- Inertial wearable sensors technology, an emerging trend, integrates consumer electronics into daily activities and addresses the changing lifestyles with the ability to be worn on any part of the body. The trend of wearable inertial sensors in the consumer electronics industry is driven by the factors such as internet connectivity As per ITU, the approximate global internet user count reached 5.4 billion in 2023. and enhanced data exchange capabilities, enabling seamless communication between devices and networks.
- The growing advancement and reduction in the size of sensors, especially pressure sensors and activators, also exp anded the scope of the wearables inertial sensor market in the consumer electronics industry. As sensors become increasingly bio-compatible, their use for healthcare and fitness activities has also significantly increased. This has led to a significant increase in wearable devices sold over the past few years. According to Cisco, the growth in connected wearable devices, from 835 million devices in 2020 to 1.105 billion in 2022, holds great promise, specifically for healthcare applications. Many compa nies are investing in developing advanced Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and digital sensors, further decreasing their sizes and covering a wide range of market applications.
- The micro-electro-mechanical sensors (MEMS) and accelerometers are used for electronic stability control and airbag deployment. Inertial Measurement Units or IMU (they are a combination of MEMS Accelerometer and MEMS Gyroscope) have been developed for wearables as technology has advanced and are influenced by the impact of consumer electronic devices being used daily, such as global positioning system (GPS) or inertial measuring unit (composed of accelerometer, gyroscope, and magnetometer) sensors. This has helped fitness-tracking wearables revolve around these sensors exclusively.
- For instance, Nintendo Switch Labo edition Joy-cons possess default sensors in the accelerometer and gyroscope, usually in electronics consumer wearables. Joy-cons and cardboard combine to build artificial wearables, such as robots, to apply to a gaming function. It is usually Nintendo's way of breaking barriers for future generations (who are more involved with technology at younger ages) in immersive experiences with simplified custom wearable tech.
- Accelerometers are motion sensors, used in wearables. Their brand of acceleration, such as gravity and linear, demonstrates their sensing capabilities. Meanwhile, their measuring ability enables the programming of measured data for different purposes. For instance, a user who runs can access their top speed output and acceleration. Further, accelerometers can track sleep patterns like smartwatches and wristbands, thus driving the demand for wearable motion sensors in the consumer electronics segment.
Asia Pacific to Dominate the Market
- The Asia Pacific region is expected to witness notable growth during the forecast period owing to a large consumer base with a growing penetration of wearable devices and digital technologies. Considering the prospects, OEMs are also creating considerable support toward the enlargement of IMUs (inertial measurement units) and MEMS technology further to enhance the penetration of the newly developed products. Furthermore, the evolution of the electronics industry, owing to the emergence of countries such as China, Taiwan, etc., also contributes to the growth of the studied market.
- The market for wearable inertial sensors has become one of the largest and fastest-growing in China. Smartwatches, fitness trackers, virtual reality (VR) headsets, and motion-capture suits all use wearable inertial sensors, which are sensors that can detect motion and direction. The rapid growth of the wearable inertial sensor market in China has been primarily fueled by the country's rising acceptance of wearable technology and its expanding population of health-conscious individuals.
- The growing popularity of wearable technology and rising demand for measuring one's health and fitness have both contributed to the enormous rise of the wearable inertial sensors market in India in recent years. Wearable inertial sensors, such as accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers, are essential for giving wearable devices information about motion and orientation, which makes them popular for customers, athletes, and healthcare professionals in the nation.
- Japan's technologically proficient environment and a society that values convenience and innovation has propelled consistent growth in the wearable inertial sensor market there. Wearable inertial sensors have several uses in the healthcare, sports, entertainment, and gaming industries, among other fields. The use of wearables with inertial sensors for monitoring and enhancing general well-being has been accelerated by Japan's aging population and a strong focus on health and wellbeing.
- Due to the nation's tech-savvy population and keen interest in wearable technology, the South Korean Wearable Inertial Sensors Market has rapidly expanded in recent years. Smartwatches, fitness bands, virtual reality headsets, and other wearable medical equipment all feature wearable inertial sensors to some extent. Due to the rising emphasis on entertainment, health, and fitness and the adoption of advanced technologies, the demand for these gadgets has increased in the South Korean market.
- The Rest of Asia Pacific's inertial sensor market, which includes nations like Singapore, Australia, Malaysia, and others perceiving demand for wearable sensors in the Rest of Asia Pacific, has been steadily increasing over the past few years, driven by a growing interest in fitness and wellness, a rising aging population, as well as advancements in technology and healthcare.
Wearable Inertial Sensors Industry Overview
Investments in research and development, along with partnerships and alliances, are expected to be some of the strategic focus of vendors operating in the market. In addition to this, investment into technological innovations and market expansions via strategic alliances are expected to be focal points for the vendors in the market. Access to distribution channels and the deep clientele is significantly higher for large vendors operating in the market. In addition to this, vendors tend to focus on expanding their capabilities in the market via partnerships and acquisitions. Overall, the competitive rivalry is expected to be high among the vendors. Some of the major vendors in the market are Texas Instruments Incorporated, Panasonic Corporation, Bosch Sensortec GmbH, Knowles Electronics, Honeywell International Inc., etc.
In January 2023, Quadric and OSRAM established a collaborative partnership to create integrated sensing modules that combine the cutting-edge Mira Family of CMOS sensors for visible and infrared light with Quadric's cutting-edge Chimera GPNPU processors. The integrated ultra-low power modules will make it possible for wearable technology to use new types of smart sensing.
In December 2022 , Analog Devices Inc. collaborated with Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU) to develop a smartwatch that detects vital mental health indicators to help address the rising mental health crisis in teens. As per the collaboration on the first and one-of-a-kind project, OHSU would leverage ADI's innovative technology and products for the burgeoning worldwide mental health crisis to save, improve, and enrich human lives.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Industry Attractiveness - Porter Five Force Analysis
- 4.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.2.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.2.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.2.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.2.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.3 Impact of COVID-19 and Macro Economic Trends on the Industry
- 4.4 Technology Snapshot
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Increasing health awareness
- 5.1.2 Growing Demand for Wearable Fitness Monitors
- 5.1.3 Rapid Technology Advancements
- 5.2 Market Restraints
- 5.2.1 Security concerns
- 5.2.2 High cost of the devices
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Product Type
- 6.1.1 Smart Watches
- 6.1.2 Fitness Bands/Activity Tracker
- 6.1.3 Smart Clothing
- 6.1.4 Sports Gear
- 6.1.5 Others
- 6.2 By End-user Type
- 6.2.1 Healthcare
- 6.2.2 Sports and Fitness
- 6.2.3 Consumer electronics
- 6.2.4 Entertainment and Media
- 6.2.5 Government and Public Utilities
- 6.2.6 Others
- 6.3 By Geography
- 6.3.1 North America
- 6.3.1.1 United States
- 6.3.1.2 Canada
- 6.3.2 Europe
- 6.3.2.1 Germany
- 6.3.2.2 United Kingdom
- 6.3.2.3 France
- 6.3.3 Asia
- 6.3.3.1 China
- 6.3.3.2 India
- 6.3.3.3 Japan
- 6.3.3.4 South Korea
- 6.3.3.5 Australia and New Zealand
- 6.3.4 Middle East and Africa
- 6.3.4.1 United Arab Emirates
- 6.3.4.2 Saudi Arabia
- 6.3.4.3 Israel
- 6.3.5 Latin America
- 6.3.5.1 Brazil
- 6.3.5.2 Argentina
- 6.3.5.3 Mexico
- 6.3.1 North America
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Company Profiles
- 7.1.1 Texas Instruments Incorporated
- 7.1.2 Panasonic Corporation
- 7.1.3 Bosch Sensortec GmbH
- 7.1.4 Knowles Electronics
- 7.1.5 Honeywell International Inc.
- 7.1.6 TE Connectivity Ltd
- 7.1.7 Analog Devices Inc
- 7.1.8 General Electric Co.
- 7.1.9 AMS osram AG
- 7.1.10 STMicroelectronics NV
- 7.1.11 Infineon Technologies AG
- 7.1.12 NXP Semiconductors NV
- 7.1.13 InvenSense, Inc. (TDK Corporation)



















