
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1851796
디지털 트윈 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Digital Twin (DT) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
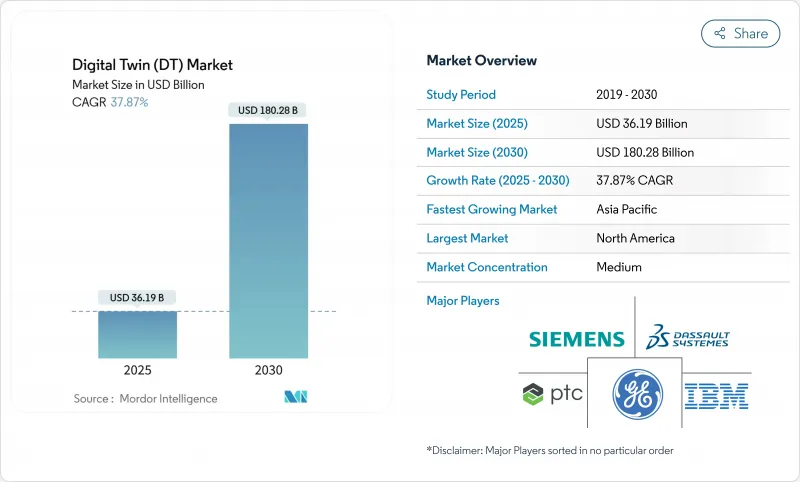
디지털 트윈 시장은 2025년에 361억 9,000만 달러, 2030년에는 1,802억 8,000만 달러에 이르고, CAGR 37.87%를 나타낼 것으로 예측됩니다.

돌풍에는 산업용 IoT 플랫폼의 성숙, 에지 AI의 광범위한 배포, 안전 중요 인프라에 대한 규제 요구 사항 등이 있습니다. 제조업은 확립된 스마트 팩토리 투자 덕분에 가장 큰 용도이지만, 석유 및 가스는 생산자가 엄격한 운영 조건 하에서 자산 통합성을 향상시키고자 했기 때문에 가장 강한 성장을 보이고 있습니다. 지역별로는 북미가 리드를 유지하고 있지만, 중국, 인도, 일본의 공공 프로그램이 대규모 디지털화를 향해 자금을 투입하고 있기 때문에 아시아태평양이 차이를 줄이고 있습니다. 현재 대부분의 지출은 솔루션이 차지하고 있지만 기업이 통합 전문 지식을 요구하기 때문에 서비스가 급속히 확대되고 있습니다. 클라우드 구축은 On-Premise를 능가하는 속도로 확장되어 원격 데이터 관리의 안전 조치와 확장성이 높은 아키텍처에 대한 신뢰가 높아지고 있음을 보여줍니다. 사이버 보안 격차와 물리적 기반 모델링 인력 부족은 채택의 주요 궤도를 바꾸지 않는 것, 성장 전망을 약화시키고 있습니다.
세계의 디지털 트윈 시장 동향과 인사이트
산업용 IoT 플랫폼의 급성장
IIoT의 광범위한 도입은 디지털 모델을 공장 현장과 동기화하는 실시간 데이터를 제공합니다. Siemens는 Xcelerator 생태계의 강점을 활용하여 2024년 디지털 비즈니스 매출을 22% 증가한 90억 유로(97억 2,000만 달러)로 보고했습니다. 하니웰의 Forge 플랫폼은 매일 30억 개 이상의 데이터 포인트를 처리하여 고객 공장의 예기치 않은 다운타임을 35% 줄였습니다. OPC UA 및 MQTT와 같은 표준화된 프로토콜은 통합 마찰을 줄여 공장이 수개월이 아닌 몇 주 내에 트윈을 배포할 수 있게 합니다. 그 결과 꾸준한 비용 회피, 신속한 근본 원인 분석, 보다 예측 가능한 용량 계획이 가능합니다.
디바이스 레벨에서 에지/AI 추론 확대
애널리틱스를 클라우드에서 에지로 마이그레이션하여 대기 시간을 줄이고 데이터 주권을 유지합니다. Microsoft와 Siemens는 자산에서 추론을 수행하는 Industrial Foundation Models를 공동 개발하여 이상 감지를 위한 밀리초 수준의 응답을 허용했습니다. 아우디는 현재 실제 생산 라인의 사이클 타임을 최적화하는 트윈을 에지에 배치하고 가상 PLC를 운영하고 있습니다. 또한 업스트림으로 이동하는 데이터는 예외적이므로 로컬 시뮬레이션은 대역폭 소비를 제한합니다. 전문화된 칩과 컨테이너화된 런타임은 Tier2 공급업체의 도입 비용을 더욱 절감하고 밸류체인 전반에 AI 대응 트윈의 보급을 가속화합니다.
IT/OT 스택 전반에 걸친 사이버 물리적 보안 취약점
스페인 국립 사이버 보안 연구소는 IT와 OT 브리지 트윈이 공격 대상 영역을 넓히고 프로세스 컨트롤러를 데이터 무결성에 대한 위협에 노출시킨다고 지적합니다. 최근의 랜섬웨어 사건에서는 트윈 데이터 레이크를 정화하는 동안 제조업은 며칠간의 생산 정지를 강요했습니다. 기업이 제로 트러스트 아키텍처를 통합하고 직원을 교육하기 위해 평균 18개월의 도입 지연이 발생했습니다. 멀티 테넌트 트윈은 파트너로부터의 액세스를 협업을 지연시키지 않고 부문화해야 하기 때문에 복잡성이 커지고 있습니다.
부문 분석
제조은 임베디드 IIoT 센서, 예지보전 프로그램, 지속적인 개선문화를 통해 2024년 디지털 트윈 시장의 35.8%를 나타냈습니다. 자동차 공장과 전자공장에서는 라인 레벨의 트윈을 도입하여 택트 타임의 변동이나 품질·수율 패턴을 분석하여 스크랩율을 2자리수 삭감하고 있습니다. 에너지 효율 향상은 특히 자원 집약적인 야금 및 시멘트 사업에서 또 다른 투자 회수층을 추가합니다. 이 업계는 다른 업계가 따라잡아도 양적 우위를 유지하고 꾸준히 확대될 것으로 예측됩니다.
석유 및 가스는 현재는 규모가 작은 것, 해양 사업자가 원격 검사와 고장 분리 기능을 필요로 하기 때문에 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 29.3%를 나타낼 것으로 예측됩니다. 업스트림 부문에서는 지진 데이터와 생산 로그를 통합한 저류층 트윈을 도입하여 엔지니어가 리그를 동원하기 전에 갱이 시추 시나리오를 시뮬레이션할 수 있도록 하고 있습니다. 중류기업은 파이프라인 누수 감지에 트윈을 적용하고, 쉘과 같은 하류 정유소에서는 DNV 기준으로 검증된 트윈을 사용하여 예정되지 않은 다운타임이 20% 삭감된 것을 기록하고 있습니다. 정부의 탈탄소화 목표는 트윈이 플레어 최소화와 열 통합 전략을 최적화하기 때문에 채택을 더욱 추진합니다. 양 분야에서 AI 시나리오 테스트는 트윈을 모니터링에서 의사 결정 지원 시스템으로 승화시켜 총 도입 대수의 점유율을 강화하고 있습니다.
솔루션 카테고리(소프트웨어 플랫폼, 물리 엔진, 커넥티드 하드웨어)는 2024년 지출액의 63.6%를 차지하며, 각 회사가 핵심 기능을 획득했습니다. 공급업체는 모델링 라이브러리와 시각화 엔진을 번들링하여 프로세스 엔지니어가 처음부터 코딩하지 않고 복제본을 만들 수 있습니다. 라이선싱 모델은 소비 기반 티어로 전환하고 있으며, Tier 2 공급업체 간의 액세스를 넓히고 있습니다.
그러나 서비스 규모는 CAGR 31.4%로 급속히 확대되고 있습니다. 구현 컨설턴트는 데이터 파이프라인을 조정하고 시맨틱 모델을 작성하며 시뮬레이션의 충실도를 검증합니다. 관리형 서비스 계약은 트윈의 상태 지표를 모니터링하고 패치를 적용하며 알고리즘의 드리프트를 조정합니다. 롤스로이스의 TotalCare는 트윈 애널리틱스를 뒷받침하는 엔진의 가동 시간을 보장합니다. 성과 기반 계약이 보급됨에 따라 서비스 파트너는 청구 가능한 시간이 아닌 효율성 향상에 요금을 연결함으로써 더 많은 위험을 감수하게 됩니다. 이 모델은 고객 로열티를 강화하고 플랫폼의 지속적인 강화를 촉진합니다.
디지털 트윈 시장 보고서는 용도별(제조, 에너지 및 전력, 항공우주 및 방위, 석유 및 가스, 자동차, 기타), 구성 요소별(솔루션/플랫폼, 서비스), 배포별(On-Premise, 클라우드), 기업 규모별(대기업, 중소기업), 지역별로 분류되어 있습니다.
지역 분석
북미는 인더스트리 4.0의 조기 전개, 항공우주 분야의 광범위한 프로그램, 산업용 SaaS에 대한 왕성한 벤처 자금 조달이 견인해 2024년의 디지털 트윈 시장 수익의 38.4%를 차지했습니다. 미국 항공 규제 당국이 시뮬레이션 기반 인증을 수락함에 따라 항공기 OEM과 Tier-1 공급업체 간에 트윈 투자가 확산되고 있습니다. 캐나다와 미국의 에너지 메이저는 환경 정책 강화에 따라 메탄 누출률을 줄이기 위해 파이프라인과 LNG 터미널에 트윈을 도입했습니다. 성숙한 사이버 보험 프레임워크와 표준화된 데이터 보호 의무로 인해 클라우드 채택은 특히 호조입니다.
아시아태평양의 CAGR은 27.2%로 가장 높으며 정부의 대형 프로젝트에 의해 지원되고 있습니다. 중국의 디지털 차이나 건설 계획에서는 새로운 인프라에 도시 지역의 디지털 트윈이 의무화되어 있으며 국내외 벤더에 대규모 조달 파이프라인이 형성되어 있습니다. 인도의 산검 디지털 트윈 계획은 6G 대응을 위해 전국적인 통신 업그레이드에 네트워크 트윈 기능을 통합합니다. 일본의 NTT 디지털 트윈 컴퓨팅 이니셔티브는 교통 및 재해 대응 알고리즘에 공급하는 도시 규모의 복제본을 지원합니다. 한국과 싱가포르는 실시간 탄소발자국 추적을 중시하고 스마트 공장과 스마트 항만의 조종사 사업을 추진하고 있습니다. 이 지역은 공급망의 핵심 역할을 하기 때문에 여기에서 배운 교훈은 세계 OEM으로 빠르게 전파됩니다.
유럽은 규제상의 요청이 중심이 되어 꾸준히 전진하고 있습니다. 디지털 제품 여권은 제조업체에게 제품 수명주기 전체에 걸친 추적 가능성의 임베디드을 강제해, 대량 생산품에는 사실상 라이트 웨이트 트윈이 필수가 되고 있습니다. 독일 Plattform Industrie 4.0은 표준화된 관리 셸 지침을 제공하여 중소기업의 통합 오버헤드를 줄입니다. 프랑스는 해군 건설의 경쟁력을 유지하기 위해 가상 조선소 트윈에 투자하고 북유럽은 넷 제로우코드를 충족시키기 위해 빌딩 트윈을 사용합니다. UAE와 사우디아라비아는 대규모 확장에 앞서 효율성과 지속가능성의 이점을 찾고 유전 트윈과 기가 프로젝트 도시 트윈을 시험적으로 도입하고 있습니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사 전제조건과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 산업용 IoT 플랫폼의 급성장
- 디바이스 레벨에서의 엣지/AI 추론의 확대
- 세이프티 크리티컬한 인프라의 디지털화를 추진하는 자산 집약형 산업 규제 강화
- 브라운필드 프로젝트의 CAPEX를 삭감하는 가상 시운전 수요
- 실시간 자산 복제 데이터가 필요한 성과 기반 서비스 계약의 상승
- EU와 미국에서의 디지털 제품 여권 보급
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- IT/OT 스택 전체의 사이버 물리적 보안 취약성
- 전문 분야에 특화된 물리 기반 모델링 전문가 부족
- 연계 트윈으로 생성된 데이터의 불투명한 IP 소유권
- 상호 운용성을 제한하는 시뮬레이션 표준의 단편화
- 중요한 규제 틀의 평가
- 밸류체인 분석
- 기술 전망
- Porter's Five Forces
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 구매자의 협상력
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업 간 경쟁 관계
- 주요 이해관계자의 영향 평가
- 주요 이용 사례와 사례 연구
- 시장의 거시경제 요인에 미치는 영향
- 투자분석
제5장 시장 세분화
- 용도별
- 제조
- 에너지 및 전력
- 항공우주 및 방위
- 석유 및 가스
- 자동차
- 기타
- 구성 요소별
- 솔루션/플랫폼
- 서비스
- 배포 모드별
- On-Premise
- 클라우드
- 기업 규모별
- 대기업
- 중소기업(SME)
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 유럽
- 영국
- 독일
- 프랑스
- 이탈리아
- 스페인
- 북유럽 국가
- 기타 유럽
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 중동
- 사우디아라비아
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 튀르키예
- 기타 중동
- 아프리카
- 남아프리카
- 이집트
- 나이지리아
- 기타 아프리카
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 인도
- 일본
- 한국
- ASEAN
- 호주
- 뉴질랜드
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- ANSYS, Inc.
- AVEVA Group plc
- Bentley Systems, Incorporated
- Cal-Tek SRL
- Cityzenith, Inc.
- Dassault Systemes SE
- General Electric Company
- Hexagon AB
- International Business Machines Corporation
- Lanner Group Limited(Royal HaskoningDHV)
- Mevea Ltd.
- Microsoft Corporation
- Oracle Corporation
- PTC Inc.
- Rescale, Inc.
- Robert Bosch GmbH(Bosch.IO)
- SAP SE
- Schneider Electric SE
- Siemens AG
- Amazon Web Services, Inc.
제7장 시장 기회와 향후 전망
KTH 25.11.17The digital twin market currently stands at USD 36.19 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 180.28 billion in 2030, advancing at a 37.87% CAGR.
Tailwinds include the maturation of industrial IoT platforms, wider edge-AI deployment, and regulatory requirements for safety-critical infrastructure. Manufacturing remains the largest application thanks to established smart-factory investments, while Oil and Gas shows the strongest growth as producers seek asset-integrity gains in harsh operating conditions. Regionally, North America retains the lead, but Asia-Pacific is closing the gap as public programs in China, India, and Japan channel funding toward large-scale digitalization. Solutions account for most spending today, yet services are scaling quickly as firms seek integration expertise. Cloud deployment is growing faster than on-premises, signaling rising confidence in remote data-management safeguards and scalable architectures. Cyber-security gaps and scarce physics-based modeling talent temper the growth outlook, though they have not altered the primary trajectory of adoption.
Global Digital Twin (DT) Market Trends and Insights
Rapid growth of industrial IoT platforms
Widespread IIoT deployment supplies real-time data that keeps digital models synchronized with factory floors. Siemens reported EUR 9 billion (USD 9.72 billion) digital business revenue in 2024, up 22% on the strength of its Xcelerator ecosystem. Honeywell's Forge platform processes 3 billion+ datapoints daily, cutting unplanned downtime by 35% in client plants. Standardized protocols such as OPC UA and MQTT reduce integration friction, enabling plants to deploy twins in weeks rather than months. The result is steady cost avoidance, quicker root-cause analysis, and more predictable capacity planning.
Expansion of edge/AI inference at the device level
Moving analytics from cloud to edge trims latency and preserves data sovereignty. Microsoft and Siemens co-developed Industrial Foundation Models that run inference at the asset, allowing millisecond-level responses for anomaly detection. Audi now operates virtual PLCs through edge-deployed twins that optimize cycle times in real manufacturing lines. Local simulation also limits bandwidth consumption because only exception of data moves upstream. Specialized chips and containerized runtimes further cut deployment costs for tier-two suppliers, accelerating the spread of AI-ready twins throughout value chains.
Cyber-physical security vulnerabilities across IT/OT stacks
The Spanish National Cybersecurity Institute notes that twins bridging IT and OT widen attack surfaces, exposing process controllers to data-integrity threats. Recent ransomware events forced manufacturers to halt production for days while cleansing twin data lakes. Average deployment delays of 18 months arise as firms integrate zero-trust architectures and train staff. Multi-tenant twins add complexity because partner access must be segmented without slowing collaboration.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Regulatory push for asset-intensive industries to digitise safety-critical infrastructure
- Demand for virtual commissioning to cut CAPEX
- Shortage of domain-specific physics-based modelling expertise
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Manufacturing contributed 35.8% of the digital twin market in 2024 thanks to embedded IIoT sensors, predictive maintenance programs, and continuous-improvement cultures. Automotive and electronics plants deploy line-level twins to analyze takt-time fluctuations and quality-yield patterns, trimming scrap rates by double digits. Energy-efficiency gains add another payback layer, particularly in resource-intensive metallurgy and cement operations. The segment is forecast to expand steadily, preserving its quantitative edge even as other verticals catch up.
Oil and Gas, though smaller today, is projected to grow at a 29.3% CAGR to 2030 as offshore operators require remote inspection and fault-isolation capabilities. The upstream segment deploys reservoir twins that integrate seismic data and production logs, allowing engineers to simulate well-workover scenarios before mobilizing rigs. Midstream companies apply pipeline twins for leak detection, while downstream refineries like Shell have documented 20% unplanned downtime reductions using twins verified by DNV standards. Government decarbonization targets further propel adoption as twins optimize flare minimization and heat-integration strategies. Across both segments, AI-assisted scenario testing elevates twins from monitoring to decision-support systems, reinforcing their share of total deployments.
The solutions category-software platforms, physics engines, and connected hardware-accounted for 63.6% of spending in 2024 as companies acquired core capabilities. Vendors bundle modeling libraries with visualization engines so process engineers can assemble replicas without coding from scratch. Licensing models are shifting to consumption-based tiers, broadening access among tier-two suppliers.
Services, however, are scaling faster at a 31.4% CAGR. Implementation consultancies align data pipelines, create semantic models, and validate simulation fidelity. Managed-service contracts monitor twin health metrics, apply patches, and tune algorithms for drift, yielding predictable OPEX for asset owners. As outcome-based agreements proliferate-Rolls-Royce TotalCare guarantees engine uptime backed by twin analytics-service partners assume more risk, tying fees to efficiency gains rather than billable hours. This model strengthens customer loyalty and encourages continuous platform enhancements.
The Digital Twin Market Report is Segmented by Application (Manufacturing, Energy and Power, Aerospace and Defense, Oil and Gas, Automotive, and Others), Component (Solutions/Platforms, and Services), Deployment Mode (On-Premises, and Cloud), Enterprise Size (Large Enterprises, and Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)), and Geography.
Geography Analysis
North America commanded 38.4% of digital twin market revenue in 2024 driven by early Industry 4.0 rollouts, extensive aerospace programs, and robust venture funding for industrial SaaS. U.S. aviation regulators' acceptance of simulation-based certification has spurred widespread twin investment among aircraft OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers. Energy majors in Canada and the United States deploy pipeline and LNG terminal twins to cut methane leak rates, aligning with tightening environmental policy. Cloud adoption is particularly strong due to mature cyber-insurance frameworks and standardized data-protection mandates.
Asia-Pacific posts the highest CAGR at 27.2%, supported by government megaprojects. China's Digital China Construction plan mandates urban digital twins for new infrastructure, creating large procurement pipelines for domestic and foreign vendors. India's Sangam Digital Twin scheme integrates network twin capability into nationwide telecom upgrades as the country moves toward 6G readiness. Japan's NTT Digital Twin Computing Initiative supports city-scale replicas that feed transportation and disaster-response algorithms. South Korea and Singapore push smart-factory and smart-port pilots, emphasizing real-time carbon-footprint tracking. The region's supply-chain centrality means lessons learned here propagate quickly to global OEMs.
Europe advances steadily as regulatory imperatives take center stage. The digital product passport forces manufacturers to embed traceability across product life cycles, effectively making a lightweight twin mandatory for high-volume goods. Germany's Plattform Industrie 4.0 provides standardized administration shell guidelines, reducing integration overhead for SMEs. France invests in virtual shipyard twins to maintain competitive edge in naval construction, while the Nordics use building twins to meet net-zero codes. The Middle East and Africa remain nascent but promising: the UAE and Saudi Arabia are piloting oil-field twins and giga-project city twins, seeking efficiency and sustainability benefits prior to large-scale expansion.
- ANSYS, Inc.
- AVEVA Group plc
- Bentley Systems, Incorporated
- Cal-Tek S.R.L.
- Cityzenith, Inc.
- Dassault Systemes SE
- General Electric Company
- Hexagon AB
- International Business Machines Corporation
- Lanner Group Limited (Royal HaskoningDHV)
- Mevea Ltd.
- Microsoft Corporation
- Oracle Corporation
- PTC Inc.
- Rescale, Inc.
- Robert Bosch GmbH (Bosch.IO)
- SAP SE
- Schneider Electric SE
- Siemens AG
- Amazon Web Services, Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rapid growth of industrial IoT platforms
- 4.2.2 Expansion of edge/AI inference at the device level
- 4.2.3 Regulatory push for asset-intensive industries to digitise safety-critical infrastructure
- 4.2.4 Demand for virtual commissioning to cut CAPEX in brownfield projects
- 4.2.5 Rise of outcome-based service contracts needing real-time asset replica data
- 4.2.6 Proliferation of digital product passports in EU and U.S.
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Cyber-physical security vulnerabilities across IT/OT stacks
- 4.3.2 Shortage of domain-specific physics-based modelling expertise
- 4.3.3 Opaque IP ownership of data generated in federated twins
- 4.3.4 Fragmentation of simulation standards limiting interoperability
- 4.4 Evaluation of Critical Regulatory Framework
- 4.5 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Impact Assessment of Key Stakeholders
- 4.9 Key Use Cases and Case Studies
- 4.10 Impact on Macroeconomic Factors of the Market
- 4.11 Investment Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Application
- 5.1.1 Manufacturing
- 5.1.2 Energy and Power
- 5.1.3 Aerospace and Defense
- 5.1.4 Oil and Gas
- 5.1.5 Automotive
- 5.1.6 Others
- 5.2 By Component
- 5.2.1 Solutions/Platforms
- 5.2.2 Services
- 5.3 By Deployment Mode
- 5.3.1 On-premises
- 5.3.2 Cloud
- 5.4 By Enterprise Size
- 5.4.1 Large Enterprises
- 5.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.2 Germany
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Spain
- 5.5.3.6 Nordics
- 5.5.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.4.1 Middle East
- 5.5.4.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.4.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.4.1.3 Turkey
- 5.5.4.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.4.2 Africa
- 5.5.4.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.4.2.2 Egypt
- 5.5.4.2.3 Nigeria
- 5.5.4.2.4 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.5 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.5.1 China
- 5.5.5.2 India
- 5.5.5.3 Japan
- 5.5.5.4 South Korea
- 5.5.5.5 ASEAN
- 5.5.5.6 Australia
- 5.5.5.7 New Zealand
- 5.5.5.8 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 ANSYS, Inc.
- 6.4.2 AVEVA Group plc
- 6.4.3 Bentley Systems, Incorporated
- 6.4.4 Cal-Tek S.R.L.
- 6.4.5 Cityzenith, Inc.
- 6.4.6 Dassault Systemes SE
- 6.4.7 General Electric Company
- 6.4.8 Hexagon AB
- 6.4.9 International Business Machines Corporation
- 6.4.10 Lanner Group Limited (Royal HaskoningDHV)
- 6.4.11 Mevea Ltd.
- 6.4.12 Microsoft Corporation
- 6.4.13 Oracle Corporation
- 6.4.14 PTC Inc.
- 6.4.15 Rescale, Inc.
- 6.4.16 Robert Bosch GmbH (Bosch.IO)
- 6.4.17 SAP SE
- 6.4.18 Schneider Electric SE
- 6.4.19 Siemens AG
- 6.4.20 Amazon Web Services, Inc.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment



















