
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1687930
비휘발성 메모리(NVM) 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Non-Volatile Memory - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
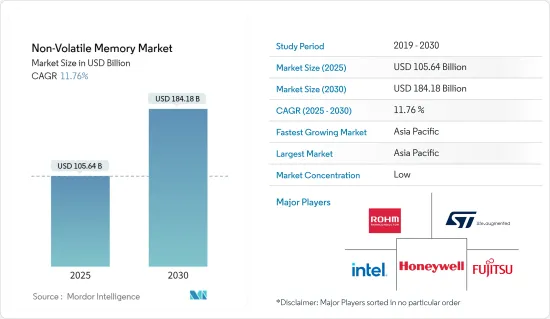
비휘발성 메모리 시장 규모는 2025년에 1,056억 4,000만 달러로 추정되고, 예측 기간 2025년부터 2030년까지 CAGR 11.76%로 성장할 전망이며, 2030년에는 1,841억 8,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예측됩니다.

지난 10년간 휴대용 시스템 시장이 성장함에 따라 반도체 산업은 대용량 저장 장치 용도의 비휘발성 메모리(NVM) 기술에 관심을 갖고 있습니다. 보다 높은 효율성, 보다 빠른 메모리 액세스, 낮은 전력 소비에 대한 수요가 NVM 시장의 성장을 뒷받침하고 있습니다.
주요 하이라이트
- 융성을 극대화하는 소비자 전자 산업에서 사용자는 장치의 지속적인 고성능화, 놀라운 속도로 새로운 기능 제공, 더 많은 영화, 사진 및 음악 저장을 기대합니다. 지난 수십년동안 플래시는 상당한 기술 혁신을 가능하게 했으나 플래시가 기술적 장애에 부딪혀 더 이상 확장할 수 없게 되었기 때문에 차세대 메모리가 필요합니다.
- 플래시 메모리는 저렴한 가격과 전력 소비로 인해 가전제품에 채택되어 시장 성장에 중요합니다. NVM은 스마트폰과 웨어러블 기기에 사용되어 더 많은 스토리지와 빠른 메모리 액세스를 가능하게 합니다.
- 이 분야에서 연구활동의 활성화도 시장 성장을 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 예를 들어 2021년 3월 Infineon Technologies LLC는 QML-Q 및 고신뢰성 산업 사양에 맞는 2세대 비휘발성 정적 RAM 출시를 발표하고 주로 항공우주 및 산업 용도와 같은 가혹한 환경에서 비휘발성 코드 스토리지를 지원합니다.
- 마찬가지로 삼성은 2021년 초에 MRAM의 MTJ 기능 개선을 발표하면서 쓰기 속도와 밀도를 향상시키기 위해 설계된 플래시형 임베디드 MRAM을 지원하고자 14nm 프로세스를 발전시켰습니다. 또한 이 회사는 IC 신흥 NVM의 웨어러블, 마이크로컴퓨터, IoT 기기에 대한 용도를 목표로 하고 있습니다.
- 그러나 시장에서 비휘발성 메모리의 문제는 읽기 및 쓰기 내구성과 데이터 보존 특성으로 인한 경우가 많습니다. 예를 들어, 상변화 메모리(PCM) 및 플래시 메모리는 내구성에 한계가 있는 NVM의 예입니다. 이러한 NVM의 내구성이 낮은 이유는 여러 번의 쓰기 사이클(PCM의 경우 RESET 사이클, 플래시 메모리의 경우 프로그램 및 소거 사이클)을 받으면 메모리 셀이 마모되어 정보를 저장할 수 없게 되기 때문입니다.
- COVID-19의 발생은 스마트폰 업계와 같은 비휘발성 메모리의 최종 사용자 업계의 일부에 부정적인 영향을 미쳤습니다. 클라우드 컴퓨팅, AI, IoT와 같은 중요한 메가 동향을 뒷받침한 자동 응답 서버 및 PC 메모리에 대한 수요의 급증이 예측 기간 동안 비휘발성 메모리의 성장을 지원할 것으로 예상됩니다.
비휘발성 메모리 시장 동향
플래시 메모리가 큰 시장 점유율을 차지할 전망
- 소비자 전자기기 수요 증가와 보급으로 디바이스 플래시 메모리의 용도가 확대되었습니다. 이 메모리 유형은 노트북, GPS, 전자 악기, 디지털 카메라, 휴대폰 및 기타 많은 장비에 적용됩니다. 또한 데이터센터 솔루션 공급업체에도 널리 채택되었습니다. 클라우드 솔루션의 급속한 보급으로 데이터센터 수요도 급증하고 있습니다.
- 또한 AI/ML 용도 및 IoT 디바이스에 대한 추세가 증가함에 따라, 저지연, 고처리량 클라우드 스토리지, 플래시 스토리지 및 기업 데이터센터가 깊은 신경망 교육에 최적화되었습니다. 데이터센터의 수와 규모 확대는 수요를 더욱 확대할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 수요 증가에 대응하기 위해 시장에서 사업을 전개하는 벤더는 보다 우수한 기능을 갖춘 새로운 솔루션의 개발에 주력하고 있습니다. 예를 들어, 2021년 2월, Kioxia Corporation과 Western Digital Corp.는 6세대 162층 3D 플래시 메모리 기술 개발을 발표했습니다. 이것은 많은 혁신과 제조 혁신을 이용한 회사에서 가장 고밀도의 첨단 3D 플래시 메모리 기술입니다.
- 또한 NOR 플래시 메모리도 초저전력 요구에 따라 지지를 모으고 있습니다. 예를 들어, 인피니언 테크놀로지스는 2022년 1월, 회사의 SEMPER NOR 플래시 디바이스 제품군을 지원하는 개발 툴의 추가를 발표했습니다. 이를 통해 개발자는 안전하고 중요하며 본질적으로 안전한 자동차, 산업 및 통신 시스템을 신속하게 설계할 수 있습니다.
- 마크로닉스 인터내셔널은 2021년 11월 1.2V 디바이스 양산을 시작한 업계 최초의 시리얼 NOR 플래시 메모리 제조업체라는 것을 발표했습니다. 이 회사에 따르면 초저전력(ULP)으로 고속 120MHz의 MX25S 시리얼 NOR 플래시 메모리는 사물인터넷(IoT), 무선 통신 기술, WiFi, 좁은 밴드 IoT 시스템, 핸드헬드 기기, 블루투스 기기, 소비자 용도 등의 용도를 타겟으로 한 신세대 제품의 선구자가 될 준비가 되어 있습니다.
아시아태평양이 큰 시장 점유율을 차지할 전망
- 온라인 엔터테인먼트, 재택 근무, 비디오 및 음성 통화 서비스 수요가 급증함에 따라 아시아태평양의 여러 국가에서 데이터센터를 포함한 새로운 인프라 건설이 증가하고 있습니다. 디지털 경제의 급속한 발전과 함께 중국과 인도와 같은 국가에서 대규모 빅 데이터센터 건설이 필요합니다.
- 중국은 NAND 메모리 사업에 대한 적극적인 노력으로 주요 국가로 부상하고 있습니다. 예를 들어 중국의 주요 메모리 기업 중 하나인 Yangtze Memory Technologies(YMTC)는 SSD를 포함한 64층의 NAND를 소량으로 국내 출하하고 있으며, 128층의 생산을 개발 중이며 2021년에 출하했습니다.
- 또한 이 지역에서는 비휘발성 메모리 관련 기술 개발에 종사하는 신흥기업이 여러 투자를 받고 있습니다. 예를 들어, 2021년 4월, InnoStar Semiconductor(상하이)는 프리시리즈 A 자금 조달 라운드에서 약 1억 달러를 조달했습니다. 이 자금조달 라운드는 상하이 리안헤 인베스트먼트가 주도했으며, 새로운 Atlas Capital과 KQ Capital이 참가했습니다. 이 회사는 이 투자로 저항 변화형 랜덤 액세스 메모리(ReRAM) 칩 및 스토리지 용도의 다른 칩을 생산하는 것을 목표로 하고 있습니다.
- 이 지역의 기업들은 다양한 산업 분야에 비휘발성 메모리를 활용합니다. 2021년 11월, 비휘발성 메모리(NVM) 기술을 제공하는 Floadia Corporation은 상하이 홍홍반 반도체 제조 유한회사 180BCD(Z8) 플랫폼에서 10년간 150도 C 유지를 지원하는 제품명 ZT의 고품질 eNVM(임베디드 비휘발성 메모리) 제공을 발표했습니다.
- 또한 이 지역에서는 비휘발성 메모리(NVM)의 연구개발 활동도 활발해지고 있습니다. 2022년 1월 Samsung Electronics는 MRAM(자기저항 랜덤 액세스 메모리)을 기반으로 세계 최초의 인메모리 컴퓨팅 데모를 발표했습니다. 이러한 동향은 예측 기간 동안 아시아태평양에서 연구 시장의 성장을 가속할 것으로 예상됩니다.
비휘발성 메모리 산업 개요
비휘발성 메모리 시장은 경쟁이 치열해 여러 대형 기업들이 진입하고 있습니다. 이 업계의 경쟁업체 간의 적대관계는 주로 혁신에 따른 지속 가능한 경쟁 우위, 시장 침투, 경쟁 전략의 힘에 달려 있습니다. 자본 집약적인 시장이기 때문에 철수 장벽도 높습니다. 이 시장에 진입하는 대기업은 Rohm Co. Ltd, STMicroelectronics NV, Fujitsu ltd, Intel Corporation 등이 있습니다. 최근 시장 개척 동향은 다음과 같습니다.
- 2022년 1월-SK하이닉스는 인텔 NAND와 SSD(SSD) 사업을 인수하는 거래의 첫 단계가 완료되었다고 발표했습니다. 이 회사에 따르면, 인텔의 SSD 사업과 중국의 대련 낸드 플래시 제조 시설을 인수하여 거래의 첫 단계를 완료했습니다.
- 2021년 10월-NSCore Inc.는 IoT 기술 용도를 위한 비휘발성 메모리 솔루션인 OTP(One-Time-Programmable Plus)를 발표했습니다. 이 회사에 따르면 40nm 초저전력 OTP NVM IP 솔루션은 신흥 시장에서 중요한 IoT 칩 재제조의 필요성을 최소화할 수 있습니다. 또한 NSCore OTP 솔루션은 표준 OTP IP 솔루션과 달리 재프로그램 및 변경이 가능합니다.
- 2021년 7월-마이크론 기술은 세계 최초의 176층 NAND 유니버설 플래시 스토리지(UFS) 3.1 모바일 솔루션의 양산 출하를 시작했다고 발표했습니다. 하이엔드 및 플래그쉽 휴대전화용으로 설계된 마이크론 UFS 3.1 디스크리트 모바일 NAND 메모리는 순차 라이트 및 랜덤 리드 속도가 이전 세대에 비해 최대 75% 향상되어 5G 잠재력을 확보합니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건 및 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 인사이트
- 시장 개요
- 업계의 매력도-Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계의 강도
- 시장에 대한 COVID-19의 영향
- 산업 밸류체인 분석
제5장 시장 역학
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 커넥티드 디바이스 및 웨어러블 디바이스에 있어서 비휘발성 메모리 수요 확대
- 엔터프라이즈 스토리지 용도 수요 증가
- 시장의 과제
- 낮은 쓰기 내구성
제6장 시장 세분화
- 유형별
- 종래의 비휘발성 메모리
- 플래시 메모리
- EEPROM
- SRAM
- EPROM
- 기타 종래의 비휘발성 메모리
- 차세대 비휘발성 메모리
- MRAM
- FRAM
- 재RAM
- 3D-X 포인트
- 나노RAM
- 기타 차세대 비휘발성 메모리
- 종래의 비휘발성 메모리
- 최종 사용자 산업별
- 소비자 일렉트로닉스
- 소매
- IT 및 통신
- 헬스케어
- 기타 최종 사용자 산업
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 유럽
- 영국
- 독일
- 프랑스
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 한국
- 인도
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 라틴아메리카
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 북미
제7장 경쟁 구도
- 기업 프로파일
- ROHM Co. Ltd
- STMicroelectronics NV
- Maxim Integrated Products Inc.
- Fujitsu Ltd
- Intel Corporation
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Micron technologies Inc.
- Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd
- Crossbar Inc.
- Infineon Technologies AG
- Avalanche Technologies Inc.
- Adesto Technologies Corporation(Dialog Semiconductor PLC)
제8장 투자 분석
제9장 시장의 미래
AJY 25.04.07The Non-Volatile Memory Market size is estimated at USD 105.64 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 184.18 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 11.76% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
In the last decade, the growth of the portable systems market attracted the interest of the semiconductor industry in non-volatile memory (NVM) technologies for mass storage applications. Demand for greater efficiency, faster memory access, and low-power consumption drive the NVM market growth.
Key Highlights
- In the flourishing consumer electronics industry, users expect their devices to continually become more powerful, provide new functionality with incredible speed, and store more movies, pictures, and music. While flash enabled substantial innovation during the past few decades, a new generation of memory is required as flash hits technology roadblocks, preventing it from scaling much further.
- The adoption of flash memories in consumer electronics due to their low price and power consumption is significant for the market's growth. NVM is used in smartphones and wearable devices to enable more storage and faster memory access.
- The increasing research activities in this space are also driving the market's growth. For instance, in March 2021, Infineon Technologies LLC announced the launch of second-generation non-volatile Static RAMs that are qualified for QML-Q and high-reliability industrial specifications to mainly support non-volatile code storage in harsh environments, including aerospace and industrial applications.
- Similarly, in early 2021, Samsung announced the improvement of its MRAM's MTJ function and advanced its 14 nm process to support its flash-type embedded MRAM designed to increase the write speed and density. In addition, the company targets the IC emerging NVM's application in wearables, microcontrollers, and IoT devices.
- However, troubles with non-volatile memories in the market are often caused by the read/write endurance and data retention characteristics. For instance, Phase-change memories (PCMs) and flash memories are examples of NVM's with limited endurance. These NVM's have little endurance because after undergoing several writing cycles (RESET cycles for PCM, program/erase cycles for flash memory), the memory cells wear out and can no longer reliably store information.
- The COVID-19 outbreak negatively impacted several end-user industries of non-volatile memories, such as the smartphone industry. Spurred demand for server and PC memory for stay-at-home activities, driven by important megatrends like cloud computing, AI, and the IoT, is expected to support the growth of non-volatile memory during the forecast period.
Non-Volatile Memory Market Trends
Flash Memory is Expected to Hold a Significant Market Share
- The growing demand and penetration of consumer electronics led to device flash memory applications. This memory type finds applications in laptops, GPS, electronic musical instruments, digital cameras, cell phones, and many others. Additionally, it is extensively adopted by data center solution vendors. With exponential growth in the adoption of cloud solutions, the demand for data centers is also surging.
- Further, with increasing propensity toward AI/ML applications and IoT devices that require high low latency and high throughput cloud storage, flash storage and enterprise data centers are optimized to train deep neural networks. The growing number and size of data centers are expected to augment demand further.
- To cater to the growing demand, vendors operating in the market focus on developing new solutions with better capabilities. For instance, in February 2021, Kioxia Corporation and Western Digital Corp. announced the development of a sixth-generation, 162-layer 3D flash memory technology. This was the company's highest density and most advanced 3D flash memory technology that utilizes many technology and manufacturing innovations.
- Furthermore, NOR Flash memory is also gaining traction due to ultra-low-power needs. For instance, in January 2022, Infineon Technologies announced additional development tools to support its family of SEMPER NOR Flash devices. It will further help developers to quickly design safety-critical and inherently secure automotive, industrial, and communication systems.
- Similarly, in November 2021, Macronix International Co., Ltd. announced itself as the industry's first Serial NOR Flash memory manufacturer to bring 1.2V devices to mass production. According to the company, the ultra-low-power (ULP), high-speed 120MHz MX25S Serial NOR Flash memories are poised to usher in a new generation of products targeted at applications that include Internet of Things (IoT), wireless communications technologies, WiFi, and Narrowband IoT systems, hand-held and Bluetooth devices, and consumer applications.
Asia Pacific is Expected to Account for a Significant Market Share
- The construction of new infrastructure, including data centers, has been growing across various countries of the Asia Pacific region, owing to a surge in demand for online entertainment, telecommuting, and video and voice call services. With the fast development of the digital economy, building large big data centers in countries such as China and India is becoming necessary.
- China has emerged as the leading country owing to its aggressive approach to the NAND memory business. For instance, Yangtze Memory Technologies Co. Ltd (YMTC), one of China's major memory companies, had shipped 64 layers of NAND domestically in low volumes, including SSDs, with 128-layer production in development and shipments in 2021.
- Furthermore, startups in the region that are engaged in developing technologies related to non-volatile memory are receiving several investments. For instance, in April 2021, InnoStar Semiconductor (Shanghai) Co. Ltd raised around USD 100 million in a pre-series A financing round. The funding round was led by Shanghai Lianhe Investment, and new investors who joined the round included state-backed Atlas Capital and KQ Capital. The company aims to use the investment to produce resistive random-access memory (ReRAM) chips and other chips for storage applications.
- Companies in the region are utilizing non-volatile memory for various industrial applications. In November 2021, Floadia Corporation, a provider of Non-Volatile Memory (NVM) technology, announced the availability of its high-quality eNVM (embedded Non-volatile Memory), with product name ZT, supporting 150 degrees C retention of 10 years, in Shanghai Huahong Grace Semiconductor Manufacturing Corporation 180BCD (Z8) platform.
- Furthermore, the region is also witnessing an increase in R&D activities in Non-Volatile Memory (NVM). In January 2022, Samsung Electronics announced the demonstration of one of the world's first in-memory computing based on MRAM (Magnetoresistive Random Access Memory). Such trends are expected to drive the growth of the studied market in the Asia Pacific region during the forecast period.
Non-Volatile Memory Industry Overview
The non-volatile memory market is competitive and consists of several major players. The competitive rivalry in this industry is primarily dependent on sustainable competitive advantage through innovation, levels of market penetration, and power of competitive strategy. Since the market is capital intensive, the barriers to exit are high as well. Some of the major players operating in the market include Rohm Co. Ltd, STMicroelectronics NV, Fujitsu ltd, and Intel Corporation. Some of the recent developments in the market are:
- January 2022 - SK Hynix Inc. announced the completion of the first phase of the transaction to acquire Intel's NAND and solid-state drive (SSD) business. According to the company, it has closed the first phase of the transaction by acquiring Intel's SSD business and the Dalian NAND flash manufacturing facility in China.
- October 2021 - NSCore Inc. introduced OTP+, One-Time-Programmable Plus, a non-volatile memory solution for IoT technology applications. According to the company, the 40 nm Ultra-Low-Power OTP NVM IP Solution can minimize the need to re-spin the fabrication of an IoT chip, which is critical in the emerging market. In addition, the NSCore OTP+ solution can be reprogramed and modified, unlike standard OTP Ip solutions.
- July 2021 - Micron Technology announced that it began mass shipping the world's first 176-layer NAND Universal Flash Storage (UFS) 3.1 mobile solution. Designed for high-end and flagship phones, Micron's UFS 3.1 discrete mobile NAND memory unlocks the potential of 5G with sequential write and random read speeds of up to 75% compared to previous generations.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.2.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.2.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.2.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.2.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.3 Impact of COVID-19 on the Market
- 4.4 Industry Value Chain Analysis
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Growing Demand for Non-volatile Memory in Connected and Wearable Devices
- 5.1.2 Increasing Demand for Enterprise Storage Applications
- 5.2 Market Challenges
- 5.2.1 Low Write Endurance Rate
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Type
- 6.1.1 Traditional Non-volatile Memory
- 6.1.1.1 Flash Memory
- 6.1.1.2 EEPROM
- 6.1.1.3 SRAM
- 6.1.1.4 EPROM
- 6.1.1.5 Other Traditional Non-volatile Memories
- 6.1.2 Next-generation Non-volatile Memory
- 6.1.2.1 MRAM
- 6.1.2.2 FRAM
- 6.1.2.3 ReRAM
- 6.1.2.4 3D-X Point
- 6.1.2.5 Nano RAM
- 6.1.2.6 Other Next-generation Non-volatile Memories
- 6.1.1 Traditional Non-volatile Memory
- 6.2 By End-user Industry
- 6.2.1 Consumer Electronics
- 6.2.2 Retail
- 6.2.3 IT and Telecom
- 6.2.4 Healthcare
- 6.2.5 Other End-user Industries
- 6.3 By Geography
- 6.3.1 North America
- 6.3.1.1 United States
- 6.3.1.2 Canada
- 6.3.2 Europe
- 6.3.2.1 United Kingdom
- 6.3.2.2 Germany
- 6.3.2.3 France
- 6.3.2.4 Rest of Europe
- 6.3.3 Asia Pacific
- 6.3.3.1 China
- 6.3.3.2 Japan
- 6.3.3.3 South Korea
- 6.3.3.4 India
- 6.3.3.5 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 6.3.4 Latin America
- 6.3.5 Middle East and Africa
- 6.3.1 North America
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Company Profiles
- 7.1.1 ROHM Co. Ltd
- 7.1.2 STMicroelectronics NV
- 7.1.3 Maxim Integrated Products Inc.
- 7.1.4 Fujitsu Ltd
- 7.1.5 Intel Corporation
- 7.1.6 Honeywell International Inc.
- 7.1.7 Micron technologies Inc.
- 7.1.8 Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd
- 7.1.9 Crossbar Inc.
- 7.1.10 Infineon Technologies AG
- 7.1.11 Avalanche Technologies Inc.
- 7.1.12 Adesto Technologies Corporation (Dialog Semiconductor PLC)



















