
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1693579
유럽의 군용 헬리콥터 시장 : 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Europe Military Helicopters - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
■ 보고서에 따라 최신 정보로 업데이트하여 보내드립니다. 배송일정은 문의해 주시기 바랍니다.
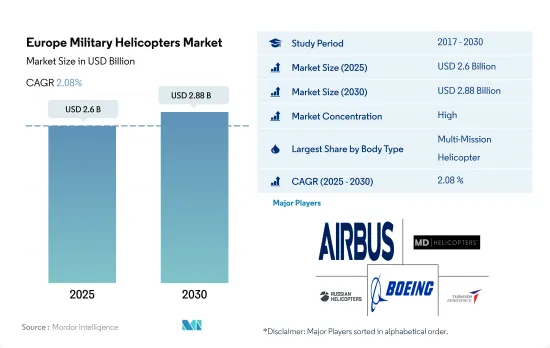
유럽의 군용 헬리콥터 시장 규모는 2025년에 26억 달러로 추정되고, 2030년에는 28억 8,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예상되며, 예측 기간 중(2025-2030년) CAGR 2.08%로 성장할 것으로 예측됩니다.

멀티미션 헬리콥터가 가장 높은 시장 점유율을 차지
- 회전익기 수요는 군사분쟁, 테러리즘, 국경분쟁, 영토침범, 위반행위 증가에 의해 부추겨지고 있습니다. 적대 세력에 대해 군사적으로 우위를 차지하기 위해, 지역의 무장 세력은 헬리콥터의 능력을 최첨단 기술로 업그레이드하고 있습니다.
- 러시아와 우크라이나 사이에 긴장이 계속되고 있기 때문에 이 지역의 여러 나라들이 NATO의 기준인 GDP의 최소 2%를 군사비에 소비하도록 촉구하고 있습니다. 따라서 각국은 효과적인 방식으로 위협에 대항하기 위해 첨단 헬리콥터 조달을 선택하고 있습니다.
- 유럽에서는 현재 3,363대의 헬리콥터가 운용되고 있습니다. 러시아는 1,632대의 헬리콥터를 운용하고 있으며, 이 지역에서 가장 많은 헬리콥터를 보유하고 있습니다. 멀티미션 헬리콥터는 지상 부대의 근접 항공 지원과 적의 장갑을 파괴하는 대전차 작전에 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 예측기간 중 유럽에서는 주로 독일, 프랑스, 영국, 러시아, 이탈리아, 스페인, 네덜란드, 기타 유럽에서 1,000대 이상의 헬리콥터 조달이 예상되며, 이 지역의 회전익 수요를 견인할 가능성이 있습니다.
항공기의 근대화와 지정학적 긴장 증가 등이 유럽 시장을 견인하고 있습니다.
- 유럽의 군용 헬리콥터 시장은 견조하고 기술적으로도 진행되고 있으며, 지정학적 우려, 근대화에 대한 대처, 국방 예산의 배분 등 다양한 요인에 의해 견인되고 있습니다. 국방 예산은 군용 헬리콥터 시장 형성에 중요한 역할을 하고 있습니다. 2022년 유럽은 군사비에 4,800억 달러를 투입하여 2021년 대비 13% 증가했습니다. 국가는 2022년 2월 러시아 우크라이나 침공에 대한 반동으로부터 군사비 증액 계획을 발표하고, GDP의 2% 이상이라는 NATO의 지출 목표를 달성하거나 웃도는 것을 목표로 했습니다.
- 2017-2022년까지 함대 조달에 관해서 이 지역은 세계 총함대의 20%를 조달했습니다.
- 또한 많은 유럽 국가들이 진화하는 안보 상황에 대응하기 위해 군용 헬리콥터의 근대화에 적극적으로 임하고 있습니다. 독일, 프랑스, 영국, 러시아, 이탈리아, 스페인, 네덜란드, 기타 유럽은 2023-2029년까지 헬리콥터의 구입을 계획하고 있습니다.
유럽 군용 헬리콥터 시장 동향
NATO 동맹이 이 지역의 국방 지출에 기여
- 2022년 유럽의 군사비는 4,800억 달러로 2021년 대비 13% 증가, 2013년 대비 38% 증가했습니다. 2021년에는 중유럽과 서유럽의 군사비의 합계는 3,450억 달러(서유럽은 3,050억 달러, 중유럽은 450억 달러)였으며, 이는 NATO의 대부분의 동맹국과 EU 회원국 모두를 포함합니다.
- 군사 연구 개발비와 무기 구입비 증가가 중유럽과 서유럽에서의 군사비 급증의 주요 요인입니다. 2022년에는 유럽의 NATO 회원국 19개국이 2014년 5개국, 2020년 13개국에서 증가하여 국방 지출의 최저 20%를 무기 구입과 군사 연구 개발에 충당했습니다.
- 2022년에는 이들 회원국의 무기와 연구개발에 대한 국방비의 평균 비율은 2020년의 22%, 2014년의 14%에서 24%로 증가했습니다. 다수의 유럽 NATO 회원국은 2022년 2월 러시아 우크라이나 침공에 대응하기 위해 NATO 지출 목표인 GDP의 2% 이상을 목표로 하는 군사비 증액 계획을 발표했습니다. 벨기에, 덴마크, 독일, 리투아니아, 네덜란드, 노르웨이, 폴란드, 루마니아가 그 멤버였습니다. 이 예산은 신병장의 구입이 중심이 될 것으로 예상되었습니다.
유럽의 군사 항공 시장에서는 고정익기가 보유전체 전체의 54%를 차지하고 있습니다.
- 2022년 현재 유럽의 현역 항공기 수는 8,326기로 그 중 고정익 항공기가 58%, 회전익이 42%를 차지했습니다.
- 고정익기와 멀티롤기의 부문이 54%를 차지하고 수송기가 16%, 훈련기가 23%, 기타가 7%였습니다. 회전익기에서는 멀티미션 헬리콥터가 38%를 차지해, 수송 헬리콥터가 30%, 기타가 32%였습니다.
- 2022년 현재 러시아 항공기의 평균 기령은 10.5년입니다. 예측 기간중, 영국, 독일, 프랑스, 이탈리아, 스페인은 현대전 수요에 부응하기 위해 차세대 항공기의 제조와 구매를 계속할 수 있습니다. 러시아와의 전쟁에서 우크라이나에 대한 지속적인 지원은 이 나라의 국방 예산에 압력을 가할 가능성이 있습니다.
유럽 군용 헬리콥터 산업 개요
유럽의 군용 헬리콥터 시장은 상당히 통합되어 있으며 상위 5개 기업에서 92.25%를 차지하고 있습니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 주요 요약과 주요 조사 결과
제2장 보고서 제안
제3장 소개
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
- 조사 방법
제4장 주요 산업 동향
- 국내총생산
- 액티브 플릿 데이터
- 국방 지출
- 규제 프레임워크
- 밸류체인 분석
제5장 시장 세분화
- 기체 유형
- 멀티미션 헬리콥터
- 수송용 헬리콥터
- 기타
- 국가명
- 프랑스
- 독일
- 이탈리아
- 네덜란드
- 러시아
- 스페인
- 튀르키예
- 영국
- 기타 유럽
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 주요 전략 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 상황
- 기업 프로파일
- Airbus SE
- BAE Systems
- Leonardo SpA
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- MD Helicopters LLC.
- Russian Helicopters
- The Boeing Company
- Turkish Aerospace Industries
제7장 CEO에 대한 주요 전략적 질문
제8장 부록
- 세계 개요
- 개요
- Porter's Five Forces 분석 프레임워크
- 세계의 밸류체인 분석
- 시장 역학(DROs)
- 정보원과 참고문헌
- 도표 일람
- 주요 인사이트
- 데이터 팩
- 용어집
The Europe Military Helicopters Market size is estimated at 2.6 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 2.88 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 2.08% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Multi-mission helicopters hold the highest market share
- The demand for rotorcrafts is being fueled by an increase in military conflicts, terrorism, border disputes, territory breaches, and violations. To gain a military advantage over the opposition, regional armed forces are upgrading the capabilities of helicopters with cutting-edge technologies.
- Ongoing tensions between Russia and Ukraine are encouraging various countries in the region to spend at least 2% of their GDP, which is a NATO standard, on their military. Thus, the countries are opting for the procurement of advanced helicopters to counter threats in an effective way.
- There are currently 3,363 helicopters in operation in Europe. With 1,632 operational helicopter forces, Russia possesses the highest number of helicopters in the region. France and Italy have the largest active fleets, with 478 and 435 helicopters, respectively, after Russia. Multi-mission helicopters are expected to record the highest CAGR during the forecast period. Multi-mission helicopters can be used for close air support for ground troops and anti-tank operations to destroy enemy armor. Multi-mission helicopters account for 38% of the total helicopter active fleet in the region, making it the largest segment, followed by other body types and transport helicopters, accounting for shares of 32% and 30%, respectively.
- More than 1000 helicopters are expected to be procured in Europe over the forecast period, mainly by Germany, France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Spain, the Netherlands, and the Rest of Europe, which may drive the demand for rotorcrafts in the region.
Factors such as fleet modernization and rising geopolitical tensions are driving the European market
- Europe has a robust and technologically advanced military helicopter market that is driven by various factors, including geopolitical concerns, modernization efforts, and defense budget allocations. The defense budgets of European countries play a crucial role in shaping the military helicopter market. Despite economic challenges, defense spending has remained a priority for many European nations due to rising security concerns. In 2022, Europe spent USD 480 billion on its military, an increase of 13% over 2021. By the end of March 2022, numerous European NATO member nations announced plans to increase military expenditure in reaction to the Russian invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, aiming to meet or exceed the NATO spending target of 2% of GDP or higher.
- During 2017-2022, in terms of fleet procurement, the region procured 20% of the global total fleet. Of these total fleets, the countries that procured most of the fleet were Italy with 33%, followed by Germany with 20%, France and the UK with 13% each, and Spain with 10%.
- Additionally, many European nations are actively engaged in modernizing their military helicopter fleets to meet the evolving security landscape. Upgrading aging platforms with state-of-the-art helicopters enables countries to enhance their operational effectiveness, increase mission versatility, and maintain interoperability with NATO and other allied forces. Germany, France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Spain, the Netherlands, and the Rest of Europe plan to purchase helicopters from 2023 to 2029. A total of 566 helicopters are expected to be delivered in Europe during the forecast period. During the forecast period, Romania and Hungary also plan to expand their fleet by procuring 60 and 18 helicopters, respectively.
Europe Military Helicopters Market Trends
NATO alliances are contributing to the region's defense spending
- In 2022, Europe spent USD 480 billion on its military, a 13% increase over 2021 and a 38% increase over 2013. In 2022, Europe accounted for 21% of the total defense expenditure in the world. In 2021, Central and Western Europe's combined military expenditure totaled USD 345 billion (USD 305 billion for Western Europe and USD 45 billion for Central Europe), including most NATO allies and all of the EU member states.
- Increased expenditures on military R&D and arms purchases were the main drivers of the surge in military spending in Central and Western Europe. In 2022, defense expenditures in Eastern Europe increased to USD 76.3 billion. In 2022, 19 European NATO member nations, up from five in 2014 and 13 in 2020, dedicated a minimum of 20% of their defense spending to arms purchases and military R&D.
- In 2022, these member states' average proportion of defense spending on weapons and R&D increased to 24% from 22% in 2020 and 14% in 2014. Only two of the 26 NATO members in Europe with a military budget, Albania and Estonia, did not increase the portion of their budgets devoted to arms purchases and R&D from 2014 to 2021. By the end of March 2022, numerous European NATO member nations announced plans to increase military expenditure in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, aiming to meet or exceed the NATO spending target of 2% of the GDP or higher. Belgium, Denmark, Germany, Lithuania, the Netherlands, Norway, Poland, and Romania were members of this group. These budgets were expected to be centered on the purchase of new armaments.
Fixed-wing aircraft accounted for 54% of the total fleet in the European military aviation market
- As of 2022, there were 8,326 active aircraft in Europe, of which fixed-wing aircraft accounted for 58% and rotorcraft for 42%. The total active aircraft fleet increased by 4% compared to 2016 in the region. Russia, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Germany, Italy, Spain, and France accounted for 95% of the total active fleet in the region.
- The fixed-wing aircraft and multi-role aircraft segments accounted for 54%, while transport aircraft, training aircraft, and others accounted for 16%, 23%, and 7%, respectively. In 2021, the active fleet of fixed-wing aircraft decreased by 3% compared to 2016. In rotorcraft, multi-mission helicopters accounted for 38%, while transport helicopters and other helicopters accounted for 30% and 32%, respectively. In 2021, the active fleet of rotorcraft increased by 1% compared to 2016.
- As of 2022, the average age of the Russian aircraft fleet was 10.5 years. The Yakovlev Yak-42 jets had the highest average age of any type of aircraft, at nearly 28 years. During the forecast period, the United Kingdom, Germany, France, Italy, and Spain may continue to build and buy next-generation aircraft to meet the demands of modern warfare. The regional armed forces are also upgrading the capabilities of helicopters with cutting-edge technology to achieve military superiority over possible invaders. The UK Ministry of Defence plans to retire several aging aircraft; however, it needs to actively continue the procurement of replacement aircraft to avoid any gaps within the fleet. The country's continued support for Ukraine in its war with Russia may add pressure on its defense budget. This factor may threaten the country's usual place as Europe's largest defense spender.
Europe Military Helicopters Industry Overview
The Europe Military Helicopters Market is fairly consolidated, with the top five companies occupying 92.25%. The major players in this market are Airbus SE, MD Helicopters LLC., Russian Helicopters, The Boeing Company and Turkish Aerospace Industries (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Gross Domestic Product
- 4.2 Active Fleet Data
- 4.3 Defense Spending
- 4.4 Regulatory Framework
- 4.5 Value Chain Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD and Volume, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Body Type
- 5.1.1 Multi-Mission Helicopter
- 5.1.2 Transport Helicopter
- 5.1.3 Others
- 5.2 Country
- 5.2.1 France
- 5.2.2 Germany
- 5.2.3 Italy
- 5.2.4 Netherlands
- 5.2.5 Russia
- 5.2.6 Spain
- 5.2.7 Turkey
- 5.2.8 UK
- 5.2.9 Rest of Europe
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles
- 6.4.1 Airbus SE
- 6.4.2 BAE Systems
- 6.4.3 Leonardo S.p.A
- 6.4.4 Lockheed Martin Corporation
- 6.4.5 MD Helicopters LLC.
- 6.4.6 Russian Helicopters
- 6.4.7 The Boeing Company
- 6.4.8 Turkish Aerospace Industries
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR AVIATION CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms
샘플 요청 목록

















