
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1836704
중형 및 대형 상용차 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Medium And Heavy Duty Commercial Vehicles - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
중형 및 대형 상용차 시장 규모는 2025년에 3,578억 1,000만 달러로 추정 및 예측되고, 예측 기간(2025-2030년) 중 CAGR 3.40%로 성장할 전망이며, 2030년에는 4,226억 달러에 달할 것으로 예측됩니다.
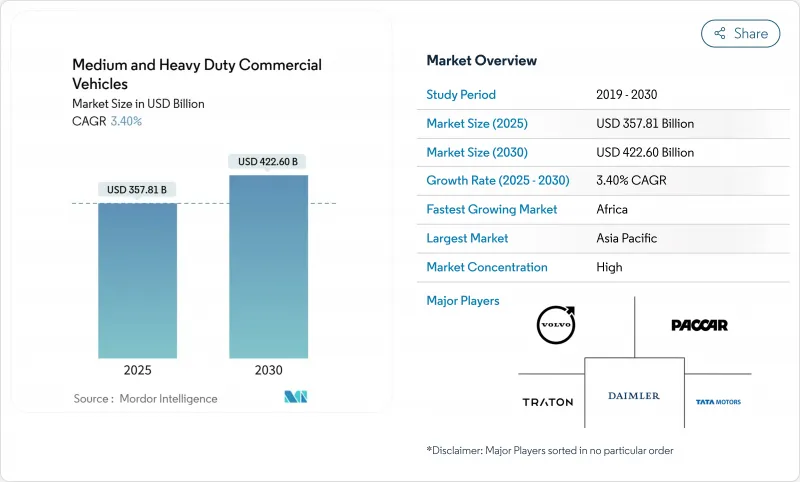
아시아태평양, 라틴아메리카, 아프리카에서 인프라가 현대화되고 있는 한편, 유럽에서는 Euro VII, 북미에서는 EPA 2027에 적합한 차량이 증가하고 있기 때문입니다. 규제 수렴으로 인한 교체 사이클은 엄격해지고 있지만 내연 엔진은 판매량의 대부분을 차지하고 있으며 배터리 전기 모델은 소규모 베이스에서 확대되고 있습니다. 도로 및 물류 회랑에 대한 공공 부문의 자극책, 가벼운 트럭에 대한 전자상거래 수요, 총 소유 비용 및 안전 분석을 개선하는 소프트웨어 정의 차량 플랫폼으로 성장이 더욱 강화됩니다.
세계의 중형 및 대형 상용차 시장 동향 및 인사이트
Euro VII와 EPA 2027년 배출가스 규제가 견인하는 차량 갱신
엄격한 NOx 및 CO2 규제에 따라, 유럽에서는 Euro VI 이전의 오래된 디젤 유닛 업데이트를 가속화하고 북미에서는 클래스 6-8 재고를 계획보다 빨리 업데이트해야 합니다. 최근 채용된 Euro VII 기준은 특히 대형차(HDV)에 엄격한 제한을 부과하고 있습니다. 이 기준에서 질소 산화물(NOX) 규제 값은 테스트 사이클에 따라 50%에서 62%로 낮아집니다. 또한 총 탄화수소(THC) 규제치를 비메탄 유기가스(NMOG) 및 메탄(CH4)에 대한 보다 엄격하고 명확한 규제치로 대체하고 있습니다. 타이밍을 조정하면 공급업체에 부담이 가해지지만 후처리 기술과 배터리 기술에는 스케일 메리트가 생깁니다. 미국 시장의 25%를 다루는 캘리포니아의 첨단 클린트랙 규정은 2030년까지 50%의 제로 방출 판매를 의무화했습니다. 조기에 도입한 사업자는 인센티브 풀과 잔존 가치 프리미엄의 혜택을 받을 수 있지만, 후발의 사업자는 공급 부족과 컴플라이언스 비용의 상승에 직면합니다. 기존 전기제품 포트폴리오를 보유한 제조업체는 선행자 이익을 누리며 두 지역에 걸쳐 개발비를 상각할 수 있습니다.
신흥국의 인프라 자극책
인도, 인도네시아, 말레이시아 및 중남미의 주요 국가에서는 정부 지원 도로 및 에너지 프로그램이 중형 및 대형 상용차 시장에 대한 수요를 계속 추진하고 있습니다. 인도의 FAME 프레임워크는 2030년까지 전기 상용차를 70% 보급하는 것을 목표로 하고 있으며, 전기 트럭 판매의 연간 49% 증가를 지지해, 공급자에게 배터리 모듈과 드라이브 트레인의 현지화를 촉구하고 있습니다. 인도네시아와 말레이시아에서는 비슷한 여러 해 동안 도로 건설 및 전기 대책이 지역 규모를 촉진하고 있습니다. 동시에 아메리카 개발은행은 협조적 인센티브를 통해 2030년까지 라틴아메리카의 세계 전기 트럭 판매에서 차지하는 비율을 0.45%에서 4%로 끌어올릴 수 있다고 추산하고 있습니다. 이러한 노력으로 보통 7년이라는 교체 시기를 넘어 구매 전망이 생기기 때문에 부품 제조업체는 생산 능력을 확보하고 설비 투자의 리스크를 경감할 수 있습니다. 경기 자극 조치와 현지 조달 규칙의 조합은 섀시, 운전실, 충전 인프라 공급업체에 대한 안정적인 주문 파이프라인을 지원합니다.
제로 방출 트랙의 높은 초기 비용
배터리 팩은 유닛 비용의 40%를 차지하고, 전기 대형 트럭의 가격은 디젤 동등차보다 20-30% 높습니다. 리튬-철-인산염 화학물질의 규모가 확대됨에 따라 4년 이내에 총 비용이 동등해질 것으로 예상되지만, 많은 소규모 운송 사업자는 자금 조달의 여력이 없습니다. Track-Az-A-Service 계약 및 배터리 임대는 제조업체가 경상 수익을 올리는 데 도움이 되는 동시에 취득 비용을 최대 42%까지 절감할 수 있습니다. 대규모 플릿 사업자는 이미 이러한 모델을 채택하고 있지만, 신흥국에서는 신용에 제약이 있는 구매자가 여전히 높은 허들 레이트에 직면하고 있어 도입이 늦어지고 있습니다.
보고서에서 분석된 기타 촉진요인 및 억제요인
- 전자상거래 물류 확대
- 텔레매틱스 인에이블의 이용 베이스 보험으로 TCO를 삭감
- 배터리 공급망 병목
부문 분석
16톤 이상의 모델은 2024년 중형 및 대형 상용차 시장 점유율의 약 60.26%를 차지하였고 중형 및 대형 상용차 시장에서 가장 큰 점유율을 확보했습니다. 수요는 충전시 편리성보다 적재량을 우선하는 장거리 화물 네트워크에 의해 지원됩니다. 이와는 대조적으로, 3.5-7.5톤 급의 중형 및 대형 상용차는 CAGR 7.81%로 확대되어 도시 배송 플랫폼의 보급에 따라 다른 모든 대역을 상회하고 있습니다. 이 부문은 100-200kWh 배터리 팩으로 일상적인 경로를 다룰 수 있으므로 배터리 요구 사항이 낮고 자본 지출과 충전 복잡성을 줄일 수 있다는 이점이 있습니다. 한편, 7.5-16톤 급의 중형 유닛은 건설이나 지자체의 조달 사이클에 연동해 안정된 교체가 행해지고 있습니다.
배터리 크기는 차량 질량에 비례하여 급격히 변화하며 대형 운반차에서는 듀티 사이클의 기대치를 충족시키기 위해 500kWh 이상이 필요합니다. 이 요구 사항은 차량 중량과 인프라 비용을 증가시키고 경량 등급과 비교하여 전동화를 지연시킵니다. 규제 당국은 차량의 총 중량으로 제한을 구별하기 때문에 제조업체는 엔지니어링 로드맵 전체에서 후처리 및 제로 방출 설계의 균형을 맞추어야 합니다. 비용 격차에도 불구하고 일부 광산 회사는 충전 네트워크가 정비되면 라이프 사이클을 절약할 수 있는 150 톤의 전기 덤프 자동차를 시험적으로 도입하고 있습니다.
2024년 중형 및 대형 상용차 시장 점유율에서 내연 엔진은 91.72%의 매출을 유지하였고 중형 및 대형 상용차 시장에서 선도를 강화하고 있습니다. 그러나 배터리 전기 트럭은 보조금, 운전 비용의 저하, 도시 지역에서의 급속한 보급에 도움이 되어 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 9.83%의 급성장 궤도를 그렸습니다. 압축 천연 가스 및 액화 천연 가스와 같은 대체 연료는 전기 항속 거리 및 송전망에 액세스하는 데 문제가 남아있는 지역의 틈새 시장에 계속 공급됩니다. 플러그인 하이브리드는 항속 거리의 유연성과 제로 방출의 도시 진입을 양립시켜야 하는 사업자에게 과도적인 솔루션 역할을 합니다.
중국은 2024년 세계 전동 대형 트럭 판매 대수의 80% 이상을 차지했으며, 협력적인 인센티브 및 지역 공급망의 영향력을 보여주고 있습니다. 연료전지 전기자동차의 프로토타입은 배터리의 질량이 적재량에 영향을 미치는 장거리 운송용으로 독일, 한국, 미국에서 초기 시험 운용이 이루어지고 있습니다. 따라서 2030년까지 추진력 믹스는 총 소유 비용 계산, 에너지 가격 동향, 인프라 전개에 의해 이질적인 것으로 보입니다.
지역 분석
아시아태평양의 2024년 매출 점유율은 45.52%로 중국의 생산 심도와 인도의 정책 확대로 인한 것입니다. 이 지역은 2030년까지 리드를 확장할 것으로 예측됩니다. 이는 주문자 상표 부착 제조업체가 배터리 공장, 소프트웨어 센터 및 부품 테스트를 가장 큰 구매자 근처에 설치했기 때문입니다. 중국에서만 2024년 9만 대 이상의 전기 대형 트럭 등록을 지원하였고, BYD와 SAIC는 관세 노출을 분산하기 위해 헝가리와 인도네시아에 키트를 수출하고 있습니다. 인도에는 14개 주에 의한 인센티브 프로그램이 있으며, 우타르 프라데시와 마하라슈트라는 3.5톤 배터리 트럭을 차지하는 도시 수준의 저 배출 가스 지역을 마련할 수 있습니다.
북미와 유럽은 성숙하면서도 유리한 시장이며, 협력 규칙이 기술의 조화를 보장합니다. EU는 2030년까지 대형 트럭의 CO2를 45% 줄이는 것을 목표로 하고 있으며, Euro VII는 2029년에 발효합니다. 캘리포니아의 고급 클린 트럭 규칙은 다른 11개 주가 그 로드맵을 채택하고 있으며, 미국의 6-8급 수요의 4분의 1을 다루기 때문에 각국의 구매 계획에 영향을 미치고 있습니다. 캐나다는 2030년까지 제로 이미션 트럭 판매량의 35%를 목표로 하고 있으며, 트랜스 캐나다 고속도로 충전 코리도에 자금을 제공합니다. 기업측에서는 볼보와 다임러가 합작회사를 설립하여 공통 운영체제를 구축하고, PACCAR는 사내 배터리 팩을 통합하여 변동으로부터 자신을 지키고 있습니다.
아프리카는 출발 시의 대수는 적음에도 불구하고, 투자 기세를 늘리고 있으며 CAGR 9.10%의 강력한 성장세를 보이고 있습니다. 모로코와 이집트는 중형 트럭과 컴포넌트를 공유하는 전기 버스를 주문했으며 지역 공급의 핵심입니다. 에티오피아는 이미 2030년 버스 전화 목표를 뛰어넘어 집약형 조달 모델의 잠재력을 보여주고 있습니다. 남아프리카공화국 백서는 기존 디젤 차량의 연비 향상과 채굴 벨트 주변의 급속 충전소에 대한 인센티브를 결합한 듀얼 플랫폼 로드맵을 설정합니다. 이러한 이니셔티브는 송전망의 신뢰성이 향상되면 2자리수의 출하 증가로 이어지는 잠재 수요를 지적하고 있습니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건 및 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- Euro-VII 및 EPA2027 배출 가스 규제에 의한 차량 갱신
- 신흥국의 인프라 자극책
- 전자상거래 물류 확대
- 광업 부문에 의한 배터리식 전기 운반 트럭 추진
- 텔레매틱스를 활용한 이용 기반의 보험이 TCO 삭감
- 2차 사용 배터리의 리스 모델
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 제로 방출 트럭 초기 비용 증가
- 파워 일렉트로닉스 및 배터리 공급망의 병목
- 디포 레벨의 송전망 용량 한계
- HV-EV 드라이브 트레인의 숙련 기술자 부족
- 밸류체인 및 공급망 분석
- 규제 상황
- 기술적 전망
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계의 강도
제5장 시장 규모 및 성장 예측 : 금액(달러) 및 수량(유닛)
- 톤수별
- 3.5-7.5톤
- 7.5-16톤
- 16톤 이상
- 추진 유형별
- 내연기관(디젤, 가솔린)
- 배터리 전기
- 플러그인 및 하이브리드 전기
- 연료전지 전기
- 대체연료(CNG, LNG, 바이오연료, LPG)
- 차량 유형별
- 리지드 트랙
- 트랙터 및 트레일러
- 티퍼 및 덤프 트럭
- 특수 및 상업용 트럭
- 최종 사용자 산업별
- 물류 및 운송
- 건설 및 광업
- 농업 및 임업
- 유틸리티 및 지자체 서비스
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 기타 북미
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 스페인
- 이탈리아
- 러시아
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 인도
- 일본
- 한국
- 호주
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 사우디아라비아
- 튀르키예
- 남아프리카
- 이집트
- 기타 중동 및 아프리카
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Daimler Truck AG
- Volvo Group
- Traton SE(MAN, Scania, Navistar)
- PACCAR Inc.
- Tata Motors Ltd.
- Hyundai Motor Co.
- CNHTC(Sinotruk)
- Dongfeng Motor Corp.
- FAW Group
- Renault Trucks
- Isuzu Motors Ltd.
- Hino Motors
- Ashok Leyland
- Iveco Group
- Kamaz PJSC
- Shacman(Shaanxi Auto)
- UD Trucks
- BYD Auto
- Nikola Corp.
제7장 시장 기회 및 전망
AJY 25.10.27The Medium and Heavy Duty Commercial Vehicles Market size is estimated at USD 357.81 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 422.60 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 3.40% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
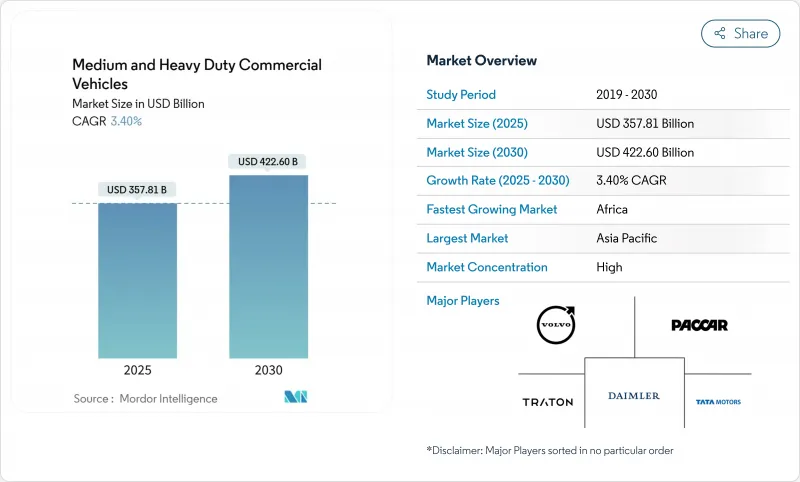
This measured expansion comes as fleets align with Euro VII in Europe and EPA 2027 in North America while modernizing infrastructure across Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa. Regulatory convergence has tightened replacement cycles, yet internal combustion engines dominate sales, and battery-electric models are scaling from a small base. Growth is further reinforced by public-sector stimulus for road and logistics corridors, e-commerce demand for lighter trucks, and software-defined vehicle platforms that improve total cost of ownership and safety analytics.
Global Medium And Heavy Duty Commercial Vehicles Market Trends and Insights
Fleet Renewal Driven by Euro VII & EPA 2027 Emission Rules
Stringent NOx and CO2 targets accelerate the replacement of pre-Euro VI and older diesel units in Europe and compel North American fleets to refresh Class 6-8 inventories sooner than planned. Recently adopted Euro 7 standards impose stricter limits, especially for heavy-duty vehicles (HDVs). These standards reduce nitrogen oxides (NOX) limits by 50% to 62%, depending on the test cycle. Additionally, they replace the total hydrocarbon (THC) limits with distinct, more stringent limits for non-methane organic gases (NMOG) and methane (CH4). Coordinated timing compresses procurement into narrow windows that strain suppliers but unlock economies of scale for after-treatment and battery technologies. California's Advanced Clean Trucks regulation, covering 25% of the US market, mandates 50% zero-emission sales by 2030. Operators that adopt early benefit from incentive pools and residual-value premiums, whereas late movers face supply shortages and higher compliance costs. Manufacturers with existing electric portfolios enjoy a first-mover edge and can amortize development expenses across both regions.
Infrastructure Stimulus in Emerging Economies
Government-backed road and energy programs continue to lift medium and heavy commercial vehicles market demand in India, Indonesia, Malaysia, and key Latin American countries. India's FAME framework targets 70% electric commercial vehicle penetration by 2030, supporting 49% annual growth in electric truck sales and encouraging suppliers to localize battery modules and drivetrains. Similar multi-year road-building and electrification measures in Indonesia and Malaysia foster a regional scale. At the same time, the Inter-American Development Bank estimates that coordinated incentives could raise Latin America's share of global electric truck sales from 0.45% to 4% by 2030. These initiatives extend purchasing visibility beyond the normal seven-year replacement horizon, enabling component makers to secure capacity and de-risk capital investment. The combination of stimulus funds and local content rules underpins a steady pipeline of orders for chassis, cabs, and charging infrastructure suppliers.
High Upfront Cost of Zero-Emission Trucks
Battery packs account for 40% of unit cost, leaving electric heavy trucks priced 20-30% above diesel equivalents. Total cost parity is projected within four years as lithium-iron-phosphate chemistries scale, yet many small carriers lack financing headroom. Truck-as-a-service contracts and battery leasing can cut acquisition costs by up to 42% while helping manufacturers generate recurring revenue. Large fleet operators are already adopting these models, but credit-constrained buyers in emerging economies still face high hurdle rates that slow take-up.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- E-Commerce Logistics Expansion
- Telematics-Enabled Usage-Based Insurance Lowers TCO
- Supply-Chain Bottlenecks for Batteries
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The above-16-ton models contributed around 60.26% of 2024 medium and heavy commercial vehicles market share, securing the largest slice of the medium and heavy commercial vehicles market. Demand is anchored by long-haul freight networks that prioritize payload capacity over convenience when charging. In contrast, the 3.5-7.5 ton class of medium and heavy commercial vehicles is expanding at 7.81% CAGR, outpacing all other bands as urban delivery platforms proliferate. This segment benefits from lower battery requirements as packs of 100-200 kWh suffice for daily routes, reducing capital outlays and charging complexity. Meanwhile, medium-duty units in the 7.5-16-ton range see stable replacement linked to construction and municipal procurement cycles.
Battery size scales steeply with vehicle mass, with heavy haulers needing 500 kWh or more to meet duty-cycle expectations. That requirement inflates curb weight and infrastructure costs, slowing electrification relative to lighter classes. Regulators differentiate limits by gross vehicle weight, compelling manufacturers to balance after-treatment and zero-emission designs across engineering roadmaps. Despite the cost gap, several mining companies are piloting 150-ton electric dumpers that yield life-cycle savings once charging networks are in place.
Internal combustion engines retained 91.72% revenue in 2024 of medium and heavy commercial vehicles market share, cementing their lead in the medium and heavy commercial vehicles market. Yet battery-electric trucks are on a steep 9.83% CAGR trajectory to 2030, helped by subsidies, lower operating costs, and rapid urban-fleet adoption. Alternative fuels such as compressed natural gas and liquefied natural gas continue to serve regional niches where electric range or grid access remains problematic. Plug-in hybrids act as transitional solutions for operators who must combine range flexibility with zero-emission urban entry.
China accounted for over 80% of global electric heavy-truck sales in 2024, illustrating the influence of coordinated incentives and local supply chains. Fuel-cell electric prototypes are under test for long-haul corridors where battery mass hurts payload, with early pilots in Germany, South Korea, and the US. The propulsion mix will therefore remain heterogeneous through 2030, driven by total cost of ownership calculations, energy-price trajectories, and infrastructure rollouts.
The Medium and Heavy Commercial Vehicle Market Report is Segmented by Tonnage (3. 5 To 7. 5 T, 7. 5 To 16 T, and Above 16 T), Propulsion Type (IC Engine, Plug-In Hybrid Electric, Battery Electric, and More), Vehicle Type (Rigid Truck and More), End-User Industry (Logistics and Transportation, Construction and Mining, and More), and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Units).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific's 45.52% 2024 revenue share stems from China's production depth and India's expanding policy push. The region is expected to extend its lead by 2030 because original-equipment manufacturers co-locate battery plants, software centers, and component testing near their largest buyers. China alone supported over 90,000 electric heavy-truck registrations in 2024, with BYD and SAIC exporting kits to Hungary and Indonesia to diversify tariff exposure. India backs 14 state incentive programs, allowing Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra to create city-level low-emission zones that favor 3.5-ton battery trucks.
North America and Europe represent mature yet lucrative markets where coordinated rules ensure technological harmonization. The EU aims for a 45% CO2 cut in heavy trucks by 2030, and Euro VII will take effect in 2029. California's Advanced Clean Trucks rule influences national purchase plans because 11 other states have adopted its roadmap, covering one quarter of the US Class 6-8 demand. Canada targets 35% zero-emission truck sales by 2030 and funds charging corridors on the Trans-Canada Highway. On the corporate side, Volvo and Daimler established a joint venture to create a common operating system, while PACCAR integrates in-house battery packs to shield itself from volatility.
Africa is gaining investment momentum despite modest starting volumes and is rapidly growing with a robust CAGR of 9.10%. Morocco and Egypt order electric buses that share components with medium-duty trucks, creating a nucleus for regional supply. Ethiopia has already exceeded its 2030 bus electrification target, illustrating the potential of aggregated procurement models. South Africa's EV White Paper sets a dual platform roadmap that combines fuel efficiency upgrades for existing diesels with incentives for fast-charge depots around mining belts. These initiatives point to latent demand that could translate into double-digit shipment growth once grid reliability improves.
- Daimler Truck AG
- Volvo Group
- Traton SE (MAN, Scania, Navistar)
- PACCAR Inc.
- Tata Motors Ltd.
- Hyundai Motor Co.
- CNHTC (Sinotruk)
- Dongfeng Motor Corp.
- FAW Group
- Renault Trucks
- Isuzu Motors Ltd.
- Hino Motors
- Ashok Leyland
- Iveco Group
- Kamaz PJSC
- Shacman (Shaanxi Auto)
- UD Trucks
- BYD Auto
- Nikola Corp.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Fleet renewal driven by Euro-VII & EPA 2027 emission rules
- 4.2.2 Infrastructure stimulus in emerging economies
- 4.2.3 E-commerce logistics expansion
- 4.2.4 Mining sector's push for battery-electric haul trucks
- 4.2.5 Telematics-enabled usage-based insurance lowers TCO
- 4.2.6 Secondary-use Battery Leasing Models
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High upfront cost of zero-emission trucks
- 4.3.2 Supply-chain bottlenecks for power-electronics & batteries
- 4.3.3 Depot-level grid-capacity limitations
- 4.3.4 Skilled-Technician Shortage for HV-EV Drivetrains
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value (USD) and Volume (Units))
- 5.1 By Tonnage
- 5.1.1 3.5 to 7.5 t
- 5.1.2 7.5 to 16 t
- 5.1.3 Above 16 t
- 5.2 By Propulsion Type
- 5.2.1 Internal-Combustion Engine (Diesel & Gasoline)
- 5.2.2 Battery Electric
- 5.2.3 Plug-in Hybrid Electric
- 5.2.4 Fuel-cell Electric
- 5.2.5 Alternative Fuels (CNG, LNG, Bio-fuel, LPG)
- 5.3 By Vehicle Type
- 5.3.1 Rigid Truck
- 5.3.2 Tractor-Trailer
- 5.3.3 Tipper / Dump Truck
- 5.3.4 Specialized & Vocational Trucks
- 5.4 By End-user Industry
- 5.4.1 Logistics & Transportation
- 5.4.2 Construction & Mining
- 5.4.3 Agriculture & Forestry
- 5.4.4 Utilities & Municipal Services
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Rest of North America
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Spain
- 5.5.3.5 Italy
- 5.5.3.6 Russia
- 5.5.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 India
- 5.5.4.3 Japan
- 5.5.4.4 South Korea
- 5.5.4.5 Australia
- 5.5.4.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.3 Turkey
- 5.5.5.4 South Africa
- 5.5.5.5 Egypt
- 5.5.5.6 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, SWOT Analysis, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Daimler Truck AG
- 6.4.2 Volvo Group
- 6.4.3 Traton SE (MAN, Scania, Navistar)
- 6.4.4 PACCAR Inc.
- 6.4.5 Tata Motors Ltd.
- 6.4.6 Hyundai Motor Co.
- 6.4.7 CNHTC (Sinotruk)
- 6.4.8 Dongfeng Motor Corp.
- 6.4.9 FAW Group
- 6.4.10 Renault Trucks
- 6.4.11 Isuzu Motors Ltd.
- 6.4.12 Hino Motors
- 6.4.13 Ashok Leyland
- 6.4.14 Iveco Group
- 6.4.15 Kamaz PJSC
- 6.4.16 Shacman (Shaanxi Auto)
- 6.4.17 UD Trucks
- 6.4.18 BYD Auto
- 6.4.19 Nikola Corp.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment



















