
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1848124
중동유럽의 화물 및 물류 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Central And Eastern Europe Freight And Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
중동유럽의 화물 및 물류 시장 규모는 2025년에 1,590억 9,000만 달러로 평가되었고, 2030년에는 1,843억 9,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며, 2025-2030년의 CAGR은 3.00%를 나타낼 전망입니다.

독일 OEM의 근거리 아웃소싱, TEN-T 회랑 가속화된 업그레이드, 그리고 지역의 디지털 전환은 모든 주요 물류 기능에 걸쳐 지속적인 수요를 강화하고 있습니다. 중국-유럽 철도 회랑을 따라 폴란드의 허브 지위, 핵심 물류 단지에서의 증가하는 5G 구축, 그리고 철도와 수로에 대한 EU 그린딜 인센티브는 중부 및 동유럽 화물 및 물류 시장을 서유럽 경쟁사들과 더욱 차별화시키고 있습니다. DSV의 DB 쉔커 인수와 같은 통합 움직임은 규모 기반 효율성을 높이고 있으며, 기술 기반 포워더들은 경쟁적 역동성을 불어넣고 있습니다. 주요 위험 요소로는 전문 운전사 부족 심화, EU 외부 국경에서의 간헐적 혼잡, 성장 모멘텀을 저해할 수 있는 냉장 유통망 역량 부족 등이 있습니다.
중동유럽 화물 및 물류시장 동향 및 인사이트
유럽연합 TEN-T 회랑 업그레이드로 복합운송 효율성 제고
최신 유럽횡단교통망(TEN-T) 자금 지원 라운드는 2024년 중동부유럽(CEE) 프로젝트에 25억 유로(27억 5,000만 달러)를 배정하여 유럽철도교통관리시스템(ERTMS) 도입을 가속화하고 국경 간 철도 체류 시간을 최대 30% 단축할 예정입니다. 바르샤바-베를린 및 부다페스트-빈 노선 운영사들은 15-20%의 효율성 향상을 보고하며, 이는 중동부 유럽 화물 및 물류 시장의 복합운송 역량을 강화하는 신규 철도-도로 서비스 제공을 뒷받침합니다. 개선된 연결성을 통해 폴란드 터미널은 더 많은 중국-유럽 철도 물량을 인접한 체코 및 슬로바키아 허브로 유입시켜, 계절적 성수기에도 운임 안정성을 유지하는 네트워크 효과를 창출합니다. 개정된 복합운송지침은 중거리 화물 운송을 도로에서 철도로 전환하도록 화주에게 추가 인센티브를 제공하여 장기적인 탄소 배출량 및 비용 절감을 촉진합니다.
독일 자동차 공급망, 폴란드와 슬로바키아 중심으로 국내화 가속
현대자동차인 Vitesco Technologies, Chasix의 3개 회사는 총 5억 7,600만 유로(6억 3,569만 달러) 이상을 CEE의 새로운 공장에 투입해 배터리 시스템과 파워트레인의 현지 생산 에코시스템을 강화하고 있습니다. 헝가리만 해도 전기이동성 분야 외국인 직접투자(FDI)로 188억 달러를 유치하며 유럽의 배터리 중심지 중 하나로 자리매김했습니다. 이전된 1차 공급업체들은 보세화물, 온도 관리 화물 및 전문 창고 시설을 필요로 하며, 이로 인해 중동부 유럽 화물 및 물류 시장에서 도로, 철도, 항공 모드 전반에 걸쳐 수요 탄력성이 증가하고 있습니다. 슬로바키아의 유리한 세제 체계와 폴란드의 확립된 자동차 클러스터는 독일 조립 공장으로의 시간 민감형 배송을 전문으로 하는 화물 운송업체에 유리한 고밀도 유통 경로를 조성합니다.
CEE 지역 도로 운송에서 만성적인 운전사 부족 현상 관측
2024년 EU 전체 운전사 부족 규모는 23만 3,000명을 넘어섰으며, 체코 운송 협회는 현지에서 2만 5,000명의 공석이 발생했다고 보고했습니다. 현재 운전사 평균 연령은 50세를 초과했으며, EU 모빌리티 패키지 하의 강화된 휴식 시간 규정이 차량 생산성을 압박하고 있습니다. 연간 15-20%의 임금 인플레이션은 도로 화물 운송 요금을 상승시켜 화주들이 철도 및 복합 운송 옵션으로 전환할 가능성을 높입니다. 폴란드의 여러 운송사들은 첨단 운전자 보조 시스템(ADAS)과 통제된 구간에서의 자율 주행 시험을 도입했으나, 완전한 상용화까지는 수년이 더 소요될 전망입니다. 지속적인 인력 부족은 중동부 유럽 화물 및 물류 시장의 수용 능력 한계와 서비스 신뢰성에 부담을 주고 있습니다.
부문 분석
2024년 도매 및 소매 무역 부문이 30.51% 점유율로 우위를 점했으며, 2025년부터 2030년까지 연평균 3.21% 성장률(CAGR)을 기록할 것으로 전망됩니다. 이는 2024년 전자상거래 총상품가치(GMV)가 429억 달러에 달할 것으로 예상되기 때문입니다. 대형 할인점 및 식료품 체인점들은 당일 배송 기준을 충족하기 위해 유통 센터를 개편하며, 중부 및 동유럽 화물 및 물류 시장에 자동화 투자를 촉진하고 있습니다.
제조업은 자동차 및 전자 산업 클러스터를 중심으로 크게 성장하고 있습니다. 폴란드와 헝가리의 배터리 기가팩토리는 ADR(미국 위험물 운송 규정) 준수 및 온도 조절 운송이 필요한 리튬 이온 셀을 포함한 특수 수입 물류를 주도하며, 운영사들의 프리미엄 수익률을 높이고 있습니다.
화물 운송은 2024년 매출의 65.13%를 차지하며 중부 및 동유럽 화물 및 물류 시장 전반의 제조 및 유통 수요 충족에 있어 핵심적 역할을 강조했습니다. 도로, 철도, 복합운송 업체들은 특히 폴란드-독일 노선을 중심으로 활발한 국경 간 무역의 혜택을 누리고 있습니다. 중동부 유럽 화물 및 물류 시장 규모는 자동차 근거리 아웃소싱과 유라시아 철도 물류 흐름에 힘입어 성장할 전망입니다. 규모는 작지만 CEP(소포 및 택배) 부문이 가장 빠르게 성장 중이며, 소포 허브 자동화와 픽업 포인트 네트워크 확대로 배송 주기가 단축되며 2025-2030년 연평균 3.44% 성장률(CAGR)을 기록할 것으로 예상됩니다. 디지털 플랫폼은 실시간 가격 확인 및 용량 매칭을 가능하게 하여 포워더가 통합 대시보드 아래 화물 운송과 CEP 서비스를 통합할 수 있게 합니다. 이러한 서비스의 상호작용은 회복탄력성을 추구하는 다국적 화주들을 끌어들이는 유연한 종단간 솔루션을 뒷받침합니다.
역사적 회복탄력성은 분명합니다. 주권 관련 문제와 팬데믹 충격으로 2020년 활동이 둔화되었으나, 전자상거래 성장이 2024년 CEP 부문 점유율을 촉진했습니다. 창고 및 보관 서비스는 옴니채널 소매업체들의 높은 재고 완충 수요로 안정적인 중단일자리 성장을 기록했습니다. 화물 운송은 무역 경로 다각화를 통해 부가가치를 창출했으며, 디지털 중개업체들은 항공사 및 철도 운영사와의 API 연결성을 활용하여 중동부 유럽 화물 및 물류 산업의 신흥 차별화 요소로 부상했습니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장의 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 인구통계
- 경제 활동별 GDP 분포
- 경제활동별 GDP 성장률
- 인플레이션
- 경제성과 및 프로파일
- 전자상거래 업계 동향
- 제조업의 동향
- 운수 및 저장부문의 GDP
- 수출 동향
- 수입 동향
- 연료 가격
- 물류 성능
- 모달 점유율
- 화물 가격 동향
- 화물 톤수의 동향
- 인프라
- 규제 틀(도로와 철도)
- 규제 틀(해상 및 공역)
- 밸류체인과 유통채널 분석
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 유럽연합 TEN-T 회랑 업그레이드로 복합운송 효율성 제고
- 독일 자동차 공급망, 폴란드 및 슬로바키아 중심으로 국내 근접화
- 유럽연합 그린딜 모달 전환 자금 지원 : 철도 및 수로
- 에너지 안보 이니셔티브 및 공급 경로 다각화
- 새로운 실크로드를 통한 중국-유럽 철도 화물 성장
- 주요 물류 거점에서의 5G/ITS의 전개
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 중유럽 및 동유럽의 도로 운송에서 만성적인 운전사 부족 현상
- EU 외부 국경에서의 국경 정체 현상
- 미개발된 콜드체인 인프라가 성장 저해
- 지역 내 분산된 A급 물류창고 공급
- 시장에서의 기술 혁신
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 구매자의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 최종 사용자 업계
- 농업, 어업, 임업
- 건설
- 제조업
- 석유 및 가스, 광업 및 채석업
- 도매업 및 소매업
- 기타
- 물류 기능
- 택배, 특송, 소포(CEP)
- 목적지 유형별
- 국내
- 국제
- 화물 포워딩
- 운송 수단별
- 항공
- 바다 및 내륙 수로
- 기타
- 화물 운송
- 운송수단별
- 항공
- 파이프라인
- 철도
- 도로
- 바다 및 내륙 수로
- 창고 및 보관
- 온도 제어 방식별
- 비온도 제어
- 온도 제어
- 기타 서비스
- 택배, 특송, 소포(CEP)
- 지역별
- 알바니아
- 불가리아
- 크로아티아
- 체코 공화국
- 에스토니아
- 헝가리
- 라트비아
- 리투아니아
- 폴란드
- 루마니아
- 슬로바키아 공화국
- 슬로베니아
- 중동유럽의 기타 지역
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 주요 전략적 움직임
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Cargus
- CMA CGM Group(Including CEVA Logistics)
- DACHSER
- DHL Group
- DSV A/S(Including DB Schenker)
- Expeditors International
- FedEx
- Gebruder Weiss
- GEODIS
- Hamburger Hafen und Logistik AG(Including METRANS)
- Kuehne Nagel
- La Poste Group(Including GeoPost)
- Magyar Posta Zrt
- NYK(Nippon Yusen Kaisha) Line
- OBB-Holding AG(Including Rail Cargo Group)
- PKP CARGO SA
- Raben Group
- Rhenus Group
- ROHLIG SUUS Logistics SA
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc.(UPS)
- Waberer's International Nyrt.
- Walter Group
제7장 시장 기회와 장래의 전망
HBR 25.11.12The Central and Eastern Europe freight and logistics market size is valued at USD 159.09 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 184.39 billion by 2030, translating into a steady 3.00% CAGR over 2025-2030.
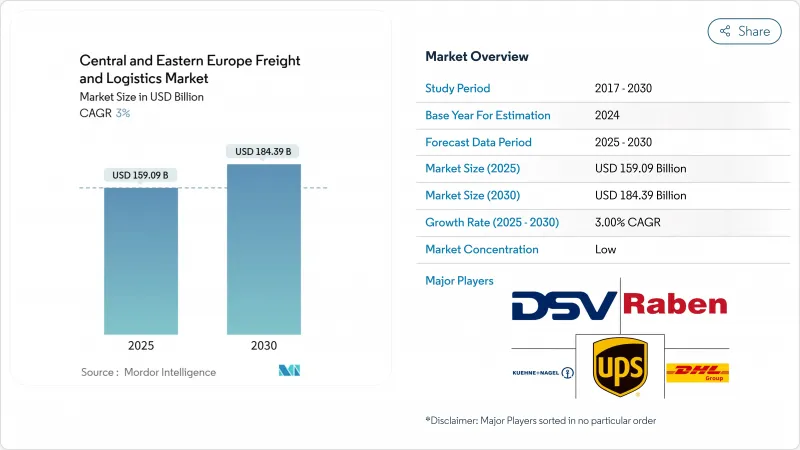
Nearshoring by German OEMs, accelerated TEN-T corridor upgrades, and the region's digital transformation are reinforcing sustained demand across all major logistics functions. Poland's hub status along the China-Europe rail corridor, rising 5G deployments in core logistics parks, and EU Green Deal incentives for rail and waterways further differentiate the Central and Eastern Europe freight and logistics market from Western European peers. Consolidation activity, such as DSV's purchase of DB Schenker, is elevating scale-driven efficiencies, while technology-enabled forwarders inject competitive dynamism. Key risks include a widening professional driver deficit, intermittent border congestion at EU external frontiers, and lagging cold-chain capacity that could temper growth momentum.
Central And Eastern Europe Freight And Logistics Market Trends and Insights
European Union TEN-T Corridor Upgrades Enabling Intermodal Efficiencies
The latest Trans-European transport network (TEN-T) financing round earmarked EUR 2.5 billion (USD 2.75 billion) for CEE projects in 2024, accelerating European rail traffic management system (ERTMS) deployment and cutting cross-border rail dwell times by up to 30%. Operators on the Warsaw-Berlin and Budapest-Vienna routes report 15-20% efficiency gains, underpinning new rail-road service offerings that deepen the Central and Eastern Europe freight and logistics market's multimodal capabilities. Improved connectivity allows Polish terminals to funnel higher China-Europe rail volumes into adjacent Czech and Slovak hubs, creating network effects that sustain rate stability during seasonal peaks. Revised Combined Transport Directive targets further incentivize shippers to shift medium-distance traffic from road to rail, fostering long-run carbon and cost savings.
German Auto Supply Chains Shift Closer to Home with Poland and Slovakia in Focus
Hyundai, Vitesco Technologies, and Chassix have collectively slated more than EUR 576 million (USD 635.69 million) toward new CEE plants, reinforcing the local production ecosystem for battery systems and powertrains. Hungary alone secured USD 18.8 billion in electromobility FDI, positioning the country among Europe's battery capitals. Relocated tier-1 suppliers require bonded, temperature-controlled freight and specialized warehousing, with lifting demand elasticity across road, rail, and air modes within the Central and Eastern Europe freight and logistics market. Slovakia's favorable tax framework and Poland's established automotive clusters cultivate dense distribution lanes that benefit freight forwarders specializing in time-critical deliveries to German assembly plants.
Chronic Driver Shortage Noticed in CEE Road Haulage
EU-wide driver gaps topped 233,000 positions in 2024, with Czech transport associations citing 25,000 vacancies locally. The average driver age now exceeds 50, and stricter rest-time mandates under the EU Mobility Package squeeze fleet productivity. Wage inflation of 15-20% annually elevates road freight tariffs, potentially nudging shippers toward rail and intermodal options. Several Polish carriers have introduced advanced driver assistance Systems (ADAS) and autonomous trials on controlled corridors, though full commercial roll-out remains years away. Persistent shortages weigh on the Central and Eastern Europe freight and logistics market's capacity ceiling and service reliability.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- China-Europe Rail Freight Growth Witnessed via New Silk Road
- European Union Green Deal Modal Shift Funding to Rail and Waterways
- Border Congestion Witnessed at EU External Frontiers
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Wholesale and retail trade dominated with a 30.51% share in 2024 and is projected to grow at a 3.21% CAGR (2025-2030) as e-commerce gross merchandise value (GMV) hits USD 42.9 billion in 2024. Big-box and grocery chains are overhauling distribution centers to meet same-day delivery benchmarks, injecting automation spending into the Central and Eastern Europe freight and logistics market.
Manufacturing is growing significantly, largely on the back of auto and electronics clusters. Battery gigafactories in Poland and Hungary drive specialized inbound flows, including lithium-ion cells that demand ADR-compliant, temperature-controlled transport, boosting premium yields for operators.
Freight transport captured 65.13% of 2024 revenue, underscoring its foundational role in meeting manufacturing and distribution needs across the Central and Eastern Europe Freight and Logistics market. Road, rail, and intermodal carriers benefit from robust cross-border trade, particularly along Poland-Germany lanes. The Central and Eastern Europe freight and logistics market size is projected to grow, supported by automotive nearshoring and Eurasian rail flows. CEP, although smaller, is rising fastest; automation in parcel hubs and expansion of pick-up point networks shorten delivery cycles and fuel a 3.44% CAGR (2025-2030). Digital platforms enable real-time price discovery and capacity matching, allowing forwarders to integrate Freight Transport and CEP services under unified dashboards. The interplay of these services underpins flexible, end-to-end solutions that attract multinational shippers seeking resilience.
Historical resilience is evident: sovereignty-related challenges and pandemic shocks slowed activity in 2020, yet e-commerce growth spurred the CEP segment's share in 2024. Warehousing and storage posted stable, mid-single-digit growth as omnichannel retailers demanded higher inventory buffers. Freight Forwarding added value through trade route diversification, with digital brokers exploiting API connectivity to airlines and rail operators, an emerging differentiator in the Central and Eastern Europe freight and logistics industry.
The Central and Eastern Europe Freight and Logistics Market Report is Segmented by End User Industry (Construction, Manufacturing, Wholesale and Retail Trade, and More), by Logistics Function (Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP), Freight Forwarding, Freight Transport, Warehousing and Storage, and More) and by Geography (Albania, Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech Republic, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Cargus
- CMA CGM Group (Including CEVA Logistics)
- DACHSER
- DHL Group
- DSV A/S (Including DB Schenker)
- Expeditors International
- FedEx
- Gebruder Weiss
- GEODIS
- Hamburger Hafen und Logistik AG (Including METRANS)
- Kuehne+Nagel
- La Poste Group (Including GeoPost)
- Magyar Posta Zrt
- NYK (Nippon Yusen Kaisha) Line
- OBB-Holding AG (Including Rail Cargo Group)
- PKP CARGO SA
- Raben Group
- Rhenus Group
- ROHLIG SUUS Logistics SA
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
- Waberer's International Nyrt.
- Walter Group
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Demographics
- 4.3 GDP Distribution by Economic Activity
- 4.4 GDP Growth by Economic Activity
- 4.5 Inflation
- 4.6 Economic Performance and Profile
- 4.6.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.6.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.7 Transport and Storage Sector GDP
- 4.8 Export Trends
- 4.9 Import Trends
- 4.10 Fuel Price
- 4.11 Logistics Performance
- 4.12 Modal Share
- 4.13 Freight Pricing Trends
- 4.14 Freight Tonnage Trends
- 4.15 Infrastructure
- 4.16 Regulatory Framework (Road and Rail)
- 4.17 Regulatory Framework (Sea and Air)
- 4.18 Value Chain and Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.19 Market Drivers
- 4.19.1 European Union TEN-T Corridor Upgrades Enabling Intermodal Efficiencies
- 4.19.2 German Auto Supply Chains Shift Closer to Home with Poland and Slovakia in Focus
- 4.19.3 European Union Green Deal Modal Shift Funding to Rail and Waterways
- 4.19.4 Energy Security Initiatives and Supply Route Diversification
- 4.19.5 China-Europe Rail Freight Growth Witnessed via New Silk Road
- 4.19.6 5G / ITS Roll-Out Witnessed in Key Logistics Hubs
- 4.20 Market Restraints
- 4.20.1 Chronic Driver Shortage Noticed in CEE Road Haulage
- 4.20.2 Border Congestion Witnessed at EU External Frontiers
- 4.20.3 Under-Developed Cold-Chain Infrastructure Curtailing Growth
- 4.20.4 Fragmented Grade-A Warehousing Supply in the Region
- 4.21 Technology Innovations in the Market
- 4.22 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.22.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.22.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.22.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.22.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.22.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 End User Industry
- 5.1.1 Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry
- 5.1.2 Construction
- 5.1.3 Manufacturing
- 5.1.4 Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying
- 5.1.5 Wholesale and Retail Trade
- 5.1.6 Others
- 5.2 Logistics Function
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
- 5.2.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.2.1.1.1 Domestic
- 5.2.1.1.2 International
- 5.2.2 Freight Forwarding
- 5.2.2.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.2.1.1 Air
- 5.2.2.1.2 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.2.1.3 Others
- 5.2.3 Freight Transport
- 5.2.3.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.3.1.1 Air
- 5.2.3.1.2 Pipelines
- 5.2.3.1.3 Rail
- 5.2.3.1.4 Road
- 5.2.3.1.5 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.4 Warehousing and Storage
- 5.2.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.2.4.1.1 Non-Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.4.1.2 Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.5 Other Services
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
- 5.3 Geography
- 5.3.1 Albania
- 5.3.2 Bulgaria
- 5.3.3 Croatia
- 5.3.4 Czech Republic
- 5.3.5 Estonia
- 5.3.6 Hungary
- 5.3.7 Latvia
- 5.3.8 Lithuania
- 5.3.9 Poland
- 5.3.10 Romania
- 5.3.11 Slovak Republic
- 5.3.12 Slovenia
- 5.3.13 Rest of CEE
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Cargus
- 6.4.2 CMA CGM Group (Including CEVA Logistics)
- 6.4.3 DACHSER
- 6.4.4 DHL Group
- 6.4.5 DSV A/S (Including DB Schenker)
- 6.4.6 Expeditors International
- 6.4.7 FedEx
- 6.4.8 Gebruder Weiss
- 6.4.9 GEODIS
- 6.4.10 Hamburger Hafen und Logistik AG (Including METRANS)
- 6.4.11 Kuehne+Nagel
- 6.4.12 La Poste Group (Including GeoPost)
- 6.4.13 Magyar Posta Zrt
- 6.4.14 NYK (Nippon Yusen Kaisha) Line
- 6.4.15 OBB-Holding AG (Including Rail Cargo Group)
- 6.4.16 PKP CARGO SA
- 6.4.17 Raben Group
- 6.4.18 Rhenus Group
- 6.4.19 ROHLIG SUUS Logistics SA
- 6.4.20 United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
- 6.4.21 Waberer's International Nyrt.
- 6.4.22 Walter Group
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment



















