
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1850128
농업용 접종제 시장 : 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Agricultural Inoculants - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
농업용 접종제 시장은 2025년에 112억 3,000만 달러, CAGR 10.5%로 성장하여 2030년에는 185억 달러에 이를 것으로 예측됩니다.

합성비료의 배출을 억제하기 위한 정책압력 증가, 생물학적 질소 고정에 보상하는 탄소 크레딧의 인센티브 강화, 엄격화하는 유기 기준에 적합한 잔류물이 없는 식품에 대한 소매 수요 증가 등입니다. 이 분야는 농부가 측정 가능한 수율의 안정성과 토양의 건전성 향상을 인식함에 따라 틈새 생물학적 투입물에서 작물 관리 도구의 주류로 이동했습니다. 공급업체는 지속가능성 목표에 부합하는 프리미엄 다중 균주 배합을 통해 매력적인 마진을 획득하고 동시에 생산자의 양분 비용을 낮추고 있습니다. 주요 자본 유입이 상승세를 강화하고 있습니다. 미생물 캡슐화 및 인공지능 유도 시용 시스템에서 벤처 기업의 자금 조달은 급속히 확대되고 있으며, 신규 기업은 차별화된 기술을 상업화하기 위한 자원을 얻고 있습니다. 동시에 기존 기업은 미생물의 생존 기간을 연장하고 농장에서의 사용을 간소화하는 차세대 전달 방법의 연구 개발을 가속화하고 있습니다. 이 혁신과 통합의 이중 궤도는 가치가 상용성 단일 균주 제품에서 검증 가능한 농학적 성과를 가져오는 통합 생물학적 플랫폼으로 전환함에 따라 시장이 지속적으로 확대되는 태세에 있음을 시사합니다.
세계 농업용 접종제 시장 동향과 통찰
유기 인증 기준으로 이동
소매업체와 소비자는 현재 잔류농약이 없는 농산물을 찾고 있으며, 엄격한 유기 기준을 충족하는 투입자재의 큰 시장을 형성하고 있습니다. EU의 Farm to Fork 전략은 2030년까지 화학농약 사용량을 50% 줄이는 것을 목표로 하며 EU 전역에서 미생물 채용을 가속화했습니다. 미국 농무부(USDA)의 전미 유기 프로그램 규칙이 업데이트되고 허용 가능한 미생물 생산 관행이 명확해짐에 따라 구매자의 불확실성이 줄어들고 공급업체의 투자가 지원되었습니다. 20%에서 40%의 유기 가격 프리미엄은 생물학적 접종제의 높은 초기 비용을 정당화합니다. 하지만 전문적인 보관 및 취급 인프라가 없는 소규모 생산자는 공급망 전체에서 인증을 유지하는 데 장애물에 직면하고 있습니다.
경작지면적 축소와 식량안전에 대한 압력
세계 1인당 경작지역은 1970년 0.38헥타르에서 2020년 0.19헥타르로 감소하여 토지 확대보다 수율 강화에 초점을 맞추게 되었습니다. 아시아태평양에서는 급속한 도시화가 이 압력을 증폭시키고 있습니다. 농장 연구에 의하면 미생물 접종제는 영양 순환과 토양 구조를 개선함으로써 저생산성 토양에서도 수율을 4.8-6.2% 향상시킬 수 있습니다. 토지 가격이 헥타르당 미화 10,000달러를 초과하는 지역에서 생물학적 입력은 비용 효과적인 증수 경로를 제공합니다. 에너지 시장의 박박으로 인해 합성 비료의 가격이 불안정하게 유지되기 때문에 이 이점은 점점 커집니다.
농부의 인식 격차와 농장에서의 취급의 복잡성
많은 농부들은 미생물 보관, 생존 시험, 시기 시기에 대한 교육을 받지 못했습니다. 보급 지도원은 비료나 농약에 중점을 두고 있는 경우가 많고, 생물학적 비료에 대해서는 지식의 갭이 있습니다. 결과적으로 제품을 잘못 취급하면 일관성 없는 성능과 회의적인 견해를 초래합니다. 뿌리 곡물에서 뿌리 박테리아를 성장시키는 브라질의 "결절 파쇄"기술은 풀뿌리 기술 혁신이 보급 격차를 메우고 도입 장벽을 낮출 수 있음을 보여줍니다.
부문 분석
작물 영양 애플리케이션은 질소 고정 및 인 가용화 미생물이 합성 비료의 일부를 대체하기 때문에 2024년수익의 52%를 차지했습니다. 비료 비용 상승이 생물학적 대체를 촉진하기 때문에 영양 분야의 농업용 접종제 시장 규모는 꾸준히 확대될 것으로 예측됩니다. 농가는 수율을 유지하면서 질소 투입량을 15-25% 절약할 수 있다고 하며, 이는 투자 회수 기간의 단축으로 이어집니다.
작물 보호 생물학적 제제는 그 공헌도가 낮은 것으로, 2030년까지의 CAGR은 10.9%를 나타낼 전망입니다. 화학농약에 대한 규제 단속과 주요 병원균의 내성 문제의 급증이 수요를 가속화하고 있습니다. 기업은 현재 미생물 보호제와 영양주를 번들로 토양에서 잎까지 종합적으로 커버할 것을 약속합니다. 이 수렴은 단일 영양제 제조업체에게 포트폴리오를 퍼뜨리거나 통합 제품에 점유율을 빼앗기는 위험을 야기합니다.
2024년 농업용 접종제 시장 점유율은 박테리아가 71%를 차지했으며, 이는 수십년에 걸쳐 콩과 식물에서의 근립균의 성공과 곡류에서의 사용 확대를 반영하고 있습니다. 이 리더십은 잘 입증된 효과, 저비용, 규제 당국 간의 친숙한 깊이 때문입니다.
곰팡이는 가장 빠르게 성장하는 그룹이며 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)은 11.5%를 나타낼 전망입니다. Tricoderma와 박테리아는 병해의 억제와 인의 흡수로 지지를 모으고 있습니다. 캡슐화의 진보로 보존 안정성이 향상되고 최근의 EPA 내성 면제에 의해 승인이 원활하게 진행됩니다. 기존의 박테리아 기업은 규모의 우위를 유지하고 있지만, 곰팡이의 혁신적인 기업은 스트레스 완화의 뛰어난 이점으로 투자를 모으고 있습니다.
지역 분석
북미는 왕성한 연구개발 활동과 확립된 투입농약 유통망에 지지되어 2024년 최대 지역 점유율을 유지했습니다. 이 지역의 2030년까지의 CAGR은 6.9%를 세계 평균 이하로 떨어지지만, 이는 많은 생산자들이 생물학적 비료가 화학 합성 비료의 신뢰성에 필적한다는 확신이 없기 때문입니다. 규제경로는 점차 개선되고 있으며, 바실러스균과 트리코델마균주에 대한 최근의 EPA 면제조치에 의해 신제품 시장 투입까지의 시간이 단축되었습니다. 농가에 대한 지속적인 교육과 탄소 크레딧의 통합은 옥수수 벨트와 프레리 주 전역에서 채택을 진행할 수 있습니다.
남미는 CAGR 10.4%로 가장 빠르게 성장하는 지역입니다. 브라질의 국가 바이오 투입물 프로그램은 2023-24년 시즌에 50억 브랜드(10억 달러)의 매출을 계상해 15% 증가했습니다. 아르헨티나의 성숙한 대두 접종 인프라는 브라질의 적극적인 신규 작물에 대한 노력을 보완하여 대륙 전체의 핫스팟을 형성합니다. ICL에 의한 Nitro 1000의 인수와 FMC의 Ballagro와의 제휴에서 볼 수 있듯이, 다국적 기업은 규제상의 발판과 생산 능력을 확보하기 위해 현지에서의 제휴를 깊게 하고 있습니다.
아시아태평양과 아프리카에는 새로운 비즈니스 기회가 있으며 각각 CAGR 9.8%와 8.3%로 성장하고 있습니다. 중국에서는 550개가 넘는 미생물 농약 제품이 등록되어 규제 기세를 보이고 있으며, 인도의 중앙 살충제 위원회(Central Insecticides Board)는 2024년 초에 416개의 생물학적 제제를 승인했습니다. 아프리카에서는 농장에서 뿌리 박테리아 성장과 같은 영세 농가 친화적인 접근이 콜드체인 제약을 피하고 있지만,보다 광범위한 시장 개척은 개선 보급 지원과 접종제 살포 시설에 대한 자금 접근에 의존합니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장의 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 유기 인증 기준으로의 전환
- 경작지의 감소와 식량 안보에의 압력
- 정부의 비료 보조금의 바이오 인풋에의 재편
- 종자 응용 생물 컨소시엄의 급속한 확대
- 미생물의 캡슐화 기술에 대한 벤처 투자
- 생물학적 질소 고정을 위한 탄소 크레딧 수익화
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 농가의 의식 갭과 농장에서의 취급의 복잡성
- 신속 대응 합성 비료에 대한 선호도
- 미생물 칵테일의 규제상의 그레이 존
- 확장 공급망의 생물학적 오염 위험
- 규제 상황
- 기술의 전망
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 구매자의 협상력
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 기능별
- 작물 영양
- 농작물 보호
- 미생물별
- 박테리아
- Rhizobacteria
- Azotobacter
- 인산화세균
- 기타 세균
- 균류
- Trichoderma
- Mycorrhiza
- 기타 균류
- 기타 미생물
- 박테리아
- 사용방법별
- 종자 접종
- 토양 접종
- 작물 유형별
- 곡물
- 콩류 및 지방종자
- 상업 작물
- 과일 및 채소
- 기타 용도
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 기타 북미
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 스페인
- 이탈리아
- 러시아
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 인도
- 호주
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 중동
- 사우디아라비아
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 기타 중동
- 아프리카
- 남아프리카
- 케냐
- 기타 아프리카
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- BASF SE
- Novonesis(Novozymes A/S)
- Corteva Agriscience
- Premier Tech Ltd.
- Lallemand Inc.
- Lesaffre-Agrauxine(Lesaffre Group)
- Bioceres Crop Solutions Corp.
- Verdesian Life Sciences(AEA Investors)
- Mapleton Agri Biotec
- New Edge Microbials
- T. Stanes and Company(Amalgamations Group)
- Valent BioSciences(Sumitomo Chemical)
- Bayer AG
- Syngenta AG(ChemChina)
제7장 시장 기회와 장래의 전망
SHW 25.11.17The agricultural inoculants market is valued at USD 11.23 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 18.50 billion by 2030, reflecting a 10.5% CAGR.
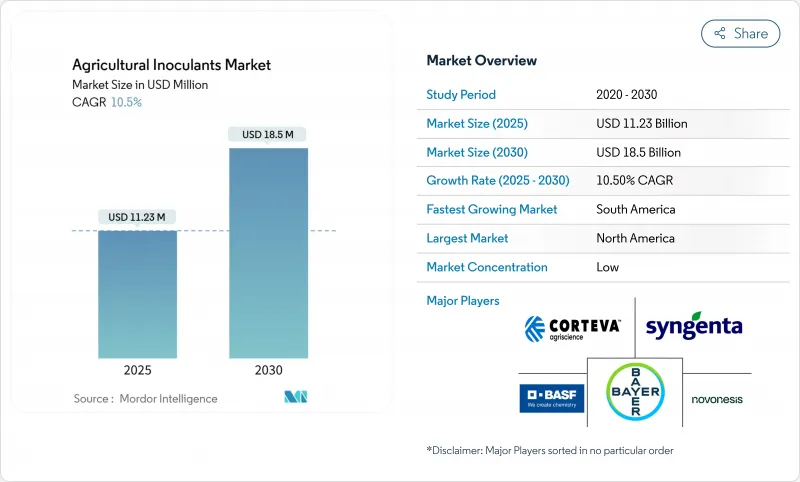
Growth now rests on these converging forces: mounting policy pressure to curb synthetic fertilizer emissions, stronger carbon-credit incentives that reward biological nitrogen fixation, and rising retail demand for residue-free food that meets tightening organic standards. The sector has moved from niche biological inputs toward mainstream crop-management tools as farmers recognize measurable yield stability and soil health gains. Suppliers capture attractive margins through premium, multi-strain formulations that align with sustainability targets while lowering nutrient costs for growers. Key capital inflows reinforce the uptrend. Venture funding in microbial encapsulation and AI-guided application systems is scaling quickly, giving start-ups the resources to commercialize differentiated technologies. At the same time, incumbents accelerate research and development in next-generation delivery methods that extend microbial viability and simplify on-farm use. This dual track of innovation and consolidation signals a market poised for continued expansion as value shifts from commodity single-strain products to integrated biological platforms that deliver verifiable agronomic outcomes.
Global Agricultural Inoculants Market Trends and Insights
Shift toward organic certification standards
Retailers and consumers now demand residue-free produce, creating a sizable market for inputs that meet strict organic standards. The European Union's Farm to Fork strategy, aiming for a 50% cut in chemical pesticide use by 2030, accelerated microbial adoption across the bloc. Updated USDA National Organic Program rules clarify acceptable microbial production practices, reducing buyer uncertainty and supporting supplier investment. Organic price premiums ranging from 20% to 40% justify higher upfront costs for biological inoculants. Nevertheless, smaller growers without specialized storage and handling infrastructure face hurdles in maintaining certification throughout the supply chain.
Shrinking arable land and food-security pressures
Global arable land per capita fell from 0.38 ha in 1970 to 0.19 ha in 2020, sharpening the focus on yield intensification rather than land expansion. In Asia-Pacific, rapid urbanization amplifies this pressure. Field studies show microbial inoculants can raise yields 4.8-6.2% in low-productivity soils by improving nutrient cycling and soil structure. For regions where land prices exceed USD 10,000 per hectare, biological inputs offer a cost-effective intensification pathway. The benefit grows as synthetic fertilizer prices remain volatile due to energy-market tightness.
Farmer awareness gaps and on-farm handling complexity
Many farmers lack training on microbial storage, viability testing, and application timing. Extension agents often focus on fertilizers and pesticides, leaving a knowledge gap for biologicals. As a result, product mishandling leads to inconsistent performance and skepticism. Brazil's "nodule crushing" technique, which lets growers propagate rhizobia from root nodules, shows that grassroots innovation can fill extension gaps and lower adoption barriers.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rapid expansion of seed-applied biological consortia
- Venture investment in encapsulation tech for microbes
- Preference for fast-response synthetic fertilizers
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Crop nutrition applications captured 52% of 2024 revenue as nitrogen-fixing and phosphorus-solubilizing microbes replaced portions of synthetic fertilizers. The agricultural inoculants market size for nutrition is projected to expand steadily as rising fertilizer costs encourage biological substitution. Farmers appreciate documented savings of 15-25% on nitrogen inputs while maintaining yields, which translates into rapid payback periods.
Crop protection biologicals, while contributing a smaller base, are set for a 10.9% CAGR through 2030. Regulatory crackdowns on chemical pesticides and a surge in resistance issues among major pathogens are accelerating demand. Companies now bundle microbial protectants with nutritional strains, promising holistic soil-to-leaf coverage. This convergence pressures standalone nutrition providers to broaden portfolios or risk losing share to integrated offerings.
Bacteria held 71% of the agricultural inoculants market share in 2024, reflecting decades of rhizobia success in legumes and growing use in cereals. This leadership rests on well-documented efficacy, low cost, and familiarity among regulators.
Fungi are the fastest-growing group, projected at an 11.5% CAGR to 2030. Trichoderma and mycorrhiza strains gain traction for disease suppression and phosphorus uptake. Advances in encapsulation enhance shelf stability, while recent EPA tolerance exemptions smooth approvals. Although bacterial incumbents retain scale advantages, fungal innovators attract investment for premium stress-mitigation benefits.
The Agricultural Inoculants Market Report is Segmented by Function (Crop Nutrition and Crop Protection), Microorganism (Bacteria, Fungi, and Other Microorganisms), Mode of Application (Seed Inoculation and Soil Inoculation), Crop Type (Grains and Cereals, Pulses and Oilseeds, and More), and Geography (North America, South America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America maintained the largest regional share in 2024, supported by robust research and development activity and well-established ag-input distribution networks. The region's 6.9% CAGR to 2030 trails the global average because many growers remain unconvinced that biologicals can match the reliability of synthetic fertilizers. Regulatory pathways are gradually improving, and recent EPA exemptions for Bacillus and Trichoderma strains shorten the time to market for new products. Continued farmer education and carbon-credit integration could lift adoption across the Corn Belt and Prairie Provinces.
South America is the fastest-growing region with a 10.4% CAGR. Brazil's National Bio-inputs Program generated BRL 5 billion (USD 1 billion) in sales in the 2023-24 season, up 15%, underscoring strong policy support. Argentina's mature soybean inoculation infrastructure complements Brazil's aggressive new-crop initiatives, creating a continent-wide hotspot. Multinational firms are deepening local partnerships, as shown by ICL's acquisition of Nitro 1000 and FMC's pact with Ballagro, to secure regulatory footholds and production capacity.
Asia-Pacific and Africa present emerging opportunities, growing at 9.8% and 8.3% CAGRs, respectively. China's registration of over 550 microbial pesticide products shows regulatory momentum, while India's Central Insecticides Board approved 416 biologic agendas in early 2024. In Africa, smallholder-friendly approaches such as on-farm rhizobia propagation bypass cold-chain constraints, but broader market development still depends on extension support and finance access for inoculant application equipment.
- BASF SE
- Novonesis (Novozymes A/S)
- Corteva Agriscience
- Premier Tech Ltd.
- Lallemand Inc.
- Lesaffre - Agrauxine (Lesaffre Group)
- Bioceres Crop Solutions Corp.
- Verdesian Life Sciences (AEA Investors)
- Mapleton Agri Biotec
- New Edge Microbials
- T. Stanes and Company (Amalgamations Group)
- Valent BioSciences (Sumitomo Chemical)
- Bayer AG
- Syngenta AG (ChemChina)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Shift toward organic certification standards
- 4.2.2 Shrinking arable land and food-security pressures
- 4.2.3 Government fertilizer subsidy realignment toward bio-inputs
- 4.2.4 Rapid expansion of seed-applied biological consortia
- 4.2.5 Venture investment in encapsulation technology for microbes
- 4.2.6 Carbon-credit monetization for biological nitrogen fixation
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Farmer awareness gaps and on-farm handling complexity
- 4.3.2 Preference for fast-response synthetic fertilizers
- 4.3.3 Regulatory gray zones for stacked microbial cocktails
- 4.3.4 Biological contamination risk in extended supply chains
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Function (Value)
- 5.1.1 Crop Nutrition
- 5.1.2 Crop Protection
- 5.2 By Microorganism (Value)
- 5.2.1 Bacteria
- 5.2.1.1 Rhizobacteria
- 5.2.1.2 Azotobacter
- 5.2.1.3 Phosphobacteria
- 5.2.1.4 Other Bacteria
- 5.2.2 Fungi
- 5.2.2.1 Trichoderma
- 5.2.2.2 Mycorrhiza
- 5.2.2.3 Other Fungi
- 5.2.3 Other Microorganisms
- 5.2.1 Bacteria
- 5.3 By Mode of Application (Value)
- 5.3.1 Seed Inoculation
- 5.3.2 Soil Inoculation
- 5.4 By Crop Type (Value)
- 5.4.1 Grains and Cereals
- 5.4.2 Pulses and Oilseeds
- 5.4.3 Commercial Crops
- 5.4.4 Fruits and Vegetables
- 5.4.5 Other Applications
- 5.5 By Geography (Value)
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Spain
- 5.5.2.5 Italy
- 5.5.2.6 Russia
- 5.5.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 Australia
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Argentina
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.6 Africa
- 5.5.6.1 South Africa
- 5.5.6.2 Kenya
- 5.5.6.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles {(includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)}
- 6.4.1 BASF SE
- 6.4.2 Novonesis (Novozymes A/S)
- 6.4.3 Corteva Agriscience
- 6.4.4 Premier Tech Ltd.
- 6.4.5 Lallemand Inc.
- 6.4.6 Lesaffre - Agrauxine (Lesaffre Group)
- 6.4.7 Bioceres Crop Solutions Corp.
- 6.4.8 Verdesian Life Sciences (AEA Investors)
- 6.4.9 Mapleton Agri Biotec
- 6.4.10 New Edge Microbials
- 6.4.11 T. Stanes and Company (Amalgamations Group)
- 6.4.12 Valent BioSciences (Sumitomo Chemical)
- 6.4.13 Bayer AG
- 6.4.14 Syngenta AG (ChemChina)



















