
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1850970
위성 안테나 시장 : 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Satellite Antenna - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
위성 안테나 시장 규모는 2025년에 63억 6,000만 달러, 2030년에는 125억 2,000만 달러에 이르고, CAGR은 14.5%를 나타낼 전망입니다.

높은 처리량 연결에 대한 왕성한 수요, 다중 궤도별자리 배치, 안테나 제조 비용의 감소로 상업 및 방어 영역에서의 채택이 가속화되고 있습니다. 소프트웨어 정의 빔 스티어링, 경량 복합재, 고도로 통합된 칩셋은 운영자의 평생 소유 비용을 낮추면서 성능을 향상시킵니다. 또한 제품 포트폴리오를 확대하는 전략적 합병과 우주 인프라를 디지털 주권의 기둥으로 취급하는 정부에 의해 성장이 강화되고 있습니다. 이러한 복잡한 요인으로 인해 위성 안테나 시장은 공급업체가 규제와 궤도 쓰레기의 복잡성을 극복하더라도 두 자릿수 성장을 계속하고 있습니다.
세계 위성 안테나 시장 동향과 통찰
LEO 광대역 위성군 급증
스타링크(Starlink)나 원웹(OneWeb)과 같은 저궤도 프로젝트는 링크 예산의 전제를 바꾸어 고속으로 이동하는 위성을 1분에 수십기 추적할 수 있는 전자 제어 어레이의 도입을 사업자에게 촉구하고 있습니다. 2024년 9월에는 411개의 별자리가 등록되었지만, 완전히 발사된 것은 불과 5%에 불과하고 안테나 공급자에게는 광대한 활주로가 남아 있습니다. 컴팩트한 위상 배열은 GNSS 수신기와 엣지 컴퓨팅을 통합하여 단말기가 LEO, MEO, GEO 레이어에서 빔을 자동으로 전환할 수 있도록 합니다. 원격지 커뮤니티, 해상 항로, 재해 대응 팀은 일찍부터 혜택을 받고 있습니다. 페이즈드 어레이는 기계 부품이 불필요하기 때문에 평생 보수 비용이 낮아 대규모 전개의 경제적 근거가 강해집니다. 듀얼 궤도 단말기를 소비자용 전자기기의 가격대에서 대량 생산할 수 있는 벤더는 위성 안테나 시장이 휴대 단말과 같은 수량으로 확대됨에 따라 큰 가치를 획득하게 됩니다.
우주의 급속한 군사화(MilSATCOM)
방위 당국은 확실하고 방해에 강한 링크를 미션 크리티컬로 간주하고 있습니다. 미국의 2025년도 예산에서는 우주 기반 시스템에 252억 달러가 할당되어 경쟁하는 전자기 환경에서 작동하는 멀티밴드, 지향성 안테나 조달의 방아쇠가 되고 있습니다. 전투에서 입증된 요구 사항에는 간섭을 완화하기 위한 사이드 로브 억제, 스푸핑 방지, 동적 빔 호핑이 포함됩니다. 유럽과 아시아태평양의 병행 프로그램은 수요를 더욱 확대하고 있습니다. 군부는 또한 소형 무인 정찰기나 하사관병에 맞도록 단말의 경량화를 추진하고 있으며, GaN 파워 앰프나 컨포멀 복합재에 있어서의 돌파구를 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 장기적으로 안전한 광 크로스 링크가 RF를 보완할 것이지만 단기 지출은 고급 위상 어레이 RF 아키텍처에 집중하고 위성 안테나 시장의 기세를 유지하고 있습니다.
적도 바로 아래의 Ku/Ka 밴드 강우 페이드
호우는 Ku 대역과 Ka 대역의 신호를 최대 20dB 감쇠시키기 때문에 사업자는 링크 마진을 오버사이즈하거나 보다 낮은 주파수로 되돌려야 합니다. 인도네시아와 브라질의 열대성 마이크로 버스트는 기업과 백홀 고객의 SLA를 손상시키는 예측 불가능한 페이드를 유발합니다. 완화책으로는 적응 코딩, 사이트 다이버시티, 폭풍우시에 C-band로 폴백하는 듀얼 밴드 단말기 등이 있지만, 이러한 솔루션은 서비스 제공업체에게 설비투자와 고정자산세(OPEX)를 끌어올리게 됩니다. 미래의 기후 변화가 불확실한 요소가 되기 때문에 일부 통신 사업자는 용량면에서 유리하지만 Ka 대역 중심의 네트워크에 소극적입니다. 그 결과, 적도 바로 아래 지역에서의 채택 동향은 세계 위성 안테나 시장 추세에 뒤처질 수 있습니다.
부문 분석
Ku 밴드는 성숙한 지상 인프라와 균형 잡힌 레인 페이드 내성을 활용하여 2024년 위성 안테나 시장의 29%를 차지했습니다. 이 부문은 방송과 VSAT 서비스의 중심이며, 특히 규제상의 인가가 이미 존재하는 곳에서의 이용이 많습니다. 이와는 대조적으로, Ka 대역은 CAGR 15.2%로 급증하고 있으며, 비트당 저비용과 유연한 스폿 빔 아키텍처를 요구하는 광대역 사업자를 끌어들이고 있습니다. 이 성장 궤도는 NASA의 지구관측 별자리에서 26Tb/일의 라우팅 요구 사항을 지원하며 Ka 터미널의 위성 안테나 시장 규모가 확대됨을 의미합니다. C 밴드는 사이클론이 발생하기 쉬운 지역에서 중요성을 유지하고 X 밴드는 간섭 내성에 의해 방어 틈새가 계속합니다. 신흥 멀티밴드 안테나는 기존의 사일로를 모호하게 하여 실시간 주파수 전환을 가능하게 합니다. 이 기능은 전체 시스템의 가용성을 높이고 위성 안테나 시장에서 공급업체가 지원할 수 있는 수익원을 확장합니다.
멀티 빔 플랫 패널 디자인은 Ku와 Ka의 동시 연결을 가능하게 하며 비로 인해 페이드될 때 트래픽을 반전시킬 수 있습니다. 프로그래머블 RF 프론트엔드를 통합하는 공급업체는 필요한 곳에 동적으로 전력을 할당하고 스펙트럼 효율을 높일 수 있습니다. 이러한 발전은 모바일 VSAT, 크루즈, 석유 및 가스 플랫폼과 같은 가치 제안을 변화시킵니다. 따라서 고주파 단말기의 위성 안테나 시장 규모는 2030년까지 두배로 될 것으로 예상되지만, 열대 지역 수요를 완전히 끌어내기 위해서는 공급업체가 날씨에 적응하는 인텔리전스를 통합해야 합니다.
파라볼라 안테나는 2024년 위성 안테나 시장 규모의 38%를 차지했고 달러당 이득이 높은 정적 게이트웨이에 선호됩니다. 기계식 짐벌은 대형 크루즈 선박과 텔레포트 허브에서 여전히 비용 효율적입니다. 그러나 CAGR 18.4%로 확대되는 평판 전자 제어 어레이는 모빌리티 이용 사례를 재정의하고 있습니다. Anokiwave를 탑재한 패널은 현재 공장에서 교정되어 설치 시간을 단축하고 내로우 바디 항공기의 등각 동체에 설치를 지원합니다. 프로토타입 중인 팽창식 접시는 20:1의 패킹 효율을 약속하며 발사 질량에 민감한 소형 위성에 대응합니다.
소형 파라볼라 부문와 위상 쉬프터 서브어레이를 결합한 하이브리드 아키텍처는 접시의 높은 이득의 이점과 ESA의 민첩성을 이끌어냅니다. 유연한 유전체 재료를 연구하는 공급업체는 안테나를 차량 지붕 주위로 구부릴 수 있으며 공기 저항으로 인한 패널티를 없앨 수 있습니다. 그 결과, 대응 가능한 위성 안테나 시장은 초박형 단말기를 필요로 하는 개인용 차량, 기차, 도시형 드론 택시로까지 확대됩니다. 리플렉터의 기존 기업은 설치된 인프라를 보호하기 위해 자동 포인팅과 상태 모니터링 펌웨어를 통합하여 2030년까지 완전한 대체가 아닌 공존 시나리오를 제공합니다.
위성 안테나 시장 보고서는 주파수 대역(C 밴드, X 밴드, Ku 밴드 등), 안테나 유형(파라볼라 안테나, 혼형 안테나, FRP 레이돔형 안테나 등), 용도(스페이스본, 에어본 등), 최종 사용자(민간 및 정부, 방어), 지역별로 분류됩니다.
지역 분석
아시아태평양은 중국, 인도, 일본, 한국이 멀티오비트 시스템과 국산 제조 규모를 확대함에 따라 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)이 14.6%로 가장 빠른 성장세를 보일 것으로 예상됩니다. 2024년 2월에 개설된 중국 다섯 번째 남극 전초 기지는 과학과 방위 분야에서 사용되는 위성 안테나를 전시합니다. 인도의 'Make in India' 정책에 따른 생산 연동형 인센티브는 피드혼, 레이돔, RFIC 서브시스템의 현지 생산을 촉진하여 지역사업자의 비용을 낮춥니다. 일본의 자동차 업계는 지상파 이외의 백홀을 이용한 커넥티드카 서비스의 준비를 진행하고 있으며, 공급업체는 옥상 통합용 안테나의 소형화를 촉구하고 있습니다.
북미는 깊은 항공우주 공급망, 엄청난 국방 지출, 기업이 정신이 넘치는 우주 벤처 덕분에 여전히 가장 큰 위성 안테나 시장입니다. 미국 우주군은 위성관제 네트워크를 유지하고 19기의 안테나를 75%의 가동률로 운용하고 있으며, 2025년부터는 새롭게 12기의 대용량 안테나를 계획 중입니다. 캐나다의 극지 통신 프로그램은 저온 내성 안테나 수요를 늘리고 있습니다. 멕시코 및 기타 라틴 국가들은 설비 투자의 압력에 의해 당면의 규모가 억제되는 것, 인터넷 커뮤니티 Wi-Fi용으로 GEO 게이트웨이를 활용하고 있습니다.
유럽은 견고한 점유율을 유지하고 있으며 군사 및 기후 모니터링 임무를 지원하는 AMPER 프로젝트의 형상 메쉬 반사기 등 ESA의 기술 입증으로 강화되었습니다. 독일과 영국은 데이터의 자율성을 보장하기 위해 소블린 텔레포트에 자금을 제공하고 모바일 네트워크 사업자는 스코틀랜드와 바이에른 주 지역에서 위성을 통해 백홀을 테스트하고 있습니다. 동유럽의 통신사업자는 환율 변동을 이기기 위해 리스 투 오운 모델을 채택하여 안테나 공급업체로의 주문 파이프라인을 원활하게 하는 전술을 취하고 있습니다. 중동에서는 GCC의 정부 펀드가 GEO VHTS 프로젝트를 지원하고 있으며, 사우디아라비아 로드맵에서는 2030년까지 국가의 우주소득이 3배가 된다고 합니다. 남미는 석유 및 가스 해상 연결에 이중 중복 안테나가 필요한 브라질에서 뒤처지지만 성장의 여지가 있습니다. 이러한 역학을 종합하면 위성안테나 시장 내에서는 지역적인 수요의 분산이 유지되어 매크로적인 충격으로부터 세계적인 수익을 지킬 수 있습니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장의 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 역학
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- LEO 광대역 위성군의 보급
- 우주의 급속한 군사화(MilSATCOM)
- 높은 처리량 위성(HTS) 페이로드 채택
- 상용 기내 접속(IFC)의 붐
- ESA 기반 플랫 패널 비용 곡선 디플레이션(UNDER-RADAR)
- 달 및 지구와 달 사이 미션 통신 수요(UNDER-RADAR)
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 적도 지역에서의 Ku/Ka 밴드 강우 감쇠
- 위상 배열 칩셋의 수출 관리 병목
- 궤도 파편 보험료의 급등(UNDER-RADAR)
- 신흥 시장의 통신사업자의 설비투자위기(미표면화된 동향)
- 밸류체인 분석
- 규제 상황
- 기술의 전망
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 구매자의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 주파수 대역별
- C 밴드
- X 밴드
- Ku 밴드
- Ka 밴드
- L/S 밴드
- VHF/UHF 밴드
- 안테나 유형별
- 파라볼라 반사경
- 플랫 패널(ESA/RSA)
- 혼
- 유전체 공진기
- FRP 레이돔
- 금속 각인
- 용도별
- 우주선
- 공수
- 해사
- 육상(이동식 및 고정식)
- 최종 사용자별
- 상업용
- 정부 및 방위
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 러시아
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 인도
- 한국
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- GCC 국가
- 튀르키예
- 남아프리카
- 기타 중동 및 아프리카
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Honeywell International Inc.
- CPI International Inc.
- Kymeta Corp.
- Norsat International Inc.
- Cobham SATCOM
- L3Harris Technologies Inc.
- Viasat Inc.
- Airbus Defence and Space
- Gilat Satellite Networks Ltd.
- Maxar Technologies
- Ball Aerospace
- Intellian Technologies
- Isotropic Systems(All.Space)
- Hanwha Phasor
- SES SA(O3b mPOWER User Terminals)
- Thales Alenia Space
- MT Mechatronics
- SatixFy Ltd.
- General Dynamics Mission Systems
- LEOcloud Inc.
- Hughes Network Systems
제7장 시장 기회와 장래의 전망
SHW 25.11.11The satellite antenna market size stands at USD 6.36 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 12.52 billion by 2030, reflecting a robust 14.5% CAGR.
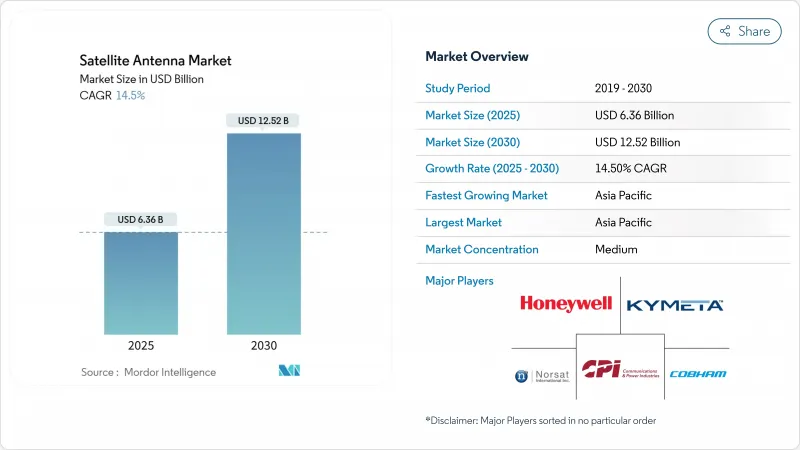
Strong demand for high-throughput connectivity, the roll-out of multi-orbit constellations, and falling antenna production costs are accelerating adoption across commercial and defense domains. Software-defined beam steering, lighter composites, and highly integrated chipsets are improving performance while lowering lifetime ownership costs for operators. Growth is also being reinforced by strategic mergers that broaden product portfolios and by governments treating space infrastructure as a pillar of digital sovereignty. These converging factors keep the satellite antenna market on a double-digit growth path even as suppliers navigate regulatory and orbital-debris complexities.
Global Satellite Antenna Market Trends and Insights
Proliferation of LEO broadband constellations
Low Earth Orbit projects such as Starlink and OneWeb are rewriting link-budget assumptions, pushing operators to deploy electronically steered arrays that can track dozens of fast-moving satellites per minute. In September 2024, 411 constellations were registered, yet only 5% were fully launched, leaving extensive runway for antenna suppliers. Compact phased arrays now include integrated GNSS receivers and edge computing, letting terminals auto-switch beams across LEO, MEO, and GEO layers. Remote communities, maritime routes, and disaster-response teams are early beneficiaries. Because phased arrays eliminate mechanical parts, lifetime maintenance costs fall, reinforcing the economic case for large-scale roll-outs. Vendors able to mass-produce dual-orbit terminals at consumer-electronics price points will capture outsized value as the satellite antenna market broadens to handset-like volumes.
Rapid militarization of space (MilSATCOM)
Defense authorities see assured, jam-resistant links as mission-critical. The U.S. FY 2025 budget allocates USD 25.2 billion to space-based systems, triggering procurement of multi-band, directive antennas that operate in contested electromagnetic environments. Battle-proven requirements include side-lobe suppression, anti-spoofing, and dynamic beam hopping to mitigate interference. Parallel programs in Europe and Asia-Pacific further widen demand. Militaries also push for lighter terminals to fit small UAVs and dismounted soldiers, encouraging breakthroughs in GaN power amplifiers and conformal composites. Over the long term, secure optical cross-links will complement RF, but near-term spending remains anchored in advanced phased-array RF architectures, sustaining momentum for the satellite antenna market.
Ku/Ka-band rain fade in equatorial regions
Heavy rainfall events attenuate Ku and Ka signals by up to 20 dB, forcing operators to oversize link margins or revert to lower frequencies. Tropical micro-bursts in Indonesia and Brazil create unpredictable fades that undermine SLAs for enterprise and backhaul customers. Mitigation tactics include adaptive coding, site diversity, and dual-band terminals that fall back to C band during storms, yet these solutions raise capex and opex for service providers. Future climate variability adds uncertainty, making some telcos reluctant to commit to Ka-centric networks despite their capacity advantages. Consequently, adoption curves in equatorial belts may lag the global satellite antenna market trend.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- High-throughput satellite (HTS) payload adoption
- Commercial in-flight connectivity (IFC) boom
- Export-control bottlenecks on phased-array chipsets
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Ku Band accounted for 29% of the satellite antenna market in 2024, capitalizing on mature ground infrastructure and balanced rain-fade resilience. The segment continues to anchor broadcast and VSAT services, especially where regulatory clearances already exist. In contrast, Ka Band is scaling rapidly at a 15.2% CAGR, attracting broadband operators that seek lower cost per bit and flexible spot-beam architectures. This growth trajectory translates to an expanding satellite antenna market size for Ka terminals, underpinned by NASA's requirement to route 26 Tb/day on its upcoming Earth-observation constellation. C Band maintains relevance in cyclone-prone zones, while X Band remains a defense niche thanks to interference immunity. Emerging multi-band antennas blur traditional silos, permitting real-time frequency switching, a capability that uplifts overall system availability and widens supplier addressable revenue streams within the satellite antenna market.
Multi-beam flat-panel designs now facilitate simultaneous Ku and Ka connectivity, enabling operators to reverse traffic when rain fade hits. Suppliers integrating programmable RF front-ends can dynamically allocate power where needed, lifting spectral efficiency. These advances transform value propositions for mobile VSAT, cruise, and oil-and-gas platforms. As such, the satellite antenna market size for high-frequency terminals is forecast to double by 2030, though suppliers must embed weather-adaptive intelligence to unlock full demand across tropical geographies.
Parabolic reflectors held 38% share of the satellite antenna market size in 2024, favored for static gateways that prize high gain per dollar. Mechanical gimbals remain cost-effective for large cruise ships and teleport hubs. Yet flat-panel electronically steered arrays, expanding at an 18.4% CAGR, are redefining mobility use cases. Anokiwave-powered panels are now factory-calibrated, slashing installation time and supporting conformal fuselage mounting on narrow-body aircraft. Inflatable dishes under prototyping promise 20:1 packing efficiency, catering to launch-mass-sensitive small satellites.
Hybrid architectures blend small parabolic segments with phase-shifter sub-arrays, extracting the high-gain benefits of dishes and the agility of ESAs. Vendors exploring flexible dielectric materials can bend antennas around vehicle roofs, erasing aerodynamic drag penalties. Consequently, the addressable satellite antenna market widens to include personal vehicles, trains, and urban drone taxis, all of which require ultra-low-profile terminals. Reflector incumbents respond by embedding auto-pointing and health-monitoring firmware to protect installed bases, signaling a coexistence rather than outright displacement scenario through 2030.
The Satellite Antenna Market Report is Segmented by Frequency Band (C Band, X Band, Ku Band, and More), Antenna Type (Parabolic Reflector, Horn, FRP-Radome, and More), Application (Spaceborne, Airborne, and More), End-User (Commercial and Government and Defense), and Geography.
Geography Analysis
Asia Pacific records the quickest expansion, charting a 14.6% CAGR to 2030 as China, India, Japan, and South Korea scale multi-orbit systems and indigenous manufacturing. China's fifth Antarctic outpost, opened in February 2024, showcases dual-use satellite dishes that serve science and defense agendas. India's production-linked incentives, aligned with its "Make in India" drive, catalyze local fabrication of feed horns, radomes, and RFIC subsystems, lowering costs for regional operators. Japan's auto sector readies connected-car services using non-terrestrial backhaul, prompting suppliers to miniaturize antennas for rooftop integration.
North America remains the largest satellite antenna market thanks to deep aerospace supply chains, heavy defense spending, and entrepreneurial space ventures. The U.S. Space Force maintains the Satellite Control Network, operating 19 dishes at 75% utilization, with plans for 12 new high-capacity antennas starting 2025. Canada's Polar communications programs add demand for low-temperature-tolerant antennas. Mexico and other Latin peers leverage GEO gateways for internet-community Wi-Fi, although capex pressures curb near-term scale.
Europe holds robust share, reinforced by ESA technology demonstrators such as the shaped mesh reflector from the AMPER project that supports military and climate-monitoring missions. Germany and the UK fund sovereign teleports to secure data autonomy, while mobile network operators test backhaul-over-satellite in rural Scotland and Bavaria. Eastern European telcos adopt lease-to-own models to overcome currency volatility, a tactic that smooths order pipelines for antenna suppliers. The Middle East, buoyed by GCC sovereign wealth funds, backs GEO VHTS projects, and Saudi Arabia's roadmap foresees a trebling of national space revenues by 2030. South America trails but shows pockets of growth in Brazil, where oil-and-gas offshore connectivity mandates dual-redundant antennas. Collectively, these dynamics keep regional demand diversified within the satellite antenna market, insulating global revenue from macro shocks.
- Honeywell International Inc.
- CPI International Inc.
- Kymeta Corp.
- Norsat International Inc.
- Cobham SATCOM
- L3Harris Technologies Inc.
- Viasat Inc.
- Airbus Defence and Space
- Gilat Satellite Networks Ltd.
- Maxar Technologies
- Ball Aerospace
- Intellian Technologies
- Isotropic Systems (All.Space)
- Hanwha Phasor
- SES S.A. (O3b mPOWER User Terminals)
- Thales Alenia Space
- MT Mechatronics
- SatixFy Ltd.
- General Dynamics Mission Systems
- LEOcloud Inc.
- Hughes Network Systems
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Proliferation of LEO broadband constellations
- 4.2.2 Rapid militarization of space (MilSATCOM)
- 4.2.3 High?throughput satellite (HTS) payload adoption
- 4.2.4 Commercial in-flight connectivity (IFC) boom
- 4.2.5 ESA-based flat-panel cost curve deflation (UNDER-RADAR)
- 4.2.6 Lunar and cislunar mission communications demand (UNDER-RADAR)
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Ku-/Ka-band rain fade in equatorial regions
- 4.3.2 Export-control bottlenecks on phased-array chipsets
- 4.3.3 Mounting orbital-debris insurance premiums (UNDER-RADAR)
- 4.3.4 CAPEX crunch at emerging-market telcos (UNDER-RADAR)
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Frequency Band
- 5.1.1 C Band
- 5.1.2 X Band
- 5.1.3 Ku Band
- 5.1.4 Ka Band
- 5.1.5 L/S Band
- 5.1.6 VHF/UHF Band
- 5.2 By Antenna Type
- 5.2.1 Parabolic Reflector
- 5.2.2 Flat-Panel (ESA/RSA)
- 5.2.3 Horn
- 5.2.4 Dielectric-Resonator
- 5.2.5 FRP-Radome
- 5.2.6 Metal-Stamp
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Spaceborne
- 5.3.2 Airborne
- 5.3.3 Maritime
- 5.3.4 Land (Mobile and Fixed)
- 5.4 By End-User
- 5.4.1 Commercial
- 5.4.2 Government and Defense
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Russia
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 APAC
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 Japan
- 5.5.4.3 India
- 5.5.4.4 South Korea
- 5.5.4.5 Rest of APAC
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 GCC Countries
- 5.5.5.2 Turkey
- 5.5.5.3 South Africa
- 5.5.5.4 Rest of MEA
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Overview, Core Segments, Financials, Strategy, Market Rank)
- 6.4.1 Honeywell International Inc.
- 6.4.2 CPI International Inc.
- 6.4.3 Kymeta Corp.
- 6.4.4 Norsat International Inc.
- 6.4.5 Cobham SATCOM
- 6.4.6 L3Harris Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.7 Viasat Inc.
- 6.4.8 Airbus Defence and Space
- 6.4.9 Gilat Satellite Networks Ltd.
- 6.4.10 Maxar Technologies
- 6.4.11 Ball Aerospace
- 6.4.12 Intellian Technologies
- 6.4.13 Isotropic Systems (All.Space)
- 6.4.14 Hanwha Phasor
- 6.4.15 SES S.A. (O3b mPOWER User Terminals)
- 6.4.16 Thales Alenia Space
- 6.4.17 MT Mechatronics
- 6.4.18 SatixFy Ltd.
- 6.4.19 General Dynamics Mission Systems
- 6.4.20 LEOcloud Inc.
- 6.4.21 Hughes Network Systems
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment



















