
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1851063
폐기물 관리 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Global Waste Management - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
폐기물 관리 시장은 2025년에 1조 4,300억 달러를 달성할 전망이며, 2030년에는 1조 9,700억 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되고, 2025년부터 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 6.62%로 성장할 전망입니다.

지속적인 규제 압력, 기업의 폐기물 제로 서약 확대, 회수물 수익화로 폐기물 관리 시장은 매립지 중심 모델에서 통합 회수 시스템으로 향하고 있습니다. 유럽 연합(EU)과 미국의 일부 주에서는 확장 생산자 책임(EPR) 법령이 제정되어 폐기 비용을 브랜드 소유자에게 이전하고, 재활용 인프라를 위한 전용 자금 풀을 생성하고 있습니다. 동시에 미국 환경보호청(EPA)과 유럽연합(EU)에 의한 강제적인 디지털 추적 플랫폼의 전개는 데이터 주도의 새로운 서비스 분야를 창출하고, 탄소 포획 기술을 갖춘 폐기물 발전(WtE) 시설에 대한 투자는 탄소 마이너스 수익의 흐름을 풀어내고 있습니다. 아시아태평양은 2024년에 가장 규모가 큰 지역이었으며 중동 및 아프리카(MEA)는 2030년까지 가장 급속히 성장할 지역이 될 전망입니다. 전자 폐기물은 전기자동차 배터리의 폐기 주기가 다가오고 있기 때문에 폐기물 흐름 중 가장 빠른 속도를 나타낼 전망입니다.
세계의 폐기물 관리 시장의 동향과 인사이트
EU와 북미의 생산자 책임 규제 확대
의무화된 EPR 제도는 현재 생산자에게 회수와 재활용을 위한 자금 조달을 의무화하고 폐기물 관리 시장의 비용 기반을 재구성하고 있습니다. 캘리포니아의 SB 54는 2032년까지 플라스틱 포장을 25% 줄이고 재활용률 65%를 달성할 것을 의무화하고 있으며, 미네소타는 2024년 EPR법을 제정하여 다른 미국 5개 주에 합류했습니다. EU는 2023년에 EPR을 섬유 제품으로 확장하여 새로운 컴플라이언스 시장을 창출했습니다. 이 시장은 폐기물 처리 사업자가 EPR의 자금 계약을 획득하기 위해 광학 선별 및 폴리머 식별 라인에 통합 및 투자하도록 장려합니다. 2024년에 케냐에서 도입된 유사한 규칙은 이 모델의 세계적인 보급을 보여줍니다.
카본 마이너스 목표가 WtE 투자 촉진
넷 제로 노력은 연소 후 탄소 포집 능력을 갖춘 WtE 플랜트로 자본을 유도하고 있습니다. 닛산의 720톤의 쓰레기를 처리하는 메트로밴쿠버의 시설은 연간 30만톤의 CO2를 제거하는 설비에 1억 100만 달러의 가격을 책정하여 배출량의 밸런스를 플러스에서 마이너스로 전환했습니다. 사우디아라비아에서는 300만 톤의 도시 고형 폐기물을 연료로 변환하는 WtE 프로그램이 재생 전력을 송전망에 공급하면서 연간 179만 톤의 CO2 절감을 목표로 하고 있습니다. 탄소 신용 시장에 대한 접근은 사업자에게 새로운 소득층이 될 것입니다.
남아시아와 아프리카에서의 비공식 부문의 단편적 이점
광범위한 비정규 노동력은 폐기물 관리 시장으로의 정규 침투를 제한합니다. 남아프리카에서는 매년 367만 톤의 가정 폐기물이 회수되지 않은 채 방치되어 불법 투기를 조장하고 지자체 수입을 잠식하고 있습니다. 남아시아의 비공식 전자 폐기물 재활용은 노동자를 중금속에 노출시키고 기관 투자자들이 현대 공장에 자금을 제공하는 의지를 저하시키고 있습니다. 이러한 근로자를 규제된 밸류체인에 통합하려면 많은 현지 사업자들이 자금 조달이 불가능한 훈련과 자본이 필요하며 회수율이 낮고 누출량이 많습니다.
부문 분석
산업폐기물은 2024년에 가장 높은 기세를 유지하면서 2030년까지의 CAGR은 8.3%를 달성할 전망인 반면, 일반 가정폐기물은 동년 폐기물 관리 시장 전체의 46.54%라는 최대의 점유율을 차지했습니다. 기업의 배출 감축 의무로 인해 제조업체는 생산 쓰레기를 자원으로 취급하게 되어 현장 포장, 용제 회수, 폐쇄 루프 물류에 대한 수요가 높아지고 있습니다. 연간 2억 5,000만 파운드의 복잡한 플라스틱을 처리하도록 설계된 이스트만의 22억 5,000만 달러의 분자 재활용 사업 전개는 산업 기회의 규모를 시사하고 있습니다. 이 변화는 중국과 ASEAN 국가에 집중하는 전자 장비, 자동차 및 소비재 공장에서 특히 두드러집니다.
주택용 폐기물의 흐름은 성숙하고 있으며 도시화가 진행되고 있기 때문에 폐기물 관리 시장 전체의 규모를 확대하는데 있어서 여전히 필수적입니다. 각국 정부는 매립지 전환 목표를 준수하기 위해 색으로 구분된 배출 프로그램과 음식물쓰레기 분해장치를 설치하고 있습니다. 소매 체인의 상업 폐기물은 EPR 수수료가 점포 앞 수거 인프라에 자금을 공급하기 때문에 안정적인 성장을 계속하고 있습니다. 건설 및 철거 폐기물은 정책적으로 주목받고 있습니다. 2025년 4월에 시행된 인도의 C&D 규정 개정에서는 거대한 프로젝트에 재활용 골재의 사용이 의무화되어 파쇄업자는 수요를 예측할 수 있게 되었습니다. 의료 폐기물과 농업 폐기물은 틈새 시장이지만 확대되고 있는 카테고리입니다. 전염병 후 감염성 폐기물의 프로토콜이 강화되어 농업 바이오매스가 농촌 지역의 혐기성 소화 플랜트에 공급됩니다.
폐기물 관리 시장 보고서는 발생원별(주택, 상업(소매, 오피스 등), 산업, 기타), 서비스 유형별(수집, 수송, 분별·선별, 처분·처리), 폐기물 유형별(도시 고형 폐기물, E-Waste, 기타), 지역별(북미, 유럽, 기타)로 분류되어 있습니다. 이 보고서는 위의 모든 부문에 대해 시장 규모 및 예측(달러)을 제공합니다.
지역별 분석
아시아태평양은 2024년 세계 매출의 56%를 차지하였으며, 고도의 처리를 필요로 하는 다소재 폐기물의 흐름을 만들어 내는 밀집한 제조업 클러스터와 급속한 도시 이동이 원동력이 되고 있습니다. 중국의 순환경제 촉진법과 일본의 플라스틱 자원 순환법은 생산자에게 재활용 가능한 설계를 의무화하고 있으며, 인도의 새로운 규칙은 공공 인프라에 재생 모래와 재생 골재를 요구하고 있습니다. 심천, 도쿄, 벵갈루루의 도시 당국은 가정에서의 분별 회수를 촉진하기 위해 종량제를 도입하고 있습니다. 싱가포르의 새로운 데이터센터에서 건설 폐기물의 전환율 85%를 달성한 Microsoft와 같은 다국적 기업은 폐기물 제로 공약을 달성하기 위해 지역별로 재활용 계약을 맺고 있습니다.
중동 및 아프리카는 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 전망이 9.1%로 가장 급성장할 것으로 예상되는 지역입니다. 사우디아라비아 투자 재활용 회사(SIRC)는 비전 2030의 순환 경제의 이정표를 달성하기 위해 쓰레기 고체 연료화 시설과 타이어에서 석유로의 전환 시설에 6억 2,500만 달러를 투입하고 있습니다. 2025년 2월에 체결된 GCC 폐기물-에너지 협력 의정서는 40%의 매립지 전환 목표를 설정하고 아부다비, 마나마, 제다 공장 EPC 파이프라인을 활성화하고 있습니다. 동시에 남아프리카와 케냐는 비공식 회수업체를 공식적으로 등록하기 위한 디지털 등록 시스템을 시험적으로 도입하고 있습니다.
북미와 유럽은 성숙한 시장이지만 규제가 많은 시장입니다. 미국 환경보호청(EPA)은 2025년에 모든 유해 폐기물 수출에 전자 매니페스트의 통과를 의무화해 데이터 컴플라이언스의 수익이 확대될 것으로 예상됩니다. 2027년까지 연방 정부 조달에서 일회용 플라스틱을 단계적으로 폐지하려는 백악관의 전략은 공급업체와의 계약에 파급 효과를 불러일으킬 것으로 예측됩니다. 2024년 5월 발효된 유럽 폐기물 운송 규제는 OECD 비가맹국으로의 수출을 제한하고 2026년까지 엔드 투 엔드의 디지털 추적을 의무화합니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 인사이트와 역학
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- EU와 북미의 생산자 책임 규제 확대
- 카본 마이너스 목표가 폐기물 에너지에 대한 투자를 촉진함
- 기업의 폐기물 제로 서약이 아시아의 산업 리사이클 계약에 박차를 가함
- 미국 환경보호국(EPA)과 유럽연합(EU)이 폐기물 흐름의 디지털 추적을 의무화
- 메가 시티의 온 디맨드 소비자용 운반 앱이 수집량을 밀어 올림
- EV 보급에 의한 리튬 이온 전지 폐기물의 급증이 전문 리사이클 수요를 창출
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 남아시아 및 아프리카에서 단편화된 비공식 섹터의 우위성
- 서유럽의 신규 매립지에 대한 규제에 의한 컴플라이언스 비용 증가
- 세계적으로 재활용 투자를 저해하는 불안정한 회수 상품 가격
- 국경을 넘은 폐기물 출하의 금지가 수익성이 높은 무역 루트를 축소시킴
- 가치/공급망 분석
- 규제 전망
- 기술의 전망
- 스타트업 및 생태계 분석
- 주요 신흥 동향
- 지정학적 쇼크의 영향
- 산업의 매력 - Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 배출원별
- 주택
- 상업(소매, 오피스 등)
- 인더스트리얼
- 의료(건강 및 의약품)
- 건설 및 철거
- 기타(시설용, 농업용 등)
- 서비스 유형별
- 수집, 수송, 선별, 분별
- 폐기/처리
- 매립지
- 재활용 및 자원 회수
- 소각 및 폐기물 발전
- 기타(화학처리, 퇴비화 등)
- 기타(컨설팅, 감사, 교육 등)
- 폐기물 유형별
- 도시 고형 폐기물
- 산업 유 해폐기물
- 전자 폐기물
- 플라스틱 폐기물
- 의료 폐기물
- 건설 및 철거 폐기물
- 농업 폐기물
- 기타 특수 폐기물(방사성 물질 등)
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 인도
- 한국
- ASEAN(인도네시아, 태국, 필리핀, 말레이시아, 베트남)
- 호주
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 유럽
- 영국
- 독일
- 프랑스
- 이탈리아
- 스페인
- 러시아
- 베네룩스(벨기에, 네덜란드, 룩셈부르크)
- 노르딕스(덴마크, 핀란드, 아이슬란드, 노르웨이, 스웨덴)
- 기타 유럽
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 사우디아라비아
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 카타르
- 튀르키예
- 남아프리카
- 이집트
- 나이지리아
- 기타 중동 및 아프리카
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Veolia Environment SA
- Waste Management Inc.
- Suez SA
- Republic Services Inc.
- Waste Connections Inc.
- Clean Harbors Inc.
- Covanta Holding Corporation
- Biffa Group
- Remondis SE & Co. KG
- Stericycle Inc.
- GFL Environmental Inc.
- FCC Environment
- Cleanaway Waste Management Ltd
- Hitachi Zosen Inova AG
- Sims Limited
- Renewi PLC
- Averda
- Daiseki Co. Ltd
- Tatweer Environmental Services
- Waste Pro USA
- Recology
제7장 시장 기회와 미래 전망
CSM 25.11.20The Waste Management Market generated USD 1.43 trillion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 1.97 trillion by 2030, advancing at a 6.62% CAGR between 2025-2030.
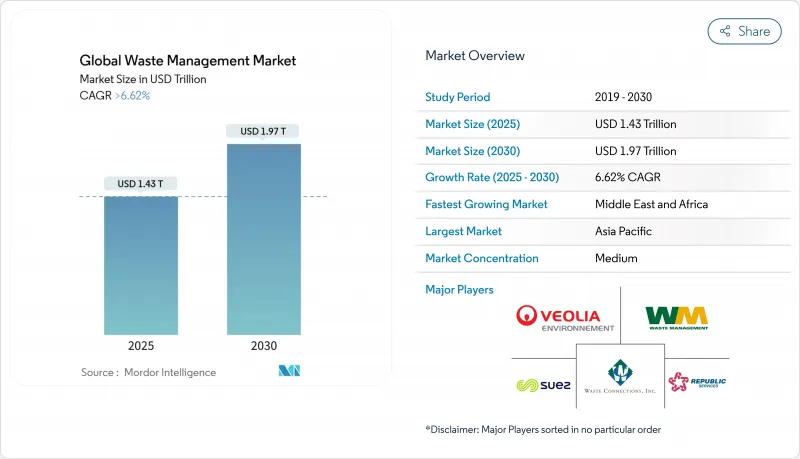
Persistent regulatory pressure, expanding corporate zero-waste pledges, and the monetization of recovered materials are steering the waste management market away from landfill-centric models and toward integrated recovery systems. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) statutes in the European Union and several U.S. states are transferring disposal costs to brand owners, creating dedicated funding pools for recycling infrastructure. At the same time, the roll-out of mandatory digital tracking platforms by the U.S. EPA and the EU is spawning new data-driven service niches, while investments in waste-to-energy (WtE) facilities equipped with carbon-capture technology are unlocking carbon-negative revenue streams. Asia-Pacific held the largest regional position in 2024, and Middle East & Africa (MEA) is on track to be the fastest-growing geography through 2030 as governments allocate capital to diversion targets. E-waste represents the highest-velocity waste stream, propelled by looming electric-vehicle battery retirements.
Global Waste Management Market Trends and Insights
Extended Producer Responsibility regulations in EU & North America
Mandatory EPR schemes now require producers to finance collection and recycling, reshaping the cost base for the waste management market. California's SB 54 compels a 25% plastic-packaging reduction by 2032 along with a 65% recycling rate, and Minnesota joined five other U.S. states with its own 2024 EPR law. The EU extended EPR to textiles in 2023, creating new compliance markets that have encouraged waste-management operators to consolidate and invest in optical-sorting and polymer-identification lines to capture EPR-funded contracts. Comparable rules introduced in Kenya in 2024 demonstrate global diffusion of the model.
Carbon-negative targets driving WtE investments
Net-zero commitments are channeling capital toward WtE plants equipped with post-combustion carbon capture. Metro Vancouver's facility, processing 720 t/day of refuse, placed a USD 101 million price tag on equipment that will remove 300,000 tCO2 annually, flipping the emissions balance from positive to negative. In Saudi Arabia, a WtE program converting 3 million t of municipal solid waste into fuel aims to cut 1.79 million tCO2 per year while delivering renewable electricity to the grid. Access to carbon credit markets adds a new income layer for operators.
Fragmented informal sector dominance in South Asia & Africa
An extensive informal workforce limits formal penetration of the waste management market. South Africa leaves 3.67 million t of household waste uncollected each year, fostering illegal dumping and eroding municipal revenues. Informal e-waste recycling in South Asia exposes workers to heavy metals, discouraging institutional investors from funding modern plants. Integrating these workers into regulated value chains requires training and capital that many local operators cannot finance, keeping collection rates low and leakage high.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Corporate zero-waste pledges spurring industrial recycling contracts in Asia
- Mandatory digital tracking of waste flows in the U.S. and EU
- Volatile recovered-commodity prices disincentivizing recycling investment
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Industrial waste retained the highest momentum in 2024 and is on course to post an 8.3% CAGR to 2030, while residential waste accounted for the largest 46.54% waste management market share that same year. Corporate emissions-reduction mandates are causing manufacturers to treat production scrap as a resource, boosting demand for on-site baling, solvent recovery, and closed-loop logistics. Eastman's USD 2.25 billion molecular-recycling roll-out, designed to handle 250 million lb of complex plastics annually, illustrates the scale of industrial opportunities. The shift is especially notable in electronics, automotive, and consumer-goods plants concentrated in China and ASEAN nations.
Residential streams, although mature, remain essential to the overall waste management market size because of rising urbanization. Governments are installing color-coded curbside programs and food-waste digesters to comply with landfill-diversion targets. Commercial waste from retail chains adds stable growth as EPR fees fund front-of-store collection infrastructure. Construction-and-demolition waste has gained policy attention; India's revised C&D rules, effective April 2025, oblige megaprojects to use recycled aggregates, generating predictable tonnage for crushers. Medical and agricultural wastes represent niche but expanding categories, with infectious-waste protocols tightened post-pandemic and agricultural biomass feeding anaerobic-digestion plants in rural zones.
The Waste Management Market Report is Segmented by Source (Residential, Commercial [Retail, Office, Etc. ], Industrial and More), by Service Type (Collection, Transportation, Sorting & Segregation and Disposal/Treatment), by Waste Type (Municipal Solid Waste, E-Waste and More) and by Geography (North America, Europe and More). The Report Offers Market Size and Forecasts in Value (USD) for all the Above Segments.
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific contributed 56% of global revenue in 2024, powered by dense manufacturing clusters and rapid urban migration that generate multi-material waste flows requiring advanced processing. China's Circular-Economy Promotion Law and Japan's Plastic Resource-Circulation Act obligate producers to design for recyclability, while India's new rules demand recycled sand and aggregate in public infrastructure. Urban authorities in Shenzhen, Tokyo, and Bengaluru have introduced pay-as-you-throw pricing that boosts household separation at source. Multinationals such as Microsoft, which achieved an 85% construction-waste diversion rate at its new Singapore data center, are executing regional recycling contracts to fulfill zero-waste pledges.
The Middle East & Africa is the fastest-expanding region, flashing a 9.1% CAGR outlook through 2030. Saudi Investment Recycling Company (SIRC) is deploying USD 625 million across refuse-derived-fuel and tire-to-oil facilities to meet Vision 2030 circular-economy milestones. The GCC Waste-to-Energy Cooperation Protocol, signed in February 2025, sets a 40% landfill-diversion target, galvanising plant EPC pipelines in Abu Dhabi, Manama, and Jeddah. Simultaneously, South Africa and Kenya are piloting digital registry systems to formalise informal collectors, though capacity gaps persist outside capital regions.
North America and Europe are mature but regulation-intensive markets. The U.S. EPA's 2025 mandate that all hazardous-waste exports traverse the e-Manifest expands data-compliance revenue. The White House strategy to phase out single-use plastics from federal procurement by 2027 is expected to ripple through supplier contracts. Europe's Waste Shipments Regulation, effective May 2024, restricts exports to non-OECD countries and requires end-to-end digital tracking by 2026.
- Veolia Environment SA
- Waste Management Inc.
- Suez SA
- Republic Services Inc.
- Waste Connections Inc.
- Clean Harbors Inc.
- Covanta Holding Corporation
- Biffa Group
- Remondis SE & Co. KG
- Stericycle Inc.
- GFL Environmental Inc.
- FCC Environment
- Cleanaway Waste Management Ltd
- Hitachi Zosen Inova AG
- Sims Limited
- Renewi PLC
- Averda
- Daiseki Co. Ltd
- Tatweer Environmental Services
- Waste Pro USA
- Recology
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Insights and Dynamics
- 4.1 Market Drivers
- 4.1.1 Extended Producer Responsibility Regulations in EU & North America
- 4.1.2 Carbon-Negative Targets Driving Waste-to-Energy Investments
- 4.1.3 Corporate Zero-Waste Pledges Spurring Industrial Recycling Contracts in Asia
- 4.1.4 Digital Tracking of Waste Flows Mandated by US EPA & EU
- 4.1.5 On-Demand Consumer Hauling Apps in Urban Mega-Cities Boosting Collection Volumes
- 4.1.6 Surge in Lithium-Ion Battery Waste from EV Adoption Creating Specialized Recycling Demand
- 4.2 Market Restraints
- 4.2.1 Fragmented Informal Sector Dominance in South Asia & Africa
- 4.2.2 Regulatory Moratoria on New Landfills in Western Europe Increasing Compliance Costs
- 4.2.3 Volatile Recovered Commodity Prices Disincentivizing Recycling Investments Globally
- 4.2.4 Cross-border Waste Shipment Bans Curtailing Profitable Trade Routes
- 4.3 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.4 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Startup Ecosystem Analysis
- 4.7 Key Emerging Trends
- 4.8 Impact of Geopolitical Shocks
- 4.9 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces
- 4.9.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.9.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.9.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.9.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.9.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, In USD Billion)
- 5.1 By Source
- 5.1.1 Residential
- 5.1.2 Commercial (Retail, Office, etc.)
- 5.1.3 Industrial
- 5.1.4 Medical (Health and Pharmaceutical)
- 5.1.5 Construction & Demolition
- 5.1.6 Others (Institutional, Agricultural, etc)
- 5.2 By Service Type
- 5.2.1 Collection, Transportation, Sorting & Segregation
- 5.2.2 Disposal / Treatment
- 5.2.2.1 Landfill
- 5.2.2.2 Recycling & Resource Recovery
- 5.2.2.3 Incineration & Waste-to-Energy
- 5.2.2.4 Others (Chemical Treatment, Composting, etc.)
- 5.2.3 Others (Consulting, Audit & Training, etc.)
- 5.3 By Waste Type
- 5.3.1 Municipal Solid Waste
- 5.3.2 Industrial Hazardous Waste
- 5.3.3 E-waste
- 5.3.4 Plastic Waste
- 5.3.5 Biomedical Waste
- 5.3.6 Construction & Demolition Waste
- 5.3.7 Agricultural Waste
- 5.3.8 Other Specialized Waste (Radio Active, etc.)
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 South America
- 5.4.2.1 Brazil
- 5.4.2.2 Argentina
- 5.4.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 Japan
- 5.4.3.3 India
- 5.4.3.4 South Korea
- 5.4.3.5 ASEAN (Indonesia, Thailand, Philippines, Malaysia, Vietnam)
- 5.4.3.6 Australia
- 5.4.3.7 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 Europe
- 5.4.4.1 United Kingdom
- 5.4.4.2 Germany
- 5.4.4.3 France
- 5.4.4.4 Italy
- 5.4.4.5 Spain
- 5.4.4.6 Russia
- 5.4.4.7 BENELUX (Belgium, Netherlands, and Luxembourg)
- 5.4.4.8 NORDICS (Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden)
- 5.4.4.9 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.4.5.3 Qatar
- 5.4.5.4 Turkey
- 5.4.5.5 South Africa
- 5.4.5.6 Egypt
- 5.4.5.7 Nigeria
- 5.4.5.8 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles {(includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)}
- 6.3.1 Veolia Environment SA
- 6.3.2 Waste Management Inc.
- 6.3.3 Suez SA
- 6.3.4 Republic Services Inc.
- 6.3.5 Waste Connections Inc.
- 6.3.6 Clean Harbors Inc.
- 6.3.7 Covanta Holding Corporation
- 6.3.8 Biffa Group
- 6.3.9 Remondis SE & Co. KG
- 6.3.10 Stericycle Inc.
- 6.3.11 GFL Environmental Inc.
- 6.3.12 FCC Environment
- 6.3.13 Cleanaway Waste Management Ltd
- 6.3.14 Hitachi Zosen Inova AG
- 6.3.15 Sims Limited
- 6.3.16 Renewi PLC
- 6.3.17 Averda
- 6.3.18 Daiseki Co. Ltd
- 6.3.19 Tatweer Environmental Services
- 6.3.20 Waste Pro USA
- 6.3.21 Recology



















