
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1910441
다이나믹 랜덤 액세스 메모리(DRAM) : 시장 점유율 분석, 업계 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2026-2031년)Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
다이나믹 랜덤 액세스 메모리(DRAM) 시장은 2025년에 1,086억 8,000만 달러로 평가되었으며, 2026년 1,263억 1,000만 달러에서 2031년까지 2,677억 7,000만 달러로 성장할 것으로 예상되며, 예측 기간(2026-2031년) 동안 연평균 성장률(CAGR)은 16.22%입니다.

AI 중심 서버의 채용 가속, 고대역폭 메모리의 급격한 보급 확대, 자동차용 인증 요건의 엄격화에 의해 구입 기준은 용량만에서 대역폭·전력 소비·열 성능을 밸런스 좋게 중시하는 방향으로 시프트하고 있습니다. 하이퍼스케일 클라우드 사업자는 2024년 동안 DDR5 및 HBM3E 모듈에 의한 랙 업데이트를 시작했으며, 아시아 휴대폰 OEM 제조업체는 주력 기종 및 미드레인지 기종의 대부분을 LPDDR5X로 이행했기 때문에 2025년 중반까지 팹 가동률은 전체로 95% 이상을 유지했습니다. 존별 아키텍처가 기존의 ECU 네트워크를 대체하여 전기자동차(EV) 1대당 메모리 탑재량이 급속히 증가하고 자동차용 DRAM 수요는 수 기가바이트 규모로 확대되었습니다. 동시에 수익성이 높은 HBM3E와 기존 DDR4 라인 간공급 배분을 둘러싼 경쟁이 가격 급등을 일으켜 PC, 스마트폰, 산업용 IoT 보드에서 비용 성능의 절충 관계를 재구성했습니다.
세계의 다이나믹 랜덤 액세스 메모리(DRAM) 시장 동향과 인사이트
하이퍼스케일 데이터센터에서 AI 및 생성형 AI 워크로드 증가 추세
NVIDIA의 2025년 Blackwell GP-AI 플랫폼은 기존 DDR 아키텍처를 능가하는 대역폭 기준을 수립하여 서버 메모리의 평균 탑재 용량을 2024년 256GB에서 2025년 중반까지 멀티 테라바이트 규모로 끌어올렸습니다. 각 HBM3E 스택이 1TB/s 이상의 성능을 발휘하는 가운데, 클라우드 사업자는 메모리 중심의 토폴로지를 바탕으로 랙의 재설계를 진행했습니다. 삼성이 양산 대응의 CXL 2.0 DRAM을 제공함으로써, Azure를 비롯한 프로바이더는 호스트간에 메모리를 풀 가능하게 되어, 이용률 향상과 추가 컴퓨팅 노드에의 설비 투자의 선송을 실현했습니다. 이를 통해 공급업체는 웨이퍼 생산을 DDR4에서 HBM으로 이동시켜 기존 등급 공급 감소를 초래하는 동시에 프리미엄 부문의 이익 성장을 가속화했습니다.
아시아태평양의 5G 플래그십 및 미드레인지 스마트폰에서의 LPDDR 채용 급증
마이크론의 1Y LPDDR5X 샘플(9,200 MT/s 동작)은 2025년 1분기에 휴대전화 제조업체에 납입되어 소비 전력을 20% 삭감하는 것과 동시에, 중국·인도용 모델의 표준 구성을 8GB에서 12GB RAM으로 끌어올렸습니다. 샤오미, OPPO, 트랜스시온 등 신흥 브랜드는 아시아태평양의 팹 생산 능력의 확대 비율을 소비하는 선도 계약을 체결하고 있으며 공급업체는 모바일과 데이터센터 라인 간의 헌신을 조정할 수밖에 없습니다. 이러한 변화로 인해 LPDDR은 2015년에 LPDDR4가 양산되기 시작한 이래 다른 모바일 메모리보다 급격한 성장 곡선을 그렸습니다.
수급 순환성이 극단적인 평균 판매 가격(ASP) 변동을 초래
고마진 HBM 수요 인상으로 팹은 2025년 초에 DDR4 생산 개시를 연기했으며, 5월에는 주류 모듈의 스팟 가격이 50% 급등했습니다. DDR5 계약 가격도 15-20% 상승했기 때문에 OEM 제조업체는 제품 BOM의 재설계와 과잉 발주에 의해 추가 가격 급등에 대한 헤지를 도모했습니다. 이 피드백 루프는 변동성을 증폭시켜 생산 계획 전망을 악화시키고 다이나믹 랜덤 액세스 메모리(DRAM) 시장 예측 CAGR을 2점 이상 밀어냈습니다.
부문 분석
2025년 시점에서는 DDR5의 다이나믹 랜덤 액세스 메모리(DRAM) 시장에서 미미한 점유율을 차지했지만, JEDEC의 JESD79-5C 규격 갱신에 의해 성능 상한이 8,800Mbps로 인상된 것을 배경으로, CAGR 29.1%로 가장 빠른 성장률을 나타냈습니다. 이 기술적 도약으로 Tier1 클라우드 벤더는 DDR5와 HBM3E를 혼재시킨 구성을 실현하여 소켓당 실효 대역폭을 두배로 늘릴 수 있게 되었습니다. 마이크론의 1Y DDR5는 2025년 2월에 9,200MT/s를 달성했으며, 이 획기적인 진전이 서버 OEM 제조업체의 플랫폼 쇄신을 앞당기는 요인이 되었습니다. 한편 DDR4는 2025년을 통해 44.78%의 다이나믹 랜덤 액세스 메모리(DRAM) 시장 점유율을 유지했습니다. 이는 기업 IT 예산이 여전히 비용 최적화 구성을 선호했기 때문입니다. 레거시한 DDR3 및 DDR2의 점유율은 산업용·자동차용 설계가 신규격으로 이행함에 따라 축소를 계속했습니다.
공급업체는 균형 조정에 직면했습니다. DDR5에 할당된 웨이퍼 1장마다 PC용 DDR4 칩공급이 감소하고, 비용 급등이 중국 노트북 조립 제조업체에 파급한 것입니다. 장기 재고 보유자는 재정 거래를 활용하여 2017년 이후 프리미엄 가격으로 축적된 DDR4를 매각했습니다. JEDEC의 새로운 CAMM2 폼 팩터는 SO-DIMM의 높이 제약을 해소하여 노트북과 에지 서버가 보다 고밀도의 단면 적층을 채용할 수 있게 했습니다. 이러한 패키징 기술의 진보는 소비자용·기업용 디바이스를 불문하고, 다이나믹 랜덤 액세스 메모리(DRAM) 시장에서의 고대역폭 규격으로의 이행을 뒷받침했습니다.
2025년 시점에서 19nm-10nm 공정대는 다이나믹 랜덤 액세스 메모리(DRAM) 시장 규모의 41.85%를 차지했고 공급자가 10nm 미만 공정의 수율 리스크에 빠지지 않고 웨이퍼당 다이 수를 증가시킴으로써 2031년까지 24.4%의 성장이 전망되고 있습니다. EUV 기술을 활용한 1Y 공정을 통한 양산은 2025년 1분기에 수익화 유닛 출하를 시작했으나 라인 수율은 성숙한 1z 라인을 적어도 8포인트 밑돌았습니다. 이로 인해 많은 디바이스 제조업체들이 비용 리스크를 완화하기 위해 1z 및 1y 등급 계약을 업데이트하여 미드노드 프로세스에 생산량을 밀어 올렸습니다.
SK하이닉스는 2027년 이후에 웨이퍼 레벨 적층을 실현하는 수직 게이트 DRAM 로드맵을 제시하여 횡방향 미세화에서 3D 구조로의 장기적인 전환을 시사했습니다. 평면 미세화의 겹치는 축소에서는 마스크 세트·재료비·감가상각을 고려하면 12% 미만의 비용 절감 밖에 얻을 수 없고, 팹은 기하학적 축소뿐만 아니라 구조적인 재설계를 모색할 수밖에 없습니다. 모바일 및 민생전자기기의 비용감응도가 높기 때문에 가격중시의 SKU용으로 20nm 이상의 노드가 유지되어 생산믹스의 계층화가 실현되었습니다. 이는 팹 생산의 다양화를 도모하고 전체적인 수익의 회복력을 지원하고 있습니다.
다이나믹 랜덤 액세스 메모리(DRAM) 시장은 아키텍처(DDR2 이전, DDR3, DDR4, DDR5, LPDDR, GDDR), 기술 노드(20nm 이상, 19nm-10nm, 10nm 미만), 용량(4GB 이하, 4-8GB, 8 -16GB, 16GB 이상), 최종 용도(스마트폰 및 태블릿, PC 및 노트북, 서버 및 하이퍼스케일 데이터센터 등), 지역(북미, 유럽, 아시아태평양, 남미, 중동 및 아프리카)으로 구분됩니다.
지역별 분석
아시아태평양은 한국, 대만, 중국 본토에 집적된 팹을 배경으로 2025년에도 30.88%의 수익 점유율을 유지했습니다. 한국공급업체는 HBM 및 기존 DRAM 생산에서 주도권 유지를 목적으로 2028년까지 120조원(840억 달러)의 생산 능력 확장을 약속했습니다. 한편 대만의 수탁 조립 업체는 로직 노드의 프론트엔드 기술을 활용하여 열저항을 저감하는 스루 실리콘 비아(TSV) 기술을 도입함으로써 높아지는 HBM4 수요에 대응하기 위해 선진 패키징 라인을 확충했습니다.
북미는 가장 큰 소비 시장을 형성했습니다. 하이퍼스케일 사업자에 의한 랙 갱신의 가속과 미국 자동차 제조업체에 의한 존 컨트롤러의 통합이 진행되었기 때문입니다. 마이크론은 새로운 메가 팹 건설을 위해 CHIPS 법에 따라 61억 달러의 자금 조달을 확보했습니다. 이는 지정학적 리스크의 경감과 국내 고객의 리드 타임 단축을 목적으로 한 움직임입니다. 유럽은 자동차·산업용도에 대한 기술적 주력을 유지하고 독일의 OEM 제조업체는 확장 온도 보증과 장수명 보증을 요구. 이것으로 프리미엄 가격이 실현되었습니다.
브라질, 아르헨티나, 멕시코가 공급의 현지화를 위해 전자기기 조립 생태계를 육성하고 있기 때문에 남미는 21.6%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)을 나타낼 것으로 예측되고 있습니다. 정책 인센티브는 국내에서 조립된 메모리 부품의 수입 관세를 낮추고 조달 전략에 속삭이면서도 의미 있는 변화를 낳고 있습니다. 중동 및 아프리카는 걸프 협력 회의 회원국에서 데이터센터를 건설하고 나이지리아와 케냐에서 스마트폰의 보급률이 증가함에 따라 한 자릿수 중반의 성장률을 보였지만 정치적 불안은 광범위한 보급을 방해하고 있습니다. 이러한 지역 상황에서 제조는 동아시아에 집중되어 있음에도 불구하고 다이나믹 랜덤 액세스 메모리(DRAM) 시장이 수익원을 다양화하고 있음을 알 수 있습니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 서포트
자주 묻는 질문
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사 전제조건 및 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 하이퍼스케일 데이터센터의 AI 및 생성형 AI 워크로드 증가 경향
- 아시아태평양의 5G 플래그십 및 미드레인지 스마트폰에서 LPDDR 채용 급증
- 자동차용 존/도메인 컨트롤러의 NOR에서 고온 DRAM으로의 이행
- 확장 온도 대응 DRAM 모듈을 필요로 하는 에지 AI 및 산업용 IoT 보드
- 클라우드 서비스 제공업체에서 CXL 연결 메모리 풀 마이그레이션
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 수급 순환성이 극단적인 평균 판매 가격(ASP) 변동을 촉진
- 10nm 이하의 EUV 공정에 있어서 수율 저하의 과제
- 중국에 대한 지정학적 수출 규제에 의한 고밀도 서버 DRAM 출하의 제한
- 밸류체인 분석
- 기술 전망
- 규제 전망
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 구매자의 협상력
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업 간 경쟁 관계
- 가격 분석
- DRAM 스팟 가격(GB당)
- 가격 동향 분석
- 거시경제의 영향 분석
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 아키텍처별
- DDR2 및 그 이전 버전
- DDR3
- DDR4
- DDR5
- LPDDR
- GDDR
- 기술 노드별
- 20nm 이상
- 19nm-10nm
- 10nm(EUV) 미만
- 용량별
- 4GB 이하
- 4-8GB
- 8-16GB
- 16GB 이상
- 최종 용도
- 스마트폰 및 태블릿
- PC 및 노트북
- 서버 및 하이퍼스케일 데이터센터
- 그래픽 및 게임 콘솔
- 자동차용 전자기기
- 소비자용 전자기기(셋톱박스, 스마트 TV, VR/AR)
- 산업용 및 IoT 디바이스
- 기타
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 유럽
- 독일
- 프랑스
- 영국
- 북유럽 국가
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 대만
- 한국
- 일본
- 인도
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 남미
- 브라질
- 칠레
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 중동
- 사우디아라비아
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 튀르키예
- 기타 중동
- 아프리카
- 남아프리카
- 기타 아프리카
- 중동
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- SK Hynix Inc.
- Micron Technology Inc.
- ChangXin Memory Technologies Inc.(CXMT)
- Nanya Technology Corporation
- Winbond Electronics Corporation
- Powerchip Semiconductor Manufacturing Corp.(PSMC)
- Fujian Jinhua Integrated Circuit Co., Ltd.(JHICC)
- GigaDevice Semiconductor(Beijing) Inc.
- Etron Technology Inc.
- Integrated Silicon Solution Inc.(ISSI)
- Elite Semiconductor Memory Technology Inc.(ESMT)
- Zentel Electronics Corporation
- Alliance Memory, Inc.
- AP Memory Technology Corp.
- Phison Electronics Corporation
- JSC Mikron(Mikron Group)
- AMIC Technology Corporation
- Utron Technology Inc.
- Hua Hong Semiconductor Limited
제7장 시장 기회와 향후 전망
KTH 26.01.22The Dynamic Random Access Memory market was valued at USD 108.68 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 126.31 billion in 2026 to reach USD 267.77 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 16.22% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
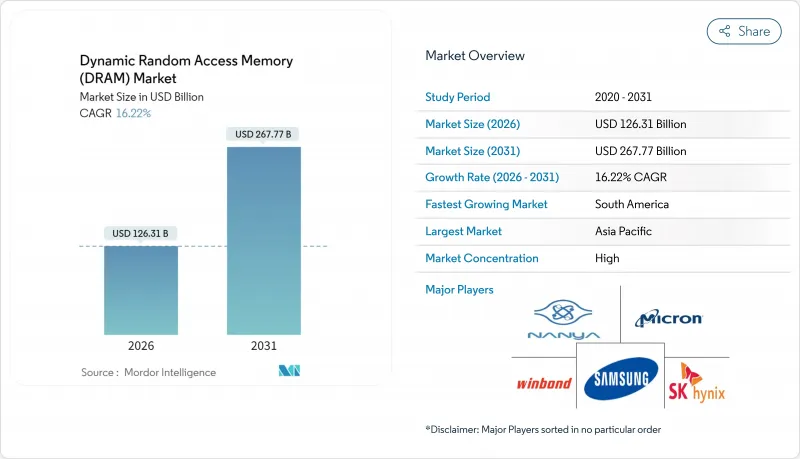
Accelerated adoption of AI-centric servers, the steep ramp-up of high-bandwidth memory, and tighter automotive qualification requirements have shifted purchasing criteria from capacity alone to a balanced focus on bandwidth, power, and thermal performance. Hyperscale cloud operators began refreshing racks with DDR5 and HBM3E modules during 2024, while handset OEMs in Asia moved much of their flagship and mid-tier portfolios to LPDDR5X, collectively keeping fab utilization above 95% through mid-2025. Memory content per electric vehicle rose quickly as zonal architectures replaced traditional ECU networks, pushing automotive DRAM demand into multi-gigabyte territory. At the same time, supply allocation conflicts between lucrative HBM3E and legacy DDR4 lines triggered price surges that reshaped cost-performance trade-offs for PCs, smartphones, and industrial IoT boards.
Global Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) Market Trends and Insights
Ascending content footprint of AI and generative-AI workloads in hyperscale data centers
NVIDIA's 2025 Blackwell GP-AI platforms established bandwidth baselines that eclipsed conventional DDR architectures, lifting average server memory from 256 GB in 2024 to multi-terabyte deployments by mid-2025. With each HBM3E stack delivering more than 1 TB/s, cloud operators re-architected racks around memory-centric topologies. Samsung delivered production-ready CXL 2.0 DRAM that allowed Azure and other providers to pool memory across hosts, improving utilization while deferring capex on additional compute nodes. Suppliers consequently shifted wafer starts from DDR4 to HBM, triggering tightness in legacy grades but accelerating profit growth in the premium segment.
Soaring LPDDR adoption in 5G flagship and mid-tier smartphones across APAC
Micron's 1Y LPDDR5X samples running at 9,200 MT/s reached handset makers in Q1 2025, cutting power by 20% and raising baseline configurations in Chinese and Indian models from 8 GB to 12 GB RAM. Xiaomi, OPPO, and emerging brands such as Transsion are locked in forward contracts that consume a growing slice of APAC fab capacity, forcing suppliers to juggle commitments between mobile and datacenter lines. The shift gave LPDDR a steeper growth curve than any other mobile memory since LPDDR4 entered mass production in 2015.
Supply-demand cyclicality driving extreme ASP volatility
High-margin HBM pull-ins persuaded fabs to postpone DDR4 runs early in 2025, igniting a 50% spot-price jump for mainstream modules in May. DDR5 contracts also climbed 15-20%, prompting OEMs to re-engineer product bills of materials or over-order to hedge against further spikes. The feedback loop amplified volatility and cut visibility for production planning, knocking two-plus points from the Dynamic Random Access Memory market's forecast CAGR.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Automotive zonal and domain controllers migrating from NOR to high-temperature DRAM
- Edge-AI and industrial IoT boards requiring extended-temperature DRAM modules
- Yield-erosion challenges below 10 nm EUV nodes
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
DDR5 accounted for a minimal share of the Dynamic Random Access Memory market in 2025, yet carried the fastest 29.1% forecast CAGR, underpinned by JEDEC's JESD79-5C update that lifted performance ceilings to 8,800 Mbps. That technical leap allowed tier-1 cloud builders to run mixed DDR5-HBM3E configurations that doubled per-socket effective bandwidth. Micron's 1Y DDR5 reached 9,200 MT/s in February 2025, a milestone that pushed server OEMs to pull forward platform refreshes. Meanwhile, DDR4 retained a 44.78% Dynamic Random Access Memory market share through 2025 because corporate IT budgets still favoured cost-optimized configurations. Legacy DDR3 and DDR2 footprints continued to shrink as industrial and automotive design-ins migrated to newer standards.
Suppliers confronted a balancing act: every wafer reassigned to DDR5 meant fewer DDR4 chips for PCs, driving cost spikes that flowed downstream to notebook assemblers in China. Holders of long-tail inventory exploited arbitrage trading, unloading stockpiled DDR4 at premiums unseen since 2017. JEDEC's new CAMM2 form factor removed the height constraints of SO-DIMMs, letting laptops and edge servers adopt denser single-sided stacks. Those packaging gains fed into the Dynamic Random Access Memory market's momentum toward higher-bandwidth norms across consumer and enterprise devices.
The 19 nm-10 nm bracket held 41.85% of the Dynamic Random Access Memory market size in 2025 and is projected to grow 24.4% through 2031 as suppliers squeeze additional dies per wafer without plunging into the yield-risk chasm of sub-10 nm. EUV-enabled 1Y production began shipping revenue units in Q1 2025, but line yields remained at least eight points below mature 1z lines. Consequently, many device makers renewed agreements for 1z and 1y grades to buffer cost risk, giving mid-node processes a volume boost.
SK Hynix laid out a vertical-gate DRAM roadmap that promises wafer-level stacking beyond 2027, signalling the long-term pivot from lateral scaling to 3D architectures. Each successive planar shrink delivers less than 12% cost reduction after mask set, materials, and depreciation are factored in, nudging fabs to look for structural redesigns rather than geometrical shrink alone. Cost sensitivity in mobile and consumer electronics kept >=20 nm nodes alive for price-focused SKUs, ensuring a stratified production mix that diversified fab output and underpinned overall revenue resiliency.
Dynamic Random Access Memory Market is Segmented by Architecture (DDR2 and Earlier, DDR3, DDR4, DDR5, LPDDR, and GDDR), Technology Node (>=20 Nm, 19 Nm-10 Nm, and <10 Nm), Capacity (<=4 GB, 4-8 GB, 8-16 GB, and >=16 GB), End-Use Application (Smartphones and Tablets, Pcs and Laptops, Servers and Hyperscale Data Centers, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and Middle East and Africa).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific retained a 30.88% revenue position in 2025 on the strength of fabs clustered across South Korea, Taiwan, and mainland China. South Korean suppliers pledged KRW 120 trillion (USD 84 billion) for capacity build-outs through 2028, a figure intended to safeguard leadership in both HBM and traditional DRAM production. Taiwan's contract assembly houses, meanwhile, expanded advanced packaging lines to service rising HBM4 demand, leveraging front-end know-how from logic nodes to introduce Through-Silicon-Via innovations that reduce thermal resistance.
North America formed the largest consumption market as hyperscale builders accelerated rack refreshes and automakers in the United States integrated zonal controllers. Micron secured USD 6.1 billion CHIPS Act funding to construct a new megafab, a move aimed at de-risking geopolitical exposure and shortening lead times for domestic clients. Europe maintained a technology focus on automotive and industrial applications, with German OEMs insisting on extended temperature and longevity guarantees that fetched premium pricing.
South America is forecast to grow at a 21.6% CAGR as Brazil, Argentina, and Mexico nurture electronics assembly ecosystems to localize supply. Policy incentives cut import tariffs on memory components assembled domestically, creating modest but meaningful shifts in sourcing strategies. The Middle East and Africa displayed mid-single-digit growth anchored by data-center build-outs in Gulf Cooperation Council states and rising smartphone penetration in Nigeria and Kenya, yet political instability continued to temper wider adoption. Combined, these regional narratives underscore how the Dynamic Random Access Memory market diversifies revenue streams even as manufacturing remains concentrated in East Asia.
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- SK Hynix Inc.
- Micron Technology Inc.
- ChangXin Memory Technologies Inc. (CXMT)
- Nanya Technology Corporation
- Winbond Electronics Corporation
- Powerchip Semiconductor Manufacturing Corp. (PSMC)
- Fujian Jinhua Integrated Circuit Co., Ltd. (JHICC)
- GigaDevice Semiconductor (Beijing) Inc.
- Etron Technology Inc.
- Integrated Silicon Solution Inc. (ISSI)
- Elite Semiconductor Memory Technology Inc. (ESMT)
- Zentel Electronics Corporation
- Alliance Memory, Inc.
- AP Memory Technology Corp.
- Phison Electronics Corporation
- JSC Mikron (Mikron Group)
- AMIC Technology Corporation
- Utron Technology Inc.
- Hua Hong Semiconductor Limited
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Ascending Content Footprint of AI and Generative-AI Workloads in Hyperscale Data Centers
- 4.2.2 Soaring LPDDR Adoption in 5G Flagship and Mid-Tier Smartphones Across APAC
- 4.2.3 Automotive Zonal/Domain Controllers Migrating from NOR to High-Temperature DRAM
- 4.2.4 Edge-AI and Industrial IoT Boards Requiring Extended-Temperature DRAM Modules
- 4.2.5 Cloud Service Providers' Transition to CXL-attached Memory Pools
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Supply-Demand Cyclicality Driving Extreme ASP Volatility
- 4.3.2 Yield-Erosion Challenges Below 10 nm EUV Nodes
- 4.3.3 Geopolitical Export Controls on China Limiting High-density Server DRAM Shipments
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Pricing Analysis
- 4.8.1 DRAM Spot Price (Per GB)
- 4.8.2 Pricing Trends Analysis
- 4.9 Macroeconomic Impact Analysis
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Architecture
- 5.1.1 DDR2 and Earlier
- 5.1.2 DDR3
- 5.1.3 DDR4
- 5.1.4 DDR5
- 5.1.5 LPDDR
- 5.1.6 GDDR
- 5.2 By Technology Node
- 5.2.1 >=20 nm
- 5.2.2 19 nm - 10 nm
- 5.2.3 <10 nm (EUV)
- 5.3 By Capacity
- 5.3.1 <=4 GB
- 5.3.2 4 - 8 GB
- 5.3.3 8 - 16 GB
- 5.3.4 >=16 GB
- 5.4 By End-use Application
- 5.4.1 Smartphones and Tablets
- 5.4.2 PCs and Laptops
- 5.4.3 Servers and Hyperscale Data Centers
- 5.4.4 Graphics and Gaming Consoles
- 5.4.5 Automotive Electronics
- 5.4.6 Consumer Electronics (Set-top Boxes, Smart TV, VR/AR)
- 5.4.7 Industrial and IoT Devices
- 5.4.8 Others
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 France
- 5.5.2.3 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.4 Nordics
- 5.5.2.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Taiwan
- 5.5.3.3 South Korea
- 5.5.3.4 Japan
- 5.5.3.5 India
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Chile
- 5.5.4.3 Argentina
- 5.5.4.4 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.5.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.2 SK Hynix Inc.
- 6.4.3 Micron Technology Inc.
- 6.4.4 ChangXin Memory Technologies Inc. (CXMT)
- 6.4.5 Nanya Technology Corporation
- 6.4.6 Winbond Electronics Corporation
- 6.4.7 Powerchip Semiconductor Manufacturing Corp. (PSMC)
- 6.4.8 Fujian Jinhua Integrated Circuit Co., Ltd. (JHICC)
- 6.4.9 GigaDevice Semiconductor (Beijing) Inc.
- 6.4.10 Etron Technology Inc.
- 6.4.11 Integrated Silicon Solution Inc. (ISSI)
- 6.4.12 Elite Semiconductor Memory Technology Inc. (ESMT)
- 6.4.13 Zentel Electronics Corporation
- 6.4.14 Alliance Memory, Inc.
- 6.4.15 AP Memory Technology Corp.
- 6.4.16 Phison Electronics Corporation
- 6.4.17 JSC Mikron (Mikron Group)
- 6.4.18 AMIC Technology Corporation
- 6.4.19 Utron Technology Inc.
- 6.4.20 Hua Hong Semiconductor Limited
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment


















