
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1910624
비침습적 산전검사(NIPT) 시장 : 점유율 분석, 업계 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2026-2031년)Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
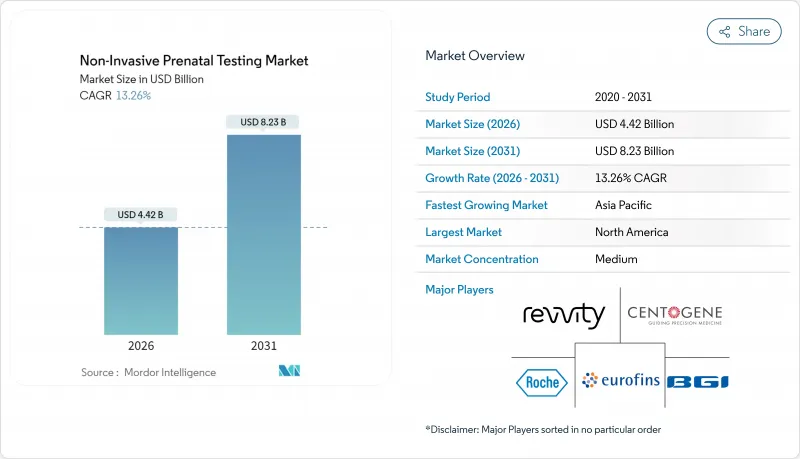
비침습적 산전검사 시장은 2025년 39억 달러로 평가되었으며, 2026년 44억 2,000만 달러에서 2031년까지 82억 3,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측됩니다.
예측기간(2026-2031년)의 CAGR은 13.26%로 전망되고 있습니다.

보다 광범위한 임상 지침은 현재 모든 임신에 대해 세포유리 DNA 스크리닝을 권장하고 있으며, 지불자 측 정책도 사전 승인 장애물을 완화하고 있으므로 위험 범주 전체에서 검사건수의 확대가 진행되고 있습니다. 시퀀싱 비용은 급락하고, 자동화된 워크플로에 의해 소요 시간이 단축되고 있기 때문에 신흥 시장에서도 검사를 보다 저렴한 가격으로 실시할 수 있게 되었습니다. FDA(미국 식품의약국)가 2024년에 발표한 연구실 개발 검사에 관한 최종 규정에서는 이행 기간 중의 컴플라이언스가 지정되었습니다. 이는 역설적으로 도입을 가속시키는 결과가 되었습니다. 대규모 상업 검사기관이 신속하게 공정 표준화를 진행했기 때문입니다. 동시에 의사 리퍼 네트워크와 병행하여 소비자를 위한 직접 판매 채널도 확대되고 있으며 임신 중인 부모가 조기 유전자 정보를 얻기 위해 자기 부담으로 검사를 받는 수요가 높아지고 있음을 반영하고 있습니다.
세계의 비침습적 산전검사(NIPT) 시장의 동향 및 인사이트
세계적인 임산부의 고령화가 염색체 이상 유병률을 증가
고령 임신은 염색체 이상의 위험을 높이고 선진국에서는 산전 스크리닝 건수가 꾸준히 증가하고 있습니다. 2024년에 발행된 보편적 가이드라인에서는 연령에 따른 위험 임계치가 폐지되었고, cfDNA 검사가 모든 임신에 대해 일차 선택 스크리닝으로 재지정되었습니다. 유산의 위험이 없는 혈액 검사를 선택하는 임산부가 늘어나면서 병원에서 침습적 치료가 줄어들고 있어 검사기관에게는 예측 가능한 수익원이 확대되고 있습니다. 대규모 집단 연구에서는 양성 예측치가 연령에 따라 상승하지만, 검사 감도는 전체 연령층에서 일관적인 것으로 확인되었습니다. 조기 발견은 평생 치료 비용을 줄이기 때문에 지불 기관은 경제성을 매력적으로 느끼고 있으며, 검사 기관은 안정적인 검사건수를 배경으로 시약의 대량 구입에 대해 가격 협상을 진행하고 있습니다.
안전성 확보를 위해 침습 검사에서 cfDNA 스크리닝으로 전환
양수 천자와 융모 채취는 모두 구체적인 유산 위험을 수반하며 이러한 불안을 해소하기 위해 비침습적 대안이 지지되고 있습니다. 임상 감사에 따르면 cfDNA 검사의 도입으로 침습적 처치건수는 최대 80% 감소했으며 이상 가능성이 높은 결과가 나왔을 경우에는 진단 확인이 가능합니다. 산부인과 의사는 의료 소송 위험이 줄어들었다고 밝혔고 보험 회사는 치료 관련 합병증의 청구가 줄어들었다고 보고했습니다. 혈액 기반 접근법은 초기 시료가 충분하지 않은 경우 신속한 재검사를 가능하게 하여 환자의 경험을 향상시킵니다. 중요한 점은 안전성의 장점은 전통적인 비용 편익 분석에서 검사 자체를 권장하지 않는 평균 위험 임신에도 효과적입니다.
우발적 소견 및 성별 선택에 관한 윤리적 및 규제상의 우려
인도의 PCPNDT법은 태아의 성별 공개를 범죄로 하고 있으며, 현지 법령 준수를 위해 공급자는 보고서의 재설계를 요구받고 있습니다. 정책 수립자는 검사 항목의 확대에 의해 친부 불일치나 모체에서 암이 판명될 가능성을 우려하고 있으며 이는 동의 취득의 복잡화를 초래하고 있습니다. 조기 IDENTIFY 시험은 보고가 필요하지 않은 사례의 절반이 모체에서 악성 종양을 숨기고 있음을 밝혀 경고 의무에 대한 논의를 불러 일으켰습니다. 생명윤리위원회는 상담 강화를 수반하는 점진적인 검사 도입을 권장하지만, 지역별 규제는 상용화 일정을 늦추고 있습니다. 따라서 공급업체는 규모의 경제를 제한하는 공개 규정의 패치워크를 신중하게 회피해야 합니다.
부문 분석
2025년 차세대 시퀀싱 기술은 비침습적 산전검사 시장에서 60.87%의 점유율을 차지하여 분석의 폭 확대와 확장성에 대한 평가를 확고히 했습니다. 한편, 롤링 서클형 복제법은 15.08%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)로 성장을 가속하고 있으며, 상온 워크플로로 인해 자원 제약이 있는 환경에 적합합니다. NGS 기반 검사는 비침습적 산전검사 시장에서 검사의 복잡화에 대응하기 위해 기존 플랫폼을 활용하는 검사기관의 증가에 따라 꾸준한 성장이 예상됩니다. 한편, 보다 간편한 화학 검사법은 고가의 시퀀서에 대한 도입 예산이 없는 신규 고객층을 개척하고 있습니다.
디지털 PCR 및 CRISPR 기술을 활용한 검사법은 파일럿 프로그램 단계에 돌입하여 보다 정밀한 태아분획 정량과 특이성 향상을 목표로 하고 있습니다. 규제 강화는 당초 품질 기준을 충족하는 기존 NGS 벤더에 유리하게 작용할 수 있지만, RCA와 등온법에 의한 파괴적 가격 설정이 신흥 시장의 규모 확대에 따라 구매 결정을 전환시킬 우려가 있습니다.
전장 유전체 cfDNA 검사는 종합적인 염색체 커버리지로 높이 평가되었으며 2025년 비침습적 산전검사 시장에서 49.11%의 점유율을 차지했습니다. 미세결실 패널은 14.32%의 높은 CAGR을 기록하고 있으며, 특정 사례에서 광범위한 돌연변이 검출이 임상적 가치를 높이는 지속적인 증거의 혜택을 받고 있습니다. 보험 환급이 제한적인 영역에서는 이수성만을 검출하는 분석이 여전히 인기가 있지만, 가이드라인의 진화에 따라 상대적인 점유율은 떨어지는 경향이 있습니다.
단일 유전자 질환과 보인자 스크리닝을 결합한 패키지 검사는 생식 계획과 산전 모니터링을 통합하여 시장 경계를 재정의할 수 있습니다. 그러나 소비자의 관심이 높아졌음에도 불구하고 환급이 여전히 장벽이 되고 보험 지불자의 승인을 얻지 못하는 한 자기부담으로 인한 경제성은 단기적인 보급을 제한할 것입니다.
임신 10-12주의 검사 기간이 2025년에는 69.05%의 점유율을 차지했으며, 임신 초기 스크리닝이 표준적인 산부인과 프로토콜이 되었습니다. 검사기관에서는 정기적인 초음파검사 시 채혈을 사전에 예약하는 경우가 많으며, 이에 따라 물류 효율과 환자의 높은 진찰률을 달성하고 있습니다. 임신 24주 이후에 실시되는 검사는 규모는 작지만, 임신 후기 관리의 요구(예를 들면 임신 후기 스캔으로 원인 불명의 이상이 인정되는 경우 등)에 의해 연간 16.34%의 성장률을 나타내고 있습니다.
임상의는 의사결정의 폭을 넓히기 위해 조기 결과를 선호하지만, 후기 검사는 초기 스크리닝이 수행되지 않았거나 결과가 불확실한 복잡한 임신에 안도감을 제공합니다. 벤더 각사는 임신 기간의 경과에 따른 태아분획의 감소에도 불구하고 감도를 유지하는 검사법의 개량을 추진하고 있어 이에 따라 대응 가능한 검사건수의 확대를 도모하고 있습니다.
지역별 분석
북미는 2025년에도 44.78%의 수익 점유율을 유지했으며, 지급자 측의 협력, 확립된 검사 네트워크, 강력한 전문의 단체의 지원을 받았습니다. 2025년 4월 주요 전국 보험사가 사전 승인 제도를 폐지한 것은 장벽 없는 접근 실현을 위한 기세를 뒷받침하는 것입니다. 캐나다에서는 주볊 자금 조달 방침에 의해 도입 격차가 계속되고 있지만, 민간 보험이 공적 부문의 부족분을 보충하면서 전국적인 검사건수는 증가하고 있습니다. 멕시코의 민간 병원에서는 현지 시퀀싱 능력 도입이 진행되고 있지만, 환급 대상은 자기 부담층에 한정되어 있습니다.
유럽에서는 윤리와 전국민 보험의 목표를 양립하는 다양한 정책 모델이 전개되고 있습니다. 영국 국민보건서비스(NHS)는 조건부 2차 스크리닝으로 cfDNA를 도입하고, 독일과 프랑스는 특정 적응증에서 1차 검사의 환급을 실시하고 있습니다. 이탈리아와 스페인에서는 지역 수준의 파일럿 사업을 전국적인 전개로 확대 중입니다. 대륙부에서는 유전 상담과 동의 절차를 중시하는 자세가 검사 단가가 높아짐에도 견고한 지원 기반을 구축하고 있습니다.
아시아태평양은 CAGR 16.18%로 성장의 최전선에 있습니다. 중국에서는 정부 지원 유전체 클러스터와 대규모 출생 집단이 규모의 경제를 뒷받침해 검사 단가를 낮추고 있습니다. 일본의 다시설 공동 실증 프로젝트는 임상적 유용성을 입증하고 민간 보험 회사의 도입을 촉진했습니다. 인도에서는 대도시권의 근대적 검사 거점과 성별 공개를 제한하는 PCPNDT(출생 전 유전자 진단)라는 이중 규제 구조가 지역에 의한 도입 격차를 낳고 있습니다. 호주에서는 자기 부담 모델이 도입되고 있으며 가격이 평균 500-800 호주 달러(330-530달러)이지만, 메디케어와의 통합을 향한 정책적 재검토가 진행중입니다.
기타 혜택
- 시장 예측(ME) 엑셀 시트
- 3개월 애널리스트 서포트
자주 묻는 질문
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사 전제조건 및 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 촉진요인
- 세계의 임산부 연령의 상승에 의한 염색체 이상 발생률 증가
- 안전성 확보를 위해 침습적 검사에서 cfDNA 스크리닝으로 전환
- 시퀀싱 비용의 저하와 자동화에 의한 검사 가격의 하락
- 평균 위험 임신에 대한 환급 범위 확대
- 산부인과의학회의 임신 초기 가이드라인 승인
- 번들형 보인자+출생 전 유전자 패널의 도입
- 억제요인
- 우발적 소견에 관한 윤리적, 규제상의 우려 및 성별 선택
- 신흥 시장에서의 한정적인 검사시설 인프라와 생물정보에 대한 전문 지식
- 쌍둥이 임신 및 체외수정(IVF) 임신에 대한 정밀 과제로 임상의의 신뢰성 하락
- 지불자에게 불확실한 미세결실 스크리닝의 임상적 유용성
- 밸류체인 분석
- 기술 전망
- Porter's Five Forces
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급자의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업 간 경쟁 관계
제5장 시장 규모 및 성장 예측
- 기술별
- 차세대 시퀀싱(NGS)
- 롤링 서클형 복제
- 마이크로어레이
- 실시간 PCR
- 기타 기술
- 검사 유형별
- 이수성 스크리닝
- 미세결실 및 미세중복 스크리닝
- 전장 유전체 cfDNA 스크리닝
- Rh-D 유전자형 판정
- 단일 유전자 질환 검사
- 임신기간별
- 10-12주
- 13-24주
- 24주 이상
- 샘플 유형별
- 모체 혈장 cfDNA
- 순환성 영양막 세포
- 컴포넌트별
- 기기
- 키트 및 시약
- 서비스
- 최종 사용자별
- 병원 및 출산 센터
- 진단 실험실
- 체외수정(IVF) 및 불임 치료 클리닉
- 연구기관
- 유통채널별
- 의사의 리퍼
- 소비자용 직접 판매(DTC)
- 용도별
- 다운 증후군(21번 삼염색체)
- 에드워즈 증후군(18번 삼염색체)
- 파타우 증후군(13번 삼염색체)
- 터너 증후군
- 기타 염색체 이상
- 지역
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 이탈리아
- 스페인
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 인도
- 호주
- 한국
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- GCC
- 남아프리카
- 기타 중동 및 아프리카
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Illumina Inc.
- Natera Inc.
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd(Ariosa)
- BGI Genomics Co. Ltd
- Laboratory Corp of America Holdings
- Eurofins Scientific SE
- Revvity, Inc.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- Agilent Technologies Inc.
- Qiagen NV
- Invitae Corporation
- Myriad Women's Health Inc.
- Centogene NV
- MedGenome Labs Ltd
- GenePlanet doo
- Genetron Health
- Berry Genomics
- Ravgen Inc.
- Bionano Genomics, Inc.
- Arup Laboratories
제7장 시장 기회 및 미래 전망
CSM 26.01.28The non-invasive prenatal testing market was valued at USD 3.90 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 4.42 billion in 2026 to reach USD 8.23 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 13.26% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
Broader clinical guidelines now recommend cell-free DNA screening for every pregnancy, while payer policies are easing prior-authorization hurdles, driving volume expansion across risk categories. Sequencing costs have plunged and automated workflows are cutting turnaround times, making tests more affordable for emerging markets. The FDA's 2024 final rule on laboratory-developed tests established transitional compliance that paradoxically accelerated adoption because large commercial laboratories moved quickly to standardize processes. At the same time, direct-to-consumer channels are expanding in parallel with physician referral networks, reflecting a growing willingness among expectant parents to pay out-of-pocket for early genetic insight.
Global Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing Market Trends and Insights
Rising Global Maternal Age Increasing Aneuploidy Prevalence
Advanced maternal age drives higher baseline risk for chromosomal abnormalities, causing prenatal screening volumes to rise steadily in developed economies. Universal guideline recommendations issued in 2024 removed the age-based risk threshold and repositioned cfDNA testing as first-line screening for every pregnancy. Hospitals are seeing fewer invasive procedures because expectant parents opt for a blood test that carries no miscarriage risk, opening a predictable revenue stream for laboratories. Large cohort studies confirm that test sensitivity remains consistent across age groups even though positive predictive value shifts upward with age. Payers find the economics attractive because earlier detection lowers lifetime treatment costs, and laboratories leverage the reliable volume to negotiate bulk reagent pricing.
Shift From Invasive Procedures to cfDNA Screening for Safety
Amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling both carry tangible miscarriage risk, causing anxiety that makes non-invasive alternatives appealing. Clinical audits show cfDNA adoption cuts invasive procedure volumes by up to 80%, yet diagnostic confirmation remains available when results indicate a high likelihood of abnormality. Obstetricians note lower medicolegal exposure, while insurers see fewer claims related to procedure-linked complications. The blood-based approach enables rapid retesting if initial samples are inadequate, improving the patient experience. Importantly, safety advantages resonate in average-risk pregnancies where historical cost-benefit analyses favored no testing at all.
Ethical & Regulatory Concerns on Incidental Findings / Sex Selection
India's PCPNDT Act criminalizes fetal sex disclosure, forcing providers to redesign reports for local compliance. Policymakers worry that expanding panels could reveal non-paternity or maternal cancer, raising consent complexities. The Early IDENTIFY trial showed that half of non-reportable cases masked maternal malignancies, sparking debate on duty-to-warn obligations. Bioethics councils recommend incremental test roll-outs with enhanced counseling, yet region-specific restrictions slow commercial timelines. Vendors must therefore navigate a patchwork of disclosure rules that limit cross-border scale economies.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Falling Sequencing Costs & Automation Lowering Test Prices
- Expansion of Reimbursement to Average-Risk Pregnancies
- Limited Lab Infrastructure & Bioinformatics Expertise in Emerging Markets
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
In 2025, next-generation sequencing commanded 60.87% of non-invasive prenatal testing market share, cementing its reputation for analytical breadth and scalability. Rolling-circle amplification, however, is accelerating at a 15.08% CAGR, its ambient-temperature workflow suiting resource-constrained settings. The non-invasive prenatal testing market size for NGS-based assays is projected to grow steadily as laboratories leverage legacy platforms to handle rising test complexity. Meanwhile, simpler chemistries unlock new customer segments that lack capital budgets for high-end sequencers.
Digital PCR and CRISPR-enabled assays are entering pilot programs, aiming for tighter fetal-fraction quantification and improved specificity. Regulatory tightening may initially advantage entrenched NGS vendors whose systems already meet quality benchmarks, yet disruptive pricing from RCA or isothermal methodologies could pivot purchasing decisions as emerging-market volumes scale.
Whole-genome cfDNA tests held 49.11% of the non-invasive prenatal testing market size in 2025, favored for their comprehensive chromosomal coverage. Microdeletion panels are registering a brisk 14.32% CAGR, benefitting from ongoing evidence that broader variant detection adds clinical value in select cases. Aneuploidy-only assays remain popular where payers reimburse a limited menu, but their relative share is edging downward as guidelines evolve.
Bundled monogenic and carrier-status screens could redraw market boundaries by merging reproductive planning with prenatal surveillance. Yet reimbursement remains the gating factor; without payer endorsement, self-pay economics will cap near-term adoption despite rising consumer curiosity.
The 10-12-week window claimed 69.05% share in 2025 as first-trimester screening became standard obstetric protocol. Laboratories often pre-schedule draws during routine ultrasound visits, ensuring logistical efficiency and high patient adherence. Tests performed after 24 weeks, although a small base, are growing 16.34% annually thanks to late-pregnancy management needs such as unexplained anomalies on third-trimester scans.
Clinicians prefer early results for decision-making latitude, but late-stage applications offer reassurance in complex pregnancies where earlier screening was missed or inconclusive. Vendors are refining assays to remain sensitive despite declining fetal fraction as gestation advances, thereby broadening addressable volume.
The Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing Market Report is Segmented by Technology (Next-Generation Sequencing, and More), Test Type (Aneuploidy Screening, and More), Gestation Window (10-12 Weeks, and More), Sample Type (Maternal Plasma CfDNA, and More), Component (Instruments, and More), End User (Hospitals, and More), Distribution Channel, Application, and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America retained 44.78% revenue share in 2025 thanks to payer alignment, established lab networks, and strong professional-society support. The April 2025 removal of prior authorization by a leading national insurer underscores momentum toward frictionless access. Canada's province-by-province funding continues to cause uptake disparity, yet national volume grows as private pay fills public-sector gaps. Mexico's private hospitals are onboarding local sequencing capacity, although reimbursement remains limited to out-of-pocket segments.
Europe reflects a mosaic of policy models that balance ethics with universal healthcare aims. The United Kingdom's National Health Service deploys cfDNA as a contingent second-tier screen, while Germany and France reimburse first-line testing for defined indications. Italy and Spain are expanding region-level pilots to full coverage. Continental emphasis on genetic counseling and consent creates robust support infrastructure, albeit at higher per-test administrative cost.
Asia-Pacific is the growth front runner at 16.18% CAGR. China's government-backed genomics clusters and large birth cohort sustain scale economies that lower per-test pricing. Japan's multi-center demonstration project validated clinical performance, catalyzing private insurer uptake. India's dual-regulation landscape-modern lab hubs in metros versus PCPNDT limitations on sex disclosure-creates uneven regional adoption. Australia operates on an out-of-pocket model averaging AUD 500-800 (USD 330-530), although policy reviews are underway to integrate tests into Medicare Benefits Schedule.
- Illumina
- Natera
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd (Ariosa)
- BGI Genomics Co. Ltd
- Laboratory Corp of America Holdings
- Eurofins
- Revvity, Inc.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Agilent Technologies
- QIAGEN
- Invitae
- Myriad Women's Health Inc.
- Centogene
- MedGenome Labs
- GenePlanet d.o.o.
- Genetron Health
- Berry Genomics
- Ravgen Inc.
- Bionano Genomics, Inc.
- ARUP Laboratories
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising Global Maternal Age Increasing Aneuploidy Prevalence
- 4.2.2 Shift From Invasive Procedures to cfDNA Screening for Safety
- 4.2.3 Falling Sequencing Costs & Automation Lowering Test Prices
- 4.2.4 Expansion of Reimbursement to Average-Risk Pregnancies
- 4.2.5 First-Trimester Guideline Endorsement by Obstetric Societies
- 4.2.6 Bundled Carrier + Prenatal Genetic Panel Adoption
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Ethical & Regulatory Concerns on Incidental Findings / Sex Selection
- 4.3.2 Limited Lab Infrastructure & Bioinformatics Expertise in Emerging Markets
- 4.3.3 Accuracy Challenges in Twin and IVF Pregnancies Reducing Clinician Confidence
- 4.3.4 Uncertain Clinical Utility of Microdeletion Screening for Payers
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Technology
- 5.1.1 Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
- 5.1.2 Rolling-Circle Amplification
- 5.1.3 Microarray
- 5.1.4 Real-Time PCR
- 5.1.5 Other Technologies
- 5.2 By Test Type
- 5.2.1 Aneuploidy Screening
- 5.2.2 Microdeletion / Microduplication Screening
- 5.2.3 Whole-Genome cfDNA Screening
- 5.2.4 Rh-D Genotyping
- 5.2.5 Monogenic Disease Testing
- 5.3 By Gestation Window
- 5.3.1 10-12 Weeks
- 5.3.2 13-24 Weeks
- 5.3.3 Greater Than 24 Weeks
- 5.4 By Sample Type
- 5.4.1 Maternal Plasma cfDNA
- 5.4.2 Circulating Trophoblastic Cells
- 5.5 By Component
- 5.5.1 Instruments
- 5.5.2 Kits & Reagents
- 5.5.3 Services
- 5.6 By End User
- 5.6.1 Hospitals & Birthing Centers
- 5.6.2 Diagnostic Laboratories
- 5.6.3 IVF & Fertility Clinics
- 5.6.4 Research Institutes
- 5.7 By Distribution Channel
- 5.7.1 Physician-Referral
- 5.7.2 Direct-to-Consumer (DTC)
- 5.8 By Application
- 5.8.1 Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21)
- 5.8.2 Edwards Syndrome (Trisomy 18)
- 5.8.3 Patau Syndrome (Trisomy 13)
- 5.8.4 Turner Syndrome
- 5.8.5 Other Chromosomal Abnormalities
- 5.9 Geography
- 5.9.1 North America
- 5.9.1.1 United States
- 5.9.1.2 Canada
- 5.9.1.3 Mexico
- 5.9.2 Europe
- 5.9.2.1 Germany
- 5.9.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.9.2.3 France
- 5.9.2.4 Italy
- 5.9.2.5 Spain
- 5.9.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.9.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.9.3.1 China
- 5.9.3.2 Japan
- 5.9.3.3 India
- 5.9.3.4 Australia
- 5.9.3.5 South Korea
- 5.9.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.9.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.9.4.1 GCC
- 5.9.4.2 South Africa
- 5.9.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.9.5 South America
- 5.9.5.1 Brazil
- 5.9.5.2 Argentina
- 5.9.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.9.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and analysis of Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Illumina Inc.
- 6.3.2 Natera Inc.
- 6.3.3 F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd (Ariosa)
- 6.3.4 BGI Genomics Co. Ltd
- 6.3.5 Laboratory Corp of America Holdings
- 6.3.6 Eurofins Scientific SE
- 6.3.7 Revvity, Inc.
- 6.3.8 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- 6.3.9 Agilent Technologies Inc.
- 6.3.10 Qiagen N.V.
- 6.3.11 Invitae Corporation
- 6.3.12 Myriad Women's Health Inc.
- 6.3.13 Centogene N.V.
- 6.3.14 MedGenome Labs Ltd
- 6.3.15 GenePlanet d.o.o.
- 6.3.16 Genetron Health
- 6.3.17 Berry Genomics
- 6.3.18 Ravgen Inc.
- 6.3.19 Bionano Genomics, Inc.
- 6.3.20 Arup Laboratories
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space & Unmet-Need Assessment

















