
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1443437
<2024> 리튬이차전지 Si-Anode 기술 현황 및 주요 업체 개발 동향<2024> LIB Si-Anode Technology Status and Outlook (~2035) |
||||||
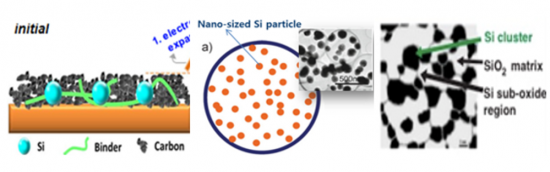
리튬이차전지의 음극활물질은 현재까지 주로 탄소재가 사용되고 있으며, 초기에는 비정질 탄소계를 많이 사용하였으나 지금은 천연흑연과 인조흑연을 주로 사용하고 있습니다. 최근에는 흑연 재료의 이론용량 한계를 극복하고 전기화학적 반응 전위 및 수명이 우수한 재료를 개발하기 위하여 Si계 음극소재를 중심으로 한 새로운 음극 재료들이 적극적으로 고려되고 있습니다. 전기자동차용 및 ESS용 중대형 배터리 시장에서 고용량 음극 소재의 필요성이 더욱 증가하면서 기존에 쓰이던 탄소계, 흑연계 음극재 중심에서 최근에는 특히 금속복합계인 실리콘(Si)계 음극재가 업계의 주목을 받고있으며, 이 소재를 확보려는 경쟁이 치열해지고 있습니다. 이와 관련하여 실리콘 음극재를 개발하고 양산하려는 신규 진입 업체들도 계속해서 증가하고 있습니다.
Si계 고용량 소재는 2020년 초에는 10-20개 업체에서만 주로 개발하고 있었으나, 현재는 60여개 이상 업체들이 개발 및 양산 준비를 하고 있습니다. Si계 소재는 향후 전기차의 주행거리 극복을 위한 고용량 전지개발 및 급속충전 요구사항을 만족하기 위해서는 필수적으로 개발되어야만 하는 소재이며, 전기차 OEM 및 배터리 업체들은 실리콘 음극재는 2035년까지 연평균 30%의 성장률이 예상됩니다. 전체 음극재 시장에서 실리콘 음극재의 비중은 2019년 1%에서 2030년 7%, 2035년 10%까지 확대할 전망입니다.
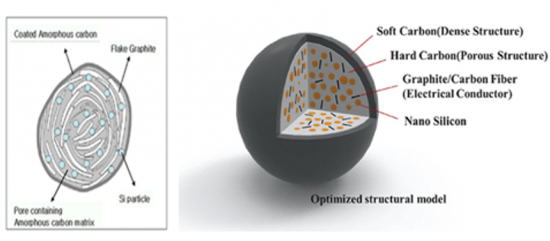
탄소계, 흑연계 외에 리튬 이차전지 고용량 음극 소재로 Si-C composite, Si-alloy, SiOx 가 대표적입니다. 그 중 SiOx 와 Si-alloy 는 가장 상품화에 근접되어 있으며, 일부 전지 메이커에서 전지에 적용하여 고용량 전지를 개발 중에 있으나, 아직까지 수명, 부피팽창(Swelling) 등의 문제가 있어 이를 개선하기 위한 노력을 진행 중입니다. 실리콘(Si)계 음극 관련하여 최근 업계와 학계의 관련 기술 개발 발표가 잇따르고 있고, 음극 소재 업체들도 신규기술 개발에 집중하며 머지 않아 상용화가 기대되고 있습니다.
본 보고서는 최근 이슈가 되고 있는 xEV, ESS, IT용 리튬이차전지의 음극재 시장 뿐 아니라 고용량 전지개발을 위한 Si계 음극개발 동향 및 성능향상에 대한 기술적 보고서로, 특히, Si계 고용량 음극[Si-alloy, SiOx, Si-C composite]소재의 업체와 학계의 최신 개발 현황과 이를 적용한 전지의 상황 및 문제점 그리고 이를 개선할 수 있는 idea를 제공함으로 향후 고용량/고출력 전지 개발에 도움을 드리고자 합니다.
본 보고서의 Strong Point
- ① 리튬이차전지 음극재의 전체적인 시장 M/S 및 기술 현황 (흑연계, 실리콘계 포함)
- ② 고용량 Si계 음극소재의 기술 이슈 및 핵심 요소 기술 정리
- ③ 배터리사의 최신 Si계 음극소재의 기술 개발 동향
- ④ 향후 Si계 음극소재의 응용 분야 및 상용화 전망
- ⑤ 글로벌 70여개의 실리콘 음극 업체 개발 동향 및 제품 소개
- Contents -
리포트 개요
Chapter Ⅰ. 리튬이차전지 개요
- 1.1 리튬이차전지 역사
- 1.2 리튬이차전지 종류 및 특징
- 1.3. 리튬이차전지 원리
- 1.3.1 충전 및 방전반응
- 1.3.2 전압
- 1.3.3 전하와 이온의 이동
- 1.3.4 이론 용량
- 1.4. 리튬이차전지 구성요소
- 1.4.1 양극활물질
- 1.4.2 음극활물질
- 1.4.3 분리막
- 1.4.4 전해질
- 1.5. 리튬이차전지 응용분야
- 1.6. 음극재 기술 현황 및 개발 Trend
Chapter Ⅱ. 리튬이차전지 음극소재 종류 및 특징
- 2.1 리튬이차전지 음극소재 요구특성 및 종류
- 2.2 탄소계 음극소재 특성
- 2.2.1 흑연계 음극소재
- 2.2.2 비정질 탄소계 음극소재
- 2.2.3 탄소계 음극소재/전해질 계면 반응
- 2.3 금속계 음극소재 특성
- 2.3.1 리튬금속 음극소재
- 2.3.2 합금계 음극소재
- 2.4 화합물계 음극소재 특성
- 2.4.1 산화물계 음극소재
- 2.4.2 질화물계 음극소재
Chapter Ⅲ. 고용량 리튬이차전지용 Si계 음극소재 기술개발 현황
- 3.1 고용량 리튬이차전지 개발 이력 및 방향
- 3.2 고용량 Si계 음극소재 기본 특성
- 3.2.1 Si계 음극소재의 리튬 삽입/탈리 반응
- 3.2.2 Si계 음극소재의 문제점 및 열화 메커니즘
- 3.2.3 Si계 음극소재의 부피팽창 제어
- 3.3 합금계 음극재의 문제점 및 해결 방안
- 3.3.1 대표적인 문제점
- 3.3.2 금속 복합계 음극재
- 3.3.3 금속-탄소 복합계 음극재
- 3.4 고용량 Si계 음극소재 기술개발 동향
- 3.4.1 SiOx 음극소재
- 구조적 특성
- 전기화학적 특성
- 제조방법
- Prelithiation 공정 적용
- 3.4.2 Si-C 복합체 음극소재
- 3.4.3 Si-M 합금 음극소재
- 3.4.4 Si계 음극재의 실제 적용 연구
- 전기화학적 거동 차이
- Si 단독 전극 및 Si/흑연 혼합 전극
- 3.4.5 다양한 나노구조의 Si계 음극소재
- Si nanostructure
- Porous Si structure
- Nano-Si/C structure
- Nano-Si/metal or polymer structure
- 3.4.6 Si계 음극소재용 바인더
- 3.4.7 Si계 음극소재용 집전체
- 3.4.8 Si계 음극의 연구동향 종합 및 앞으로의 연구방향
- 3.4.9 Si계 음극소재 학계/업계 개발 사례
- 3.4.10 Si계 음극소재 주요 기술로드맵
- 3.4.1 SiOx 음극소재
Chapter Ⅳ. 고출력 Si계 음극소재 기술개발 현황
- 4.1 고출력 음극재의 개요
- 4.2 고출력 급속충전용 음극소재
- 4.2.1 Intercalation소재
- 4.2.2 합금계 소재 / 전이 소재
- 4.2.3 nano 구조 마이크로 입자 (Nano-structured micro-sized particles)
- 4.2.4 Si-흑연 hybrid 소재 (SEAG)
- 4.2.5 Graphene-SiO2 소재 (Graphene Ball)
- 4.3 음극 관점에서 급속 충전
- 4.3.1 음극재(활물질)의 영향 인자
- 4.3.2 전극의 영향 인자
- 4.3.3 주요 배터리 업체의 급속충전 기술 설계
- 4.4.4 종합 및 향후 전망
Chapter Ⅴ. LiB 음극재 시장 동향 및 전망
- 5.1 리튬이차전지 음극소재 시장 현황
- 5.1.1 국가별 음극재 수요 현황
- 5.1.2 소재별 음극재 수요 현황
- 5.1.3 공급 업체별 시장 현황
- 5.1.4 LIB 업체별 수요 현황
- SDI/LGES/SKon/Panasonic/CATL/ATL/BYD/Lishen/Guoxuan/AESC/CALB
- 5.2 리튬이차전지 음극소재 수급 전망
- 5.2.1 음극재 생산캐파 전망
- 5.2.2 음극재 출하실적 현황 및 전망
- 5.2.3 음극재 수급 전망
- 5.2 리튬이차전지 음극소재 수급 전망
- 5.2.1 음극재 생산캐파 전망
- 5.2.2 음극재 출하실적 현황 및 전망
- 5.2.3 음극재 수급 전망
- 5.3 리튬이차전지 음극소재 가격 전망
- 5.3.1 음극재 가격 구조
- NG/AG/Si계
- 5.3.2 음극재 가격 동향
- NG/AG/Si계
- 5.3.3 흑연 종류별 가격 현황
- 5.3.4 Needle coke, Pitch 가격 현황
- 5.3.5 음극재 업체별 가격 전망
- 5.3.1 음극재 가격 구조
Chapter Ⅵ. 리튬이차전지 음극소재 생산업체 현황
- 6.1 리튬이차전지 음극소재 업체 요약
- 6.2 리튬이차전지 음극소재 생산업체 현황
- 흑연/카본계 중심 음극재 생산업체
- 흑연/카본계 중심 음극재 생산업체
- 1. BTR
- 2. Shanshan
- 3. Zichen
- 4. Shinzoom(Changsha Xingcheng)
- 5. Kaijin
- 6. XFH(XiangFengHua)
- 7. Hitachi Chemical(Resonac)
- 8. Mitsubishi Chemical
- 9. JFE Chemical
- 10. 포스코퓨처엠
- 11. 애경케미칼
- 실리콘계 중심 음극재 생산업체 (한국/아시아계)
- 12. 대주 전자재료
- 13. Shin-Etsu
- 14. MK전자
- 15. 일진전기
- 16. EG
- 17. 한솔케미칼
- 18. 이녹스에코켐
- 19. FIC 신소재
- 20. LPN
- 21. Osaka Titan
- 22. 포스코실리콘솔루션
- 23. 티씨케이((TOKAI CARBON KOREA)
- 24. NM Tech(트루윈 인수)
- 25. KBG
- 26. Neo Battery Materials
- 27. 한국메탈실리콘
- 28. 이엔플러스
- 29. 롯데에너지머티리얼즈
- 30. 동진세미켐
- 31. SJ신소재
- 32. 아이엘사이언스
- 33. 에스머티리얼
- 34. ㈜HNS
- 35. 와이파인텍
- 36. 하나 머티리얼즈
- 실리콘계 중심 음극재 생산업체 (미주,유럽계)
- 47. Group14 (With SK 머티리얼즈)
- 48. NEXEON (With SKC)
- 49. Sila Nano Technologies
- 50. Enovix
- 51. Enervate
- 52. EO Cell
- 53. Amprius Technologies
- 54. Nanotek' Instrument
- 55. One D
- 56. Nanograf
- 57. LeydenJar
- 58. ADVANO
- 59. Targray
- 60. 스토어닷(StoreDot)
- 61. Trion Battery
- 62. Black Diamond Structures
- 63. Nanospan
Chapter Ⅶ. 참고 문헌
The anode material for lithium-ion batteries has predominantly been carbon-based to date. In the early stages, amorphous carbon materials were widely used, but presently, natural and synthetic graphite are the primary choices. Recently, there has been active consideration of new anode materials, particularly those centered around silicon (Si), to overcome the theoretical capacity limits of graphite materials and develop materials with excellent electrochemical reaction potential and extended lifespan. The demand for high-capacity anode materials has been increasing, particularly in the market for large-scale batteries used in electric vehicles and energy storage systems. While carbon and graphite-based anode materials were traditionally prevalent, there is a growing focus, especially within the industry, on silicon-based anode materials, which are metal composites. The competition to secure these materials has intensified as the need for high-capacity anode rises. In this context, there is a continual increase in new entrants developing and manufacturing silicon-based anode materials.
As of early 2020, silicon-based high-capacity materials were primarily developed by only 10-20 companies. However, the current landscape shows that over 60 companies are actively engaged in the development and preparation for mass production of silicon-based materials. Silicon-based materials are essential for the development of high-capacity batteries to address the range limitations of electric vehicles and meet the demand for fast-charging capabilities. Electric vehicle OEMs and battery companies anticipate a projected annual growth rate of 30% for silicon anode materials until 2035. The market share of silicon anode materials in the overall anode material market is expected to expand from 1% in 2019 to 7% in 2030 and further to 10% by 2035.
In addition to carbon-based and graphite-based materials, Si-C composite, Si-alloy, and SiOx are representative high-capacity anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Among these, SiOx and Si-alloy are the closest to commercialization, with some battery manufacturers actively developing high-capacity batteries by incorporating them. However, challenges such as lifespan and volume expansion (swelling) persist, prompting ongoing efforts to address these issues. In the realm of silicon (Si)-based anodes, recent announcements of related technological developments have been made by both industry and academia. Anode material companies are also concentrating on new technology development, fostering expectations for imminent commercialization.
This report serves as a technical document focusing on recent developments in the anode material market for lithium-ion batteries used in xEV (electric vehicles), ESS (energy storage systems), and IT applications. Specifically, it delves into the technological advancements and performance enhancements in Si-based anode development for high-capacity batteries. The report provides an overview of the latest developments in Si-based high-capacity anode materials (Si-alloy, SiOx, Si-C composite) by both industry and academia. It also examines the current status and challenges associated with batteries incorporating these materials, aiming to offer insights and potential solutions for future developments in high-capacity/high-output battery technologies.
Strong Point of this report:
- 1. Overall market share and technological status of anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. (including graphite-based and silicon-based materials.)
- 2. Technical issues and key technological factors related to high-capacity silicon-based anode materials.
- 3. Recent technological developments in silicon-based anode materials by battery manufacturers.
- 4. Applications and commercialization prospects for future silicon-based anode materials.
- 5. Technological trends and product introductions from over 70 global silicon-based anode material companies.
Table of Contents
Report Overview
Chapter I. Overview of LIBs
- 1.1. History of LIBs
- 1.2. Types and Characteristics of LIBs
- 1.3. Principle of LIBs
- 1.3.1. Charging / Discharging Reactions
- 1.3.2. Voltage
- 1.3.3. Movement of Charge and Ions
- 1.3.4. Theoretical Capacity
- 1.4. Components of LIBs
- 1.4.1. Cathode active materials
- 1.4.2. Anode active materials
- 1.4.3. Seperator
- 1.4.4. Electrolyte
- 1.5. Application areas of LIBs
- 1.6. Technology Status and Development Trend of Anode Materials
Chapter II. Types and Characteristics of LIB Anode Materials
- 2.1. Required Characteristics and Types of LIB Anode Materials
- 2.2. Characteristics of Carbon-based Anode Materials
- 2.2.1. Graphite-based Anode Materials
- 2.2.2. Amorphous Carbon-based Anode Materials
- 2.2.3. Carbon-based Anode Materials / Electrolyte Interfacial Reaction
- 2.3. Characteristics of Metal-based Anode Materials
- 2.3.1. Lithium Metal Anode Materials
- 2.3.2. Alloy-based Anode Materials
- 2.4. Characteristics of Compound-Based Anode Materials
- 2.4.1. Oxide-Based Anode Materials
- 2.4.2. Nitride-Based Anode Materials
Chapter III. Current Status of Technological Development for High-Capacity Si-Based Anode Materials for Lithium-ion Batteries
- 3.1. Development History and Direction of High-Capacity Lithium-ion Batteries
- 3.2. Basic Characteristics of High-Capacity Si-based Anode Materials
- 3.2.1. Lithium Insertion/Extraction Reactions of Si-based Anode Materials
- 3.2.2. Issues of Si-based Anode Materials and Degradation Mechanisms
- 3.2.3. Volume Expansion Control of Si-based Anode Materials
- 3.3. Problems and Solutions for Alloy-based Anode Materials
- 3.3.1. Representative Problems
- 3.3.2. Metal Composite-based Anode Materials
- 3.3.3. Metal-Carbon Composite-based Anode Materials
- 3.3. Trends in the Technological Development of High-Capacity Si Anode Materials
- 3.3.1. SiOx Anode Materials
- Structural Characteristics
- Electrochemical Properties
- Manufacturing Methods
- Application of Prelithiation Process
- 3.3.2. Si-C Composite Anode Materials
- 3.3.3. Si-M Alloy Anode Materials
- 3.3.4. Practical Application Research of Si Anode Materials
- Differences of Electrochemical Behavior
- Si Single Electrode and Si/Graphite Hybrid Electrode
- 3.3.5. Various Nanostructures of Si-based Anode Materials
- Si nanostructure
- Porous Si structure
- Nano-Si/C structure
- Nano-Si/metal or polymer structure
- 3.3.6. Binders for Si-based Anode Materials
- 3.3.7. Current Collectors for Si-based Anode Materials
- 3.3.8. Comprehensive Review of Research Trends in Si-based Anodes and Future Research Directions
- 3.3.9. Examples of Si-based Anode Material Developments in Academic/Industries
- 3.3.10. Key Technology Roadmap for Si-Based Anode Materials
- 3.3.1. SiOx Anode Materials
Chapter IV. Current Status of High-Output Si-Based Anode Material Technology Development
- 4.1. Overview of High-Output Anode Materials
- 4.2. Anode Materials for High-Output Fast Charging
- 4.2.1. Intercalation Materials
- 4.2.2. Alloy-based Materials / Transition Materials
- 4.2.3. Nano-Structured Micro-Sized Particles (Nano-structured micro-sized particles)
- 4.2.4. Si-Graphite Hybrid Materials (SEAG)
- 4.2.5. Graphene-SiO2 Materials (Graphene Ball)
- 4.3. Fast Charging from Anode Perspective
- 4.3.1. Factors Influencing Anode Materials (Active Materials)
- 4.3.2. Factors Influencing Electrodes
- 4.3.3. Design of Fast Charging Technology by Major Battery Companies
- 4.4.4. Summary and Future Outlook
Chapter V. Trends and Outlook in the LIB Anode Material Market
- 5.1. Current Status of LIB Anode Material Market
- 5.1.1. Demand for Anode Materials by Country
- 5.1.2. Demand for Anode Materials by Material Type
- 5.1.3. Market Status by Supplier
- 5.1.4. Demand for Anode Materials by LIB Companies
- SDI/LGES/SKon/Panasonic/CATL/ATL/BYD/Lishen/Guoxuan/AESC/CALB
- 5.2. Supply Outlook for LIB Anode Materials
- 5.2.1. Outlook of Anode Material Production Capacity
- 5.2.2. Status and Outlook of Anode Material Shipments
- 5.2.3. Supply Outlook for Anode Materials
- 5.3. Price Outlook for LIB Anode Materials
- 5.3.1. Anode Material Price Structure
- NG/AG/Si-based
- 5.3.2. Anode Material Price Trends
- NG/AG/Si-based
- 5.3.3. Price Status of Different Types of Graphite
- 5.3.4. Price Status of Needle Coke and Pitch
- 5.3.5. Price Outlook by Anode Material Suppliers
- 5.3.1. Anode Material Price Structure
Chapter VI. Current Status of LIB Anode Material Manufacturers
- 6.1. Summary of LIB Anode Material Companies
- 6.2. Current Status of LIB Anode Material Manufacturers
Graphite/Carbon-Based Anode Material Manufacturers
- 1. BTR
- 2. Shanshan
- 3. Zichen
- 4. Shinzoom(Changsha Xingcheng)
- 5. Kaijin
- 6. XFH(XiangFengHua)
- 7. Hitachi Chemical(Resonac)
- 8. Mitsubishi Chemical
- 9. JFE Chemical
- 10. POSCO FutureM
- 11. Aekyung Chemical
Si-based Anode Material Manufacturers (Korean/Asian)
- 12. Daejoo Electronic Materials
- 13. Shin-Etsu
- 14. MK Electronics
- 15. Il-jin Electric
- 16. EG
- 17. Hansol Chemical
- 18. Innox Eco Chemical
- 19. FIC Advanced Materials
- 20. LPN
- 21. Osaka Titan
- 22. POSCO Silicon Solution
- 23. TCK((TOKAI CARBON KOREA)
- 24. NM Tech(Acquired by Truewin)
- 25. KBG
- 26. Neo Battery Materials
- 27. Korea Metal Silicon
- 28. EN PLUS
- 29. Lotte Energy Materials
- 30. Dong-jin Semichem
- 31. SJ Advanced Materials
- 32. IEL Science
- 33. S Materials
- 34. HNS
- 35. Y-Fine Tech
- 36. Hana Materials
Si-Based Anode Material Manufacturers (Chinese)
- 37. Haoxin Tech
- 38. Longtime Tech
- 39. Gotion
- 40. Shinghwa
- 41. Tianmulake
- 42. Chengdu Guibao
- 43. Jereh
- 44. Huawei
- 45. Xinan
- 46. Kingi
Si-based Anode Material Manufacturers (North America, Europe)
- 47. Group14 (With SK Materials)
- 48. NEXEON (With SKC)
- 49. Sila Nano Technologies
- 50. Enovix
- 51. Enervate
- 52. EO Cell
- 53. Amprius Technologies
- 54. Nanotek' Instrument
- 55. One D
- 56. Nanograf
- 57. LeydenJar
- 58. ADVANO
- 59. Targray
- 60. StoreDot
- 61. Trion Battery
- 62. Black Diamond Structures
- 63. Nanospan
Chapter VII. References
(주말 및 공휴일 제외)


















