
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1687080
군용 위성 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Military Satellite - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
■ 보고서에 따라 최신 정보로 업데이트하여 보내드립니다. 배송일정은 문의해 주시기 바랍니다.
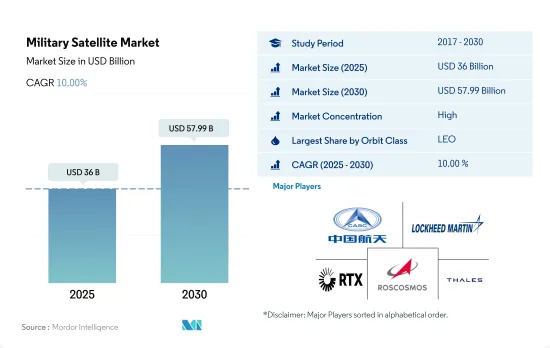
군용 위성 시장 규모는 2025년에 360억 달러로 추정되고, 2030년에는 579억 9,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며, 예측 기간 중(2025-2030년) CAGR은 10.00%를 나타낼 전망입니다.

통신 중계의 고속화가 LEO 부문의 주요 점유율을 차지할 것으로 예상
- 위성이나 우주선은 일반적으로 지구 주변의 여러 특수 궤도 중 하나에 배치되거나 용도에 따라 행성 간 여행으로 발사될 수 있습니다.
- 많은 기상 및 통신 위성은 지표에서 가장 멀리 떨어져 있는 높은 지구궤도를 사용하는 경향이 있습니다. MEO 궤도에 있는 위성에는 특정 지역을 모니터링하도록 설계된 내비게이션 및 특수 위성이 포함됩니다. 각 거리에는 커버리지 증가, 에너지 효율 감소 등 장점과 과제가 있습니다. NASA의 지구 관측 시스템 팀을 포함한 대부분의 과학 위성은 저지구 궤도에 있습니다.
- 2017-2022년에 걸쳐 MEO 궤도에서 발사된 57개의 위성 중 대부분은 내비게이션 및 글로벌 포지셔닝 목적으로 제작되었습니다. 마찬가지로 GEO 궤도에 있는 147개의 위성 중 대부분은 통신 및 지구 관측 목적으로 배치되었습니다.
- 전자 정보, 지구 과학 및 기상학, 레이저 이미징, 광학 이미징 등의 분야에서 위성 사용이 증가함에 따라 예측 기간 동안 위성 개발에 대한 수요가 증가할 것으로 예상됩니다.
세계의 군용 위성 수의 급증이 군용 위성 시장을 뒷받침할 전망
- 2022년 전 세계 국방비는 2조 달러를 넘어섰으며, 주요 군사 강국인 미국은 국방비를 7,730억 달러로 급증시켰습니다. 미국 우주군의 중요성이 커지는 이유는 모든 군용 통신 위성의 운영을 맡고 있기 때문입니다.
- 미국의 뒤를 이어 중국, 인도, 러시아, 영국도 각각 14%, 5%, 6.8%, 13%씩 국방비를 늘렸습니다. 예를 들면, 2022년 3월, 프랑스 국방성은 우주 영역에 7억 600만 달러의 지출을 계획해, 2019-2025년 동안 군사 우주 역량 및 서비스에 53억 유로를 배정했습니다.
- 군용 위성 시장에서 새로운 위성 버스 개발을 강조하고 있습니다. 예를 들어, 2023년 1월, 록히드 마틴의 첫 번째 다중 임무 우주선인 LM 400은 군사용에 적합한 유연한 중형 위성으로, 회사의 디지털 팩토리 생산 라인에서 준비되어 2023년에 발사될 예정입니다. 2017년부터 2022년까지 약 230개 이상의 위성이 제작 및 발사되어 북미의 군 및 정부 기관에서 소유하고 있습니다.
세계의 군용 위성 시장 동향
전 세계적으로 위성 소형화에 대한 수요가 증가하면서 시장 성장을 주도
- 기존 위성의 거의 모든 기능을 적은 비용으로 수행할 수 있는 소형 위성의 능력으로 인해 소형 위성의 구축, 발사, 운영 가능성이 높아졌습니다.
- 유럽의 시장 수요는 주로 독일, 프랑스, 러시아, 영국이 주도하고 있으며, 이들 국가는 매년 가장 많은 수의 소형 위성을 제작하고 있습니다. 2017-2022년 동안 다양한 지역 업체들이 50개 이상의 나노 및 마이크로 위성을 궤도에 올렸습니다. 전자 부품과 시스템의 소형화 및 상용화로 인해 시장 참여가 활발해지면서 현재 시장 상황을 활용하고 개선하려는 새로운 시장 플레이어가 등장했습니다. 예를 들어, 영국에 본사를 둔 스타트업 Open Cosmos는 ESA와 제휴하여 최종 사용자에게 상업용 나노위성 발사 서비스를 제공하면서 약 90%의 비용 절감 효과를 보장하고 있습니다.
- 아시아태평양 수요는 주로 매년 가장 많은 수의 소형 위성을 제조하는 중국, 일본, 인도에서 주도하고 있습니다. 2017년부터 2022년까지 190개 이상의 나노 및 초소형 위성이 다양한 지역 업체들에 의해 궤도에 진입했습니다. 중국은 우주 기반 역량을 강화하기 위해 상당한 자원을 투자하고 있습니다. 중국은 현재까지 아시아 태평양 지역에서 가장 많은 수의 나노 및 마이크로 위성을 발사했습니다.
투자 기회가 급증하면서 글로벌 위성 제조 시장이 활성화될 것으로 예상
- 북미 지역의 우주 프로그램에 대한 전 세계 정부 지출은 2021년 약 1,030억 달러를 기록했습니다. 이 지역은 세계 최대 우주 기관인 NASA가 있는 우주 혁신과 연구의 진원지입니다. 2022년 미국 정부는 우주 프로그램에 약 620억 달러를 지출하여 세계에서 우주 프로그램에 가장 많은 예산을 지출할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 유럽 국가들은 우주 영역에 대한 다양한 투자의 중요성을 인식하고 글로벌 우주 산업에서 경쟁력을 유지하기 위해 혁신 활동에 대한 지출을 늘리고 있습니다. 2022년 11월, ESA는 지구 관측 분야에서 유럽의 주도권을 유지하고, 내비게이션 서비스를 확대하며, 미국과 우주 탐사 파트너로 남기 위해 향후 3년간 우주 예산을 25% 증액할 것을 제안했다고 발표했습니다.
- 아시아태평양 지역의 우주 관련 활동 증가에 따라 2022년 일본의 예산 초안에는 14억 달러가 넘는 우주 예산이 증가했습니다.마찬가지로 22 회계연도 인도의 우주 프로그램 예산안은 18억 3,000만 달러였습니다.
군용 위성 산업 개요
군용 위성 시장은 상위 5개 기업이 85.32%를 점유하며 상당히 통합되어 있습니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월의 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 주요 요약과 주요 조사 결과
제2장 보고서 제안
제3장 소개
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
- 조사 방법
제4장 주요 산업 동향
- 위성의 소형화
- 위성 질량
- 우주 프로그램에 대한 지출
- 규제 프레임워크
- 세계
- 호주
- 브라질
- 캐나다
- 중국
- 프랑스
- 독일
- 인도
- 이란
- 일본
- 뉴질랜드
- 러시아
- 싱가포르
- 한국
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 영국
- 미국
- 밸류체인과 유통채널 분석
제5장 시장 세분화
- 위성 질량
- 10-100kg
- 100-500kg
- 500-1,000kg
- 10kg 이하
- 1,000kg 이상
- 궤도 클래스
- GEO
- LEO
- MEO
- 위성 하위 시스템
- 추진 하드웨어 및 추진제
- 위성 버스 및 하위 시스템
- 태양전지 어레이와 전원 하드웨어
- 구조, 하네스 및 메커니즘
- 용도
- 통신
- 지구 관측
- 네비게이션
- 우주 관측
- 기타
- 지역
- 아시아태평양
- 유럽
- 북미
- 기타
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 주요 전략 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 상황
- 기업 프로파일
- Airbus SE
- BAE Systems
- China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation(CASC)
- Elbit Systems
- General Dynamics
- Indian Space Research Organisation(ISRO)
- Information Satellite Systems Reshetnev
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- Raytheon Technologies Corporation
- ROSCOSMOS
- Thales
- Viasat, Inc.
제7장 CEO에 대한 주요 전략적 질문
제8장 부록
- 세계 개요
- 개요
- Five Forces 분석 프레임워크
- 세계의 밸류체인 분석
- 시장 역학(DROs)
- 출처 및 참고문헌
- 도표 일람
- 주요 인사이트
- 데이터 팩
- 용어집
The Military Satellite Market size is estimated at 36 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 57.99 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 10.00% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Faster relay of communication is driving the LEO segment to occupy a major share of 84.8% in 2023
- A satellite or a spacecraft is usually placed into one of many special orbits around the Earth, or it can be launched into an interplanetary journey based on its intended application. Out of the three orbits, namely low Earth orbit (LEO), geostationary orbit (GEO), and medium Earth orbit (MEO), the LEO orbit is the most widely preferred one because of its proximity to the Earth.
- Many weather and communication satellites tend to have high Earth orbits, which are farthest from the surface. Satellites in mean (medium) Earth orbit include navigational and specialized satellites designed to monitor a specific area. Each distance has benefits and challenges, including increased coverage and decreased energy efficiency. Most science satellites, including NASA's Earth Observation System team, are in low Earth orbit.
- During 2017-2022, out of the 57 satellites launched in the MEO orbit, most were built for navigation/global positioning purposes. Similarly, out of the 147 satellites in the GEO orbit, most were deployed for communication and Earth observation purposes. Around 4,131 LEO satellites manufactured and launched were owned by North American organizations in that period.
- The increasing use of satellites in areas such as electronics intelligence, Earth science/meteorology, laser imaging, and optical imaging is expected to drive the demand for the development of satellites during the forecast period.
The surge in the number of defense satellites globally is expected to aid the military satellites market
- The global defense expenditure crossed over USD 2 trillion in 2022, with the major military power, the United States, surging its defense expenditure by USD 773 billion. The increasing importance of the US Space Force is due to it taking over the operation of all military satellite communications satellites. The US armed forces are integrating space systems with air, land, and sea platforms as military forces increasingly rely on satellites for operations.
- The United States was followed by China, India, Russia, and the United Kingdom, which also increased their defense expenditures by 14%, 5%, 6.8%, and 13%, respectively. The major defense players have well-established budgets for their defense satellite domain. For instance, in March 2022, France's Armed Forces Ministry planned to spend USD 706 million in the space domain and earmarked EUR 5.3 billion on military space capabilities and services during 2019-2025.
- The market is witnessing the entry of private players spending huge amounts on R&D to exploit new opportunities in the industry. Companies in North America have emphasized developing new satellite buses in the military satellite market. For instance, in January 2023, Lockheed Martin's first multi-mission spacecraft, the LM 400, is a flexible mid-sized satellite adaptable for military users, readied from the company's Digital Factory production line and scheduled for launch in 2023. During 2017-2022, around 230+ satellites manufactured and launched were owned by military and government organizations in North America. High military budget spending and technology development are expected to drive the North American market at a healthy growth rate, amounting to 91%, during 2023-2029.
Global Military Satellite Market Trends
Rising demand for satellite miniaturization globally is driving market growth
- The ability of small satellites to perform nearly all the functions of traditional satellites at a fraction of their cost has increased the viability of building, launching, and operating small satellite constellations. The demand from North America is primarily driven by the United States, which manufactures the largest number of small satellites each year. In North America, during 2017-2022, a total of 596 nanosatellites were placed into orbit by various regional players. NASA is also currently involved in several projects aimed at developing these satellites.
- The market demand in Europe is primarily driven by Germany, France, Russia, and the United Kingdom, which manufacture the largest number of small satellites each year. During 2017-2022, more than 50 nano and microsatellites were placed into orbit by various regional players. The miniaturization and commercialization of electronic components and systems have driven market participation, resulting in the emergence of new market players who aim to capitalize on and enhance the current market scenario. For instance, UK-based startup Open Cosmos partnered with ESA to provide commercial nanosatellite launch services to end users while ensuring competitive cost savings of around 90%.
- The demand from Asia-Pacific is primarily driven by China, Japan, and India, which manufacture the largest number of small satellites annually. During 2017-2022, more than 190 nano and microsatellites were placed into orbit by various regional players. China is investing significant resources toward augmenting its space-based capabilities. The country has launched the most significant number of nano and microsatellites in Asia-Pacific to date.
The surge in investment opportunities is expected to boost the global satellite manufacturing market
- In North America, global government expenditure for space programs reached a record of approximately USD 103 billion in 2021. The region is the epicenter of space innovation and research, with the presence of the world's biggest space agency, NASA. In 2022, the US government spent nearly USD 62 billion on its space programs, making it the highest spender on space programs in the world. In the United States, federal agencies receive aid from Congress every year, known as funding, NASA received USD 32.33 billion in 2023 for its subsidiaries.
- European countries are recognizing the importance of various investments in the space domain and are increasing their spending on innovative activities to remain competitive in the global space industry. In November 2022, ESA announced that it had proposed a 25% boost in space funding over the next three years designed to maintain Europe's lead in Earth observation, expand navigation services, and remain a partner in space exploration with the United States. The European Space Agency (ESA) is asking its 22 nations to back a budget of some EUR 18.5 billion for 2023-2025. Germany, France, and Italy are the major contributors.
- In line with the increase in space-related activities in the Asia-Pacific region, in 2022, Japan's draft budget registered a rise in its space budget, which amounted to over USD 1.4 billion. It included the development of the H3 rocket, Engineering Test Satellite-9, and the nation's Information Gathering Satellite (IGS) program. Similarly, the proposed budget for India's space programs for FY22 was USD 1.83 billion. In 2022, the South Korean Ministry of Science and ICT announced a space budget of USD 619 million for manufacturing satellites, rockets, and other key space equipment.
Military Satellite Industry Overview
The Military Satellite Market is fairly consolidated, with the top five companies occupying 85.32%. The major players in this market are China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), Lockheed Martin Corporation, Raytheon Technologies Corporation, ROSCOSMOS and Thales (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Satellite Miniaturization
- 4.2 Satellite Mass
- 4.3 Spending On Space Programs
- 4.4 Regulatory Framework
- 4.4.1 Global
- 4.4.2 Australia
- 4.4.3 Brazil
- 4.4.4 Canada
- 4.4.5 China
- 4.4.6 France
- 4.4.7 Germany
- 4.4.8 India
- 4.4.9 Iran
- 4.4.10 Japan
- 4.4.11 New Zealand
- 4.4.12 Russia
- 4.4.13 Singapore
- 4.4.14 South Korea
- 4.4.15 United Arab Emirates
- 4.4.16 United Kingdom
- 4.4.17 United States
- 4.5 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Satellite Mass
- 5.1.1 10-100kg
- 5.1.2 100-500kg
- 5.1.3 500-1000kg
- 5.1.4 Below 10 Kg
- 5.1.5 above 1000kg
- 5.2 Orbit Class
- 5.2.1 GEO
- 5.2.2 LEO
- 5.2.3 MEO
- 5.3 Satellite Subsystem
- 5.3.1 Propulsion Hardware and Propellant
- 5.3.2 Satellite Bus & Subsystems
- 5.3.3 Solar Array & Power Hardware
- 5.3.4 Structures, Harness & Mechanisms
- 5.4 Application
- 5.4.1 Communication
- 5.4.2 Earth Observation
- 5.4.3 Navigation
- 5.4.4 Space Observation
- 5.4.5 Others
- 5.5 Region
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.3 North America
- 5.5.4 Rest of World
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments).
- 6.4.1 Airbus SE
- 6.4.2 BAE Systems
- 6.4.3 China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC)
- 6.4.4 Elbit Systems
- 6.4.5 General Dynamics
- 6.4.6 Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
- 6.4.7 Information Satellite Systems Reshetnev
- 6.4.8 Lockheed Martin Corporation
- 6.4.9 Raytheon Technologies Corporation
- 6.4.10 ROSCOSMOS
- 6.4.11 Thales
- 6.4.12 Viasat, Inc.
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SATELLITE CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms
샘플 요청 목록

















