
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1844699
정적 RAM(SRAM) : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
세계의 정적 RAM(SRAM) 시장 규모는 2025년에 17억 1,000만 달러로 평가되었고, CAGR은 5.60%를 나타낼 것으로 예측되며, 2030년에 22억 5,000만 달러에 달할 전망입니다.

성장은 AI 중심 컴퓨팅, 5G 도입, 실시간 에지 처리로의 전환을 반영했으며, 이 모든 것은 캐시 계층 구조를 위한 SRAM의 초저지연성에 의존합니다. 반도체 업체들은 전력 예산을 관리하면서 더 큰 L2/L3 캐시를 지원하기 위해 2nm 공정에서 SRAM 셀 축소를 최우선 과제로 삼았습니다. 데이터센터 현대화는 스위치 및 가속기용 고속 버퍼 수요를 촉진한 반면, 소비자 기기 교체 주기는 안정적인 기준선을 유지했습니다. 2024년 대만 지진으로 파운드리 생산이 차질을 빚으면서 공급망 회복탄력성이 핵심 과제로 부상했으며, 이에 따라 지역 다각화 노력이 가속화되었습니다. 한편 MRAM과 같은 신흥 비휘발성 메모리는 배터리 지원 설계에서 기존 SRAM에 대한 경쟁 압박을 강화했습니다.
세계의 정적 RAM(SRAM) 시장 동향 및 인사이트
더 빠른 캐시 메모리에 대한 수요 증가
2025년 출시된 고급 CPU 및 GPU는 추론 지연 시간을 줄이기 위해 더 큰 온칩 캐시를 탑재했으며, 인텔 제온 6은 캐시 최적화와 연계된 1.4배 성능 향상을 보였다. TSMC의 2nm 플랫폼은 경쟁사 18A 노드보다 높은 SRAM 셀 밀도를 제공하여 하이퍼스케일 고객에게 와트당 더 많은 L3 캐시를 제공했습니다. 마벨은 6Gb의 저전력 메모리를 탑재한 2nm 맞춤형 SRAM을 공개했으며, 이는 기존 노드 대비 에너지 사용량을 66% 절감했습니다. 이러한 혁신으로 AI 가속기는 모델 매개변수를 컴퓨팅 유닛에 더 가깝게 유지할 수 있게 되어 처리량을 유지하면서 DRAM 트래픽을 억제할 수 있었습니다. 결과적으로 정적 랜덤 액세스 메모리 시장은 데이터센터 및 에지 실리콘 전반에 걸친 지속적인 용량 업그레이드의 혜택을 받았습니다.
데이터센터와 5G 네트워크 구축
클라우드 운영사들은 AI 서버 호스팅을 위해 랙 밀도를 두 배로 늘렸으며, 이로 인해 랙 상단 스위치에서 SRAM 기반 패킷 버퍼의 사용이 확대되었습니다. 마이크로소프트는 서버 홀에서 246-275GHz 무선 백플레인을 테스트했으며, 여기서는 마이크로초 단위의 버퍼링이 고속 SRAM에 의존했습니다. 시스코의 통합 5G 전송은 결정론적 지연 시간을 촉진하여 라우터에 깊은 SRAM 큐가 필요했습니다. 코닝은 AI 랙당 광섬유 수요가 18배 증가할 것으로 전망했는데, 이는 동기식 SRAM 기반 스위치 버퍼 확장과 유사한 추세다. 이러한 인프라 물결은 정적 랜덤 액세스 메모리 시장의 단기 매출 가시성을 강화했습니다.
DRAM/NAND 대비 높은 비트당 비용
SRAM은 일반 DRAM보다 비트당 비용이 몇 배 더 비싸서, 디자이너들이 대중 시장 기기에서 사용량을 줄이도록 압박했습니다. DDR4 모듈 가격은 2025년 상반기 약 50% 상승하며 메모리 스택 전반의 변동성을 보여주었다. 삼성은 공급 부족을 활용해 LPDDR4 가격을 인상했으나, 이 전략은 원자재 비용 절감을 위한 하이브리드 SRAM-DRAM 아키텍처에 대한 OEM 관심을 가속화할 위험이 있었다. 결과적으로 정적 랜덤 액세스 메모리 시장은 밀도 대 비용 균형이 개선될 때까지 저가형 소비자 부문에서 저항에 직면했습니다.
부문 분석
2024년 동기식 SRAM은 정적 랜덤 액세스 메모리 시장 점유율 58.4%를 차지하며 CPU, GPU, 네트워크 ASIC의 결정론적 캐시 운영에 필수적임을 입증했습니다. 자동차용 MCU는 운전자 지원 작업 부하에 대한 엄격한 실시간 요구 사항을 충족하기 위해 동기식 어레이를 사용했습니다. 고급 노드가 주파수 범위를 확장하고 코어 전압을 낮추면서 해당 부문는 주도권을 유지할 것입니다.
비동기식 SRAM은 연평균 6.4% 성장률을 기록하며 전력 예산이 지연 시간 목표보다 우선시되는 IoT 웨어러블 및 엣지 게이트웨이 분야에서 점유율을 확대했습니다. 에너지 효율적인 설계는 클록 트리를 제거하고 기판 레이아웃을 단순화하여, Syntiant의 신경 공프로세서를 채택한 배터리 구동 의료 기기에 큰 이점을 제공했습니다. 이러한 분화는 일률적인 성능 추구가 아닌 애플리케이션별 최적화를 지향하는 SRAM 시장 트렌드를 부각시켰습니다.
의사-SRAM(Pseudo-SRAM)은 SRAM 스타일 인터페이스 뒤에 DRAM 셀을 내장해 시스템 수준의 리프레시 관리 없이 높은 밀도를 달성하며 2024년 54.4% 점유율을 기록했습니다. RAAAM 메모리 테크놀로지스와 NXP는 기존 고밀도 SRAM 대비 면적 50%, 전력 10배 절감을 주장하며 대중 시장용 마이크로컨트롤러 시장에 어필했습니다.
비휘발성 SRAM은 공장 및 차량의 전압 강하 시 데이터 무결성 요구로 8.7% CAGR로 가장 빠르게 성장했습니다. 산업 자동화 업체들은 공정 변수 보호를 위해 nvSRAM 모듈을 선택하여 비용이 많이 드는 가동 중단을 방지했습니다. 비록 틈새 시장이지만, 이 그룹은 부가가치 내구성 기능으로 정적 랜덤 액세스 메모리 시장 환경을 풍부하게 했습니다.
지역 분석
아시아태평양은 2024년에 61.4%의 스태틱 RAM(SRAM) 시장 점유율을 유지해 대만 주조의 우위성, 한국의 메모리 혁신, 중국의 규모 확대 노력이 그 원동력이 됩니다. SK Hynix는 세계 DRAM 생산량의 36%를 차지할 때까지 성장하여 이 지역의 기술력의 높이를 부각시켰습니다. 그러나 2024년 대만 지진은 집중 위험을 드러내 일본과 싱가포르에 유사사를 위한 공장 건설을 촉구했습니다. 일본은 26년도 반도체 장치 매출을 5조 5,100억엔(383억 5,000만 달러)으로 예측해 생산 능력 증진의 지속을 강조하였습니다.
중동 및 아프리카 지역은 7.5%의 가장 빠른 연평균 성장률(CAGR)을 기록했으며, 걸프 지역을 삼대륙 데이터 허브로 자리매김하기 위한 국부펀드 지출이 이를 견인했습니다. 해당 지역의 창고 자동화 시장은 2025년까지 연간 17.5% 성장해 16억 달러 규모로 확대될 전망이며, 이는 신뢰성 있는 온보드 캐시 수요를 촉진할 것입니다. 아프리카 에너지 프로젝트는 2030년까지 신규 설비 투자로 7,300억 달러를 배정했으며, 결정론적 응답을 위해 SRAM에 의존하는 산업용 제어 시스템이 필요할 전망입니다.
북미는 AI 데이터센터 구축에 집중한 반면, 유럽은 430억 유로 규모의 칩스 법(Chips Act)을 통해 주권 확보에 박차를 가했습니다. ST마이크로전자는 이탈리아에 실리콘 카바이드 캠퍼스 건설을 위해 50억 유로(54억 달러)를 확보하며, 특수 SRAM을 소비하는 전력 전자 분야의 지역 역량을 확대했습니다. 그러나 인력 부족이 확장을 위협하는 가운데, ASML은 이민 정책이 강화될 경우 운영을 이전할 수 있다고 경고했습니다. 이러한 대비는 정적 랜덤 액세스 메모리 시장을 형성하는 다양한 지역적 요인을 부각시킵니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 고속 캐시 메모리에 대한 수요 증가
- 데이터센터와 5G 네트워크 구축
- IoT와 웨어러블 디바이스의 보급
- 칩릿용 3D 통합 SRAM
- LEO 위성용 내방사선 SRAM
- 인메모리 AI 가속기 채택
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- DRAM/NAND 대비 높은 비트당 비용
- 5nm 이하 노드에서의 전력 증가
- 신흥 비휘발성 메모리(MRAM/ReRAM)의 대체 효과
- 리소그래피의 변동에 의한 수율 저하
- 밸류체인 분석
- 규제 상황
- 기술적 전망
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 라이벌의 격렬함
- 거시경제 요인의 영향
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 기능별
- 비동기식 SRAM
- 동기식 SRAM
- 제품 유형별
- 의사-SRAM(PSRAM)
- 비휘발성 SRAM(nvSRAM)
- 기타 제품 유형
- 메모리 밀도별
- 8Mb 이하
- 8-64Mb
- 64-256Mb
- 256Mb 초과
- 최종 사용자별
- 소비자 가전
- 산업
- 통신 인프라
- 자동차 및 항공우주
- 기타 최종 사용자
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 이탈리아
- 러시아
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 한국
- 인도
- 대만
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 중동
- 튀르키예
- 이스라엘
- GCC 국가
- 기타 중동
- 아프리카
- 남아프리카
- 나이지리아
- 기타 아프리카 국가
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장의 집중
- 전략적인 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- GSI Technology Inc.
- Cypress Semiconductor Corp.(Infineon)
- Renesas Electronics Corp.
- Integrated Silicon Solution Inc.
- Alliance Memory Inc.
- Everspin Technologies Inc.
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- Toshiba Electronic Devices & Storage Corp.
- STMicroelectronics NV
- SK hynix Inc.
- Micron Technology Inc.
- Nanya Technology Corp.
- Winbond Electronics Corp.
- Elite Semiconductor Memory Technology Inc.
- Chiplus Semiconductor Corp.
- Powerchip Semiconductor Mfg. Corp.
- Puya Semiconductor Technology Co., Ltd.
- Lyontek Inc.
- ON Semiconductor Corporation
- Texas Instruments Incorporated
- Integrated Device Technology Inc.
- NXP Semiconductors NV
- Etron Technology Inc.
- Espressif Systems(Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
- SKYHigh Memory Ltd.
제7장 시장 기회와 전망
HBR 25.11.07The global Static Random Access Memory market size stood at USD 1.71 billion in 2025 and is forecast to advance at a 5.60% CAGR to reach USD 2.25 billion by 2030.
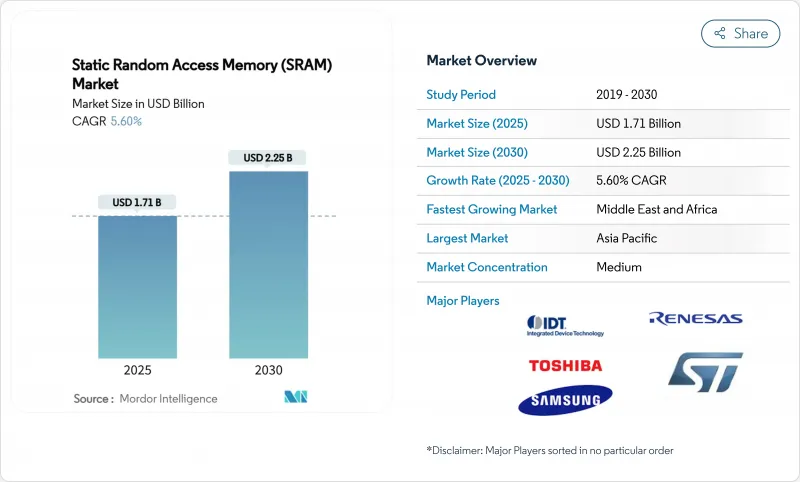
Growth reflected the transition toward AI-centric compute, 5G roll-outs, and real-time edge processing, all of which rely on SRAM's ultra-low latency for cache hierarchies. Semiconductor vendors prioritized shrinking SRAM cells at 2 nm to support larger L2/L3 caches while keeping power budgets in check. Data-center modernization drove demand for high-speed buffers in switches and accelerators, whereas consumer device refresh cycles maintained a steady baseline. Supply-chain resilience became pivotal after the 2024 Taiwan earthquake disrupted foundry output, prompting geographic diversification initiatives. Meanwhile, emerging non-volatile memories such as MRAM intensified competitive pressure on conventional SRAM in battery-backed designs.
Global Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) Market Trends and Insights
Rising demand for faster cache memories
Advanced CPUs and GPUs shipped in 2025 featured larger on-chip caches to cut inference latency, with Intel's Xeon 6 showing a 1.4X performance lift tied to cache optimization. TSMC's 2 nm platform delivered higher SRAM cell density than competing 18A nodes, giving hyperscale customers more L3 cache per watt. Marvell unveiled 2 nm custom SRAM that packs 6 Gb of low-power memory, reducing energy use by 66% versus prior nodes. Such innovations enabled AI accelerators to keep model parameters closer to compute units, sustaining throughput while containing DRAM traffic. Consequently, the Static Random Access Memory market benefited from recurring capacity upgrades across data-center and edge silicon.
Data-center and 5G network build-out
Cloud operators doubled rack densities to host AI servers, prompting wider use of SRAM-based packet buffers in top-of-rack switches. Microsoft tested 246-275 GHz wireless backplanes in server halls, where microsecond-scale buffering relied on high-speed SRAM. Cisco's converged 5G transport promoted deterministic latency, necessitating deep SRAM queues in routers. Corning forecasts an 18X jump in fiber demand per AI rack, mirroring the scaling of switch buffers built on synchronous SRAM. This infrastructure wave reinforced near-term revenue visibility for the Static Random Access Memory market.
High cost per bit vs. DRAM/NAND
SRAM remained several times more expensive per bit than commodity DRAM, pressuring designers to trim usage in mass-market gadgets. DDR4 module prices climbed roughly 50% in H1 2025, illustrating volatility across the memory stack. Samsung leveraged tightening supply to lift LPDDR4 pricing, but that tactic risked accelerating OEM interest in hybrid SRAM-DRAM architectures to curb bills of materials. Consequently, the Static Random Access Memory market faced pushback in entry-level consumer segments until density-versus-cost trade-offs improved.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- IoT and wearable device proliferation
- In-memory AI accelerators adoption
- Emerging NVM (MRAM/ReRAM) displacement
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Synchronous SRAM captured 58.4% Static Random Access Memory market share in 2024, underscoring its indispensability for deterministic cache operation in CPUs, GPUs, and network ASICs. Automotive MCUs used synchronous arrays to meet stringent real-time requirements for driver-assistance workloads. The segment will maintain leadership as advanced nodes extend frequency envelopes and reduce core voltages.
Asynchronous SRAM expanded at a 6.4% CAGR and increasingly served IoT wearables and edge gateways where power budgets override latency targets. Energy-efficient designs eliminated clock trees and simplified board layouts, a boon for battery-operated healthcare devices employing Syntiant's neural coprocessors. This divergence emphasized the Static Random Access Memory market trend toward application-specific optimization rather than one-size-fits-all performance chasing.
Pseudo-SRAM held a 54.4% share in 2024 by embedding DRAM cells behind an SRAM-style interface, achieving higher density without refresh management at the system level. RAAAM Memory Technologies and NXP claimed 50% area and 10X power savings versus classic high-density SRAM, appealing to mass-market microcontrollers.
Non-volatile SRAM grew fastest at 8.7% CAGR as factories and vehicles demanded data integrity during brownouts. Industrial automation players selected nvSRAM modules to protect process variables, avoiding costly downtime. Although niche, this cohort enriched the Static Random Access Memory market landscape with value-added resilience features.
Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) Market is Segmented by Function (Asynchronous SRAM, and Synchronous SRAM), Product Type (Pseudo SRAM, Non-Volatile SRAM, and Other Product Types), Memory Density (<=8 Mb, 8-64 Mb, 64-256 Mb, and >256 Mb), End User (Consumer Electronics, Industrial, Communication Infrastructure, and More), and Geography (North America, South America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Middle East and Africa).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific retained 61.4% Static Random Access Memory market share in 2024, fueled by Taiwan's foundry dominance, South Korea's memory innovation, and China's scale-up efforts. SK Hynix's rise to 36% of global DRAM output highlighted the region's technology depth. Yet the 2024 Taiwan quake exposed concentration risk, prompting contingency fabs in Japan and Singapore. Japan projected semiconductor equipment sales of JPY 5.51 trillion (USD 38.35 billion) in FY26, underscoring continued capacity build-out.
Middle East and Africa charted the fastest 7.5% CAGR, anchored by sovereign-fund spending to position the Gulf as a tri-continent data hub. Warehouse automation in the region was set for 17.5% annual growth to USD 1.6 billion by 2025, driving demand for reliable on-board caches. Africa's energy projects earmarked USD 730 billion in new capex to 2030, requiring industrial control systems that lean on SRAM for deterministic response.
North America focused on AI datacenter roll-outs, while Europe doubled down on sovereignty through the EUR 43 billion Chips Act. STMicroelectronics secured EUR 5 billion (USD 5.4 billion) for a Silicon Carbide campus in Italy, widening regional competency in power electronics that also consume specialized SRAM. Talent shortages, however, threatened expansion, with ASML warning it might shift operations if immigration tightened. These contrasts highlight diverse regional levers shaping the Static Random Access Memory market.
- GSI Technology Inc.
- Cypress Semiconductor Corp. (Infineon)
- Renesas Electronics Corp.
- Integrated Silicon Solution Inc.
- Alliance Memory Inc.
- Everspin Technologies Inc.
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- Toshiba Electronic Devices & Storage Corp.
- STMicroelectronics N.V.
- SK hynix Inc.
- Micron Technology Inc.
- Nanya Technology Corp.
- Winbond Electronics Corp.
- Elite Semiconductor Memory Technology Inc.
- Chiplus Semiconductor Corp.
- Powerchip Semiconductor Mfg. Corp.
- Puya Semiconductor Technology Co., Ltd.
- Lyontek Inc.
- ON Semiconductor Corporation
- Texas Instruments Incorporated
- Integrated Device Technology Inc.
- NXP Semiconductors N.V.
- Etron Technology Inc.
- Espressif Systems (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
- SKYHigh Memory Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising demand for faster cache memories
- 4.2.2 Data-center and 5G network build-out
- 4.2.3 IoT and wearable device proliferation
- 4.2.4 3D-integrated SRAM for chiplets
- 4.2.5 Radiation-hardened SRAM for LEO satellites
- 4.2.6 In-memory AI accelerators adoption
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High cost per bit vs. DRAM/NAND
- 4.3.2 Escalating power at <=5 nm nodes
- 4.3.3 Emerging NVM (MRAM/ReRAM) displacement
- 4.3.4 Yield loss from lithography variability
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Rivalry
- 4.8 Impact of Macroeconomic Factors
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Function
- 5.1.1 Asynchronous SRAM
- 5.1.2 Synchronous SRAM
- 5.2 By Product Type
- 5.2.1 Pseudo SRAM (PSRAM)
- 5.2.2 Non-Volatile SRAM (nvSRAM)
- 5.2.3 Other Product Types
- 5.3 By Memory Density
- 5.3.1 <=8 Mb
- 5.3.2 8 - 64 Mb
- 5.3.3 64 - 256 Mb
- 5.3.4 >256 Mb
- 5.4 By End User
- 5.4.1 Consumer Electronics
- 5.4.2 Industrial
- 5.4.3 Communication Infrastructure
- 5.4.4 Automotive and Aerospace
- 5.4.5 Other End Users
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Russia
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 Japan
- 5.5.4.3 South Korea
- 5.5.4.4 India
- 5.5.4.5 Taiwan
- 5.5.4.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 Turkey
- 5.5.5.1.2 Israel
- 5.5.5.1.3 GCC Countries
- 5.5.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Nigeria
- 5.5.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 GSI Technology Inc.
- 6.4.2 Cypress Semiconductor Corp. (Infineon)
- 6.4.3 Renesas Electronics Corp.
- 6.4.4 Integrated Silicon Solution Inc.
- 6.4.5 Alliance Memory Inc.
- 6.4.6 Everspin Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.7 Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.8 Toshiba Electronic Devices & Storage Corp.
- 6.4.9 STMicroelectronics N.V.
- 6.4.10 SK hynix Inc.
- 6.4.11 Micron Technology Inc.
- 6.4.12 Nanya Technology Corp.
- 6.4.13 Winbond Electronics Corp.
- 6.4.14 Elite Semiconductor Memory Technology Inc.
- 6.4.15 Chiplus Semiconductor Corp.
- 6.4.16 Powerchip Semiconductor Mfg. Corp.
- 6.4.17 Puya Semiconductor Technology Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.18 Lyontek Inc.
- 6.4.19 ON Semiconductor Corporation
- 6.4.20 Texas Instruments Incorporated
- 6.4.21 Integrated Device Technology Inc.
- 6.4.22 NXP Semiconductors N.V.
- 6.4.23 Etron Technology Inc.
- 6.4.24 Espressif Systems (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.25 SKYHigh Memory Ltd.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment



















