
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1683907
중동 및 유럽의 택배, 특송, 소포(CEP) : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Central and Eastern Europe Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
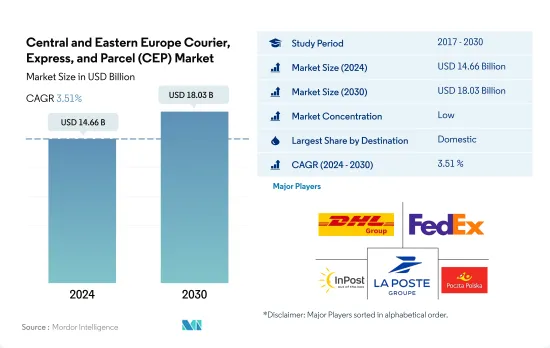
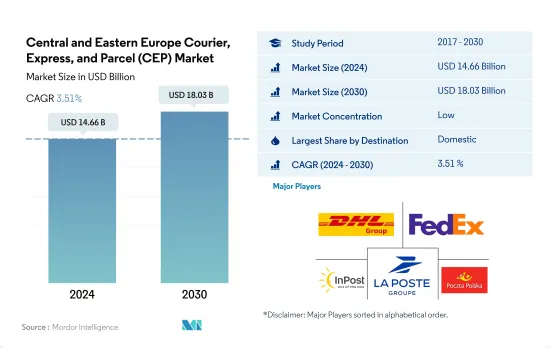
중동 및 유럽의 택배, 특송, 소포(CEP) 시장 규모는 2024년에 146억 6,000만 달러에 달했습니다. 2030년에는 180억 3,000만 달러에 이르고, 예측 기간 중(2024-2030년) CAGR은 3.51%를 나타낼 것으로 예측됩니다.
서비스 확대, 요금 인하, 전자상거래 이용 확대로 CEP 분야는 동지역에서 개발 중
- 2022년 헝가리의 CEP 사업자는 이 분야의 개발에 나섰습니다. 예를 들어, 헝가리 사업자인 Magyar Posta는 2022년 Leonardo의 새로운 분류 시스템을 도입하여 물류 능력을 강화했습니다. Leonardo는 소포 및 소포 자동화 솔루션의 선도적인 공급업체입니다. 2023년 공급된 이 시스템은 국내 및 국제 소포를 처리하도록 설계되었으며 연간 최대 1억 개의 소포를 처리할 수 있습니다. 또한 헝가리에 본사를 둔 FoxPost는 헝가리에서 20,000개 기업에 서비스를 제공하며 헝가리 국내에 2500개의 소포 로커를 보유하고 있습니다.
- 유럽의 주요 온라인 패션, 라이프 스타일 플랫폼인 Zalando는 2021년체코의 물류 및 기술 회사 Zasilkovna와 제휴했습니다. 이 움직임은 체코 4명 중 1명이 수령 장소를 선택하고 소포 로커에서 수취를 선호하는 경향이 3년간 0%에서 6%로 상승했다는 체코 고객의 선호도 변화에 대응하는 것입니다. 이 파트너십을 통해 Zalando 고객은 1,500개 Zasilkovna 사물함과 4,700개 픽업 포인트를 이용할 수 있으며, 결제 방법 중 하나로 대금 상환을 선택할 수 있습니다. 그 목적은 체코 고객의 취향에 대응하고 체코 고객에게 편리함을 제공하는 것입니다. 또한 우크라이나의 주요 우편 사업자인 노바 포슈타는 2022년 폴란드에 개인 물품을 보낼 때 관세를 2.5배로 낮추었는데, 이는 전쟁의 영향으로 폴란드에 머무르는 우크라이나인의 수가 증가했기 때문입니다.
- 전자상거래는 이 지역에서 CEP 수요의 주요 추진력입니다. 예를 들어 슬로바키아 온라인 소비자의 85.07%는 2022년에 온라인으로 구매할 가능성이 가장 높았습니다. 루마니아와 불가리아의 인터넷 사용자 점유율은 2022년 각각 51.46%와 48.78%에 달했습니다. 슬로바키아에서는 2027년까지 전자상거래 이용자의 보급률이 318만 명에 달할 것으로 추정되기 때문에 CEP 수요도 이 지역에서 증가할 것으로 예측됩니다.
CEE 지역의 전자상거래 시장은 2022년에 346억 3,000만 달러에 이르렀고 CEP 배송 수요를 창출했습니다.
- CEE 지역의 전자상거래 시장은 2022년에 346억 3,000만 달러에 이르렀으며, 패션 분야가 31.68%, 전자 분야가 28.10%로 수익 점유율을 이끌었습니다. 2022년에는 폴란드(278억 달러)의 전자상거래 점유율이 이 지역에서 가장 높았고 체코(130억 달러)가 그 다음을 이었습니다. 2022년에는 슬로바키아 주민(85%)이 CEE 국가에서 가장 온라인 쇼핑을 이용할 가능성이 높았습니다. 슬로바키아 사람들이 온라인으로 쇼핑하는 비율은 2022년 EU 평균에 비해 10% 높았습니다. 체코, 헝가리, 에스토니아는 EU27개국 중 전자상거래 이용률이 평균 이상으로 평가되었습니다.
- 폴란드는 또한 이 지역에서 국내 및 국제 익스프레스 딜리버리 서비스를 제공하는 국가입니다. 국영 우편 서비스인 Poczta Polska는 속달 우편 서비스(EMS)를 통해 이러한 서비스를 제공합니다. Poczta Polska는 170여 개국에 EMS를 통한 도어 투 도어 국제 익스프레스 배송을 제공합니다. 국내 및 국제화물의 최대 중량은 20kg입니다. 체코 공화국과 슬로바키아는 가깝기 때문에 국영 우편은 체코 공화국과 슬로바키아에 배달되는 EMS화물의 요금을 특별히 저렴합니다.
- 수요가 증가함에 따라 루마니아는 이 지역에서 국내 및 국제 익스프레스 배송 서비스를 제공하는 국가 중 하나가 되었습니다. 루마니아의 국영 우편인 루마니아 우편은 EMS를 통해 이 서비스를 제공합니다. 국내 배송의 무게 제한은 일반 소포에서 15km, 보이지 않는 내용물로 20kg입니다. 국제 스피드 우편은 루마니아에서 약 105개국으로의 국제 배송을 지원합니다. 국제 택배는 루마니아에서 약 105개국으로 배송이 가능하며 배송 시 최대 중량은 31.5kg입니다.
중동 및 유럽의 택배, 특송, 소포(CEP) 시장 동향
알바니아는 세계적 과제 중 성장 둔화에 직면하면서 불가리아, 체코, 폴란드는 임팩트의 큰 인프라 투자를 강화
- 세계은행은 알바니아의 2023년 경제 성장률을 불과 2.2%로 예측했습니다. 우크라이나 전쟁과 에너지 위기의 심각화, 유로존의 경기침체를 일으켜 운송비용이 상승할 수 있기 때문에 알바니아의 경제 성장은 2024년에 더욱 약해질 가능성이 있었습니다. 그러나 불가리아는 불가리아의 부흥 강인화 계획(RRP)에 할당된 15억 달러와 더불어 11억 달러와 4억 3,100만 달러를 국가 기금에서 기부하고 3개 프로젝트에 투자했습니다. 여기에는 2026년까지 루세 교외에 완성될 예정인 지역간 허브 건설이 포함됩니다.
- 2023년 체코 공화국은 100km 이상의 고속도로와 18km의 i급 도로 건설 계획을 포함하여 최대 118km의 새로운 고속도로를 개통할 예정이었습니다. 이 전략은 교통 체증 완화, 이동 시간 단축, 교통 안전 향상을 기대합니다. 또한 고속도로와 도로건설 프로젝트는 새로운 고용을 창출하고 국가 경제 성장을 뒷받침하는 등 큰 경제 효과를 가져올 수 있습니다. 교통 인프라가 개선되면 접근성과 연결성도 향상되어 기업이 국가를 통해 상품과 서비스를 쉽게 이동할 수 있습니다.
- 폴란드 정부는 철도 인프라에 175억 달러, 도로 인프라에 366억 달러의 투자를 계획하고 있습니다. 국도·자동차도 총국(GDDKiA), 폴란드 철도 PKP SA, 폴란드 철도 네트워크(PKP-PLK), 경제 개발·기술성, 인프라스트럭처성 등의 주요 조직이 전국 또는 특정 지역에 걸친 프로젝트를 담당하고 있습니다.
불가리아 유틸리티규제 당국 승인 후 가스요금은 세금 제외로 30.7% 인하
- 헝가리는 에너지 가격을 낮게 유지하기 위한 가격 규제책을 실시해, 그 결과 유럽에서 가장 저렴한 가스·전기 요금의 하나가 되고 있습니다. 헝가리의 가스 요금은 연간 1,729 입방 미터까지 약 0.25 유로(0.26 USD)의 할인 단가로 구입할 수 있습니다. 한편, 유로존에서 가장 인플레이션이 높은 에스토니아는 에너지 비용 상승에 어려움을 겪고 있으며, 정부는 2024년 4월까지 전력과 연료 물품세를 동결해 연료에 대한 감세 등 다른 대책을 검토함으로써 가계에 미치는 영향을 완화할 계획입니다.
- 2021년 천연가스 가격은 2020년부터 49.41% 상승했습니다. 러시아·우크라이나 전쟁의 영향으로 천연가스 가격은 약 7배, 석탄가격은 약 4배로 상승하여 에너지 정세가 불안정해졌고, 특히 에스토니아, 리투아니아, 라트비아의 발트 3국에서는 소비자 물가의 인플레이션이 진행되었습니다. 2023년 6월에는 에스토니아가 리터당 미화 1.84달러와 중동 및 유럽 국가 중 가장 높은 가솔린 가격을 기록했으며 알바니아는 리터당 미화 1.79달러로 이어졌습니다.
- 2023년 불가리아 유틸리티 규제당국은 2월 규제가스 가격의 30.7% 인하를 승인했으며, 그 결과 신가격은 1MWh당 124.34BGN(67.8달러)이 되었습니다(운송비, 물품세, 부가가치세 제외). 이번 가격 인하는 유럽의 온난한 기후와 충분한 가스 저장량을 배경으로 국제 가스 시장의 가격이 하락한 것에 따릅니다. 이 가격 인하는 많은 소비자에게 혜택을 줄 것으로 예상되었으며, 규제 당국은 겨울 난방 시즌의 나머지 기간 동안 중앙 난방 가격을 유지하기로 결정했습니다.
중동 및 유럽의 택배, 특송, 소포(CEP) 산업 개요
중동 및 유럽의 택배, 특송, 소포(CEP) 시장은 단편화되어 상위 5개사에서 31.80%를 차지하고 있습니다. 이 시장 주요 기업은 다음과 같습니다. DHL Group, FedEx, InPost, La Poste Group and Poczta Polska SA(알파벳순 정렬).
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 애널리스트에 의한 3개월간의 지원
목차
제1장 주요 요약과 주요 조사 결과
제2장 보고서 제안
제3장 소개
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
- 조사 방법
제4장 주요 산업 동향
- 인구동태
- 경제 활동별 GDP 분포
- 경제 활동별 GDP 성장률
- 인플레이션율
- 경제성과 및 프로파일
- 전자상거래 산업의 동향
- 제조업의 동향
- 운수·창고업의 GDP
- 수출 동향
- 수입 동향
- 연료 가격
- 물류 실적
- 인프라
- 규제 프레임워크
- 중동 및 유럽(CEE)
- 밸류체인과 유통채널 분석
제5장 시장 세분화
- 목적지
- 국내
- 국제
- 배송 속도
- 특급 배송
- 비특급 배송
- 모델
- 기업 대 기업(B2B)
- 기업 대 소비자(B2C)
- 소비자 대 소비자(C2C)
- 배송 중량
- 중량 배송
- 경량 배송
- 중간 중량 배송
- 수송 형태
- 항공편
- 도로
- 기타
- 최종 사용자
- 전자상거래
- 금융 서비스(BFSI)
- 헬스케어
- 제조업
- 제1차 산업
- 도매·소매업(오프라인)
- 기타
- 국가명
- 알바니아
- 불가리아
- 크로아티아
- 체코 공화국
- 에스토니아
- 헝가리
- 라트비아
- 리투아니아
- 폴란드
- 루마니아
- 슬로바키아 공화국
- 슬로베니아
- 기타 CEE
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 주요 전략적 움직임
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 상황
- 기업 프로파일
- CARGUS SRL
- DHL Group
- Fan Courier
- FedEx
- InPost
- International Distributions Services(including GLS)
- La Poste Group
- Poczta Polska SA
- Posta Romana SA
제7장 CEO에 대한 주요 전략적 질문
제8장 부록
- 세계 개요
- 개요
- Five Forces 분석 프레임워크
- 세계의 밸류체인 분석
- 시장 역학(DROs)
- 기술의 진보
- 정보원과 참고문헌
- 도표 목록
- 주요 인사이트
- 데이터 팩
- 용어집
The Central and Eastern Europe Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Market size is estimated at 14.66 billion USD in 2024, and is expected to reach 18.03 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 3.51% during the forecast period (2024-2030).
Developing CEP segment in the region owing to services expansion, reducing tariffs, and growing e-commerce usage
- In 2022, CEP players in Hungary have taken the initiative to develop the segment. For instance, Hungarian operator Magyar Posta increased its distribution capacity with Leonardo's new sorting system in 2022. Leonardo is a major provider of automated solutions for small packets and parcels. The system, which would be supplied during 2023, is designed to process domestic and international parcels, wherein it could potentially process up to 100 million parcels a year. Also, Hungary-based FoxPost serves 20,000 businesses in Hungary, with 2,500 parcel lockers in Hungary.
- Zalando, Europe's leading online fashion and lifestyle platform, partnered with local logistics and technology Czech company Zasilkovna in 2021. The move responds to the shift in preferences of Czech customers wherein 1 in 4 Czechs chose pick-up points, and the preference for pick-up via parcel lockers rose from 0% to 6% in 3 years. Through the partnership, Zalando customers can use 1,500 Zasilkovna lockers and 4,700 pick-up points, with cash on delivery as one of the payment options. The aim is to cater to local customer preferences and provide convenience to Czech customers. Also, Nova Poshta, a major Ukrainian postal carrier, made a 2.5-fold reduction in tariffs for sending personal items to Poland in 2022, and this was done owing to the rise in the number of Ukrainians in Poland due to the war.
- E-commerce is a major driver for CEP demand in the region. For instance, 85.07% of online consumers in Slovakia were most likely to make purchases online in 2022. Share of internet users in Romania and Bulgaria stood at 51.46% and 48.78%, respectively, in 2022. With e-commerce user penetration to touch 3.18 million by 2027 in Slovakia, the demand for CEP is also projected to rise in the region.
E-commerce market in the CEE region hit USD 34.63 billion in 2022 generating the demand for CEP deliveries
- The e-commerce market in the CEE region reached a value of USD 34.63 billion in 2022, with the fashion and electronics segments leading the revenue shares with 31.68% and 28.10%, respectively. In 2022, Poland (USD 27.80 billion) had the highest e-commerce share in the region, followed by Czechia (USD 13 billion). In 2022, residents of Slovakia (85%) were the most likely to shop online in CEE countries. The percentage of people in Slovakia shopping online was 10% higher compared to the EU average in 2022. Czechia, Hungary, and Estonia were rated above average for using e-commerce among the 27 EU countries.
- Poland is another country in the region providing domestic and international express delivery services. Poczta Polska, the national postal service, provides these services via express mail service (EMS). Poczta Polska facilitates door-to-door international express deliveries via EMS to over 170 countries. The maximum weight of shipments of domestic and international goods is 20 kg. The national postal service has special lowered rates for EMS shipments being delivered to the Czech Republic and Slovakia due to their proximity.
- Due to increased demand, Romania is one of the countries in the region providing domestic and international express delivery services. The Romanian Post, the national postal service, provides this service via its EMS. The domestic delivery weight limit is 15 kg for ordinary parcels and 20 kg for invisible contents. The express delivery service can cater to international deliveries to about 105 countries from Romania. The maximum weight of parcels for these shipments at the time of posting and delivery should be 31.5 kg.
Central and Eastern Europe Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Market Trends
Albania faces slower growth amid global challenges, while Bulgaria, Czech Republic, and Poland ramp up high-impact infrastructure investments
- The World Bank predicts that Albania's economy will grow by only 2.2% in 2023. Albania's economic growth may be even weaker in 2024 due to the war in Ukraine and the energy crisis deepening and causing an economic downturn in the eurozone, which may increase transportation costs. However, Bulgaria invested in three projects with USD 1.5 billion allocated to Bulgaria's Recovery and Resilience Plan (RRP), along with USD 1.1 billion and USD 431 million from National Funding. This includes the construction of an intermodular regional hub outside of Rousse, which is expected to be finished by 2026.
- In 2023, the Czech Republic was expected to open up to 118 km of new highway stretches, including a plan to build over 100 km of highway and 18 km of Class I road. This strategy is expected to reduce traffic congestion, reduce travel time, and improve road safety. The highway and road construction projects may also have a significant economic impact, creating new jobs and boosting the country's economic growth. Improved transportation infrastructure may also enhance accessibility and connectivity, making it easier for businesses to move goods and services across the country.
- The Polish government plans to invest USD 17.5 billion in railway infrastructure and USD 36.6 billion in road infrastructure. The key organizations, such as the General Directorate of National Roads and Motorways (GDDKiA), Polish Railway PKP SA, Polish Railway Networks (PKP-PLK), and the Ministry of Economic Development and Technology and the Ministry of Infrastructure, are taking charge of projects spanning across the nation or specific regions.
Post approval from Bulgaria's utilities regulator, gas prices reduced by 30.7%, excluding taxes
- Hungary has implemented price regulation measures to keep energy prices low, resulting in one of the lowest gas and electricity prices in Europe. Gas prices in Hungary are available at a reduced unit price of approximately EUR 0.25 (USD 0.26) for up to 1,729 cubic meters per year. On the other hand, Estonia, which has the highest inflation rate in the Eurozone, struggles with rising energy costs, and the government plans to alleviate the impact on households by freezing excise duty on electricity and fuel until April 2024 and considering other measures, such as reducing taxes on fuels.
- In 2021, the price of natural gas increased by 49.41%, up from 2020. The price of natural gas increased by almost seven times, and coal prices quadrupled due to the Russian-Ukraine War, leading to an unstable energy situation and increased consumer price inflation, particularly in the Baltic countries of Estonia, Lithuania, and Latvia. In June 2023, Estonia recorded the highest gasoline prices among Central and Eastern European countries, at 1.84 USD per liter, followed by Albania at 1.79 USD/liter.
- In 2023, Bulgaria's utilities regulator gave its approval for a reduction of 30.7% in the regulated gas price for February, resulting in a new price of BGN 124.34 (USD 67.8) per MWh (excluding transportation costs, excise, and value-added tax). The price reduction is attributed to the lower prices in international gas markets, owing to warm weather and sufficient gas storage in Europe. This price reduction is expected to benefit significant consumers, and the regulator has decided to maintain central heating prices for the rest of the winter heating season.
Central and Eastern Europe Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Industry Overview
The Central and Eastern Europe Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Market is fragmented, with the top five companies occupying 31.80%. The major players in this market are DHL Group, FedEx, InPost, La Poste Group and Poczta Polska SA (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Demographics
- 4.2 GDP Distribution By Economic Activity
- 4.3 GDP Growth By Economic Activity
- 4.4 Inflation
- 4.5 Economic Performance And Profile
- 4.5.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.5.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.6 Transport And Storage Sector GDP
- 4.7 Export Trends
- 4.8 Import Trends
- 4.9 Fuel Price
- 4.10 Logistics Performance
- 4.11 Infrastructure
- 4.12 Regulatory Framework
- 4.12.1 Central and Eastern Europe (CEE)
- 4.13 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes Market Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Destination
- 5.1.1 Domestic
- 5.1.2 International
- 5.2 Speed Of Delivery
- 5.2.1 Express
- 5.2.2 Non-Express
- 5.3 Model
- 5.3.1 Business-to-Business (B2B)
- 5.3.2 Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
- 5.3.3 Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
- 5.4 Shipment Weight
- 5.4.1 Heavy Weight Shipments
- 5.4.2 Light Weight Shipments
- 5.4.3 Medium Weight Shipments
- 5.5 Mode Of Transport
- 5.5.1 Air
- 5.5.2 Road
- 5.5.3 Others
- 5.6 End User Industry
- 5.6.1 E-Commerce
- 5.6.2 Financial Services (BFSI)
- 5.6.3 Healthcare
- 5.6.4 Manufacturing
- 5.6.5 Primary Industry
- 5.6.6 Wholesale and Retail Trade (Offline)
- 5.6.7 Others
- 5.7 Country
- 5.7.1 Albania
- 5.7.2 Bulgaria
- 5.7.3 Croatia
- 5.7.4 Czech Republic
- 5.7.5 Estonia
- 5.7.6 Hungary
- 5.7.7 Latvia
- 5.7.8 Lithuania
- 5.7.9 Poland
- 5.7.10 Romania
- 5.7.11 Slovak Republic
- 5.7.12 Slovenia
- 5.7.13 Rest of CEE
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles
- 6.4.1 CARGUS SRL
- 6.4.2 DHL Group
- 6.4.3 Fan Courier
- 6.4.4 FedEx
- 6.4.5 InPost
- 6.4.6 International Distributions Services (including GLS)
- 6.4.7 La Poste Group
- 6.4.8 Poczta Polska SA
- 6.4.9 Posta Romana SA
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR CEP CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.1.5 Technological Advancements
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms



















