
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1852016
인도의 농업 기계 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)India Agricultural Machinery - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
인도의 농업 기계 시장 규모는 2025년에 181억 5,000만 달러로 추정되고, 예측 기간 중 CAGR 8.5%로 성장할 전망이며, 2030년에는 272억 9,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예측됩니다.

공공 부문의 강력한 인센티브, 농촌의 노동력 부족 지속, 급속한 디지털화가 전국적인 기기 도입을 가속시키는 요인이 되고 있습니다. 농업 기계화에 관한 제출(SMAM)에 근거한 보조금은 트랙터, 관개 시스템, 정밀기계의 초기 비용을 낮추는 반면, 특주고용센터는 영세 농가에 대한 접근을 확대합니다. 도시로의 이주가 증가하고 농업 작업에 사용할 수 있는 노동력이 감소하고 있기 때문에 생산자는 적시 심기 및 수확 작업을 유지할 수 있는 기계화 솔루션으로 향하고 있습니다. 이와 병행하여 디지털 농업 미션(Digital Agriculture Mission)은 농가 등록 및 지오태그 작물 데이터베이스를 구축하여 정밀 장비의 배치와 데이터 중심의 대출을 지원합니다. 배출가스 규제와 낮은 배출가스 트랙터에 대한 새로운 우대조치가 보다 깨끗한 파워트레인에 대한 투자에 박차를 가하고 전기 및 하이브리드 모델을 신흥이지만 전략적 성장 포켓으로 자리매김합니다. 경쟁업체 간 적대 관계는 격화되어 상위 5개사의 벤더가 81.5%의 점유율을 차지하며, 미드파워 트랙터와 스마트 인플루먼트를 향한 신제품 출시와 생산 능력의 확장을 촉진하고 있습니다.
인도의 농업 기계 시장 동향 및 인사이트
기계화 도입을 뒷받침하는 정부 제도
SMAM의 정책 개입은 개별 기계 구매에 대해 40%-50%, 맞춤형 고용 센터에 대해 최대 80%의 보조금을 지급합니다. 우타르 프라데시 주에서도 SMAM은 2014-2024년 656억 6,000만 루피(7억 9,000만 달러)를 지출하였고, 17만 6,000대의 기계를 배포하였으며, 10,769의 주문 센터를 설립했습니다. 크산 드론 보조금과 국가 식량 안보 미션의 작물별 지원 등 보완적인 이니셔티브는 고정밀 기구 수요를 더욱 확대합니다. 이러한 프로그램은 초기 비용을 최소화할 뿐만 아니라 판매 후 네트워크를 강화함으로써 다양한 농업 기후대에서 지속적인 기계화를 촉진합니다.
도시 지역으로의 지속적인 이주로 인한 농촌 지역의 노동력 부족
가계 조사 데이터에 따르면 농업에 종사하는 주요 소득자는 9%에 불과하며 50%가 넘는 역사적인 수준에서 떨어졌습니다. 계절적 이익은 모내기와 수확 시기에 피크를 맞아 노동력 부족이 심각화되지만, 기계화가 적시에 경작, 파종, 수확을 실시함으로써 이것을 보충할 수 있습니다. 콤바인 수확기는 노동력을 최대 30% 삭감하고 포스트하베스트 로스를 2-4포인트 삭감합니다. 특주센터를 통해 기계를 공유함으로써 노동력이 부족한 지구에서 작부 집약도를 유지하기 위해 부족한 기계를 더욱 활용할 수 있습니다.
높은 장비 비용 및 제한된 신용 액세스
두꺼운 보조금에도 불구하고 중마력 트랙터 1대에는 60만 루피(7,200달러)를 넘는 지출이 필요하며, 많은 영세 농가에게는 손이 닿지 않는 금액입니다. 정식 금융기관은 담보를 요구하는 경우가 많고, 금리 스프레드는 프라임 론보다 200-300 베이시스 포인트 높게 남아 있기 때문에 대규모 투자를 생각하고 머물고 있습니다. 특주고용센터는 비용면의 장애물을 완화하고 있지만, 그 분포는 편향되어 있으며, 인도 동부에서는 1지구당 12센터 미만인 반면 북부에서는 45센터 이상이며 지역간 격차를 조장하고 있습니다.
부문 분석
트랙터는 2024년 매출 점유율 40.5%를 유지했으며, 다양한 제작 체계에서의 경운 및 운반의 기초적인 역할을 명확히 했습니다. 관개 기계는 마이크로 관개 펌프와 드립 시스템이 CAGR 10.5%로 가장 빠르게 성장하는 부문이며, 가뭄 완화 프로그램과 정밀 급수를 지지하는 전기 요금의 상승에 추진되고 있습니다. 쟁기, 후광 및 로토베이터를 포함한 장비 부문은 영세 농가에서 기계화를 추진함으로써 혜택을 받으며, 이러한 기구는 트랙터보다 낮은 자본 투자로 끝나는 입문 수준의 기계화 솔루션을 제공합니다. 수확기계는 바쁜 기간 동안 노동력 부족이 심각해짐에 따라 꾸준한 성장을 이루고 있으며, 콤바인 수확기 및 폴리지 수확기는 상업적 농업 경영에서 작물을 적시에 수집하는 데 필수적입니다.
전 지구 항법 위성 시스템과 종래의 기구를 융합시키는 어댑터는 종래의 트랙터를, 직진 경기와 종자 배치를 -2.5cm 이내의 정밀도로 실행해, 투입의 낭비를 6%-8% 삭감하는 스마트 머신으로 바꾸고 있습니다. 전동 어시스트 로터베타와 배터리 구동 과수원 분무기는 저소음과 제로 방출이 중시되는 과수 재배 농가들 사이에서 인기를 끌고 있습니다. 인도의 농업기계 시장은 베일러, 잔디깎기, 말처가 야외 야키하타의 억제를 목적으로 하는 잔사 관리 방식으로 관련성을 늘리고 다양화가 계속되고 있습니다. 시장 리더는 모듈형 어태치먼트 에코시스템으로 대응하고, 1대의 트랙터 섀시로 20개 이상의 작업 지향 인플루먼트를 지원할 수 있게 함으로써 소유 비용을 여러 수익원에 분산시키고 있습니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건 및 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 기계화의 도입을 뒷받침하는 정부 계획
- 도시로의 지속적인 이주에 의한 농촌의 노동력 부족
- FPO 및 계약 재배의 집적
- 대출을 가능하게 하는 디지털 크레딧 플랫폼
- 보급을 가속하는 전기 기기 인센티브
- 기계화 재배에 유리한 기후보험
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 높은 장비 비용 및 제한된 신용 접근
- 세분화된 토지 보유가 스케일 효율 제한
- 배출 규제는 주마다 상이
- 숙련된 텔레매틱스 기술자의 부족
- 규제 상황
- 기술의 전망
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 구매자의 협상력
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업 간 경쟁 관계
제5장 시장 규모 및 성장 예측
- 유형별
- 트랙터
- 50 HP 미만
- 50-75 HP
- 76-100 HP
- 101-150 HP
- 150 HP 이상
- 기기
- 경운기
- 헬로
- 로토베이터 및 경운기
- 종자 및 비료용 드릴
- 기타 기기(포스트홀 디거, 파워 제초기 등)
- 관개 기계
- 스프링클러 관개
- 점적 관개
- 기타 관개 기계(센터 피벗 시스템, 마이크로 스프링클러 등)
- 수확 기계
- 콤바인 수확기
- 폴리지 수확기
- 기타 수확기(사탕수수 수확기, 감자 수확기 등)
- 건초 및 목장용 기계
- 잔디깎기 기계 및 컨디셔너
- 베일러
- 기타 건초 및 메이플용 기계(테더, 레이크 등)
- 트랙터
- 최종 사용자 농장 규모별
- 소규모 농가(5헥타르 미만)
- 중규모 농장(5-20 ha)
- 대규모 농장(20헥타르 이상)
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd
- TAFE Motors and Tractors Limited
- Deere & Company
- CNH Industrial NV
- International Tractors Limited(Sonalika)
- Escorts Kubota Limited
- VST Tillers Tractors Ltd.
- AGCO Corporation
- CLAAS KGaA mbH
- Yanmar Holdings Co., Ltd.
- SDF Group SpA
- Tirth Agro Technology Private Limited
- Kirloskar Group
- Jain Irrigation Systems Ltd.
제7장 시장 기회 및 향후 전망
AJY 25.11.26The India Agricultural Machinery Market size is estimated at USD 18.15 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 27.29 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 8.5% during the forecast period.
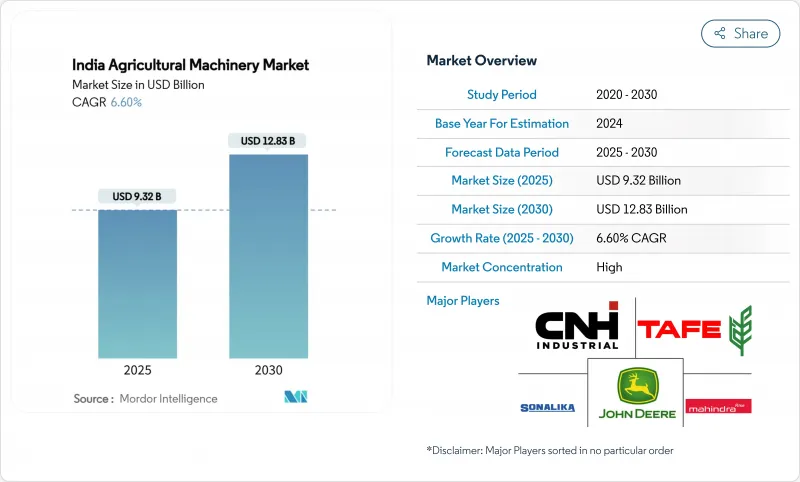
Robust public-sector incentives, persistent rural labor shortages, and rapid digitalization are converging to accelerate equipment adoption nationwide. Subsidies under the Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM) lower the upfront cost of tractors, irrigation systems, and precision implements, while custom-hiring centers extend access to smallholder farmers. Rising urban migration reduces available farm labor, pushing growers toward mechanized solutions that can sustain timely planting and harvesting operations. In parallel, the Digital Agriculture Mission is creating a farmer registry and geotagged crop database that will underpin precision equipment deployment and data-driven financing. Emission regulations plus emerging incentives for low-emission tractors spur investment in cleaner powertrains, positioning electric and hybrid models as a nascent but strategic growth pocket. Competitive rivalry intensifies as the top five vendors command an 81.5% share, prompting new product launches and capacity expansions geared toward mid-power tractors and smart implements.
India Agricultural Machinery Market Trends and Insights
Government schemes boosting mechanization adoption
Policy interventions under SMAM provide 40%-50% subsidies on individual machinery purchases and up to 80% on custom-hiring centers. In Uttar Pradesh alone, SMAM disbursed INR 65.66 billion (USD 790 million) between 2014 and 2024, distributing 176,000 machines and establishing 10,769 custom-hiring centers, which collectively expand access to high-capacity equipment across smallholder communities. Complementary initiatives such as the Kisan Drone subsidy and crop-specific support under the National Food Security Mission channel further demand high-precision implements. These programs not only minimize upfront costs but also strengthen after-sales networks, thereby fostering sustained mechanization across diverse agro-climatic zones.
Rural labor shortage caused by sustained migration to urban centers
Household survey data indicate that only 9% of main income earners remain in farming, down from historic norms above 50%. Seasonal out-migration peaks during planting and harvesting, intensifying labor deficits that mechanization can bridge through timely tillage, sowing, and harvesting. Combine harvesters cut labor requirements by up to 30% and reduce post-harvest losses by 2-4 percentage points, making them indispensable in rice-wheat rotations. Equipment sharing through custom-hiring centers further leverages scarce machinery to maintain cropping intensities in labor-scarce districts.
High equipment cost and limited credit access
Despite generous subsidies, a mid-horsepower tractor still requires an outlay exceeding INR 600,000 (USD 7,200), a sum beyond the reach of many marginal growers. Formal lenders often demand collateral, and interest spreads remain 200-300 basis points above prime lending, deterring big-ticket investments. Custom-hiring centers cushion the cost hurdle but are unevenly distributed, eastern India hosts fewer than 12 centers per district versus 45-plus in parts of the north, perpetuating regional disparities.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- FPOs and contract farming aggregation
- Digital credit platforms enabling financing
- Fragmented landholdings limit scale efficiency
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Tractors retained a 40.5% revenue share in 2024, underscoring their foundational role in tillage and haulage across diverse cropping systems. Irrigation Machinery is the fastest growing segment with micro-irrigation pumps and drip systems advancing at a 10.5% CAGR, propelled by drought-mitigation programs and rising electricity tariffs that favor precision watering. Equipment segments, including plows, harrows, and rotovators, benefit from the mechanization push in smallholder farming, where these implements provide entry-level mechanization solutions that require lower capital investment than tractors. Harvesting machinery experiences steady growth as labor shortages intensify during peak seasons, with combine harvesters and forage harvesters becoming essential for timely crop collection in commercial farming operations.
Adapters that merge global navigation satellite systems with traditional implements are converting conventional tractors into smart machines that execute straight-line plowing and seed placement within +-2.5 cm precision, reducing input waste by 6%-8%. Electric-assist rotovators and battery-powered orchard sprayers are gaining traction among fruit growers, where low noise and zero emissions are prized. The India agricultural machinery market continues to diversify as balers, mowers, and mulchers gain relevance in residue-management schemes aimed at curbing open-field burning. Market leaders respond with modular attachment ecosystems, allowing a single tractor chassis to support over 20 task-oriented implements, thereby spreading ownership cost over multiple revenue streams.
The India Agricultural Machinery Market Report is Segmented by Type (Tractors, Equipment, Irrigation Machinery, Harvesting Machinery, and More) and by End-User Farm Size (Smallholdings, Medium Farms, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd
- TAFE Motors and Tractors Limited
- Deere & Company
- CNH Industrial N.V.
- International Tractors Limited (Sonalika)
- Escorts Kubota Limited
- VST Tillers Tractors Ltd.
- AGCO Corporation
- CLAAS KGaA mbH
- Yanmar Holdings Co., Ltd.
- SDF Group S.p.A.
- Tirth Agro Technology Private Limited
- Kirloskar Group
- Jain Irrigation Systems Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Government Schemes Boosting Mechanization Adoption
- 4.2.2 Rural labor shortage caused by sustained migration to urban centers
- 4.2.3 FPOs and Contract Farming Aggregation
- 4.2.4 Digital Credit Platforms Enabling Financing
- 4.2.5 Electric Equipment Incentives Accelerating Adoption
- 4.2.6 Climate Insurance Favoring Mechanized Cultivation
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Equipment Cost and Limited Credit Access
- 4.3.2 Fragmented Landholdings Limit Scale Efficiency
- 4.3.3 Emission Norms Vary Across States
- 4.3.4 Lack of Skilled Telematics Technicians
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 Tractors
- 5.1.1.1 Less than 50 HP
- 5.1.1.2 50 to 75 HP
- 5.1.1.3 76 to 100 HP
- 5.1.1.4 101 to 150 HP
- 5.1.1.5 Greater than 150 HP
- 5.1.2 Equipment
- 5.1.2.1 Plows
- 5.1.2.2 Harrows
- 5.1.2.3 Rotovators and Cultivators
- 5.1.2.4 Seed and Fertilizer Drills
- 5.1.2.5 Other Equipment (Post-Hole Diggers, Power Weeders, etc.)
- 5.1.3 Irrigation Machinery
- 5.1.3.1 Sprinkler Irrigation
- 5.1.3.2 Drip Irrigation
- 5.1.3.3 Other Irrigation Machinery (Center-Pivot Systems, Micro-Sprinklers, etc.)
- 5.1.4 Harvesting Machinery
- 5.1.4.1 Combine Harvesters
- 5.1.4.2 Forage Harvesters
- 5.1.4.3 Other Harvesting Machinery (Sugarcane Harvesters, Potato Harvesters, etc.)
- 5.1.5 Haying and Forage Machinery
- 5.1.5.1 Mowers and Conditioners
- 5.1.5.2 Balers
- 5.1.5.3 Other Haying and Forage Machinery (Tedders, Rakes, etc.)
- 5.1.1 Tractors
- 5.2 By End-User Farm Size
- 5.2.1 Smallholdings (Less than 5 ha)
- 5.2.2 Medium Farms (5 to 20 ha)
- 5.2.3 Large Farms (Greater than 20 ha)
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd
- 6.4.2 TAFE Motors and Tractors Limited
- 6.4.3 Deere & Company
- 6.4.4 CNH Industrial N.V.
- 6.4.5 International Tractors Limited (Sonalika)
- 6.4.6 Escorts Kubota Limited
- 6.4.7 VST Tillers Tractors Ltd.
- 6.4.8 AGCO Corporation
- 6.4.9 CLAAS KGaA mbH
- 6.4.10 Yanmar Holdings Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.11 SDF Group S.p.A.
- 6.4.12 Tirth Agro Technology Private Limited
- 6.4.13 Kirloskar Group
- 6.4.14 Jain Irrigation Systems Ltd.



















