
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1910921
말레이시아의 택배, 특송 및 소포(CEP) 시장 : 점유율 분석, 업계 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2026-2031년)Malaysia Courier, Express, And Parcel (CEP) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
말레이시아의 택배, 특송 및 소포(CEP) 시장은 2025년에 16억 8,000만 달러로 평가되었고, 2026년의 17억 8,000만 달러에서 2031년까지 23억 7,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되고 있습니다.
예측기간(2026-2031년)의 CAGR은 5.91%로 전망되고 있습니다.

견고한 소포 취급량의 성장은 확대되는 전자상거래, 현금없는 결제의 급속한 보급, 크로스보더 통관절차를 간소화하는 정부 프로그램에 기인하고 있습니다. 사업자 각사는 배송 속도를 향상시키기 위해 AI를 활용한 분류 시스템, 전동화 차량, 다크 스토어와의 제휴에 투자를 추진하고 있습니다. 한편, 2024년 보조금 개혁에 따라 디젤 가격 56%의 급등에 대한 대응도 요구되고 있습니다. 경쟁 격화로 인해 산업 전체의 영업 이익률은 5% 미만인 가격 규율이 요구되고 있지만, 규모의 경제와 기술 도입으로 J&T 익스프레스 등 대기업에서는 수익성 회복의 조짐이 나타나고 있습니다. 이 회사는 2024년 지역 순이익 1억 1,000만 달러를 기록했습니다. 말레이시아의 택배, 특송 및 소포(CEP) 시장은 의료 물류 수요에 의해 더욱 뒷받침되고 있으며, 의약품 콜드체인 운송이 타업종을 상회하는 성장을 보이고 있습니다. 지리적으로, 클랑 밸리는 KLIA(쿠알라룸푸르 국제공항)와 포트 클랑(클랑 항구)에 대한 근접성으로 인해 소포 유통의 중심지로 계속되고 있지만, 동말레이시아에서는 여전히 인프라 격차나 멀티모달 제약에 대한 대응에 직면하고 있습니다.
말레이시아의 택배, 특송 및 소포(CEP) 시장의 동향 및 인사이트
전자상거래의 급성장과 디지털 네이티브 소비자의 기대 상승
온라인 소매 시장은 2030년까지 239억 3,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예측되고 있으며, 크로스보더 주문이 전체 거래의 40%를 차지하면서 간선 운송 계획과 소포 구성을 재구축하고 있습니다. 90%가 넘는 인터넷 보급률과 모바일 월렛의 보급으로 대금교환불(COD) 이용률은 주문의 약 20%로 증가하고 있으며, 택배 업체는 역물류의 현금 회수 워크플로에 대한 개선을 요구받고 있습니다. 연말연시나 라마단 기간의 계절적 피크 시에는 일시적 수송 능력의 증강이 필요하며, 사업자는 쿠알라룸푸르 근교에 임시 구분 라인을 설치해야만 합니다. 소셜 커머스의 실시간 전달은 배송량의 변동성을 증가시키고 평균 소포 가치의 감소로 이익률을 압박하기 때문에 네트워크의 밀도화와 동적 라우팅이 요구되고 있습니다. 그 결과 말레이시아의 택배, 특송 및 소포(CEP) 시장은 잦은 소량 배송에 치우치고 있어 확대 가능한 자동화가 요구되고 있습니다.
정부 지원 디지털 자유무역지역이 크로스보더 풀필먼트를 가속화
ePAM 제도에 의해 CIF 가격 500 링깃 이하의 소포는 항공기 도착 2시간 전에 간이 신고가 가능해져, 거의 즉각적인 통관이 실현되고 따라서 쿠알라룸푸르 국제공항(KLIA), 페낭, 쿠칭에서의 체류시간이 단축되었습니다. 현재 7곳의 공항에서 운용을 개시하고 있으며, 이는 항공화물 제휴처나 통관업무에 대한 전문성을 가진 운송업자에게 결정적인 우위성을 제공하고 있습니다. 말레이시아와 충칭을 연결하는 ASEAN 특급 철도의 시험 운행은 9일간의 수송 기간을 실현하고, 정부가 지역 물류의 기반 구축을 목표로 하는 자세를 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 그러나 500 링깃의 역치가 항공화물에만 적용되기 때문에 해상화물과 트럭 운송은 여전히 사무처리가 복잡하고 말레이시아의 택배, 특송 및 소포(CEP) 시장에서의 항공 중심 경향은 계속되고 있습니다. 여러 운송 모드를 취급하는 사업자는 추가 비용 절감을 실현하기 위해 공정한 조건을 요구하는 로비 활동을 실시했습니다.
격렬한 가격경쟁으로 5%를 밑도는 영업이익률
공급업체의 분산화는 운임 하락을 초래하고 보조금 폐지 후 경유 가격이 56% 상승했음에도 불구하고 순이익률은 5% 미만인 수준에 그쳤습니다. 대기업은 자동화와 연료 헤지 계약을 활용하여 변동을 극복하고 있지만, 중소 사업자는 대응 수단이 부족하여 철수 또는 통합이 진행되고 있습니다. SKDS 2.0 구제책은 대상 차량의 경유 비용의 일부를 보조하지만, 배분 상한에 의해 많은 사업자가 일부를 부담하고 있습니다. 성수기 할증 요금은 일시적인 완화책에 불과하며 말레이시아의 택배, 특송 및 소포(CEP) 시장에서는 서비스 제공 비용의 관리와 수익 관리가 매우 중요해지고 있습니다.
부문 분석
2025년 소포 수요의 37.92%를 전자상거래 주문이 차지했지만, 의료 부문은 엄격한 콜드체인 규제와 의료기기의 보급에 의해 2026-2031년에 걸쳐 6.12%라는 가장 높은 CAGR을 기록할 전망입니다. 온도 관리 밴과 GDP 인증 창고는 높은 부가가치 수익을 제공합니다.
금융 서비스, 제조업, 도매업은 예측 가능한 B2B 경로를 유지하여 계절적인 EC 수요 변동을 완화합니다. 운송 사업자의 다양한 산업에 대한 노출은 수익을 안정화하여 말레이시아의 택배, 특송 및 소포(CEP) 시장에서 서비스 폭을 확대합니다.
국제화물은 2026-2031년에 걸쳐 CAGR 6.11%로 증가할 것으로 예상되지만, 2025년 시점에서는 국내 화물이 말레이시아의 택배, 특송 및 소포(CEP) 시장에서 64.42%의 점유율을 차지하였습니다. 크로스보더 EC, ASEAN 특급 철도 파일럿 사업, 디지털 자유무역권의 진전으로 중소기업의 해외용 화물이 확대되어 통관에 대응 가능한 항공 네트워크에 대한 수요가 높아지고 있습니다. 국내 노선은 클랑 밸리의 도시 밀집지역을 활용하여 높은 노선망의 밀도와 거의 100퍼센트에 가까운 배달 성공률로 안정적인 현금 흐름을 확보하고 있습니다.
ePAM을 통한 통관 처리 시간 단축과 팬아시아 철도 네트워크를 통해 중국행 운송 일수가 9일로 단축되면서 국제 물류의 규모는 말레이시아의 택배, 특송 및 소포(CEP) 시장에서 확대될 것으로 기대됩니다. 그러나 항공편에만 적용되는 최저 과세 기준액 500 링깃이 복합수송으로의 이행을 억제하고 있으며, 도로 및 해상수송의 화물은 여전히 수작업 검사를 거쳐야 하기 때문에 엔드 투 엔드에서의 비용 절감이 방해되고 있습니다. 복합 운송 브로커 업무를 수행하는 운송업체는 이러한 격차를 해소하기 위한 최적의 위치에 있습니다.
기타 혜택
- 시장 예측(ME) 엑셀 시트
- 3개월 애널리스트 서포트
자주 묻는 질문
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사 전제조건 및 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 인구통계
- 경제활동별 GDP 분포
- 경제활동별 GDP 성장률
- 인플레이션
- 경제성과와 개요
- 전자상거래 산업의 동향
- 제조업의 동향
- 운수 및 창고업의 GDP
- 수출 동향
- 수입 동향
- 연료 가격
- 물류 성능
- 인프라
- 규제 프레임워크
- 밸류체인 및 유통채널 분석
- 촉진요인
- 전자상거래의 급성장과 디지털 네이티브 소비자의 기대 상승
- 정부 지원의 디지털 자유무역지역(DFTZ)이 크로스보더 풀필먼트를 가속화
- 클랑 밸리에서 즉시 배달 '다크 스토어'의 급속한 확대
- AI 구동형 분류 허브와 경로 계획에 의한 네트워크 최적화
- 라스트마일 배송 차량의 전동화에 의한 단위 배송 비용의 절감
- ASEAN 역내 3-5일 배송을 위한 절약형 소포 회랑이 중소기업용 수출량 확대의 새로운 가능성을 제시
- 억제요인
- 격렬한 가격경쟁에 의해 5%를 밑도는 영업이익률
- 동말레이시아 지방의 주소 정보 부족으로 인한 배송 재시도 발생
- 두 자릿수의 유류할증료 변동
- 소액면세제도 개혁에도 불구하고 저가 B2C 수입품의 통관 병목 발생
- 시장에서의 기술 혁신
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급자의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업 간 경쟁 관계
제5장 시장 규모 및 성장 예측
- 배송지
- 국내
- 국제
- 배송 속도
- 특송
- 비송
- 모델
- B2B
- B2C
- C2C
- 출하 중량
- 중량화물
- 경량화물
- 고중량화물
- 수송 수단
- 항공
- 육로
- 기타
- 최종 사용자 산업
- 전자상거래
- 금융 서비스(BFSI)
- 의료
- 제조업
- 제1차 산업
- 도매 및 소매업(오프라인)
- 기타
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 주요 전략적 움직임 경쟁 환경 : 시장 집중도, 주요 전략적 동향, 시장 점유율 분석 및 기업 개요
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- City-Link Express
- DHL Group
- FedEx
- GDEX Group
- J& T Express
- Ninja Van
- POS Malaysia Bhd
- SF Express(KEX-SF)
- SkyNet Worldwide Express
- United Parcel Service(UPS)
제7장 시장 기회 및 미래 전망
CSM 26.02.04The Malaysia courier, express, and parcel market was valued at USD 1.68 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 1.78 billion in 2026 to reach USD 2.37 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 5.91% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
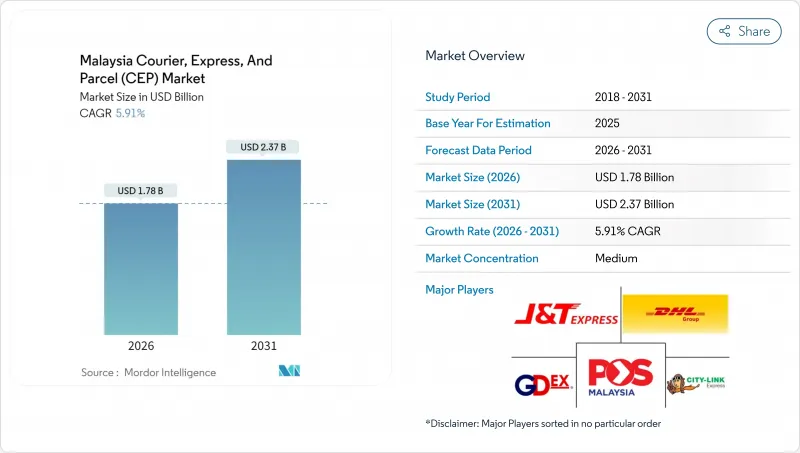
Solid parcel volume growth stems from expanding e-commerce, rapid adoption of cash-less payments, and government programs that simplify cross-border clearance. Operators are investing in AI-enabled sorting, electrified fleets, and dark-store partnerships to improve delivery speed while managing the 56% spike in diesel prices that followed subsidy reforms in 2024. Competitive intensity has forced pricing discipline below a 5% industry-wide operating margin, yet scale advantages and technology deployments are beginning to restore profitability for larger firms such as J&T Express, which reported USD 110 million in regional net profit for 2024. The Malaysia courier, express, and parcel market is additionally buoyed by healthcare logistics demand, with pharmaceutical cold-chain shipments outpacing other verticals. Geographically, Klang Valley remains the epicenter of parcel flows thanks to proximity to KLIA and Port Klang, whereas East Malaysia continues to wrestle with addressing gaps and multimodal constraints.
Malaysia Courier, Express, And Parcel (CEP) Market Trends and Insights
E-commerce Boom and Growing Digital-Native Consumer Expectations
Online retail is forecast to reach USD 23.93 billion by 2030, with cross-border orders forming 40% of all transactions, a mix that reshapes line-haul planning and parcel mix. Ninety-plus percent internet penetration and mobile wallets have increased cash-on-delivery uptake to roughly 20% of orders, compelling couriers to refine reverse-logistics cash collection workflows. Seasonal peaks during Lunar New Year and Ramadan force temporary capacity layering, nudging operators to install pop-up sorting lines near Kuala Lumpur. Social-commerce live-streaming adds volume volatility and squeezes margins because of lower average parcel value, prompting network densification and dynamic routing. As a result, the Malaysia courier, express, and parcel market is skewing toward frequent, low-weight shipments that demand scalable automation.
Government-Backed Digital Free Trade Zone Accelerating Cross-Border Fulfillment
The ePAM regime allows simplified declarations two hours before aircraft arrival for parcels under RM500 CIF, triggering near-instant release and trimming dwell time at KLIA, Penang, and Kuching. Seven airports are now live on the system, creating a decisive advantage for carriers with air-freight partnerships and customs brokerage depth. ASEAN Express rail pilots linking Malaysia to Chongqing promise 9-day transit, underscoring the administration's bid to anchor regional logistics. However, because the RM500 threshold applies only to air, sea freight and trucking remain administratively heavier, preserving an air-centric bias in the Malaysia courier, express, and parcel market. Operators with multimodal reach are lobbying for parity to unlock further cost savings.
Sub-5% Operating Margin Pressure from Intense Price Wars
A fragmented vendor field has triggered tariff undercutting that keeps net margins under the 5% threshold even as diesel prices jump 56% post-subsidy removal. Large-scale players exploit automation and contract fuel hedging to ride out volatility, whereas small firms lack leverage and are exiting or consolidating. The SKDS 2.0 relief card offsets some diesel cost for eligible fleets, but allocation ceilings leave many operators partially exposed. Peak-season surcharges provide fleeting relief, making cost-to-serve discipline and yield management crucial for the Malaysia courier, express, and parcel market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rapid Expansion of Instant-Delivery Dark Stores in Klang Valley
- Network Optimization via AI-Driven Sorting Hubs and Route Planning
- Rural Addressing Gaps in East Malaysia Causing Delivery Retries
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
E-commerce orders made up 37.92% of 2025 parcel demand, but healthcare recorded the fastest 6.12% CAGR between 2026-2031 due to stricter cold-chain compliance and medical device proliferation. Temperature-controlled vans and GDP-certified warehouses lend premium margins.
Financial services, manufacturing, and wholesale trade sustain predictable B2B lanes that smooth seasonal e-commerce volatility. For carriers, diversified vertical exposure insulates revenue and reinforces service breadth in the Malaysia courier, express, and parcel market.
International consignments are climbing at a 6.11% CAGR between 2026-2031, even though domestic traffic held 64.42% of the Malaysia courier, express, and parcel market share in 2025. Cross-border e-commerce, ASEAN Express rail pilots, and the Digital Free Trade Zone elevate outbound SME parcels, sharpening demand for customs-compliant air connectivity. Domestic lanes capitalize on urban density in Klang Valley, where route density and near-zero failed-delivery rates secure stable cash flow.
The Malaysia courier, express, and parcel market size for cross-border flows is primed to widen as ePAM cuts clearance turnaround and the Pan-Asian Railway Network slashes transit to China to 9 days. Nonetheless, the RM500 air-only de-minimis cap restrains multimodal shift; road and sea consignments still wade through manual inspections, constricting end-to-end cost savings. Carriers with multimodal brokerage are best placed to arbitrage these gaps.
The Malaysia Courier, Express, and Parcel Market Report is Segmented by End User Industry (E-Commerce and More), Destination (Domestic and International), Speed of Delivery (Express and Non-Express), Shipment Weight (Heavy Weight Shipments and More), Mode of Transport (Air, Road, and Others), and Model (Business-To-Business, Business-To-Consumer, and Consumer-To-Consumer). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- City-Link Express
- DHL Group
- FedEx
- GDEX Group
- J&T Express
- Ninja Van
- POS Malaysia Bhd
- SF Express (KEX-SF)
- SkyNet Worldwide Express
- United Parcel Service (UPS)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Demographics
- 4.3 GDP Distribution by Economic Activity
- 4.4 GDP Growth by Economic Activity
- 4.5 Inflation
- 4.6 Economic Performance and Profile
- 4.6.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.6.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.7 Transport and Storage Sector GDP
- 4.8 Export Trends
- 4.9 Import Trends
- 4.10 Fuel Price
- 4.11 Logistics Performance
- 4.12 Infrastructure
- 4.13 Regulatory Framework
- 4.14 Value Chain and Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.15 Market Drivers
- 4.15.1 E-Commerce Boom and Growing Digital-Native Consumer Expectations
- 4.15.2 Government-Backed Digital Free Trade Zone (DFTZ) Accelerating Cross-Border Fulfilment
- 4.15.3 Rapid Expansion of Instant-Delivery "Dark Stores" in Klang Valley
- 4.15.4 Network Optimization via AI-Driven Sorting Hubs and Route Planning
- 4.15.5 Electrification of Last-mile Fleets Lowering Unit Delivery Cost
- 4.15.6 Cross-Border ASEAN 3-5-day Economy-Parcel Corridors Opening New SME Export Volumes
- 4.16 Market Restraints
- 4.16.1 Sub-5% Operating Margin Pressure from Intense Price Wars
- 4.16.2 Rural Addressing Gaps in East Malaysia Causing Delivery Retries
- 4.16.3 Double-Digit Fuel-Surcharge Volatility
- 4.16.4 Customs-Clearance Bottlenecks for Low-Value B2C Imports Despite De-Minimis Reforms
- 4.17 Technology Innovations in the Market
- 4.18 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.18.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.18.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.18.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.18.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.18.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 Destination
- 5.1.1 Domestic
- 5.1.2 International
- 5.2 Speed of Delivery
- 5.2.1 Express
- 5.2.2 Non-Express
- 5.3 Model
- 5.3.1 Business-to-Business (B2B)
- 5.3.2 Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
- 5.3.3 Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
- 5.4 Shipment Weight
- 5.4.1 Heavy Weight Shipments
- 5.4.2 Light Weight Shipments
- 5.4.3 Medium Weight Shipments
- 5.5 Mode of Transport
- 5.5.1 Air
- 5.5.2 Road
- 5.5.3 Others
- 5.6 End User Industry
- 5.6.1 E-Commerce
- 5.6.2 Financial Services (BFSI)
- 5.6.3 Healthcare
- 5.6.4 Manufacturing
- 5.6.5 Primary Industry
- 5.6.6 Wholesale and Retail Trade (Offline)
- 5.6.7 Others
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 City-Link Express
- 6.4.2 DHL Group
- 6.4.3 FedEx
- 6.4.4 GDEX Group
- 6.4.5 J&T Express
- 6.4.6 Ninja Van
- 6.4.7 POS Malaysia Bhd
- 6.4.8 SF Express (KEX-SF)
- 6.4.9 SkyNet Worldwide Express
- 6.4.10 United Parcel Service (UPS)
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment


















