
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1911329
프랑스의 CEP(택배, 특송 및 소포) 시장 : 점유율 분석, 업계 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2026-2031년)France Courier, Express, And Parcel (CEP) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
프랑스의 CEP(택배, 특송 및 소포) 시장은 2025년 187억 2,000만 달러로 평가되었으며, 2026년 193억 5,000만 달러에서 2031년까지 228억 3,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측됩니다.
예측 기간(2026-2031년) 동안의 CAGR은 3.36%로 전망됩니다.

이 성장 궤도를 형성하는 것은 전자상거래 확대, 아시아의 크로스보더 물류, 저배출형 운영을 촉진하는 규제 변경입니다. 매장 소매를 뛰어넘는 온라인 소비가 증가함에 따라 소포 취급량이 증가하고 옥외 네트워크(OOH)는 사업자의 배송 거점 밀도 향상과 배달 실패 감소에 기여하고 있습니다. 국제 마켓플레이스는 수입 소형 화물의 흐름을 촉진하고 간선 수송거리를 증가시키는 한편 신고 가격이 낮아 이익률을 압박합니다. 한편, 프랑스의 25개의 저배출존(ZFE-M) 등 지속가능성에 관한 규제에 의해 밀집 도시의 중심부에서는 차량의 전동화나 화물용 자전거의 도입이 가속되어, 라스트마일의 비용 구조가 영구적으로 변화하고 있습니다. 기존 사업자와 신규 진출기업이 서비스 품질을 유지하면서 비용과 환경 목표를 달성하기 위해 허브 시설, 디지털 툴, 대체 연료 차량의 업그레이드를 경쟁함으로써 경쟁이 격화되고 있습니다.
프랑스의 CEP(택배, 특송 및 소포) 시장의 동향 및 분석
전자상거래 침투율 급증
2024년 2분기 국내 온라인 소매 매출은 전년 대비 8.4% 증가하여 주요 도시 전역에서 소포 취급량이 증가했습니다. 배송거점 밀도 향상으로 차량 가동률이 상승하는 한편, 옴니채널 소매업체는 택배 및 클릭&콜렉트(매장 픽업)의 흐름을 추가하여 출하거점의 다양화를 촉진하고 있습니다. 파리의 다크 스토어 운영자는 현재 2시간 미만의 서비스 제공을 목표로 하고 있으며, 운송 회사는 마이크로플루필먼트 존을 위한 루트 설계를 검토할 필요가 있습니다. 프랑스 우체국이 운영하는 128,000곳의 집계 거점은 배달 실패 위험을 줄이고 간선 경로를 단축하여 비용 관리를 지원합니다. 전자상거래 이용자는 지속가능한 선택을 점점 선호하게 되고, 탄소 저감 서비스를 인증한 운송회사는 프리미엄 배송층에서 가격 결정력을 획득하고 있습니다.
아시아에서 크로스보더 소형 화물 증가
2024년에는 약 46억개의 소형 소포가 유럽으로 유입되었으며, 그 중 91%가 중국에서 발송됨에 따라 국내 네트워크의 경제 구조가 재구성되었습니다. 사업자는 부피를 차지하면서 이익률이 낮은 저가치 상품을 대량으로 처리할 수밖에 없습니다. 중국의 마켓플레이스와 국제 택배 회사(예 : Temu와 DHL의 제휴)와의 제휴로 이미 EC 피크시 화물을 처리하고 있는 프랑스 공항을 통한 물류가 발생하고 있습니다. EU가 제안한 저가치화물에 대한 과세개혁은 전략적 불확실성을 초래하는 반면, 최저가치면제가 폐지되면 수익률 향상으로 이어질 가능성도 있습니다. 국내 사업자는 이에 대응하고, 통관 데이터의 자동 취득이나 게이트웨이 거점에서의 보세 구분 공간의 확대에 의해 통관 처리의 신속화와 취급 비용 절감을 도모하고 있습니다.
가격 경쟁과 인건비에 따른 이익률 압박
2024년 4분기 도로운송사의 도산건수는 35.4% 증가했습니다. 이는 운임이나 연료비의 상승을 화주에게 전가하지 못하고 고전한 사업자가 많았기 때문입니다. 대규모 EC 계약을 둘러싼 격렬한 입찰 경쟁으로 간선 운송 요금은 낮은 수준으로 추이하고 있습니다. 한편, 고용 옵션이 풍부한 대도시권에서는 라스트마일의 임금이 상승하고 있습니다. 세계 통합사업자들은 인력 감축을 추진했으며, 페덱스는 소프트 프라이싱 환경 하에서 이익률 유지를 위해 2025년 유럽에서 최대 2,000명의 고용을 감축했습니다. 분단화된 개인사업자 운전자의 하청 계약은 많은 노선에서 수요를 웃도는 운송 능력으로 가격 규율을 더욱 약화시키고 있습니다.
부문 분석
제조업은 2025년 수익의 33.01%를 차지하였고 정밀한 B2B 배송을 필요로 하는 자동차 및 항공우주, 그리고 기계 수출이 기반이 되고 있습니다. 2026-2031년에 CAGR 4.24%로 확대될 전망인 전자상거래는 네트워크 설계를 재구축하는 높은 볼륨의 주택배송을 창출하고 있습니다. 의료 및 금융 서비스는 규제나 보안 요건에 의해 틈새이면서 높은 이익률을 유지하고 있습니다.
다양한 수요 구조가 특정 부문에서의 부진의 영향을 완화합니다. 고정 간격 산업용 집하는 오프 피크시의 차량 가동률을 향상시키고, 야간 주택 배송은 자산 활용률을 높입니다. 산업 물류와 소비자 물류 간의 균형을 유지하는 사업자는 프랑스의 택배, 특송 및 소포 시장에서 우위성을 발휘할 전망입니다.
국제 서비스는 2025년 국내 서비스를 능가하는 CAGR을 나타냈으며 2026년부터 2031년까지 연평균 CAGR 4.05%를 유지할 전망입니다. 다만, 2025년 시점에서는 국내 배송이 65.62%의 점유율을 차지하면서 프랑스의 CEP(택배, 특송 및 소포) 시장을 여전히 주도하였습니다. 아시아 플랫폼으로부터의 저가치 수입품은 파리 샤를 드골 공항 및 리옹 생텍쥐페리 공항의 소포 취급량을 증가시키고 있으며, 운송 사업자는 운송 시간을 확보하기 위해 통관 자동화 고도화를 요구받고 있습니다. 국내 수송량은 소비자의 기대에 따른 조밀한 집하거점 네트워크와 단기간 납기에 의해 혜택을 받고 있지만, 화주는 크로스보더 서비스의 가격 대비 수익 압박에 직면하고 있습니다.
국제배송에서의 소비자 신뢰 획득을 위해, 사업자는 관세 포함 옵션과 실시간 추적 기능으로 차별화를 도모하고 있습니다. 프랑스 우체국의 2024년 크로스보더 OOH(매장 픽업) 취급량이 52% 증가한 사례는 유연한 픽업 방법이 라스트마일 비용 상승을 완화한다는 것을 보여줍니다. 통관 데이터를 수집하고 엔드 투 엔드의 가시성을 제공하는 운송 사업자는 확대하는 프랑스의 CEP(택배, 특송 및 소포) 시장의 크로스보더 부문에서 보다 높은 이익률을 확보할 수 있을 것으로 예측됩니다.
기타 혜택
- 시장 예측(ME) 엑셀 시트
- 3개월 애널리스트 서포트
자주 묻는 질문
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사 전제조건 및 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 인구동태
- 경제활동별 GDP 분포
- 경제활동별 GDP 성장률
- 인플레이션
- 경제적 성과와 기업 프로파일
- 전자상거래 업계 동향
- 제조업 동향
- 운수 및 창고업의 GDP
- 수출 동향
- 수입 동향
- 연료 가격
- 물류 성능
- 인프라
- 규제 프레임워크
- 밸류체인과 유통채널 분석
- 촉진요인
- 전자상거래의 침투율 급증
- 아시아로부터의 크로스보더 소형 화물 유통량 증가
- 라스트마일 배송의 고속화와 OOH 옵션에 대한 수요
- 제로 에미션 차량으로 지속가능성 추진
- 파리 2024 대회용 물류 개선책(배달 오토바이 전용 구역)
- Z세대에 의한 중고 마켓플레이스의 급성장(C2C)
- 억제요인
- 가격 경쟁과 인건비에 의한 이익률 압박
- 도시 토지 이용과 ZFE-M 규제
- 아시아 거점으로부터의 저가치물류로 수익률 저하
- 도시 주변 창고에서의 고출력 EV 충전 설비 부족
- 시장에서의 기술 혁신
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급자의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업 간 경쟁 관계
제5장 시장 규모 및 성장 예측
- 배송지
- 국내
- 국제
- 배송 속도
- 특급
- 일반
- 모델
- B2B
- B2C
- C2C
- 출하 중량
- 중량물 배송
- 저중량물 배송
- 고중량물 배송
- 수송 수단
- 항공
- 육로
- 기타
- 최종 사용자 업계
- 전자상거래
- 금융 서비스(BFSI)
- 의료
- 제조업
- 제1차산업
- 도매 및 소매업(오프라인)
- 기타
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 주요 전략적 움직임
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- DHL Group
- FedEx
- GEODIS
- Integer Capital Group
- International Distributions Services(including GLS)
- La Poste Group
- STERNE Group
- United Parcel Service(UPS)
- Walden Group
제7장 시장 기회 및 미래 전망
CSM 26.01.23The France courier, express, and parcel market was valued at USD 18.72 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 19.35 billion in 2026 to reach USD 22.83 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 3.36% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
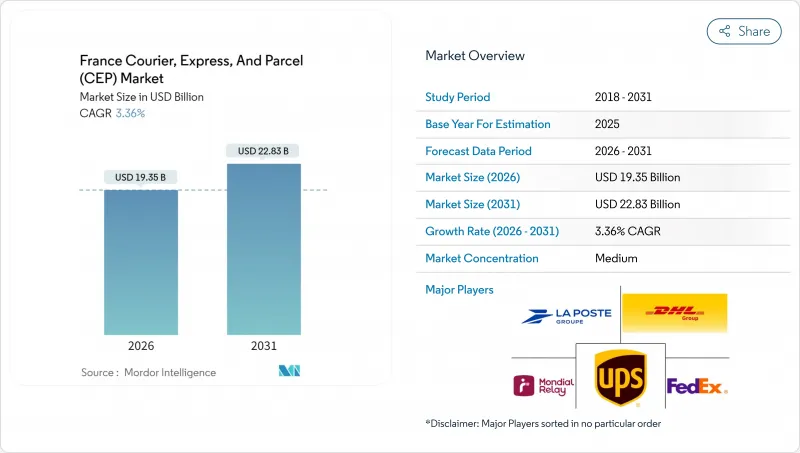
E-commerce growth, cross-border flows from Asia, and regulatory changes that favor low-emission operations shape this trajectory. Parcel volumes climb as online spending grows faster than store-based retail, while out-of-home (OOH) networks help operators raise stop density and limit failed deliveries. International marketplaces drive inbound small-parcel flows that boost line-haul mileage yet compress margins because of their low declared value. Meanwhile, sustainability mandates such as France's 25 active low-emission zones (ZFE-M) accelerate fleet electrification and cargo-bike adoption in dense city cores, permanently shifting last-mile cost structures. Competitive intensity rises as incumbents and new entrants race to upgrade hubs, digital tools, and alternative-fuel fleets in order to preserve service quality while meeting cost and environmental targets.
France Courier, Express, And Parcel (CEP) Market Trends and Insights
E-Commerce Penetration Surge
National online retail sales grew 8.4% year-on-year in Q2 2024, widening the parcel pool in every major city. Higher stop density lifts vehicle utilization, while omnichannel retailers add home-delivery and click-and-collect flows that broaden shipment origin points. Dark-store operators in Paris now target sub-two-hour service windows, forcing carriers to redesign routing for micro-fulfillment zones. Pickup-point expansion underpins cost control, as La Poste operates 128,000 sites that lower failed-delivery risk and shorten trunk routes. E-commerce shoppers increasingly favor sustainable options, and carriers that certify carbon-reduced services gain pricing power within premium delivery tiers.
Rising Cross-Border Parcel Flows from Asia
About 4.6 billion small parcels entered Europe in 2024, with 91% dispatched from China, reshaping domestic network economics. Operators must process vast volumes of low-value items that occupy capacity yet generate slender margins. Partnerships between Chinese marketplaces and global express firms, such as Temu's tie-ups with DHL, channel traffic through French airports that already handle peak e-commerce flows. Proposed EU tax reforms on low-value consignments inject strategic uncertainty but could also lift yields if minimum-value exemptions disappear. Domestic players respond by automating customs data capture and expanding bonded sortation space at gateway hubs to speed clearance and cut handling costs.
Margin Squeeze from Price Wars and Labor Costs
Road-transport company insolvencies rose 35.4% in Q4 2024 as operators struggled to pass wage and fuel hikes onto shippers. Fierce bidding for large e-commerce contracts keeps line-haul rates low, even as last-mile wages climb in dense cities where employment alternatives abound. Global integrators rationalize headcounts FedEx cut up to 2,000 European jobs in 2025 to protect margins in a soft-pricing environment. Fragmented owner-driver subcontracting further dampens pricing discipline because capacity outstrips demand on many lanes.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Demand for Faster Last-Mile and OOH Options
- Sustainability Push for Zero-Emission Fleets
- Urban Land-Use and ZFE-M Restrictions
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Manufacturing produced 33.01% of 2025 revenue, anchored by automotive, aerospace, and machinery exports that require precise B2B deliveries. E-commerce, advancing at a 4.24% CAGR between 2026-2031, injects high-volume residential drops that reshape network design. Healthcare and financial services stay niche yet high-margin due to regulatory and security requirements.
Diversified demand shields carriers from sector-specific slowdowns. Fixed-interval industrial collections fill off-peak van capacity, while evening residential rounds improve asset utilization. Operators that balance industrial and consumer flows are positioned to outperform in the France courier, express, and parcel market.
International services grew faster than domestic in 2025 and are on course for a 4.05% CAGR between 2026-2031, even though the France courier, express, and parcel market size remains dominated by domestic deliveries at 65.62% share in 2025. Low-value imports from Asian platforms swell parcel counts at Paris-CDG and Lyon Saint-Exupery, compelling carriers to refine customs-clearance automation to protect transit times. Domestic volumes benefit from dense pickup-point networks and short lead times that align with consumer expectations, yet face yield pressure when shippers benchmark prices against cross-border offers.
Operators differentiate through duty-paid options and real-time tracking to win shopper trust on international consignments. La Poste's 52% jump in cross-border OOH traffic in 2024 demonstrates that flexible collection mitigates last-mile cost inflation. Carriers that master customs data capture and offer end-to-end visibility are expected to secure higher margins on the expanding cross-border segment of the France courier, express, and parcel market.
The France Courier, Express, and Parcel Market Report is Segmented by End User Industry (E-Commerce and More), Destination (Domestic and International), Speed of Delivery (Express and Non-Express), Shipment Weight (Heavy Weight Shipments and More), Mode of Transport (Air, Road, and Others), and Model (Business-To-Business, Business-To-Consumer, and Consumer-To-Consumer). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- DHL Group
- FedEx
- GEODIS
- Integer Capital Group
- International Distributions Services (including GLS)
- La Poste Group
- STERNE Group
- United Parcel Service (UPS)
- Walden Group
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Demographics
- 4.3 GDP Distribution by Economic Activity
- 4.4 GDP Growth by Economic Activity
- 4.5 Inflation
- 4.6 Economic Performance and Profile
- 4.6.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.6.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.7 Transport and Storage Sector GDP
- 4.8 Export Trends
- 4.9 Import Trends
- 4.10 Fuel Price
- 4.11 Logistics Performance
- 4.12 Infrastructure
- 4.13 Regulatory Framework
- 4.14 Value Chain and Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.15 Market Drivers
- 4.15.1 E-Commerce Penetration Surge
- 4.15.2 Rising Cross-Border Parcel Flows from Asia
- 4.15.3 Demand for Faster Last-Mile and OOH Options
- 4.15.4 Sustainability Push for Zero-Emission Fleets
- 4.15.5 Paris-2024 Logistics Upgrades (Cargo-Bike Zones)
- 4.15.6 Gen-Z Second-Hand Marketplace Boom (C2C)
- 4.16 Market Restraints
- 4.16.1 Margin Squeeze from Price Wars and Labor Costs
- 4.16.2 Urban Land-Use and ZFE-M Restrictions
- 4.16.3 Low-Value Parcels from Asian Sites Erode Yields
- 4.16.4 Sparse High-Power EV Charging at Peri-Urban Depots
- 4.17 Technology Innovations in the Market
- 4.18 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.18.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.18.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.18.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.18.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.18.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 Destination
- 5.1.1 Domestic
- 5.1.2 International
- 5.2 Speed of Delivery
- 5.2.1 Express
- 5.2.2 Non-Express
- 5.3 Model
- 5.3.1 Business-to-Business (B2B)
- 5.3.2 Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
- 5.3.3 Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
- 5.4 Shipment Weight
- 5.4.1 Heavy Weight Shipments
- 5.4.2 Light Weight Shipments
- 5.4.3 Medium Weight Shipments
- 5.5 Mode of Transport
- 5.5.1 Air
- 5.5.2 Road
- 5.5.3 Others
- 5.6 End User Industry
- 5.6.1 E-Commerce
- 5.6.2 Financial Services (BFSI)
- 5.6.3 Healthcare
- 5.6.4 Manufacturing
- 5.6.5 Primary Industry
- 5.6.6 Wholesale and Retail Trade (Offline)
- 5.6.7 Others
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 DHL Group
- 6.4.2 FedEx
- 6.4.3 GEODIS
- 6.4.4 Integer Capital Group
- 6.4.5 International Distributions Services (including GLS)
- 6.4.6 La Poste Group
- 6.4.7 STERNE Group
- 6.4.8 United Parcel Service (UPS)
- 6.4.9 Walden Group
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment


















