
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1911804
유럽의 택배, 특송 및 소포(CEP) 시장 : 점유율 분석, 업계 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2026-2031년)Europe Courier, Express, And Parcel (CEP) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
유럽 택배, 특송 및 소포(CEP) 시장 규모는 2026년 1,456억 5,000만 달러로 추정됩니다. 이는 2025년 1,407억 4,000만 달러에서 증가한 수치입니다. 2031년에는 1,729억 3,000만 달러에 이르고, 2026-2031년 동안 CAGR은 3.49%를 나타낼 전망입니다.

이 완만한 성장 곡선은 전자상거래 확대, 규제 조화, 기술 도입이 대륙 전체의 마지막 마일 네트워크를 재구성하는 동안 더 깊은 구조적 변화를 가리고 있습니다. 소매업체는 배송 경험의 차별화를 선호합니다. 유럽 구매자의 81%가 원하는 배송 옵션을 사용할 수 없는 경우 구매를 포기하기 때문에 경쟁의 초점은 가격에서 서비스 품질로 전환하고 있습니다. 2035년까지 단계적으로 실시되는 EU 수준의 디지털 시대의 부가가치세(VAT) 개혁(ViDA)은 국경 간 데이터 흐름을 표준화하고 첨단 컴플라이언스 시스템을 보유한 대규모 사업자를 선호합니다. 한편, 50만명이 넘는 운전자 부족이 자동화 투자를 가속화하고 있으며, 사업자는 노동력 부족에 직면하고 있습니다. 특히 네덜란드에서 지속가능성 요건을 강화하고 도시 중심부의 제로 배출구역 도입은 전기자동차 플릿과 택배 로커의 밀도 확대를 시급히 하고 있으며, 녹색자산 투자가 가능한 운송사업자 간의 통합을 촉진하고 있습니다.
유럽 택배, 특송 및 소포(CEP) 시장 동향 및 인사이트
폭발적인 전자상거래와 옴니채널 소매의 급성장
소셜 커머스의 기세로 인해 소포 유통은 전통적인 계절성이 아니라 예측 불가능한 동향 주도의 피크로 향하고 있으며, 유럽의 택배, 특송 및 소포(CEP) 시장 전체에서 유연한 용량 계획이 요구되고 있습니다. 독일의 전자상거래용 포장자재 지출은 2025년에 39억 9,000만 달러에 이르렀으며, 2034년까지의 연평균 성장률(CAGR) 14.03%(2025-2030년)로 성장할 것으로 전망되고 있으며, 이 성장에 있어서의 포장 자재의 중요성을 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 반품이 어렵게 느껴지면 구매자의 79%가 구매를 취소하므로 역 물류의 고도화가 추가 기능에서 핵심 능력으로 전환되고 있습니다. 헬스케어 부문의 소포 배송도 이 옴니 채널의 파도를 타고 있습니다. DHL이 20억 유로(22억 달러)를 들여 전개하는 헬스케어 물류 사업은 전자 약국의 보급 확대에 대응한 전문적인 콜드체인 서비스를 자금면에서 지원하고 있습니다. 인플루언서 프로모션과 관련된 배송량의 집중화로 인해 운송 회사는 서비스 수준을 유지하면서 급증하는 트래픽을 흡수하기 위해 동적 라우팅 알고리즘의 설계를 강요하고 있습니다.
EU역내 자유화된 국경 간 거래와 부가가치세(VAT) 개혁
2030년 7월에 시행되는 ViDA의 전자 송장 의무화는 EU 역내 B2B 거래의 모든 형태가 EN16931 규격에 통일되어, 수작업에 의한 서류 처리가 삭감되어, 통관 수속이 신속화됩니다. 2028년 7월 원스톱 숍 시스템 확장은 회원국 간에 단일 VAT ID를 유지할 수 있게 해주며, 매일 수백만 건의 국경 간 소포를 취급하는 유럽 택배, 특송 및 소포(CEP) 시장에 큰 혜택을 제공합니다. 과세 사건 발생 후 10일 이내의 신고 의무화에 따라 고도의 IT 시스템 개수가 요구됩니다. 이로 인해 이미 통합 데이터 레이크를 운영하는 사업자가 이점을 얻을 수 있습니다. 동시에 수입관리시스템 2(ICS2)는 EU 국경을 통과하기 전에 상세한 수입 개요 제출을 의무화하고 보안 강화와 제품 수준의 상세 데이터 파이프라인을 가진 운송업체들에게 경쟁 우위를 제공합니다. 이러한 조치는 판매 확대 장벽을 줄이면서 디지털 컴플라이언스의 기준을 높이고 국제 통합을 향한 장기적인 변화를 촉진합니다.
가격경쟁과 용적중량제로 마진압박
유통 후 과잉 공급으로 인해 사업자가 점유율 방어를 위해 할인을 재개한 결과 유럽 택배, 특송 및 소포(CEP) 시장에서 취급량이 증가했음에도 불구하고 수익성이 떨어지고 있습니다. 체적 소비를 반영해야 하는 체중 중량 요금은 전략적 고객을 위해 면제되는 경우가 많으며 비용 효율성보다 빠른 속도로 마진을 압박합니다. 임포스트에 의한 요 Dell Inc와 센딩사의 인수는 고정비를 희석하기 위한 비유기적 밀도 확대로의 전환을 부각하고 있습니다. 운송회사는 피크시 요금이나 연료 서치를 추가하지만, 화주측은 멀티 캐리어 소프트웨어를 활용하여 요금 차익을 추구하고 이에 반발하고 있습니다. 이 줄다리기 상태는 단기적인 가격 회복을 제한하는 동시에 추가 산업 재편을 촉진합니다.
부문 분석
2025년의 EC부문의 점유율은 34.45%를 유지했지만, 2026-2031년에 걸쳐 의료품 소포가 CAGR 3.79%로 가장 급속히 확대될 전망입니다. 고령화와 온라인 약국의 확대로 온도관리된 라스트마일 배송이 우선 과제가 되고 있습니다.
DHL의 20억 유로(22억 달러) 규모의 프로그램은 GDP 준수 시설, 쿨 체인 포장 및 전용 관리 타워에 대한 투자를 추진합니다. 제조업체는 부품 전용 배송 경로가 필요하며 금융 서비스 문서는 보안 쿨리에의 틈새 시장을 지원합니다. 운송회사는 소매업의 한산기 동안 차량의 가동률 저하를 보완하기 위해 당일 집하의 바이오메디컬 항공편을 크로스셀하고 있습니다.
2025년 국제 소포 유통은 수익의 34.28%를 차지했으며, 국내 서비스는 유럽 택배, 특송 및 소포(CEP) 시장 점유율의 나머지를 유지했습니다. 국제화물은 2026-2031년에 걸쳐 CAGR 3.73%로 증가할 것으로 전망되며, VAT 결제의 간소화와 판매업체의 필필먼트 집중화로 국내 성장을 상회하는 속도로 확대됩니다.
유럽 소비자는 배송 시간이 국내 기준과 일치함에 따라 이웃 국가로부터의 구매를 증가시키고 있습니다. InPost가 2024년 11월에 EU8개국에서 전개한 네트워크는 수작업에 의한 분류나 통관 지연을 회피하는 로커간 배송 모델을 채택하고 있습니다. ICS2 데이터 요구사항은 역외 조달 품목의 리드타임을 초기에 연장하지만, EU 역내 루트에서는 마찰점이 감소합니다. 서비스의 예측가능성 향상으로 중소수출업체가 증가하고 기존 우편사업자는 추적시스템의 강화와 프리미엄 국경 간 서비스의 확충을 추진하고 있습니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형태 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 애널리스트에 의한 3개월간의 지원
자주 묻는 질문
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장의 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 인구통계
- 경제 활동별 GDP 분포
- 경제활동별 GDP 성장률
- 인플레이션
- 경제적 성능과 프로파일
- 전자상거래 산업의 동향
- 제조업의 동향
- 운수 및 창고업의 GDP
- 수출 동향
- 수입 동향
- 연료 가격
- 물류 성능
- 인프라
- 규제 프레임워크
- 중동유럽(CEE)
- 프랑스
- 독일
- 이탈리아
- 네덜란드
- 북유럽 국가
- 러시아
- 스페인
- 스위스
- 영국
- 밸류체인과 유통채널 분석
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 폭발적인 전자상거래와 옴니채널 소매의 급성장
- EU역내 자유화된 국경 간 무역과 부가가치세(VAT) 개혁
- 택배 로커와 PUDO 네트워크의 확대
- 자동화와 AI에 의한 업무 효율화
- 탄소 비용의 내부화에 의한 그린 CEP 플릿의 우위성
- 복수 운송 회사 대응의 소포 관리 플랫폼의 대두
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 가격 경쟁과 치수 베이스 요금 체계에 의한 이익률의 압박
- 심각한 드라이버와 창고 작업원의 부족
- 국가 수준에서의 택배 노동자 최저 임금법
- 사이버 보안 및 데이터 주권 컴플라이언스 비용 상승
- 시장에서의 기술 혁신
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 목적지
- 국내
- 국제
- 배송 속도
- 특송
- 비특송
- 모델
- B2B
- 기업 - 소비자 간 거래(B2C)
- 소비자간 거래(C2C)
- 출하 중량
- 대형화물
- 소형화물
- 중형화물
- 수송 수단
- 항공
- 도로
- 기타
- 최종 사용자 산업
- 전자상거래
- 금융 서비스(BFSI)
- 헬스케어
- 제조업
- 제1차 산업
- 도매 및 소매업(오프라인)
- 기타
- 국가
- 알바니아
- 불가리아
- 크로아티아
- 체코 공화국
- 덴마크
- 에스토니아
- 핀란드
- 프랑스
- 독일
- 헝가리
- 아이슬란드
- 이탈리아
- 라트비아
- 리투아니아
- 네덜란드
- 노르웨이
- 폴란드
- 루마니아
- 러시아
- 슬로바키아 공화국
- 슬로베니아
- 스페인
- 스웨덴
- 스위스
- 영국
- 기타 유럽
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 주요 전략적 움직임 경쟁 환경 : 시장 집중도/주요 전략적 동향/시장 점유율 분석/기업 개요/DHL 그룹/
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- DHL Group
- FedEx
- GEODIS
- International Distributions Services(including GLS)
- La Poste Group
- Logista
- Otto GmbH & Co. KG
- Post NL
- Poste Italiane
- Sterne Group
- United Parcel Service(UPS)
제7장 시장 기회와 장래의 전망
SHW 26.02.05The Europe courier, express, and parcel (CEP) market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 145.65 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 140.74 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 172.93 billion, growing at 3.49% CAGR over 2026-2031.
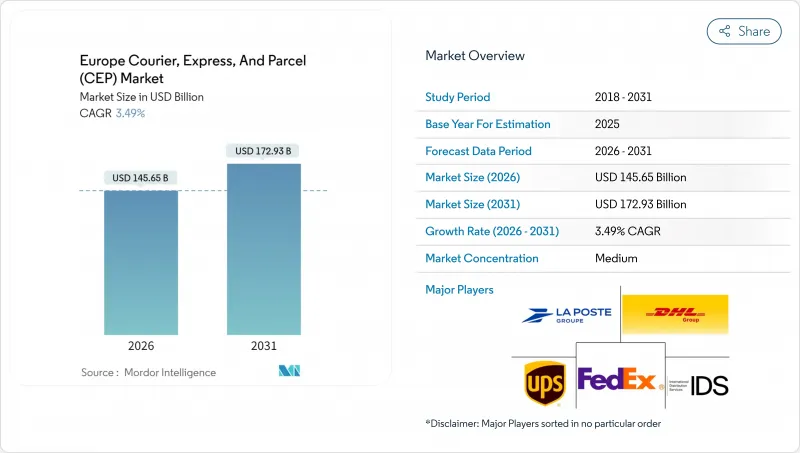
This moderate trajectory masks deeper structural shifts as e-commerce expansion, regulatory harmonization, and technology adoption reshape last-mile networks across the continent. Retailers are prioritizing delivery-experience differentiation because 81% of European shoppers abandon baskets when preferred options are unavailable, tilting competitive focus from price to service quality. EU-level VAT in the Digital Age (ViDA) reforms, phased through 2035, are standardizing cross-border data flows, favoring scale players with advanced compliance systems. Meanwhile, a driver shortfall exceeding 500,000 openings has accelerated automation investment as operators grapple with labor scarcity. Heightened sustainability mandates and city-center zero-emission zones, notably in the Netherlands, add urgency for electric fleets and parcel-locker density, reinforcing consolidation among carriers that can fund green assets.
Europe Courier, Express, And Parcel (CEP) Market Trends and Insights
Explosive E-Commerce and Omnichannel Retail Boom
Social-commerce momentum is steering parcel flows toward unpredictable, trend-driven peaks rather than traditional seasonality, requiring flexible capacity planning across the Europe courier, express, and parcel (CEP) market. German e-commerce packaging spend reached USD 3.99 billion in 2025, reflecting 14.03% CAGR (2025-2030) expectations through 2034, underlining the packaging intensity of this growth. Reverse-logistics sophistication is turning from add-on to core capability, as 79% of shoppers cancel purchases when returns appear difficult. Healthcare parcels are piggybacking on this omnichannel wave; DHL's EUR 2 billion (USD 2.20 billion) health-logistics rollout funds specialized cold-chain services aligned with rising e-pharmacy penetration. Volume concentration around influencer promotions compels carriers to design dynamic routing algorithms to absorb traffic surges without impairing service-level compliance.
Liberalized Intra-EU Cross-Border Trade and VAT Reforms
ViDA's e-invoicing mandate arriving in July 2030 will standardize EN16931 formats for all intra-EU B2B trades, shrinking manual paperwork and accelerating customs clearances. The July 2028 expansion of the One-Stop Shop lets merchants maintain a single VAT ID across member states, a boon for the Europe courier, express, and parcel (CEP) market handling millions of cross-border parcels daily. Advanced IT retrofits are required because declarations must be filed within 10 days of chargeable events, favoring operators that already run integrated data lakes. Concurrently, Import Control System 2 obliges detailed entry summaries before crossing EU borders, tightening security and tilting the playing field to carriers with rich product-level data pipelines. Together, these measures reduce friction in sales expansion while raising digital-compliance thresholds, shaping a long-run shift toward international consolidation.
Margin Squeeze from Price Wars and Dimension-Based Tariffs
Post-pandemic overcapacity has resurrected discounting as operators defend share, eroding yields despite volume growth in the Europe courier, express, and parcel (CEP) market. Dimensional-weight pricing, meant to reflect cubic consumption, often gets waived for strategic accounts, compressing margins faster than cost-line efficiencies. InPost's acquisitions of Yodel and Sending highlight the pivot toward inorganic density to dilute fixed overhead. Carriers add peak or fuel surcharges but shippers push back, leveraging multicarrier software to arbitrage rates. The tug-of-war limits near-term price recovery while stoking further consolidation.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Expansion of Parcel Lockers and PUDO Networks
- Automation and AI-Driven Operational Efficiency
- Acute Driver and Warehouse-Labor Shortages
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
E-commerce retained a 34.45% share in 2025, yet healthcare parcels are set to rise fastest at 3.79% CAGR between 2026-2031. Aging populations and e-pharmacy expansion make temperature-controlled last-mile a priority.
DHL's EUR 2 billion (USD 2.20 billion) program funds GDP-compliant facilities, cool-chain packaging, and dedicated control towers. Manufacturers require part-express lanes, and financial-services documents sustain secure-courier niches. Carriers cross-sell same-day biomedical pickup to monetize vehicle downtime during retail off-peak cycles.
Cross-border parcel flows accounted for 34.28% of revenues in 2025 as domestic services retained the remainder of Europe courier, express, and parcel (CEP) market share. International consignments are forecast to climb at a 3.73% CAGR between 2026-2031, outpacing domestic growth as ViDA simplifies VAT settlement and merchants centralize fulfillment.
European shoppers increasingly purchase from neighboring states once delivery times align with domestic benchmarks. InPost's November 2024 network activation across eight EU countries uses a locker-to-locker model that bypasses manual sorting and customs delays. ICS2 data prerequisites initially elongate lead-times for goods sourced outside the bloc, but EU-internal routes face fewer friction points. Improved service predictability attracts SME exporters, prompting postal incumbents to upgrade track-and-trace and push into premium cross-border offerings.
The Europe Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Market Report is Segmented by End User Industry (E-Commerce and More), Destination (Domestic and International), Speed of Delivery (Express and Non-Express), Shipment Weight (Heavy Weight Shipments, and More), Mode of Transport (Air, Road, and Others), and Model (Business-To-Business, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- DHL Group
- FedEx
- GEODIS
- International Distributions Services (including GLS)
- La Poste Group
- Logista
- Otto GmbH & Co. KG
- Post NL
- Poste Italiane
- Sterne Group
- United Parcel Service (UPS)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Demographics
- 4.3 GDP Distribution by Economic Activity
- 4.4 GDP Growth by Economic Activity
- 4.5 Inflation
- 4.6 Economic Performance and Profile
- 4.6.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.6.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.7 Transport and Storage Sector GDP
- 4.8 Export Trends
- 4.9 Import Trends
- 4.10 Fuel Price
- 4.11 Logistics Performance
- 4.12 Infrastructure
- 4.13 Regulatory Framework
- 4.13.1 Central and Eastern Europe (CEE)
- 4.13.2 France
- 4.13.3 Germany
- 4.13.4 Italy
- 4.13.5 Netherlands
- 4.13.6 Nordics
- 4.13.7 Russia
- 4.13.8 Spain
- 4.13.9 Switzerland
- 4.13.10 United Kingdom
- 4.14 Value Chain and Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.15 Market Drivers
- 4.15.1 Explosive E-Commerce and Omnichannel Retail Boom
- 4.15.2 Liberalized Intra-EU Cross-Border Trade and VAT Reforms
- 4.15.3 Expansion of Parcel Lockers and PUDO Networks
- 4.15.4 Automation and AI-Driven Operational Efficiency
- 4.15.5 Carbon-Cost Internalization Favouring Green CEP Fleets
- 4.15.6 Rise of Multicarrier Parcel-Management Platforms
- 4.16 Market Restraints
- 4.16.1 Margin Squeeze from Price Wars and Dimension-Based Tariffs
- 4.16.2 Acute Driver and Warehouse-Labor Shortages
- 4.16.3 Country-Level Courier Wage-Floor Legislation
- 4.16.4 Rising Cyber-Security and Data-Sovereignty Compliance Costs
- 4.17 Technology Innovations in the Market
- 4.18 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.18.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.18.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.18.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.18.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.18.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 Destination
- 5.1.1 Domestic
- 5.1.2 International
- 5.2 Speed of Delivery
- 5.2.1 Express
- 5.2.2 Non-Express
- 5.3 Model
- 5.3.1 Business-to-Business (B2B)
- 5.3.2 Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
- 5.3.3 Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
- 5.4 Shipment Weight
- 5.4.1 Heavy Weight Shipments
- 5.4.2 Light Weight Shipments
- 5.4.3 Medium Weight Shipments
- 5.5 Mode of Transport
- 5.5.1 Air
- 5.5.2 Road
- 5.5.3 Others
- 5.6 End User Industry
- 5.6.1 E-Commerce
- 5.6.2 Financial Services (BFSI)
- 5.6.3 Healthcare
- 5.6.4 Manufacturing
- 5.6.5 Primary Industry
- 5.6.6 Wholesale and Retail Trade (Offline)
- 5.6.7 Others
- 5.7 Country
- 5.7.1 Albania
- 5.7.2 Bulgaria
- 5.7.3 Croatia
- 5.7.4 Czech Republic
- 5.7.5 Denmark
- 5.7.6 Estonia
- 5.7.7 Finland
- 5.7.8 France
- 5.7.9 Germany
- 5.7.10 Hungary
- 5.7.11 Iceland
- 5.7.12 Italy
- 5.7.13 Latvia
- 5.7.14 Lithuania
- 5.7.15 Netherlands
- 5.7.16 Norway
- 5.7.17 Poland
- 5.7.18 Romania
- 5.7.19 Russia
- 5.7.20 Slovak Republic
- 5.7.21 Slovenia
- 5.7.22 Spain
- 5.7.23 Sweden
- 5.7.24 Switzerland
- 5.7.25 United Kingdom
- 5.7.26 Rest of Europe
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 DHL Group
- 6.4.2 FedEx
- 6.4.3 GEODIS
- 6.4.4 International Distributions Services (including GLS)
- 6.4.5 La Poste Group
- 6.4.6 Logista
- 6.4.7 Otto GmbH & Co. KG
- 6.4.8 Post NL
- 6.4.9 Poste Italiane
- 6.4.10 Sterne Group
- 6.4.11 United Parcel Service (UPS)
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment


















