
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1911343
인도네시아의 윤활유 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 업계 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2026-2031년)Indonesia Lubricants - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
인도네시아의 윤활유 시장은 2025년 12억 리터로 평가되었고, 2026년 12억 3,000만 리터에서 2031년까지 14억 1,000만 리터에 이를 것으로 예측됩니다. 예측기간(2026-2031년)의 CAGR은 2.71%를 나타낼 전망입니다.

전기자동차 정책이 다가오고 있는 가운데도 수요는 인도네시아의 꾸준한 산업 확장, 확고한 인프라 계획, 탄력적인 차량 보유량에 따라 계속 추적되고 있습니다. 미네랄 오일 제품은 여전히 전체 물량의 3분의 2를 차지하지만, 연장된 오일 교환 주기가 평생 운영 비용 절감을 추구하는 차량 운영자에게 매력적이기 때문에 합성 오일로의 프리미엄 전환이 가속화되고 있습니다. 셸의 신규 그리스 공장부터 엑슨모빌의 현장 MACHINEXT 서비스에 이르기까지 다국적 기업의 생산 능력 증설은 기술, 현지 생산 및 유통망이 경쟁 우위를 형성하는 방식을 보여줍니다. 한편, 의무적인 SNI 인증, B40 바이오디젤 도입, 변동성 높은 원유 가격은 비용 압박을 가중시켜 부식 방지 첨가제 및 바이오 기반 혼합유로의 포트폴리오 업그레이드를 촉진하고 있습니다. 17,000개 섬에 걸친 공급망의 복잡성은 특히 외곽 지역의 고부가가치 광산 및 산업용 응용 부문에 도달하는 데 물류적 어려움을 야기합니다.
인도네시아의 윤활유 시장 동향 및 인사이트
자동차 보유량 증가
인도네시아의 확장되는 자동차 부문은 승용차 증가와 군도 물류 네트워크 전반에 걸친 상업용 차량 현대화를 통해 윤활유 소비를 주도하고 있습니다. 국제자동차제조업체협회(OICA)에 따르면, 2024년 인도네시아의 자동차 생산량은 119만 대를 기록했습니다. 자동변속기 오토바이로의 전환은 매틱(matic) 애플리케이션을 위한 특수 윤활유 제형에 대한 수요를 창출하고 있습니다. 전자상거래 확대와 라스트마일 배송의 확산은 차량 이용률을 증가시켜 기존 소비자 패턴을 넘어 윤활유 교체 주기를 단축시키고 있습니다. 정부의 전기차 추진 정책과 2040년까지 내연기관 차량 단계적 퇴출 계획은 자동차용 윤활유 수요 증가에 구조적 한계를 설정합니다. 지역 유통망은 인도네시아 외곽 섬 지역을 효율적으로 서비스하는 데 어려움을 겪어, 신흥 자동차 클러스터 시장 진출을 제한하는 공급 병목 현상을 초래합니다.
급속한 산업 및 제조업의 성장
인도네시아 제조업 부문의 성장세는 금속 가공, 발전, 중장비 응용 부문 전반에 걸친 산업용 윤활유 소비 증가로 직접 연결됩니다. 세계 최대 니켈 생산국으로서의 지위는 제련 공정에서 특수 금속 가공 유체 및 유압 시스템 윤활유 수요를 증폭시킵니다. 제조업 투자는 초기 윤활유 충전과 지속적인 유지보수 프로그램이 필요한 신규 산업 설비를 창출합니다. 엑슨모빌이 2024년 6월 출시한 현장 윤활 관리 기술 'MACHINEXT'는 디지털 최적화가 총소유비용을 절감하면서 장비 수명 주기를 연장하는 방식을 보여줍니다. 자바 섬에 제조업이 집중되면서 물류상 이점이 발생하지만, 인프라 개발이 산업 투자에 뒤처진 자원 풍부한 외곽 지역의 성장 잠재력은 제한됩니다.
거시경제와 상품가격의 변동이 설비 가동률을 억제
인도네시아의 윤활유 산업은 거시경제적 불확실성과 원자재 가격 변동으로 인해 산업 활동과 소비자 지출 패턴이 위축되면서 설비 가동률에 어려움을 겪고 있습니다. 국내 산업의 가동률은 약 60% 수준입니다. 세계의 공급망 차질과 통화 변동성은 베이스 오일 수입 비용에 영향을 미쳐 제조업체들이 가격 전략을 조정하고 수요 탄력성에 미치는 영향을 고려하도록 강요합니다. 팜유 및 광업과 같은 수출 의존형 부문은 원자재 가격 하락기에 산업용 윤활유 소비를 감소시키는 주기적 침체를 경험합니다. 자바 섬에 제조 역량이 집중되면서 지역적 불균형이 발생하고, 외곽 섬 지역 사업체들은 경제 혼란 시 공급망 안정성 문제에 직면합니다. 의무적 SNI 기준에 따른 규제 준수 비용은 마진 압박 시기에는 중소 업체가 쉽게 흡수하기 어려운 운영 부담을 가중시킵니다.
부문 분석
자동차 엔진 오일은 2025년 인도네시아 윤활유 시장 점유율의 35.80%를 차지하며, 이는 인도네시아의 차량 중심 윤활유 소비 패턴과 승용차 및 상용차 부문 전반에 걸친 내연 기관의 지배력을 반영합니다. 유압유는 2026-2031년 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 3.51%로 가장 빠르게 성장하는 제품군으로, 고성능 유압 시스템이 필요한 인프라 건설 및 광산 장비 확장에 힘입어 성장할 전망입니다. 산업용 엔진 오일은 발전 및 해양 응용 부문에 사용되며, 변속기 오일은 오토바이 산업의 자동변속기 붐으로 혜택을 볼 것입니다. 기어 오일은 칼리만탄과 술라웨시 전역의 광산 운영을 중심으로 인도네시아의 중장비 및 산업 기계 기반을 지원합니다.
고무 공정유 및 백색유를 포함한 공정유은 인도네시아의 타이어 제조 및 석유화학 산업에 사용되며, 금속 가공 유체는 확대되는 제조 부문을 지원합니다. 터빈 오일과 변압기 오일은 발전 인프라에 공급되며, 그리스는 자동차 섀시 윤활부터 산업용 베어링 시스템에 이르기까지 다양한 용도로 사용됩니다. 제품 구성의 진화가 특수 제형으로 이동하는 것은 인도네시아의 산업 정교화 증가와 OEM 사양의 영향력 확대를 반영합니다. 이러한 OEM 사양은 API, JASO, ACEA 인증과 같은 국제 기준을 충족하는 고성능 윤활유를 요구합니다.
인도네시아의 윤활유 시장 보고서는 제품 유형(자동차 엔진 오일, 산업 엔진 오일, 변속기 오일, 기어 오일, 브레이크 플루드, 유압유, 그리스 등), 최종 사용자 산업(자동차, 선박, 항공우주, 중기, 산업), 기유 유형(미네랄 오일 기반, 합성 오일, 반합성 오일, 바이오)으로 분류됩니다. 시장 예측은 수량(리터) 단위로 제공됩니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 애널리스트의 3개월간 지원
자주 묻는 질문
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 자동차 보유량 증가
- 급속한 산업 및 제조업의 성장
- 전국적인 인프라 정비와 광업 활동의 활황
- 해양 및 어업 선단 현대화
- 바이오디젤 관련 윤활유 오염으로 인한 고성능 첨가제 수요 증가
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 거시경제 및 원자재 가격 변동성으로 인한 설비 가동률 저하
- 합성 오일의 연장 교환 간격에 의한 사용량 감소/차량당
- 원유 가격 변동으로 인한 마진 압박 및 가격 민감형 구매자 증가
- 밸류체인 분석
- 규제 프레임워크
- 최종 사용자 동향
- 자동차산업
- 제조업
- 발전업계
- Porter's Five Forces
- 공급기업 협상력
- 구매자 협상력
- 신규 참가업체 위협
- 대체품 위협
- 경쟁도
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 제품 유형별
- 자동차 엔진 오일
- 산업 엔진 오일
- 변속기 오일
- 기어 오일
- 브레이크 오일
- 유압유
- 그리스
- 공정유(고무 공정유 및 백색유)
- 금속 가공유
- 터빈 오일
- 변압기 오일
- 기타 제품 유형
- 최종 사용자 업계별
- 자동차
- 승용차
- 상용차
- 이륜차
- 선박
- 항공우주
- 중장비
- 건설
- 광업
- 농업
- 산업용
- 발전
- 야금 및 금속가공
- 섬유
- 석유 및 가스
- 기타 최종 이용 산업
- 자동차
- 기유유형별
- 미네랄 오일 기반 윤활유
- 합성 윤활유
- 반합성 윤활유
- 바이오 기반 윤활유
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율(%)/순위 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- BP Plc(Castrol)
- Chevron Corporation
- Exxon Mobil Corporation
- FUCHS
- Gulf Oil International Ltd
- Idemitsu Kosan Co., Ltd.
- PETRONAS Lubricants International
- PT Pertamina Lubricants
- PT Wiraswasta Gemilang Indonesia
- Shell plc
- The Lubrizol Corporation
- TOP 1 Oil Products Company
- TotalEnergies
제7장 시장 기회와 장래의 전망
제8장 CEO를 위한 주요 전략적 과제
HBR 26.01.29The Indonesian Lubricants Market was valued at 1.20 billion liters in 2025 and estimated to grow from 1.23 billion liters in 2026 to reach 1.41 billion liters by 2031, at a CAGR of 2.71% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
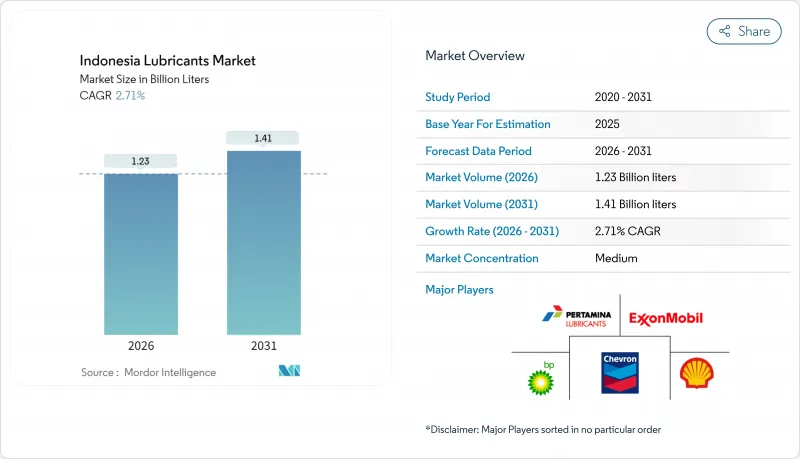
Demand continues to track Indonesia's steady industrial expansion, resolute infrastructure pipeline, and resilient vehicle parc, even as electric-mobility policies loom. Mineral-oil products still account for two-thirds of volume, yet the premium shift to synthetics accelerates because extended drain intervals appeal to fleet operators seeking lower lifetime operating costs. Capacity additions by multinationals-from Shell's new grease plant to ExxonMobil's on-site MACHINEXT service-underline how technology, localized production, and distribution reach shape competitive advantage. Meanwhile, mandatory SNI certification, B40 biodiesel adoption, and volatile crude prices intensify cost pressures, prompting portfolio upgrades toward anti-corrosion additives and bio-based blends. Supply-chain complexity across 17,000 islands creates logistical challenges, particularly for reaching high-value mining and industrial applications in outer regions.
Indonesia Lubricants Market Trends and Insights
Growing Automotive Parc Expansion
Indonesia's expanding automotive sector drives lubricant consumption through both passenger vehicle growth and commercial fleet modernization across the archipelago's logistics networks. According to the International Organization of Motor Vehicle Manufacturers (OICA), the country produced 1.19 million vehicles in 2024. The shift toward automatic transmission motorcycles creates demand for specialized lubricant formulations for matic applications. E-commerce expansion and the proliferation of last-mile delivery increase vehicle utilization rates, leading to a higher frequency of lubricant replacement beyond traditional consumer patterns. The government's push for electric vehicles and its planned phase-out of internal combustion engines by 2040 creates a structural ceiling for growth in automotive lubricant volumes. Regional distribution networks struggle to efficiently serve Indonesia's outer islands, creating supply bottlenecks that limit market penetration in emerging automotive clusters.
Rapid Industrial and Manufacturing Growth
Indonesia's manufacturing sector momentum directly translates to heightened industrial lubricant consumption across metalworking, power generation, and heavy equipment applications. The country's position as the world's largest nickel producer amplifies demand for specialized metalworking fluids and hydraulic systems lubricants in smelting operations. Manufacturing investment creates new industrial capacity requiring initial lubricant fills and ongoing maintenance programs. ExxonMobil's MACHINEXT on-site lubrication management technology, launched in June 2024, demonstrates how digital optimization reduces the total cost of ownership while extending equipment life cycles. The concentration of manufacturing on Java Island creates logistical advantages but limits growth potential in resource-rich outer regions where infrastructure development lags behind industrial investment.
Macroeconomic and Commodity-Price Volatility Dampening Cap-Utilization
Indonesia's lubricant industry faces capacity utilization challenges due to macroeconomic uncertainty and fluctuations in commodity prices, which dampen industrial activity and consumer spending patterns. The domestic industry operates at approximately 60% capacity utilization. Global supply chain disruptions and currency volatility impact base oil import costs, forcing manufacturers to adjust their pricing strategies and consider the effect on demand elasticity. Export-dependent sectors, such as palm oil and mining, experience cyclical downturns that reduce industrial lubricant consumption during commodity price slumps. The concentration of manufacturing capacity on Java island creates regional imbalances, while outer island operations struggle with supply chain reliability during economic turbulence. Regulatory compliance costs under mandatory SNI standards add operational overhead that smaller players cannot easily absorb during periods of margin compression.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Nation-wide Infrastructure and Mining Activity Boom
- Marine and Fisheries Fleet Modernization
- Longer Drain-Interval Synthetic Formulations Lowering Volume/Vehicle
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Automotive engine oil commands 35.80% Indonesia's lubricant market share in 2025, reflecting Indonesia's vehicle-centric lubricant consumption patterns and the dominance of internal combustion engines across passenger and commercial segments. Hydraulic fluids represent the fastest-growing product category, with a 3.51% CAGR for 2026-2031, driven by infrastructure construction and the expansion of mining equipment, which require high-performance hydraulic systems. Industrial engine oil serves power generation and marine applications, while transmission fluids benefit from the automatic transmission boom in the motorcycle industry. Gear oils support Indonesia's heavy equipment and industrial machinery base, particularly in mining operations across Kalimantan and Sulawesi.
Process oils, including rubber process oil and white oil, serve the tire manufacturing and petrochemical industries in Indonesia, while metalworking fluids support the country's expanding manufacturing sector. Turbine oils and transformer oils cater to the power generation infrastructure, while greases serve a diverse range of applications, from automotive chassis lubrication to industrial bearing systems. The evolution of the product mix toward specialized formulations reflects Indonesia's increasing industrial sophistication and the growing influence of OEM specifications, which demand performance lubricants that meet international standards, such as API, JASO, and ACEA certifications.
The Indonesia Lubricants Market Report is Segmented by Product Type (Automotive Engine Oil, Industrial Engine Oil, Transmission Fluids, Gear Oil, Brake Fluids, Hydraulic Fluids, Greases, and More), End-User Industry (Automotive, Marine, Aerospace, Heavy Equipment, and Industrial), and Base Stock Type (Mineral Oil-Based, Synthetic, Semi-Synthetic, and Bio-Based). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Volume (Liters).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- BP Plc (Castrol)
- Chevron Corporation
- Exxon Mobil Corporation
- FUCHS
- Gulf Oil International Ltd
- Idemitsu Kosan Co., Ltd.
- PETRONAS Lubricants International
- PT Pertamina Lubricants
- PT Wiraswasta Gemilang Indonesia
- Shell plc
- The Lubrizol Corporation
- TOP 1 Oil Products Company
- TotalEnergies
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Growing automotive parc expansion
- 4.2.2 Rapid industrial and manufacturing growth
- 4.2.3 Nation-wide infrastructure and mining activity boom
- 4.2.4 Marine and fisheries fleet modernization
- 4.2.5 Biodiesel-linked lubricant contamination driving premium additives
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Macroeconomic and commodity-price volatility dampening cap-utilization
- 4.3.2 Longer drain-interval synthetic formulations lowering volume/vehicle
- 4.3.3 Crude-oil price swings squeezing margins and price-sensitive buyers
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Framework
- 4.6 End-User Trends
- 4.6.1 Automotive Industry
- 4.6.2 Manufacturing Industry
- 4.6.3 Power Generation Industry
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Volume)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Automotive Engine Oil
- 5.1.2 Industrial Engine Oil
- 5.1.3 Transmission Fluids
- 5.1.4 Gear Oil
- 5.1.5 Brake Fluids
- 5.1.6 Hydraulic Fluids
- 5.1.7 Greases
- 5.1.8 Process Oil (Including Rubber Process Oil and White Oil)
- 5.1.9 Metalworking Fluids
- 5.1.10 Turbine Oil
- 5.1.11 Transformer Oil
- 5.1.12 Other Product Types
- 5.2 By End-user Industry
- 5.2.1 Automotive
- 5.2.1.1 Passenger Vehicles
- 5.2.1.2 Commercial Vehicles
- 5.2.1.3 Two-Wheelers
- 5.2.2 Marine
- 5.2.3 Aerospace
- 5.2.4 Heavy Equipment
- 5.2.4.1 Construction
- 5.2.4.2 Mining
- 5.2.4.3 Agriculture
- 5.2.5 Industrial
- 5.2.5.1 Power Generation
- 5.2.5.2 Metallurgy and Metalworking
- 5.2.5.3 Textiles
- 5.2.5.4 Oil and Gas
- 5.2.5.5 Other End-Use Industries
- 5.2.1 Automotive
- 5.3 By Base Stock Type
- 5.3.1 Mineral Oil-Based Lubricants
- 5.3.2 Synthetic Lubricants
- 5.3.3 Semi-Synthetic Lubricants
- 5.3.4 Bio-Based Lubricants
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share (%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 BP Plc (Castrol)
- 6.4.2 Chevron Corporation
- 6.4.3 Exxon Mobil Corporation
- 6.4.4 FUCHS
- 6.4.5 Gulf Oil International Ltd
- 6.4.6 Idemitsu Kosan Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.7 PETRONAS Lubricants International
- 6.4.8 PT Pertamina Lubricants
- 6.4.9 PT Wiraswasta Gemilang Indonesia
- 6.4.10 Shell plc
- 6.4.11 The Lubrizol Corporation
- 6.4.12 TOP 1 Oil Products Company
- 6.4.13 TotalEnergies
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment


















